Identifying safe, effective, and affordable evidence-based dermatologic treatments for older adults can be challenging because of age-related changes in the skin, comorbidities, polypharmacy, mobility issues, and cognitive changes. Phototherapy has been shown to be an effective nonpharmacologic treatment option for multiple challenging dermatologic conditions1-8; however, few studies have specifically examined its effectiveness in older adults. The challenge for older patients with psoriasis and dermatitis is that the conditions can be difficult to control and often require multiple treatment modalities.9,10 Patients with psoriasis also have a higher risk for diabetes, dyslipidemia, and cardiovascular disease compared to other older patients,11,12 which poses treatment challenges and makes nonpharmacologic treatments even more appealing.
Recent studies show that phototherapy can help decrease the use of dermatologic medications. Foerster and colleagues2 found that adults with psoriasis who were treated with phototherapy significantly decreased their use of topical steroids (24.5% fewer patients required steroid creams and 31.1% fewer patients required psoriasis-specific topicals)(P<.01) while their use of non–psoriasis-specific medications did not change. Click and colleagues13 identified a decrease in medication costs, health care utilization, and risk for immunosuppression in patients treated with phototherapy when compared to those treated with biologics and apremilast. Methotrexate is a common dermatologic medication that is highly associated with increased risks in elderly patients because of impaired immune system function and the presence of comorbidities (eg, kidney disease, obesity, diabetes, fatty liver),14 which increase in prevalence with age. Combining phototherapy with methotrexate can substantially decrease the amount of methotrexate needed to achieve disease control,15 thereby decreasing the methotrexate-associated risks. Findings from these studies suggest that a safe, effective, cost-effective, and well-tolerated nonpharmacologic alternative, such as phototherapy, is highly desirable and should be optimized. Unfortunately, most studies that report the effectiveness of phototherapy are in younger populations.
This retrospective study aimed to (1) identify the most common dermatologic conditions treated with phototherapy in older adults, (2) examine the effectiveness and safety of phototherapy in older adults, and (3) compare the outcomes with 2 similar studies in the United Kingdom16 and Turkey.17
Methods
Design, Setting, Sample, and Statistical Analysis
The institutional review boards of Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute, Seattle, and the University of Washington, Seattle, approved this study. It was conducted in a large US multispecialty health care system (Group Health, Seattle, Washington [now Kaiser Permanente Washington]) serving approximately 600,000 patients, using billing records to identify all patients treated with phototherapy between January 1, 2015, and December 31, 2015, all who received narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) phototherapy. All adults 65 years and older who received phototherapy treatment during the 12-month study period were included. Patients were included regardless of comorbidities and other dermatologic treatments to maintain as much uniformity as possible between the present study and 2 prior studies examining phototherapy in older adult populations in the United Kingdom16 and Turkey.17 Demographic and clinical factors were presented using frequencies (percentages) or means and medians as appropriate. Comparisons of dermatologic conditions and clearance levels used a Fisher exact test. The number of phototherapy treatments to clearance and total number of treatments were compared between groups of patients using independent sample t tests.
Phototherapy Protocol
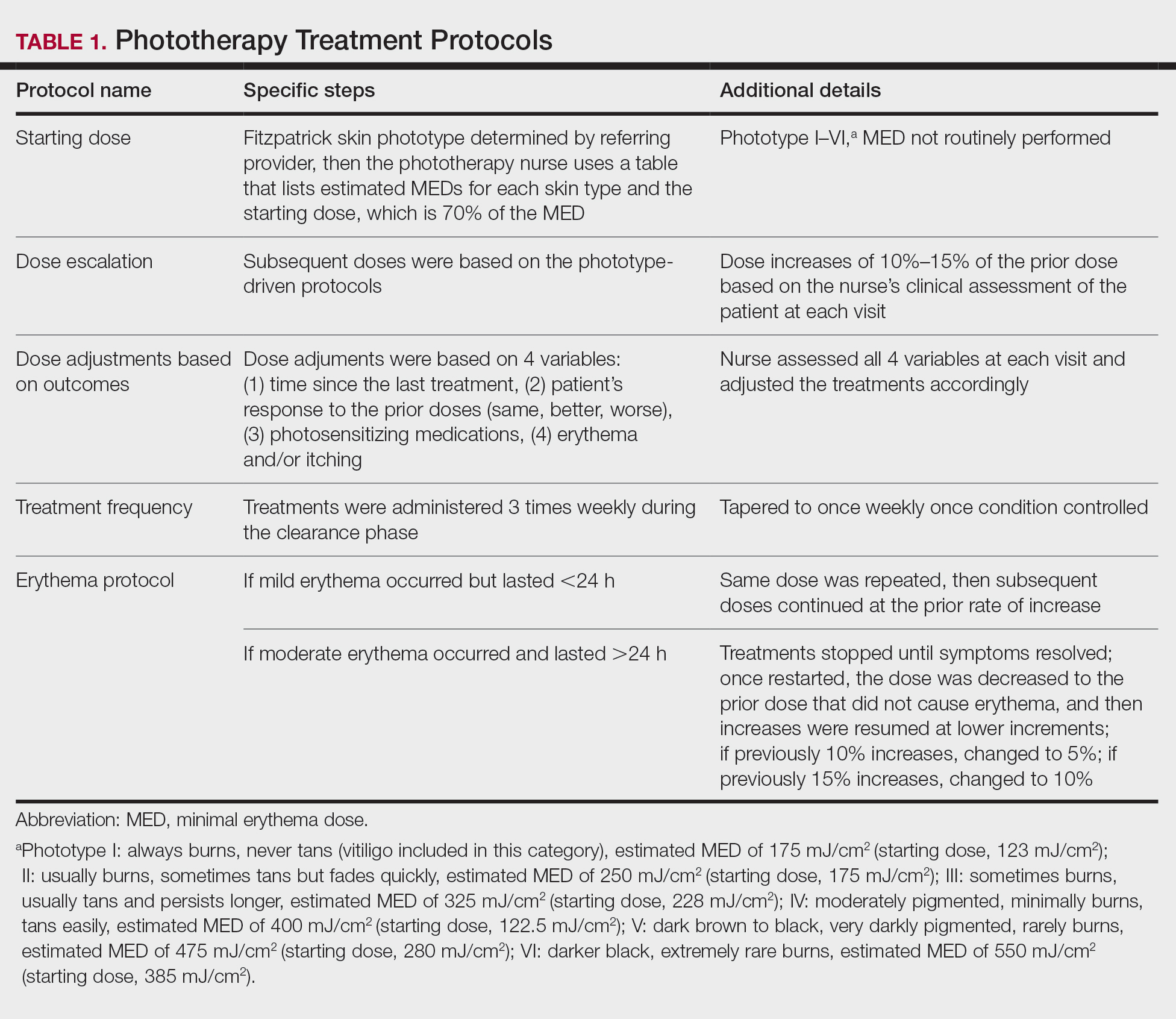
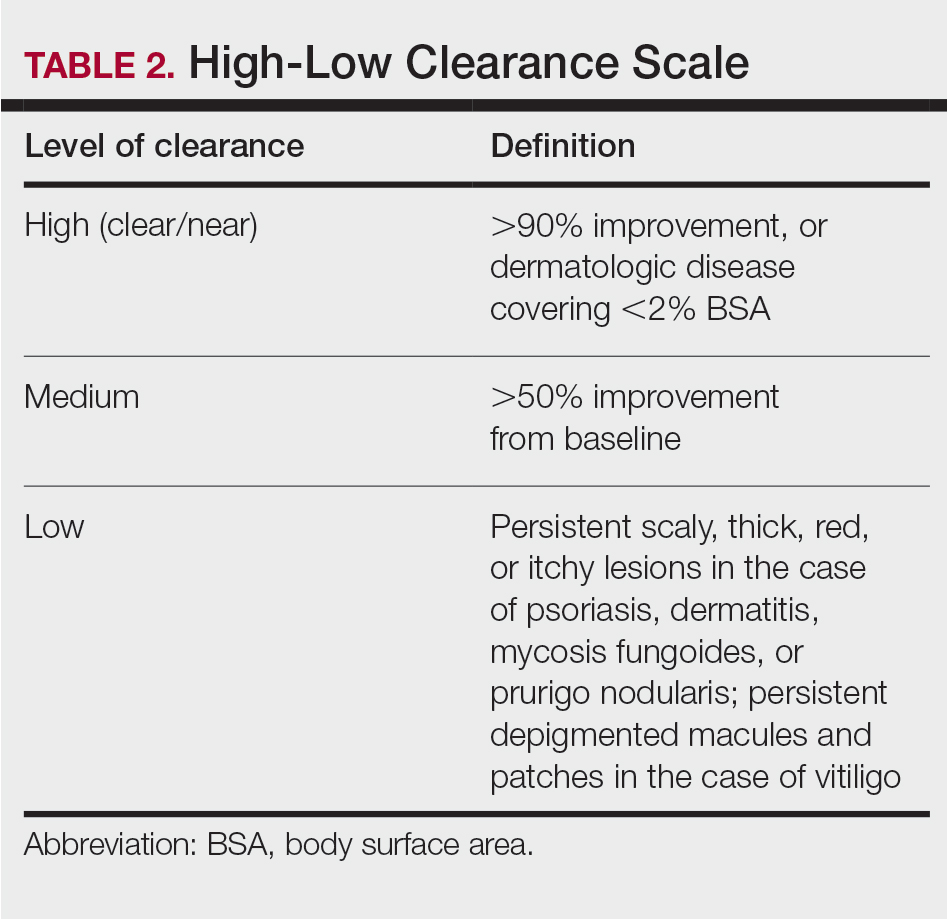
All patients received treatments administered by specially trained phototherapy nurses using a Daavlin UV Series (The Daavlin Company) or an Ultralite unit (Ultralite Enterprises, Inc), both with 48 lamps. All phototherapy nurses had been previously trained to provide treatments based on standardized protocols (Table 1) and to determine the patient’s level of disease clearance using a high to low clearance scale (Table 2). Daavlin’s treatment protocols were built into the software that accompanied the units and were developed based on the American Academy of Dermatology guidelines. The starting dose for an individual patient was determined based on the estimated minimal erythema dose for each phototype. If the patient was using photosensitizing medications, then the protocol guided the nurse to start the patient at a lower dose appropriate for their phototype. Patients with vitiligo were treated with the same starting and escalation doses as patients with Fitzpatrick phototype I because of the assumption that their vitiliginous skin had an increased risk for photosensitivity. A more recent review of the evidence has indicated that this assumption was overly conservative,18 and Kaiser Permanente Washington’s vitiligo protocol has been adjusted.
Results
Patients
Billing records identified 229 total patients who received phototherapy in 2015, of whom 52 (22.7%) were at least 65 years old. The median age was 70 years (range, 65–91 years). Twenty-nine (56%) were men and 35 (67%) had previously received phototherapy treatments.
Dermatologic Conditions Treated With Phototherapy
Our primary aim was to identify the most common dermatologic conditions treated with phototherapy in older adults. Psoriasis and dermatitis were the most common conditions treated in the sample (50% [26/52] and 21% [11/52], respectively), with mycosis fungoides being the third most common (10% [5/52]) and vitiligo tied with prurigo nodularis as fourth most common (6% [3/52])(Figure 1).