Sun exposure and sunburns sustained during childhood are linked to an increased risk for development of skin cancers in adulthood. In infants, the skin is particularly vulnerable and is considered to be at increased risk for UV radiation damage,1 even as early as the first 6 months of life.2 Sun-safe behaviors instituted from a young age may help reduce the risk for future skin cancers.3 To effectively teach parents proper sun-safe practices, it is essential to understand their existing perceptions and behaviors. This study sought to examine differences in infant sun-safety practices during the first 6 months of life among black, Hispanic, and non-Hispanic white (NHW) parents in Miami, Florida.
Methods
Parents presenting to the University of Miami general pediatrics clinic from February 2015 through April 2015 with a child younger than 5 years were administered a 15-item questionnaire that included items on demographics, sun-safety strategies, sunburns and tanning, beliefs and limitations regarding sunscreen, and primary information source regarding sun safety (eg, physician, Internet, media, instincts). Parents were approached by the investigators consecutively for participation in scheduled blocks, with the exception of those who were otherwise engaged in appointment-related tasks (eg, paperwork). The study was approved by the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine institutional review board. The primary objective of this study was to determine the sun protection behaviors that black and Hispanic parents in Miami, Florida, employ in infants younger than 6 months. Secondary objectives included determining if this patient population is at risk for infant sunburns and tanning, beliefs among parents regarding sunscreen's efficacy in the prevention of skin cancers, and limitations of sunscreen use.
All data were analyzed using SAS software version 9.3. Wilcoxon signed rank test, Kruskal-Wallis test, Fisher exact test, and proportional-odds cumulative logit model were used to compare nonparametric data. Parents reporting on the full first 6 months of life (ie, the child was older than 6 months at the time of study completion) were included for analysis of sun-safety strategies. All survey respondents were included for analysis of secondary objectives. Responses from parents of infants of mixed racial and ethnic backgrounds were excluded from applicable subgroup analyses.
Results
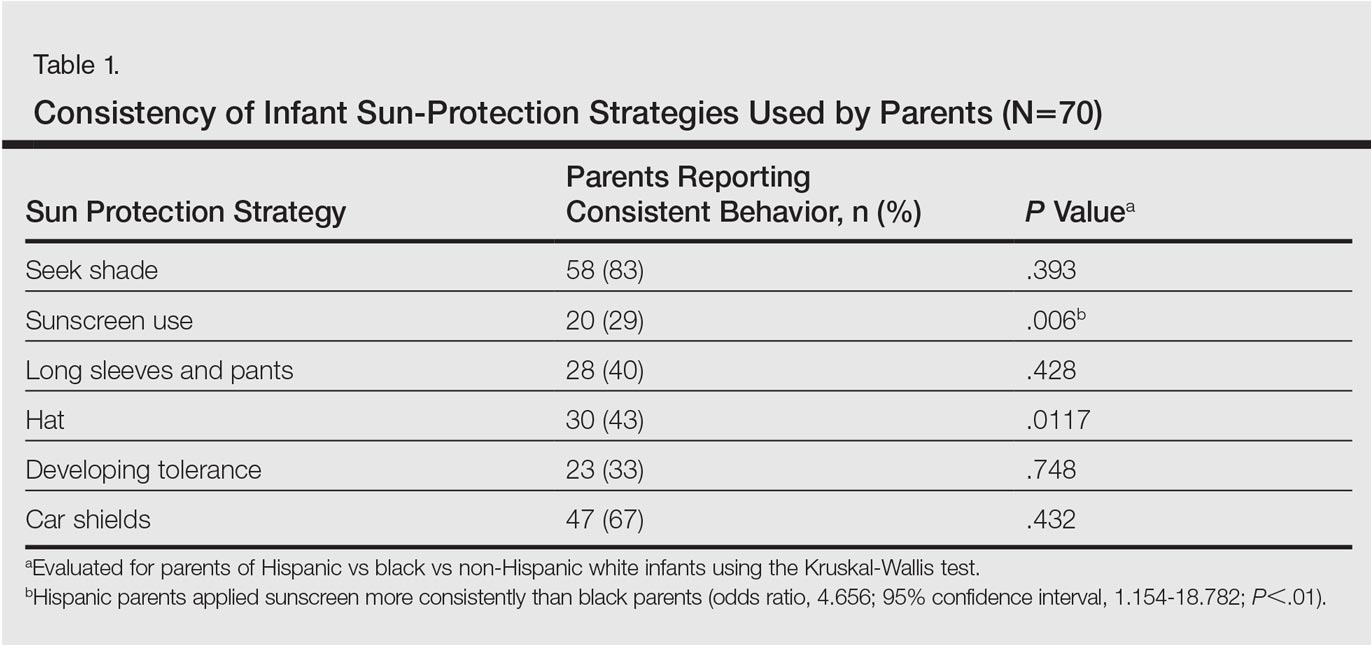
Ninety-eight parents were approached for participation in the study; 97 consented to participate and 95 completed the survey. Seventy parents had children who were at least 6 months of age and were included for analysis of the primary objectives (ie, sun-protection strategies in the first 6 months of life). The cohort included 49 Hispanic parents, 26 black parents, and 9 NHW parents; 5 parents indicated their child was of mixed racial and ethnic background. Six respondents indicated another minority group (eg, Native American, Pacific Islander). Eighty-three respondents were mothers, 72 were educated beyond high school, and 14 were Spanish-speaking only. Four reported a known family history of skin cancer.
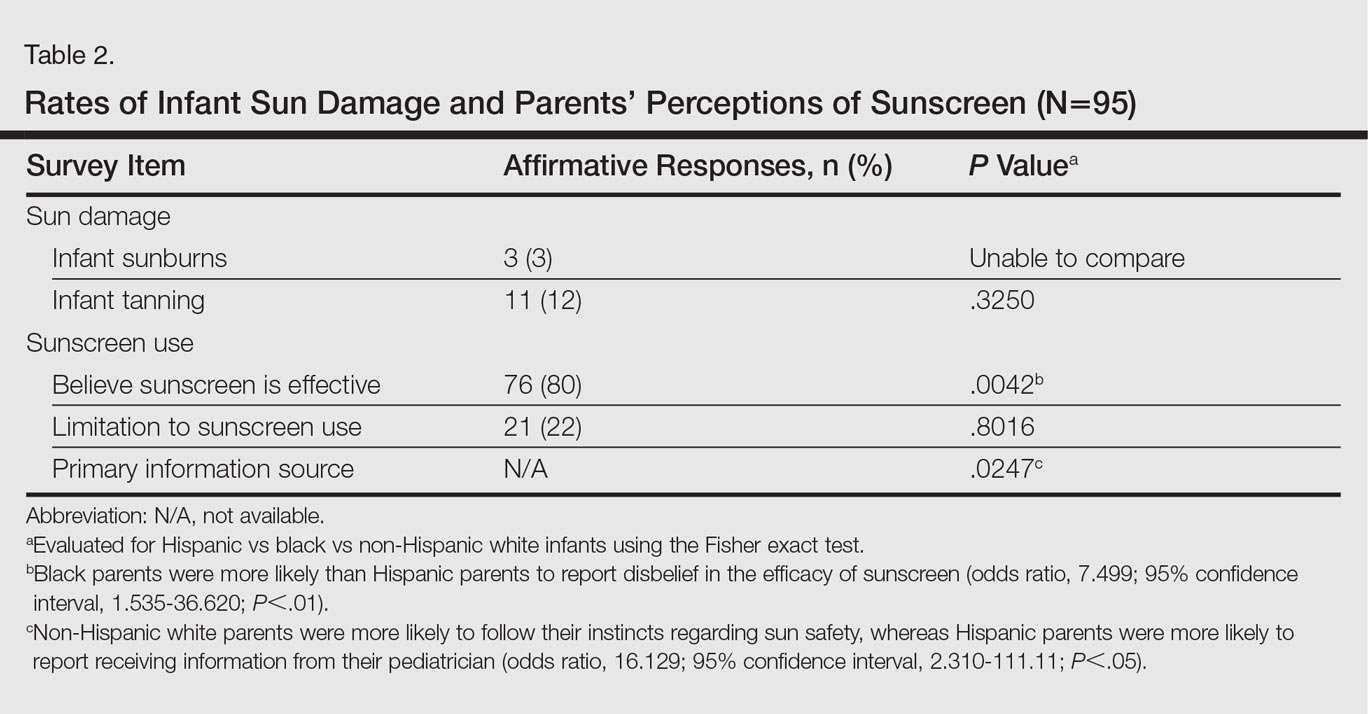
There were notable differences in application of sunscreen, belief in the efficacy of sunscreen, and primary source of information between parents (Tables 1 and 2). Hispanic parents reported applying sunscreen more consistently than black parents (odds ratio, 4.656; 95% confidence interval, 1.154-18.782; P<.01). Hispanic parents also were more likely than black parents to believe sunscreen is effective in the prevention of skin cancers (odds ratio, 7.499; 95% confidence interval, 1.535-36.620; P<.01). Hispanic parents were more likely to report receiving information regarding sun-safety practices for infants from their pediatrician, whereas NHW parents were more likely to follow their instincts regarding how and if infants should be exposed to the sun (P<.05). No significant differences were found in the reported primary source of information in black versus Hispanic parents or in black versus NHW parents. Three percent (3/95) of respondents reported a sunburn in the infant's first 6 months of life, and 12% (11/95) reported tanning of infants' skin from sun exposure. Tanning was associated with inconsistent shade (P<.01), inconsistent clothing coverage (P<.01), and consistently allowing infants to "develop tolerance to the sun's rays by slowly increasing sun exposure each day" (P<.05).