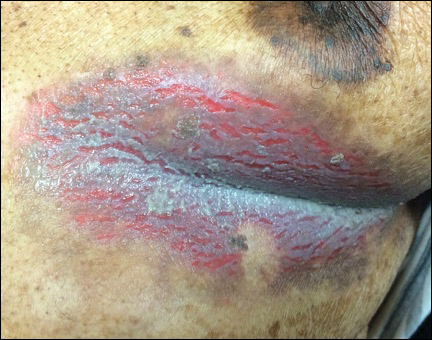
The Diagnosis: Hailey-Hailey Disease (Benign Familial Chronic Pemphigus)
Our patient had a long-standing history of Hailey-Hailey disease, as confirmed by multiple prior skin biopsies at outside institutions as well as our affiliated site. He began treatment with oral doxycycline 50 mg twice daily for 2 weeks, triamcinolone cream 0.1% twice daily to the affected region, and aluminum acetate solution soaks and chlorhexidine wash daily along with petroleum jelly, which resulted in good control of the disease. The differential diagnosis of eroded plaques, particularly in the axillary, crural, and inframammary folds, is broad and includes candidiasis, inverse psoriasis, contact dermatitis, dermatophyte infection, pemphigus vegetans or foliaceus, and granular parakeratosis.
Hailey-Hailey disease is a genetic disorder with a prevalence of 1 in 50,000 individuals. Most patients develop symptoms during the second or third decades of life.1 Hailey-Hailey disease exhibits an autosomal-dominant pattern of inheritance secondary to mutation in the human ATP2C1 gene, which codes for the ATPase secretory pathway of the Ca2+ transporting pump type 1 (SPCA1) localized in the Golgi apparatus.2 Altered SPCA1 protein reduces concentration of Ca2+ within the Golgi lumen, which in turn impairs the processing of junctional proteins needed for normal cell-to-cell adhesion.1
Clinically, Hailey-Hailey disease is characterized by vesicular or erosive plaques that have a predilection for intertriginous areas of the body.1 The primary lesions often are flaccid vesicles that easily rupture, leaving behind crusted erosions that spread peripherally. The lesions also can appear as macerated plaques resembling torn tissue paper, as in our case. Friction, heat, and sweat exacerbate the disease. Complications occur from secondary bacterial, fungal, and viral colonization. Malodor and vegetations can indicate bacterial or fungal infections and can lead to persistence of skin lesions. Herpes simplex virus infections can exacerbate preexisting lesions.3 Hailey-Hailey disease of the anogenital region also can be complicated by infection with oncogenic strains of human papillomavirus and lead to cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.4
Hailey-Hailey disease histologically appears as suprabasal and intraepidermal keratinocyte acantholysis,5 which typically is widespread in the epidermis, with large areas of dyscohesion with a dilapidated brick wall-like appearance.1 In more chronic lesions, epidermal hyperplasia, parakeratosis, and focal crusts may be observed. A moderate perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate can be observed in the superficial dermis. Direct immunofluorescence typically is negative.
Topical corticosteroids and antimicrobials are first-line therapies that often only provide temporary suppression. When the disease is refractory to topical therapies, intralesional corticosteroids may be attempted. There is no strong evidence to support the use of systemic therapy, aside from antimicrobial agents (eg, doxycycline) for the use of superinfections. In severe cases, immunomodulating therapies such as prednisone, cyclosporine, methotrexate, dapsone, alefacept, and oral retinoids may be effective.6-8 Surgical therapy also can be considered for recalcitrant disease, including wide excision and grafting, though these techniques can be associated with morbidity.9
Superficial ablative techniques including dermabrasion, laser therapy with CO2 and erbium-doped YAG, photodynamic therapy, and electron beam radiation have been shown to be effective modalities in severe cases.5,9-11 It has been hypothesized that keratinocytes expressing the molecular defect are ablated, while the surrounding normal adnexal epithelium can regenerate normal epithelium. It also is thought that dermal fibrosis leads to better support of the diseased epidermis and decreases the risk for ulceration and fissuring.9