Toluidine blue (TB), a dye with metachromatic staining properties, was developed in 1856 by William Henry Perkin.1 Metachromasia is a perceptible change in the color of staining of living tissue due to the electrochemical properties of the tissue. Tissues that contain high concentrations of ionized sulfate and phosphate groups (high concentrations of free electronegative groups) form polymeric aggregates of the basic dye solution that alter the absorbed wavelengths of light.2 The function of this characteristic is to use a single dye to highlight different structures in tissue based on their relative chemical differences.3
Toluidine blue primarily was used within the dye industry until the 1960s, when it was first used in vital staining of the oral mucosa.2 Because of the tissue absorption potential, this technique was used to detect the location of oral malignancies.4 Since then, TB has progressively been used for staining fresh frozen sections in Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS). In a 2003 survey study (N=310), 16.8% of surgeons performing MMS reported using TB in their laboratory.5 We sought to systematically review the published literature describing the uses of TB in the setting of fresh frozen sections and MMS.
Methods
We conducted a systematic search of the PubMed and Cochrane databases for articles published before December 1, 2019, to identify any relevant studies in English. Electronic searches were performed using the terms toluidine blue and Mohs or Mohs micrographic surgery. We manually checked the bibliographies of the identified articles to further identify eligible studies.
Eligibility Criteria—The inclusion criteria were articles that (1) considered TB in the context of MMS, (2) were published in peer-reviewed journals, (3) were published in English, and (4) were available as full text. Systematic reviews were excluded.
Data Extraction and Outcomes—All relevant information regarding the study characteristics, including design, level of evidence, methodologic quality of evidence, pathology examined, and outcome measures, were collected by 2 independent reviewers (T.L. and A.D.) using a predetermined data sheet. The same 2 reviewers were used for all steps of the review process, data were independently obtained, and any discrepancy was introduced for a third opinion (D.H.) and agreed upon by the majority.
Quality Assessment—The level of evidence was evaluated based on the criteria of the Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine. Two reviewers (T.L. and A.D.) graded each article included in the review.
Results
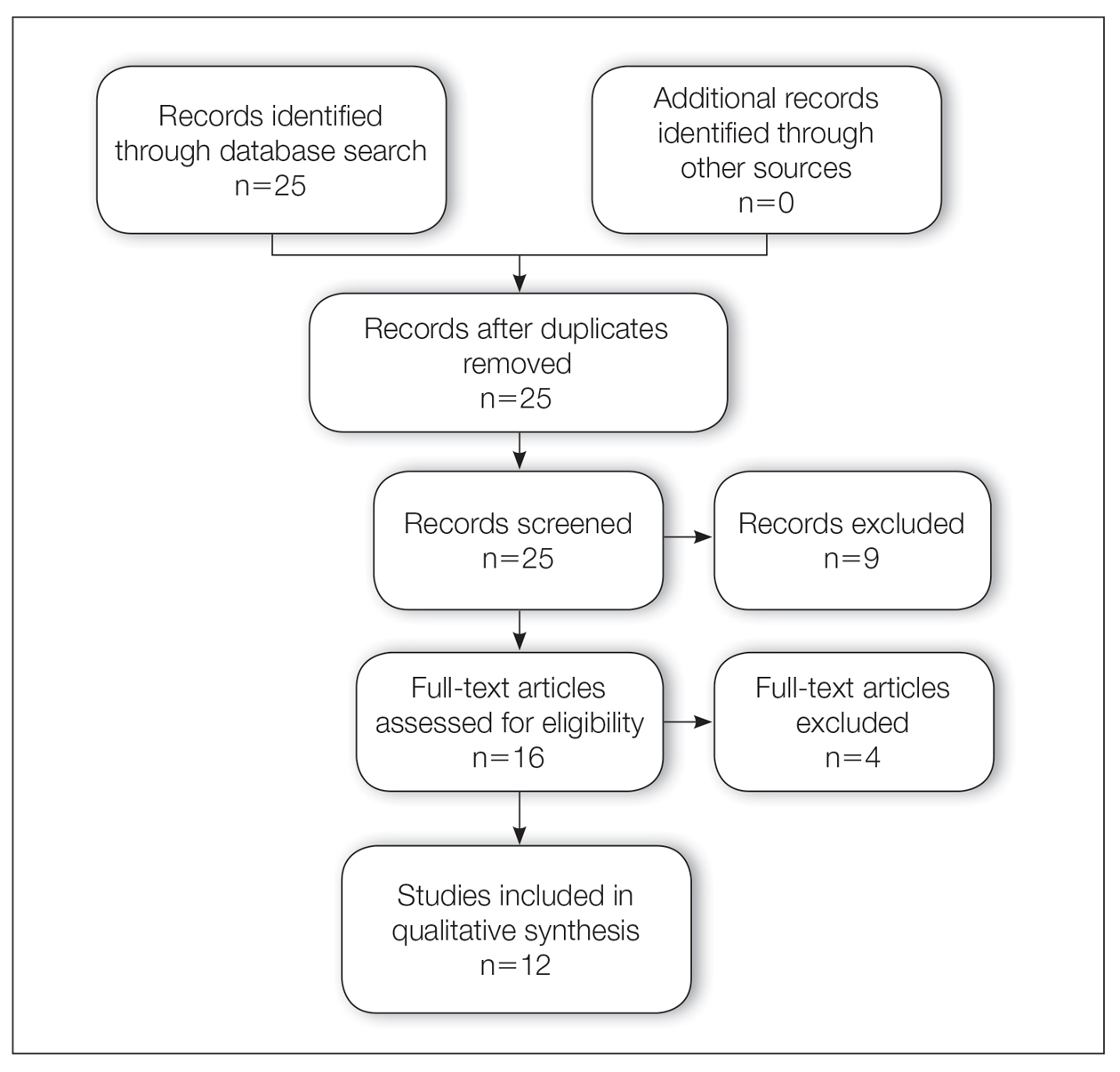
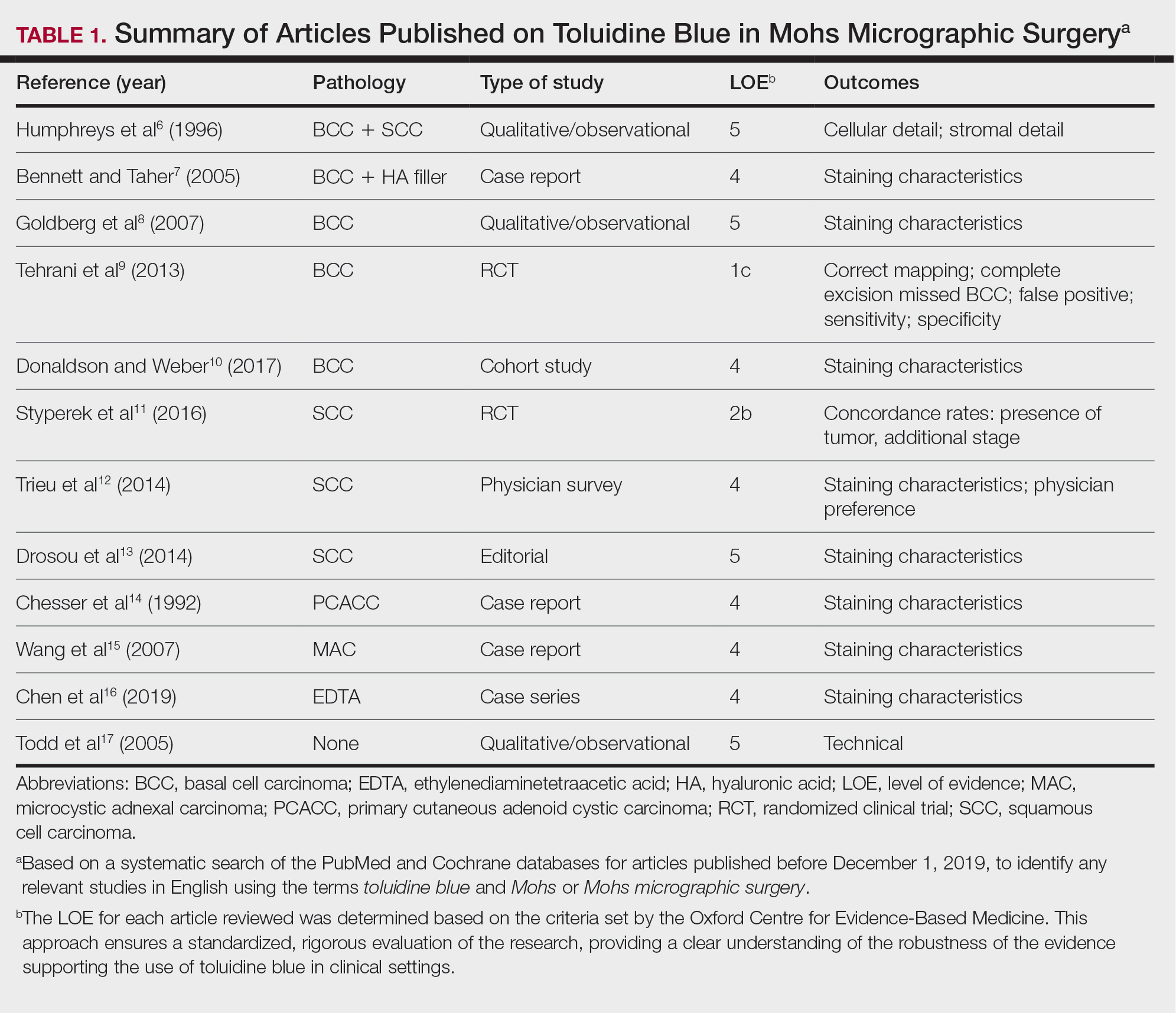
A total of 25 articles were reviewed. After the titles and abstracts were screened for relevance, 12 articles remained (Figure 1). Of these, 1 compared basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), 4 were related to BCC, 3 were related to SCC, 1 was related to microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC), 1 was related to primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma (PCACC), and 2 were related to technical aspects of the staining process (Table 1).