To the Editor:
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EDV) is a rare generalized form of epidermal dysplasia that is linked to certain subtypes of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and inherited or acquired states of immunodeficiency.1-3 The inherited form most commonly manifests via autosomal-recessive inactivation of the EVER1 and EVER2 genes that encode integral membrane proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum, though cases of autosomal-dominant and X-linked inheritance have been reported.1-3 Acquired cases have been reported in patients lacking immunocompetency, including transplant recipients and patients living with HIV.4-11 We present the case of a patient with HIV-associated EDV who was treated successfully with intralesional Candida albicans antigen, oral acitretin, and cryotherapy.
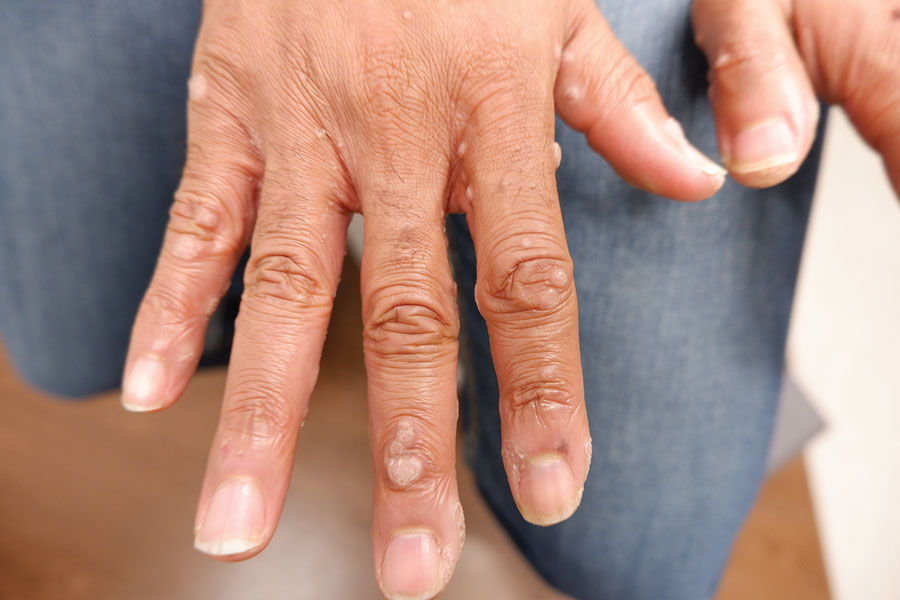
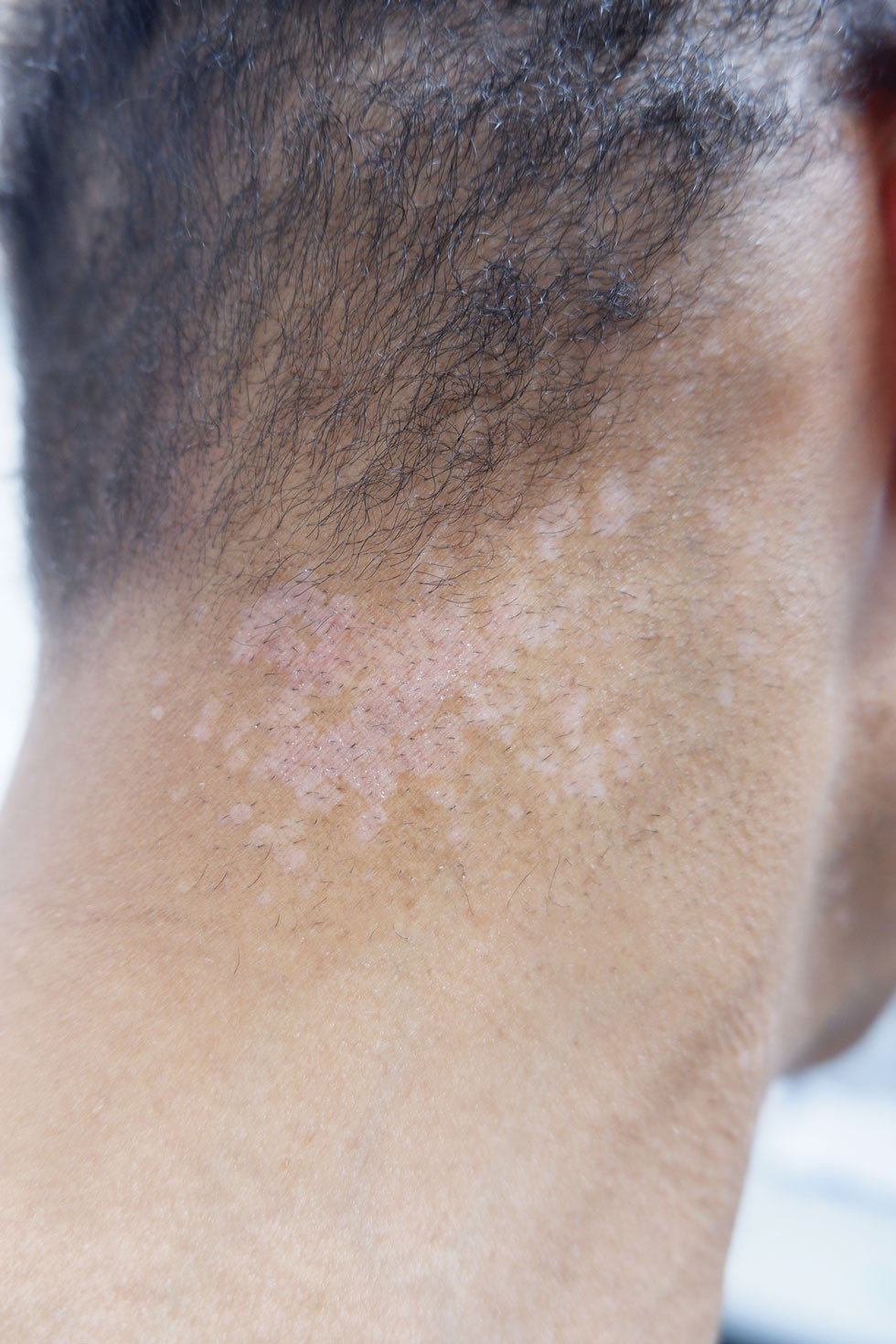
A 56-year-old man presented for evaluation of several cutaneous lesions that had developed over several months on the neck and over many years on the hands and feet. He had a 16-year history of HIV, Castleman disease, and primary effusion lymphoma in remission that was treated with rituximab, etoposide phosphate, prednisone, vincristine sulfate, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin hydrochloride 10 or more years ago. The patient denied pruritus or pain associated with the skin lesions. He was intermittently taking immunosuppressants and antiretrovirals including dolutegravir and emtricitabine-tenofovir for 3 years. Prior treatments of the lesions included cryotherapy and over-the-counter 17% salicylic acid. Physical examination revealed the presence of innumerable, clustered, verrucous, scaly papules on the dorsal and palmoplantar regions of the hands (Figure 1), as well as hypopigmented macules clustered on the neck that morphologically resembled tinea versicolor (Figure 2). The physical examination was otherwise unremarkable.
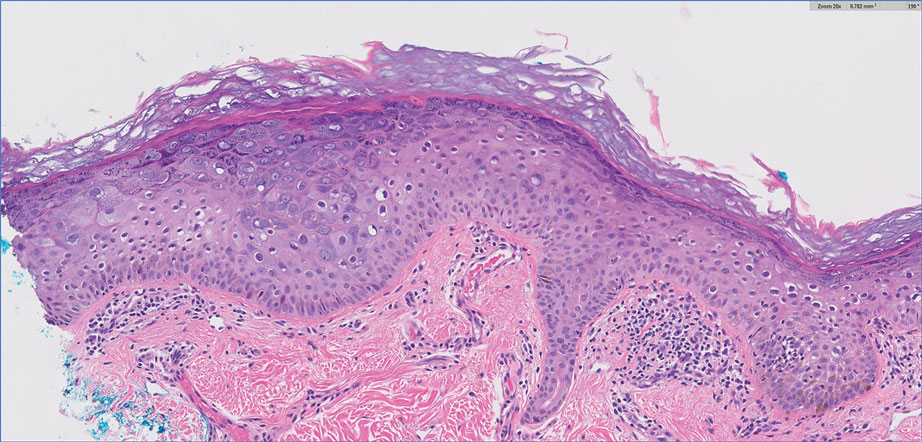
Complete blood cell counts as well as lipid, liver, and renal function panel results were unremarkable. Laboratory examination also revealed a CD4 cell count of 373/µL (reference range, 320–1900/µL) and an undetectable HIV copy number (<40 copies/mL). A punch biopsy of a hypopigmented macule on the left side of the neck revealed epidermal acanthosis, hypergranulosis, and hyperkeratosis, with blue-gray cytoplasm observed in the keratinocytes (Figure 3). Koilocytes with perinuclear clearing associated with keratinocytes in the upper epidermis were noted. Based on the clinical and histopathologic correlation, acquired EDV was diagnosed.
Given that HIV-associated EDV often is recalcitrant and there is a lack of consistent and effective treatment, the patient initially was prescribed oral acitretin 25 mg/d with intralesional C albicans antigen injected once per month into the lesions along with concurrent cryotherapy. At subsequent monthly follow-ups, the involved areas were notably thinner and flat. The patient reported no remarkable side effects from the systemic retinoid treatment such as abdominal pain, photosensitivity, or headaches, though he did experience mild xerosis. Complete resolution of EDV occurred with multimodal therapy—acitretin, cryotherapy, and intralesional Candida antigen. Palmar verrucae were much improved, and he is currently continuing therapy.
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis is a rare genodermatosis associated with an abnormal susceptibility to cutaneous HPV and can be acquired in immunocompromised patients. Patients with EDV present with a clinically heterogeneous disease that can manifest as hypopigmented, red-brown macules with scaling on the trunk, neck, and extremities, which are morphologically similar to tinea versicolor, or patients can present with flat wartlike papules that are most commonly found on the face, hands, and feet.2,3 Epidermodysplasia verruciformis can be distinguished from EDV-like eruptions and other generalized verrucoses by its characteristic histologic appearance and by the demonstration of HPV within the lesions, typically subtypes HPV-5 and HPV-8.1-3 Classic EDV histopathologic findings include mild to moderate acanthosis and hyperkeratosis with enlarged keratinocytes featuring blue-gray cytoplasm and perinuclear halos.1
The histologic differential diagnosis of EDV is quite broad and includes common verrucae, which may be distinguished by the absence of blue-gray discoloration of the cytoplasm among the individual keratinocytes.1 Verruca plana and condylomata also may mimic EDV, and patients may present with minimal papillomatosis of the surface epidermis.2 Squamous cell carcinoma in situ (SCC-IS) and particularly bowenoid papulosis also may share similar histologic features.2 However, in SCC-IS, there typically is full-thickness dysplasia of the epidermis, which is not present in EDV. Nonetheless, EDV is equivalent to SCC-IS in its clinical behavior. Bowenoid papulosis shares similar findings, but lesions generally are located in the genital areas and linked to HPV-16 and HPV-18.2 Additional histologic features of EDV have been described in the entity of EDV acanthoma, specifically incidental findings present in association with other cutaneous neoplasms including acantholytic acanthomas, condylomas, intradermal nevi, and seborrheic keratoses.12
The pathophysiology of EDV is thought to be specifically associated with patients with immunocompromised conditions. Particular attention has been paid to the association between EDV and HIV. Anselmo et al13 reported a case of HIV-associated acquired EDV with preexisting lesions that were spread along the distribution of the patient’s tattoo, suggesting potential autoinoculation. In individuals living with HIV, the cutaneous features of EDV are not associated with immune status.14