Case Report
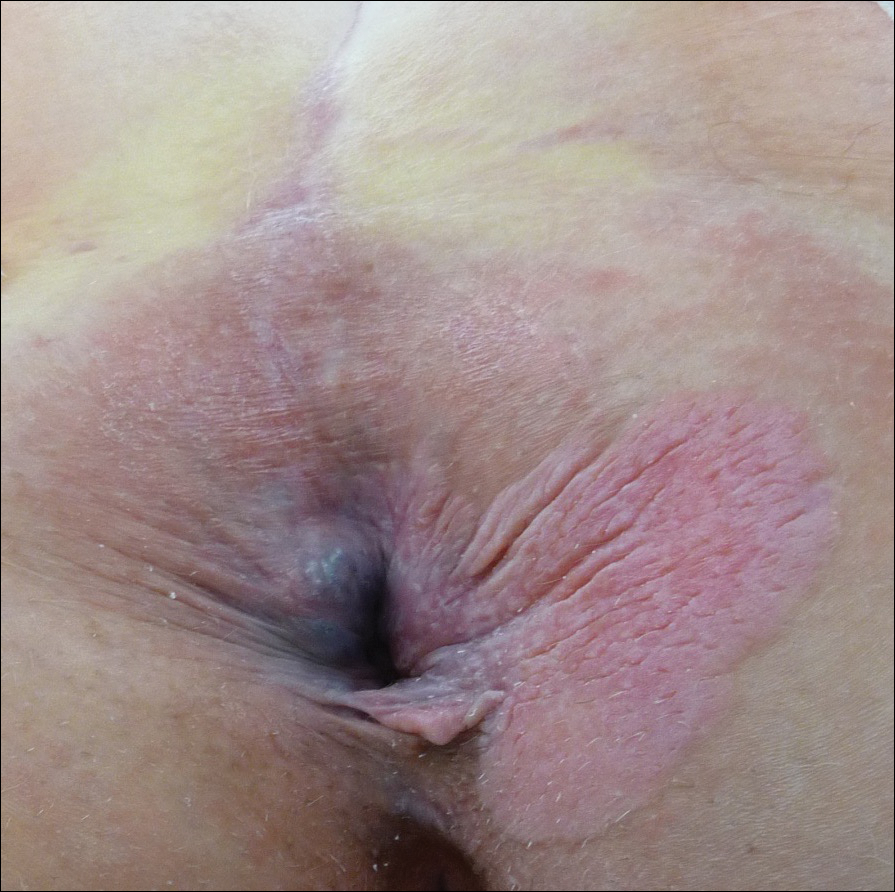
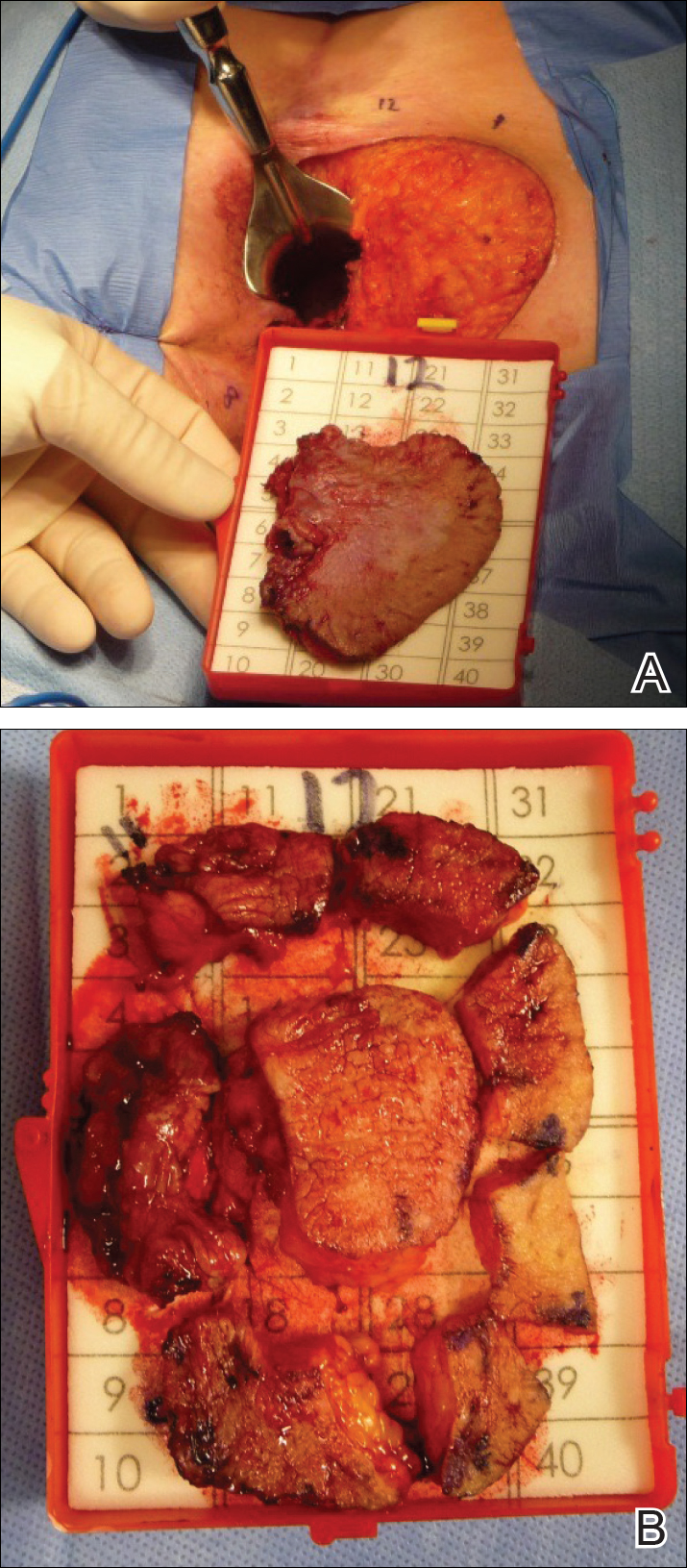
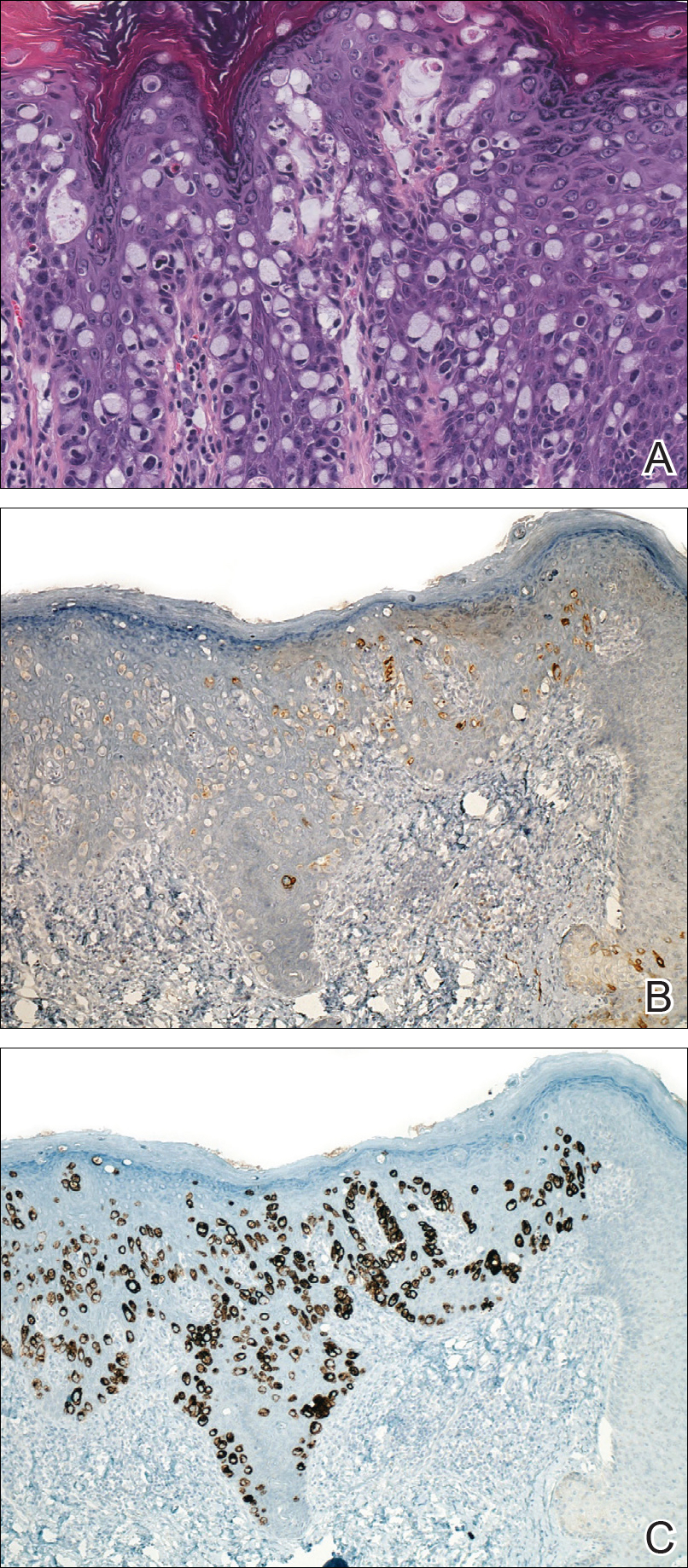
A 56-year-old woman with well-controlled hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and gastroesophageal reflux disease initially presented with itching and a rash in the perianal region of 1 year’s duration. She had been treated intermittently by her primary care physician over the past year for presumed hemorrhoids and a perianal fungal infection without improvement. Physical examination at the time of intitial presentation revealed a single, well-demarcated, scaly, pink plaque on the perianal area on the right buttock extending toward the anal canal (Figure 1). Histologic sections of a punch biopsy of the lesion showed a proliferation of cells with atypical nuclei and clear cytoplasm located throughout the epidermis (Figure 2A). Immunohistochemistry was positive for cytokeratin 7 (Figure 2B) and cytokeratin 20 (Figure 2C) and negative for melanoma antigen and human melanoma black 45. Following a negative workup for internal malignancy, which included basic laboratory testing (including serum carcinoembryonic antigen and cancer antigen 125 levels), computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis, positron-emission tomography, Papanicolaou test, mammography, and colonoscopy, a diagnosis of primary extramammary Paget disease (EMPD) was made. The patient underwent wide local excision (Figure 3A) of the lesion with Mohs micrographic surgery tissue processing of marginal tissue (Figure 3B) with clear margins and reconstruction of the perianal region.
Four years later, the patient returned with new symptoms of bleeding when wiping the perianal region, pruritus, and fecal urgency of 3 to 4 months’ duration. Physical examination revealed scaly patches on the anus that were suspicious for recurrence of EMPD. Biopsies from the anal margin and anal canal confirmed recurrent EMPD involving the anal canal. Repeat evaluation for internal malignancy was negative.
Given the involvement of the anal canal, repeat wide local excision would have required anal resection and would therefore have been functionally impairing. The patient refused further surgical intervention as well as radiotherapy. Rather, a novel 16-week immunomodulatory regimen involving imiquimod cream 5% cream and low-dose oral cimetidine was started. To address the anal involvement, the patient was instructed to lubricate glycerin suppositories with the imiquimod cream and insert intra-anally once weekly. Dosing was adjusted based on the patient’s inflammatory response and tolerability, as she did initially report some flulike symptoms with the first few weeks of treatment. For most of the 16-week course, she applied 250 mg of imiquimod cream 5% to the perianal area 3 times weekly and 250 mg into the anal canal once weekly. Oral cimetidine initially was dosed at 800 mg twice daily as tolerated, but due to stomach irritation, the patient self-reduced her intake to 800 mg 3 times weekly.
To determine treatment response, scouting biopsies of the anal margin and anal canal were obtained 4 weeks after treatment cessation and demonstrated no evidence of residual disease. The patient resumed topical imiquimod applied once weekly into the anal canal and around the anus for a planned prolonged course of at least 1 year. To reduce the risk of recurrence, the patient continued taking oral cimetidine 800 mg 3 times weekly. Recommended follow-up included annual anoscopy or colonoscopy, serum carcinoembryonic antigen evaluation, and regular clinical monitoring by the dermatology and colorectal surgery teams.
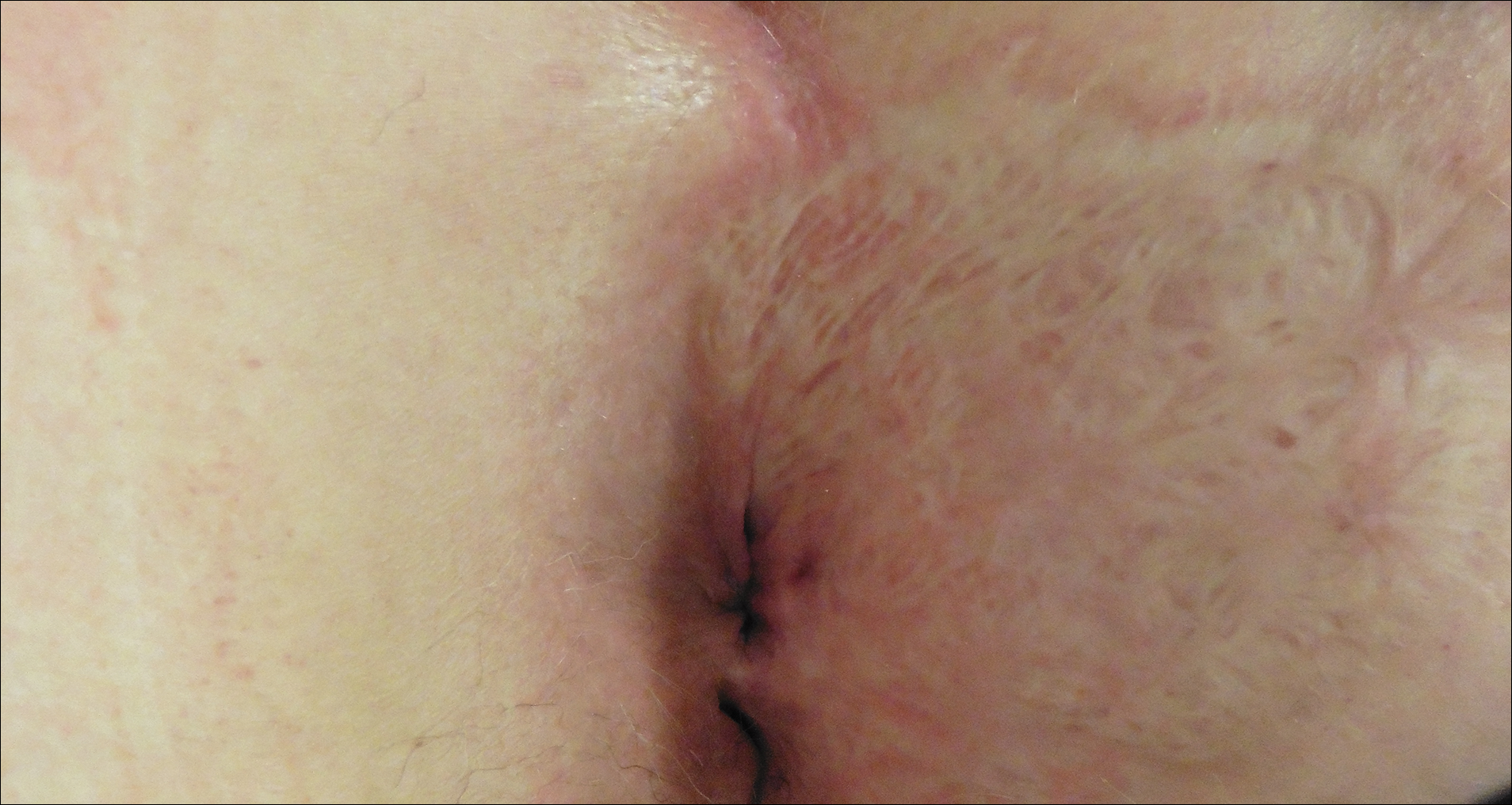
Six months after completing the combination therapy, she was seen by the dermatology department and remained clinically free of disease (Figure 4). Anoscopy examination by the colorectal surgery department 4 months later showed no clinical evidence of malignancy.