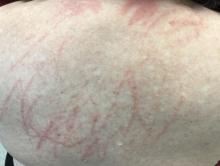
Shiitake mushroom flagellate dermatitis
that resemble whiplash marks. The lesions may be extremely pruritic, and petechiae may be present in the streaks. The trunk is most commonly affected, although lesions can occur on the limbs. Mucosa is not affected. Sun exposure may exacerbate the condition. The dermatitis has been described in all ages and races, and males seem to be more affected than females.
Shiitake mushroom flagellate dermatitis typically occurs following the ingestion of raw or undercooked shiitake mushrooms (Lentinula edodes). The mushrooms contain a polysaccharide called lentinan. Ingestion of lentinan activates interleukin-1 (IL-1), resulting in vasodilation and the subsequent dermatitis that can occur within a few hours and up to 5 days post ingestion. Associated gastrointestinal symptoms, fever, and localized swelling have been reported. The rash will resolve spontaneously over a few days to weeks.
Flagellate erythema has been described with bleomycin treatment. Other reported associations include peplomycin (a bleomycin derivative) and docetaxel. The rash may appear following administration of bleomycin by any route and has been shown to be dose independent. Onset occurs anywhere from 1 day to several months after exposure. Over time, the erythema will develop into postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Dermatomyositis may present with flagellate erythema. Other symptoms include muscle weakness and an inflammatory myopathy. A heliotrope rash on the eyelids, Gottron’s papules on the hands, ragged cuticles with prominent vessels on nail folds may be seen. Blood work may reveal elevated antinuclear antibodies (ANA), anti–Mi-2 and anti–Jo-1. Adult-onset Still disease is characterized by fever, arthritis, and salmon-colored patches.
Our patient’s dermatitis resolved spontaneously without treatment.
This case and photo were provided by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.