Photo Challenge
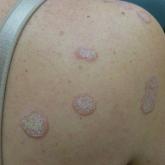
Hyperkeratotic Nummular Plaques on the Upper Trunk
A 48-year-old woman with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis presented with papules and plaques on the upper...
Dr. Bolick is from the Brody School of Medicine, East Carolina University, Greenville, North Carolina. Drs. Trivedi and Elston are from the Department of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Dirk M. Elston, MD, Department of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery, Medical University of South Carolina, 135 Rutledge Ave, MSC 578, Charleston, SC 29425 (elstond@musc.edu).

A 52-year-old woman with a history of rheumatoid arthritis presented with a rash on the palms and soles of 7 years' duration that started around the onset of menopause. Physical examination revealed thick hyperkeratotic plaques with multiple deep fissures on the palms and soles. The patient's current medications included methotrexate for rheumatoid arthritis. She previously had been prescribed adalimumab by an outside physician for the rash, which provided no relief, and currently was using urea ointment, which caused a burning sensation on the palms and soles. The patient denied a personal or family history of psoriasis.
Keratoderma climactericum was first reported in 1934 by Haxthausen1 as nonpruritic circumscribed hyperkeratosis located mainly on the palms and soles. The initial eruption was described as discrete lesions with an oval or round shape that progressed to less-defined, confluent, hyperkeratotic patches with fissures.1 Keratoderma climactericum also may be referred to as Haxthausen disease and is considered an acquired palmoplantar keratoderma.2
Keratoderma climactericum is a rare dermatologic disorder that presents in women of menopausal age who have no family or personal history of skin disease. Keratoderma climactericum is associated with hypertension and obesity.2 Keratotic lesions usually first occur on the plantar surfaces with eventual development of fissuring and hyperkeratosis that causes painful walking. The keratotic lesions on the plantar surfaces often are nonpruritic and gradually become confluent over time. As the disease progresses, keratotic lesions appear on the central palms, which can lead to confluent hyperkeratosis on the palmar surfaces (Figure 1).2 The exact mechanism of keratoderma climactericum has not been described but is believed to be due to hormonal dysregulation.2
In 1986, Deschamps et al3 presented 10 cases of keratoderma climactericum occurring in menopausal women with an average age of 57 years. The lesions began on the soles at areas of greatest pressure. Histopathology for each patient showed orthokeratotic hyperkeratosis, irregular hyperplasia, interpapillary ridges, and exocytosis of lymphocytes in the epidermis. Seven patients were treated with etretinate, which first led to the removal of palmar lesions, followed by improvement in plantar lesions and pain when walking. There was no association of keratoderma climactericum and sex hormones, as hormone levels were negative or normal for each patient.3
Three cases of keratoderma climactericum following bilateral oophorectomy in young women were reported by Wachtel4 in 1981. Unlike in women of menopausal age, there was no association of keratoderma climactericum with hypertension or obesity. Additionally, the lesions on the palms and soles were more diffusely distributed than in women of menopausal age. Estrogen administration completely reversed each patient's hyperkeratotic palms and soles.4 A definitive pathogenic role of estrogens in the development of keratoderma climactericum has yet to be determined.2
Histopathology is not specific for keratoderma climactericum, making the disease a clinical diagnosis. However, a biopsy may be useful to rule out palmoplantar psoriasis.2 Clinical information such as the age and sex of the patient, distribution of disease, presence of fissuring, and progression of disease from soles to palms should be considered when making a diagnosis of keratoderma climactericum. The differential diagnosis of keratoderma climactericum should include fungal infections, contact dermatitis, irritant dermatitis, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, underlying malignancy, and pityriasis rubra pilaris.
Treatment options for keratoderma climactericum include salicylic acid, emollients, oral retinoids, urea ointments, estriol cream, and topical steroids.5,6 Our patient was prescribed acitretin 25 mg daily and ammonium lactate to apply topically as needed for dry skin. Five months after the initial presentation, fissures and dry skin on the bilateral soles were still present. Ammonium lactate was discontinued, and the patient was prescribed urea cream 40%. Fifteen months after the initial presentation, the patient reported substantial improvement on the hands and feet and noted that she no longer needed the urea cream. Physical examination revealed no presence of hyperkeratosis or fissuring on the palms (Figure 2), and mild hyperkeratosis was present on the plantar surfaces of the feet (Figure 3). The patient continued to use acitretin to prevent disease relapse.

A 48-year-old woman with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis presented with papules and plaques on the upper...
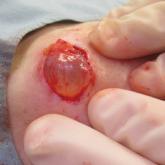
A 70-year-old woman presented to the outpatient dermatology clinic with an acute-onset lesion on the right shoulder. She first noticed a “cyst”...
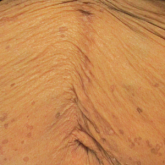
A 50-year-old Black woman with systemic lupus erythematosus and a renal transplant 15 years prior due to lupus nephritis presented with a...
