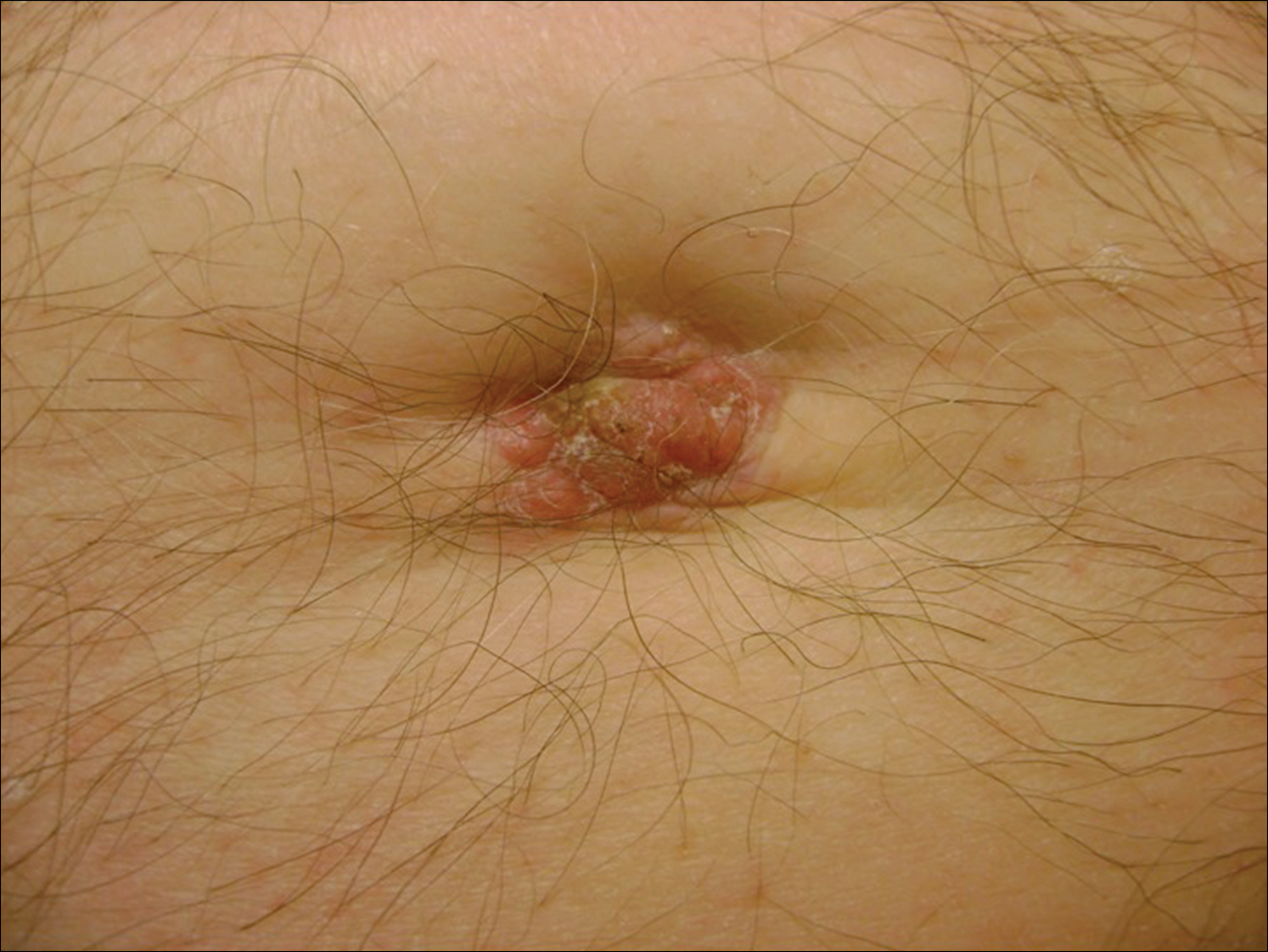
The Diagnosis: Sister Mary Joseph Nodule
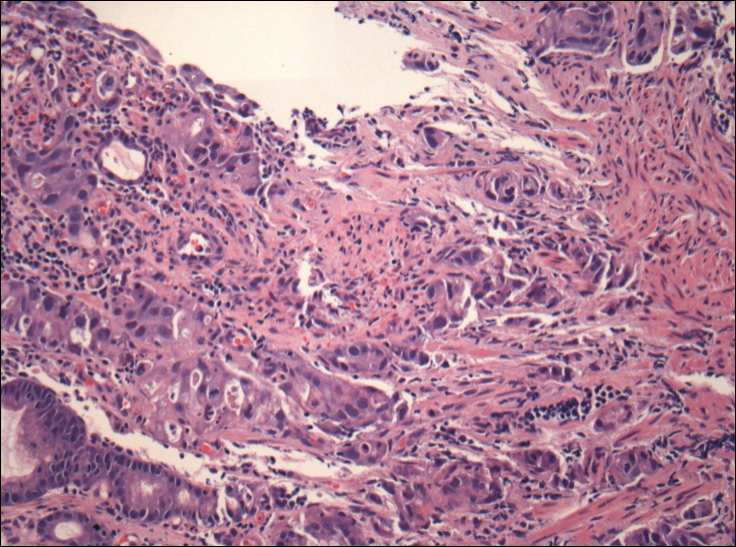
The umbilical skin biopsy revealed a moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma (Figure) that was positive for cytokeratin 20 and CDX2 and negative for cytokeratin 7 and transcription termination factor 1. The patient subsequently underwent computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis, which showed multiple soft-tissue nodules on the greater omentum, a soft-tissue density at the umbilicus, and thickening of the gastric mucosa. An upper endoscopy was then performed, which revealed a large fungating ulcerated mass in the stomach. Biopsy of this mass showed an invasive moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma, which was ERBB2 (formerly HER2) negative. Histopathologically, these pleomorphic glands looked similar to the glands seen in the original skin biopsy. With this diagnosis of metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma, our patient chose palliative chemotherapy but declined precipitously and died 2 months after the initial skin biopsy of the umbilical lesion.
When encountering a patient with an umbilical lesion, it is important to consider benign and malignant lesions in the differential diagnosis. A benign lesion may include scar, cyst, pyogenic granuloma, hemangioma, umbilical hernia, endometriosis, polyp, abscess, or the presence of an omphalith.1 Inflammatory dermatoses such as psoriasis or eczema also should be considered. Malignant lesions could be either primary or secondary, with metastatic disease being the most common.2 Sister Mary Joseph nodule (SMJN) is the eponymgiven to an umbilical lesion representing metastatic disease. Sister Mary Joseph was a nurse and surgical assistant to Dr. William Mayo in Rochester, Minnesota, in what is now known as the Mayo Clinic. She is credited to be the first to observe and note the association between an umbilical nodule and intra-abdominal malignancy. Metastasis to the umbilicus is thought to occur by way of contiguous, hematogenous, lymphatic, or direct spread through embryologic remnants from primary cancers of nearby gastrointestinal or pelvic viscera. It is a rare cutaneous sign of internal malignancy, with an estimated prevalence of 1% to 3%.3 The most common primary cancer is gastric adenocarcinoma, though cases of metastasis from pancreatic, endometrial, and less commonly hematopoietic or supradiaphragmatic cancers have been reported.4 It is more common in women, likely due to the addition of gynecologic malignancies.1