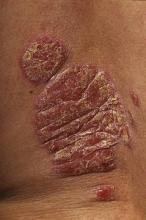
GOTHENBURG, SWEDEN – Blockade of the receptor for the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-17 using a novel fully human IgG2 monoclonal antibody has shown promise as a treatment for chronic plaque psoriasis.
In a small, phase I, double-blind randomized study, a single dose of AMG 827 was well tolerated and led to rapid clinical improvement accompanied by reversal of the molecular, cellular, and histologic hallmarks of the disease, Dr. David A. Martin reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Based upon these findings, a phase II study of AMG 827 in patients with plaque psoriasis is underway, added Dr. Martin, an employee of the drug’s manufacturer and study sponsor, Amgen (Seattle).
He reported on 20 psoriasis patients who were randomized 4:4:1 to a single IV dose of AMG 827 at either 350 mg or 700 mg or to placebo. Biopsies were obtained from lesional and nonlesional skin at baseline and from lesional skin on days 8, 15, and 43.
By day 15 the 16 patients who received AMG 827 showed roughly a mean 60% improvement over baseline in terms of Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) scores. By day 43 the group treated with the 700-mg dose showed continued gains, with an 85% improvement in PASI scores over baseline. A PASI 75, or a 75% improvement over baseline, was achieved by day 43 in five of eight patients in the 350-mg group, seven of eight who got 700 mg of AMG 827, and none of four placebo-treated controls.
Physician’s Global Assessment ratings of psoriasis as "clear" or "minimal" were attained by all eight patients in the 700-mg group, five of eight who received 350 mg, and none of four controls.
At baseline, roughly 10,000 gene expression sequences were abnormally up- or downregulated in lesional skin. By day 8, this was reduced to about 2,000 abnormally expressed gene sequences. By day 15, the abnormal gene expression signature in the 700-mg group had dropped to roughly 500 abnormal sequences, nearly the same as in nonlesional skin at baseline.
The low level of abnormal gene expression was maintained in the 700-mg group out to day 43. Meanwhile, the abnormal gene expression signature in the 350-mg group improved from 2,000 sequences on day 8 to about 1,000 on day 43, Dr. Martin said.
Histopathologic findings in lesional skin included significant reductions in epidermal thickness, keratin-16 mRNA levels, Ki-67 cell counts, and the number of infiltrating leukocyte subsets by day 15, with further improvements noted by day 43.
AMG 827 is also under study for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases. Interleukin-17 is known to activate local expression of a range of cytokines, metalloproteinases, chemokines, and antimicrobial peptides.