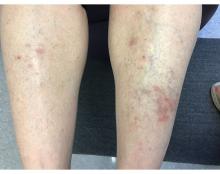
. Lesions may have a covering of scale. HLP commonly affects middle aged men and women. Lesions are most commonly located bilaterally on the shins and ankles and can be painful or pruritic. The differential diagnosis for the condition includes lichen simplex chronicus, connective tissue disease, and other skin disorders that cause hyperkeratosis. This wide differential makes histopathological analysis a useful tool in confirming the diagnosis of HLP.
A definitive diagnosis can be made via skin biopsy. Histopathology reveals hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and a band-like lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis. An eosinophilic infiltrate may be present. Other common features include saw tooth rete ridges and Civatte bodies, which are apoptotic keratinocytes. The lymphocytic infiltrate may indicate an autoimmune etiology in which the body’s immune system erroneously attacks itself. However, the exact cause is not known and genetic and environmental factors may play a role.
The treatment of HLP includes symptomatic management and control of inflammation. Topical steroids can be prescribed to manage the inflammation and associated pruritus, and emollient creams and moisturizers are helpful in controlling the dryness. Oral steroids, immunosuppressant medications, or retinoids may be necessary in more severe cases. In addition, psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA) light therapy has been found to be beneficial in some cases. Squamous cell carcinoma may arise in lesions.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Donna Bilu Martin, MD; Premier Dermatology, MD, Aventura, Florida. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
Arnold DL, Krishnamurthy K. Lichen Planus. [Updated 2023 Jun 1]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526126/
Jaime TJ et al. An Bras Dermatol. 2011 Jul-Aug;86(4 Suppl 1):S96-9.
Mirchandani S et al. Med Pharm Rep. 2020 Apr;93(2):210-2. .
Whittington CP et al. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2023 Jun 19. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2022-0515-RA.