To the Editor:
Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum (PPG) is a rare entity first described in 1984.1 Lesions usually begin as pustules that coalesce into an erythematous skin ulceration that contains purulent material. The lesion appears on the skin that surrounds an abdominal stoma. Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum typically is associated with Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis, cancer, blood dyscrasia, diabetes mellitus, and hepatitis.2 We describe a case of PPG following an ileostomy in a patient with colon cancer and a related history of Crohn disease.
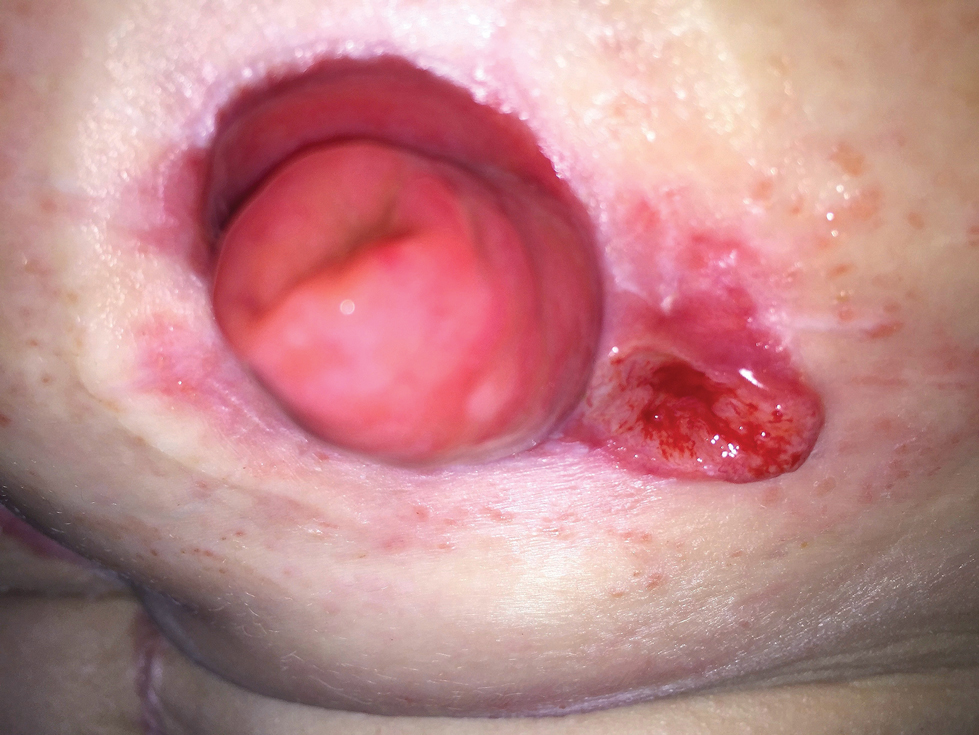
A 32-year-old woman presented to a dermatology office with a spontaneously painful, 3.2-cm ulceration that was extremely tender to palpation, located immediately adjacent to the site of an ileostomy (Figure). The patient had a history of refractory constipation that failed to respond to standard conservative measures 4 years prior. She underwent a colonoscopy, which revealed a 6.5-cm, irregularly shaped, exophytic mass in the rectosigmoid portion of the colon. Histopathologic examination of several biopsies confirmed the diagnosis of moderately well-differentiated adenocarcinoma, and additional evaluation determined the cancer to be stage IIB. She had a medical history of pancolonic Crohn disease since high school that was treated with periodic infusions of infliximab at the standard dose of 5 mg/kg. Colon cancer treatment consisted of preoperative radiotherapy, complete colectomy with ileoanal anastomosis, and creation of a J-pouch and formation of a temporary ileostomy, along with postoperative capecitabine chemotherapy.
The ileostomy eventually was reversed, and the patient did well for 3 years. When the patient developed severe abdominal pain, the J-pouch was examined and found to be remarkably involved with Crohn disease. However, during the colonoscopy, the J-pouch was inadvertently punctured, leading to the formation of a large pelvic abscess. The latter necessitated diversion of stool, and the patient had the original ileostomy recreated.
Prior to presentation to dermatology, various consultants suspected the ulceration was possibly a deep fungal infection, cutaneous Crohn disease, a factitious ulceration, or acute allergic contact dermatitis related to some element of ostomy care. However, dermatologic consultation suggested that the troublesome lesion was classic PPG and recommended administration of a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α–blocking agent and concomitant intralesional injections of dilute triamcinolone acetonide.
The patient was treated with subcutaneous adalimumab 40 mg once weekly, and received near weekly subcutaneous injections of triamcinolone acetonide 10 mg/mL. After 2 months, the discomfort subsided, and the ulceration gradually resolved into a depressed scar. Eighteen months later, the scar was barely perceptible as a minimally erythematous depression. Adalimumab ultimately was discontinued, as the residual J-pouch was removed, and the biologic drug was associated with extensive alopecia areata–like hair loss. There has been no recurrence of PPG in the 40 months since clinical resolution.
Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum is an uncommon subtype of pyoderma gangrenosum, which is characterized by chronic, persistent, or recurrent painful ulceration(s) close to an abdominal stoma. In total, fewer than 100 cases of PPG have been reported thus far in the readily available medical literature.3 Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is the most frequently diagnosed systemic condition associated with PPG, though other associated conditions include diverticular disease, abdominal malignancy, and neurologic dysfunction. Approximately 2% to 4.3% of all patients who have stoma creation surgery related to underlying IBD develop PPG. It is estimated that the yearly incidence rate of PPG in all abdominal stomas is quite low (approximately 0.6%).4
Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum can occur at any age, but it tends to predominate in young to middle-aged adults, with a slight female predilection. The etiology and pathogenesis of PPG are largely unknown, though studies have shown that an abnormal immune response may be critical to its development. Risk factors for PPG are not well defined but potentially include autoimmune disorders, a high body mass index, and females or African Americans with IBD.4 Because PPG does not have characteristic histopathologic features, it is a diagnosis of exclusion that is based on the clinical examination and histologic findings that rule out other potential disorders.