WAIKOLOA, HAWAII – Many dermatologists find melanonychia to be intimidating. The clinical features are ambiguous, and the prospect of doing a painful nail apparatus biopsy can be daunting for the inexperienced. As a result, the biopsy gets delayed and melanoma of the nail is often initially a missed diagnosis, not uncommonly for years, with devastating consequences.
Here are five at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by the Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
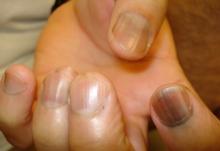
Rule #1: Always look beyond the nail
When a light-skinned person presents with more than one nail with pigmentation, the likelihood that one of them is melanoma is much less than if there is only one nail with melanonychia, according to Dr. Jellinek, a dermatologist in private practice in East Greenwich, R.I.
Also, be sure to look at the skin and mucosa. Consider the medications the patients may be taking: For example, cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) is notorious for causing nail changes as a side effect. A past medical history of lichen planus, carpal tunnel syndrome, Addison disease, or other conditions may explain the melanonychia.
Laugier-Hunziker syndrome is a condition worth getting to know. It’s an acquired disorder characterized longitudinal melanonychia and other pigmentary changes, which may include diffuse hyperpigmentation of the orolabial mucosa, ocular pigment, and/or pigmented palmoplantar lesions. It’s said to be rare, but Dr. Jellinek disagrees.
“Learn this one if you don’t know it. I see a case about every 2 weeks. It’s not heritable and not associated with any other medical condition,” he said.
Rule #2: Your dermatoscope is great for nails
What Dr. Jellinek considers to be among the all-time best papers on the value of dermoscopy for nail pigmentation was authored by French investigators. They analyzed 148 consecutive cases of longitudinal melanonychia and concluded that the dermoscopic combination of a brown background coupled with irregular longitudinal lines in terms of color, spacing, diameter, and/or lack of parallelism strongly suggests melanoma. A micro-Hutchinson’s sign, while a rare finding, occurred only in melanoma, where it represented periungual spread of a radial growth phase malignancy (Arch Dermatol. 2002 Oct;138[10]:1327-33).
“I think nail dermoscopy is most helpful for subungual hemorrhage. I average one referral per week for hemorrhage under the nail. On dermoscopy it’s as if someone took paint and threw it at the nail. Purple to brown blood spots, with no background color. This should be a doorway diagnosis of hemorrhage,” Dr. Jellinek said.
Rule #3: Know when you don’t know
“This is really the key for me,” the dermatologist commented. “There are automatic cases for biopsy, and more commonly routine cases for reassurance. But the gray zone, when you know you don’t know, is the key decision making moment.”
When something just doesn’t feel right, there’s absolutely nothing wrong with getting a second opinion, he stressed.
“It’s worthwhile getting to know people whose opinions you trust. There’s a saying I like to teach our fellows: ‘Never worry alone.’ So if you’re worried about someone, listen to that inner voice. There’s no shame in getting a second opinion. It’s great! Patients are never upset, either. They feel really well taken care of,” he said.