Dermpath Diagnosis
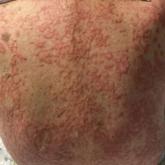
Annular Erythematous Plaques on the Back
An 84-year-old man presented to the clinic for evaluation of a pruritic rash on the back of 6 months’ duration that spread to the neck and chest...
Peichi Chou is from the School of Medicine, University of California, Riverside. Drs. Lee and Elsensohn are from the Department of Dermatology, Loma Linda University, California.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Peichi Chou, BA, University of California Riverside, School of Medicine, 900 University Ave, Riverside, CA 92521 (Peichi.Chou@medsch.ucr.edu).

A 28-year-old man presented with an 8-mm, tender, mildly hyperkeratotic nodule on the right knee (top) of unknown duration. He had a history of mild keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness (KID) syndrome that was diagnosed based on the presence of congenital erythrokeratoderma, hearing issues identified at 2 years of age, palmoplantar keratoderma, keratitis, photophobia, chronic fungal nail infections, and alopecia and later was confirmed with a chromosome microarray for the GJB2 gene, which is associated with a connexin 26 mutation. A shave biopsy of the nodule was performed (bottom).
Histopathology revealed an extensive lobulated epithelial proliferation in a characteristic “rolls and scrolls” pattern (Figure 1). This finding along with the patient’s prior diagnosis of keratitis-ichthyosisdeafness (KID) syndrome supported the diagnosis of a proliferating pilar cyst.
Pilar (or trichilemmal) cysts are common dermal cysts typically found on the outer root sheath of hair follicles. They clinically manifest as multiple yellow dome-shaped nodules without central puncta. They are slow growing and histologically are characterized as cysts with a stratified squamous epithelium demonstrating lack of a granular layer (trichilemmal keratinization) with bright red keratin contents and central focal calcification (Figure 2). Pilar cysts are more common in adult women and may be inherited through an autosomal-dominant pattern.1
Proliferating pilar cysts represent less than 3% of all pilar cysts.2 In addition to the characteristic features of a pilar cyst, proliferating pilar cysts generally are larger (can be >6-cm wide) and are more ulcerative.3 Histopathology of proliferating pilar cysts reveals a more extensive epithelial proliferation, yielding a rolls and scrolls appearance, and may demonstrate nuclear atypia.4 Proliferating pilar cysts classically manifest as large, raised, smooth and/or ulcerated nodules on the scalp accompanied by areas of excessive hair growth in older women. They generally arise from pre-existing pilar cysts but also may occur sporadically.4
The development of multiple proliferating pilar cysts has been observed in patients with KID syndrome, a rare congenital ectodermal disorder characterized by a triad of vascularizing keratitis, hyperkeratosis, and sensorineural deafness.5,6 It is caused by a missense mutation of the GJB2 gene encoding for connexin 26, a gap junction that facilitates intercellular signaling and is expressed in a variety of structures including the cochlea, cornea, sweat glands, and inner and outer root sheaths of hair follicles.7
The differential diagnosis for proliferating pilar cysts includes pilomatrixomas, squamous cell carcinomas, and malignant proliferating pilar tumors. Pilomatrixomas (or calcifying epitheliomas of Malherbe) are the most common adnexal skin tumors in the pediatric population and most commonly present on the head, neck, and arms.8 They also can manifest in adults. Pilomatrixomas are benign dermal-subcutaneous tumors encapsulated by connective tissue that are found on the hair matrix and are histologically characterized by basaloid cells, shadow (or ghost) cells, dystrophic calcifications, and giant cells.9 The amount of basaloid cells and shadow cells can vary. Tumor progression results in the enucleation of the basaloid cells to form eosinophilic shadow cells in which calcification can occur. Giant cell granulomas may form contiguous with the calcifications. Both proliferating pilar cysts and pilomatrixomas have a rolls and scrolls appearance on low-power microscopy, but the latter are differentiated by their shadow cells and basaloid areas (Figure 3).
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the second most common nonmelanoma skin cancer and more commonly affects men. Risk factors for SCC include immunosuppression and exposure to UV radiation. Histopathology of well-differentiated SCCs reveals invasive squamous cells with larger nuclei and a glassy appearance in addition to possible mitotic figures and keratin pearls (Figure 4). They typically manifest in sun-exposed areas such as the scalp, face, forearms, dorsal aspects of the hands, and lower legs.10 Proliferating pilar tumors often lack the nuclear atypia and invasive architecture of a well-differentiated SCC.
Features of malignant proliferating pilar tumors overlap with proliferating pilar cysts. In addition to the proliferative epithelium with abrupt trichilemmal keratinization that is typical of a proliferating pilar cyst, a malignant proliferating pilar tumor will demonstrate invasion into the surrounding tissue and lymph nodes, mitotic and architectural atypia, and necrosis (Figure 5).11 Malignant proliferating pilar tumors grow rapidly, ranging in size from 1 to 10 cm, and may develop from pre-existing or proliferating pilar cysts or de novo.
The development of multiple proliferating pilar cysts and thus increased risk for progression to malignant proliferating pilar tumors has been observed in patients with KID syndrome.6 Our case highlights the importance of early screening and recognition of proliferating pilar tumors in patients with this condition.

An 84-year-old man presented to the clinic for evaluation of a pruritic rash on the back of 6 months’ duration that spread to the neck and chest...
A 31-year-old woman presented with a slow-growing, tender, pruritic lesion on the right cheek of 4 to 5 months’ duration. Shave and punch biopsies...
