Keratoacanthomas (KAs) are rapidly growing tumors most prominently found on sun-exposed areas of the skin. The normal progression of a KA is to show rapid growth followed by spontaneous resolution.1 Most KAs are solitary; however, there are several variants of multiple KAs including the familial Ferguson-Smith type, Gryzbowski syndrome (generalized eruptive KAs), KA centrifugum marginatum, Muir-Torre syndrome, and xeroderma pigmentosum.2-4 Keratoacanthomas also may develop in areas of trauma, including burns, laser treatment, radiation, and surgical margins from excisional biopsies or skin grafting.5 Treatment of multiple KAs can be difficult due to a potentially large field size and number of lesions.6 We present a case of multiple KAs developing both in the surgical margins and de novo that responded dramatically to treatment with intralesional methotrexate (MTX).
Case Report
A 55-year-old man with a history of a surgically treated squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) on the anterior aspect of the right leg developed multiple nodules involving the surgical scar. He previously underwent Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS); within a month after the second surgery the patient noticed increased pruritus along with scaly pink changes at the site of the surgical scar.
One month prior to presentation, biopsies from the anterior aspect of the right leg demonstrated well-differentiated SCC and he was subsequently treated with MMS; however, examination 1 month after MMS revealed an 11×7-cm indurated plaque with multiple nodules ranging from 1 to 2 cm near the periphery of the plaque with central atrophy and scarring, reminiscent of KA centrifugum marginatum (Figure, A). In a similar fashion, an 8×5-cm plaque composed of 7 nodular areas was noted on the posterior aspect of the right leg (Figure, B). The patient denied any history of trauma to this area. There was no palpable regional lymphadenopathy and the remainder of the skin examination was normal, except for signs of venous stasis in both legs.
Based on the location and morphology of the lesions, the clinical presentation was consistent with multiple KAs. Histologic examination from punch biopsies taken from the plaque's periphery demonstrated well-differentiated SCC (KA type), as well as a lichenoid inflammatory process, epidermal hyperplasia, and cystic and endophytic squamous proliferation suggestive of hypertrophic lichen planus (HLP).
In consideration of the size and number of the lesions as well as the prolonged wound healing with prior surgery, the patient consented to treatment with intralesional MTX (1 mL of 12.5 mg/mL every 2 weeks) rather than undergoing further surgery. The MTX injection was distributed between the lesions on the anterior and posterior aspects of the lower right leg. At each injection session, the size, thickness, and nodularity of the tumor decreased with markedly less pruritus and symptomatic relief was achieved. After 3 injection sessions, resulting in a total of 3 mL of 12.5 mg/mL of MTX, biopsies were taken from the residual atrophic scar on the anterior aspect of the right leg and the remaining 3 papules on the posterior aspect of the right leg to rule out HLP and invasive SCC. The pathology report commented on the presence of prurigo nodules without any evidence of SCC.
At 3-month follow-up, the patient demonstrated no new lesions or recurrence (Figure, C and D). The right leg continued to heal with scarring and postinflammatory pigmentary changes. The patient was monitored for recurrence and to determine the diagnosis of HLP.
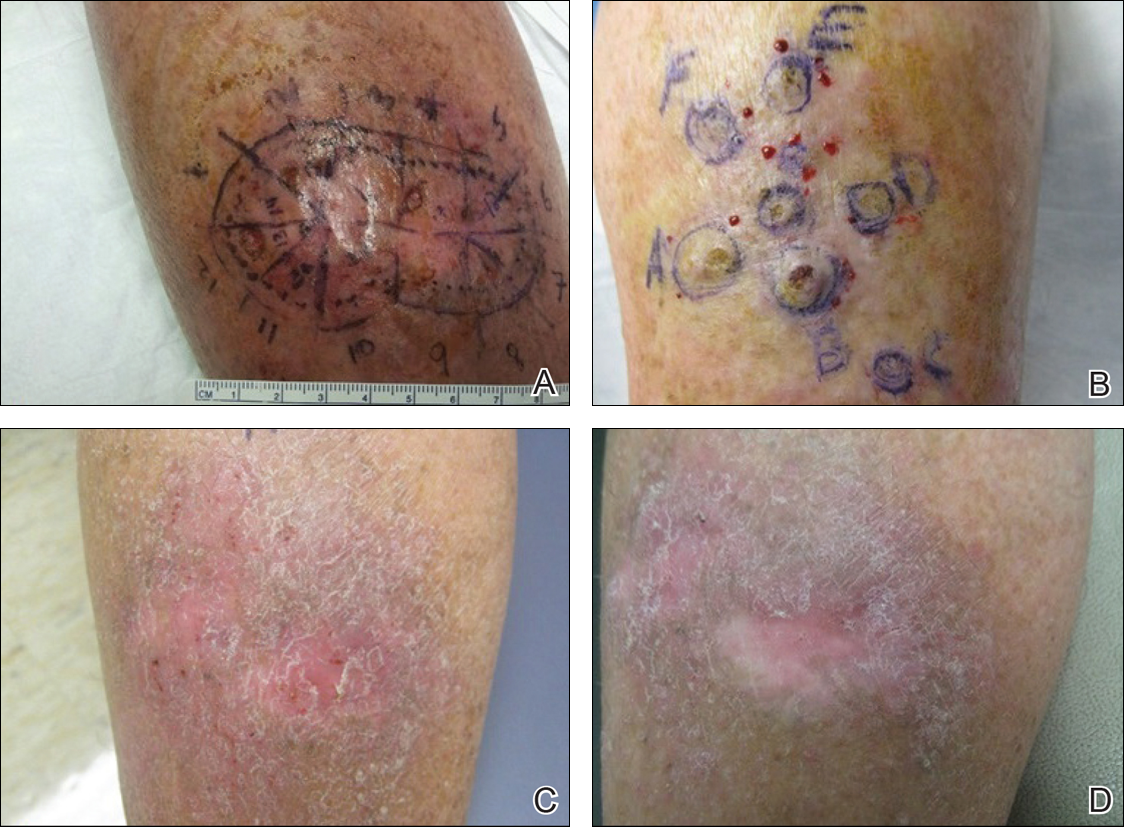
Initial presentation after Mohs micrographic surgery of 2 lesions of keratoacanthoma centrifugum marginatum on the anterior (A) and posterior aspects of the right leg (B). At 3-month follow-up, a well-healed surgical site with no evidence of cancer recurrence was noted following treatment with 3 rounds of intralesional methotrexate (C [anterior] and D [posterior]).

