The Diagnosis: Levamisole-Induced Cutaneous Vasculopathy
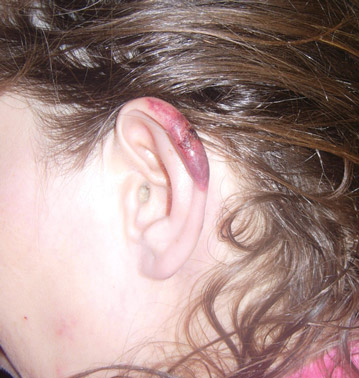
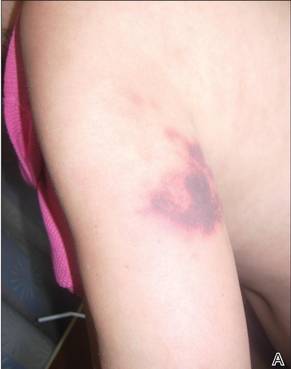
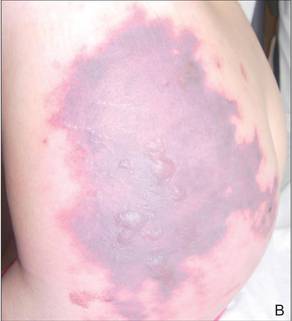
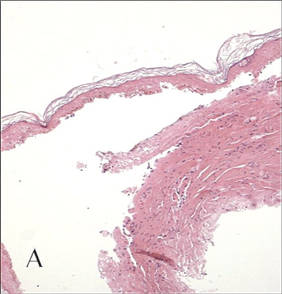
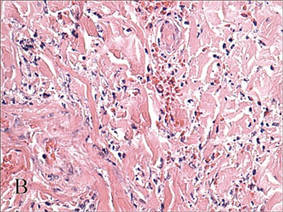
In our patient, tender stellate purpura and occasional bullae were present on the ears, arms and legs, groin, and buttocks (Figure 1). Histopathologic examination revealed subepidermal detachment, perivascular neutrophilic infiltrate, and red blood cell extravasation, consistent with early leukocyctoclastic vasculitis (Figure 2).
Figure 1. Left arm with tender stellate purpura (A). Left side of the lower back with large area of purpura and few scattered tense bullae (B). |
Levamisole-induced vasculopathy is a condition related primarily to cocaine use. Levamisole is an immunomodulatory agent, historically used as a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug for rheumatoid arthritis and as adjuvant chemotherapy for various types of cancer. However, levamisole for human use was banned from US and Canadian markets in 1999 and 2003, respectively, due to increased risk for agranulocytosis, retiform purpura, and epilepsy.1 Currently, veterinarians use levamisole as an anthelminthic agent to deworm house and farm animals. In Europe, pediatric nephrologists use it as a steroid-sparing agent in children with steroid-dependent nephritic syndrome.
Over the last decade, levamisole has increasingly been used as a cocaine adulterant or bulking agent. This contaminant closely resembles cocaine physically and is theorized to prolong or attenuate cocaine’s “high.” Approximately 69% of cocaine sampled by the US Drug Enforcement Administration is adulterated with levamisole.2 Similarly, levamisole-contaminated cocaine also has been found in Europe, Australia, and other parts of the world. Potential complications include vasculitis, thromboembolism, neutropenia, and agranulocytosis.3
Levamisole-induced vasculopathy appears to affect cocaine users of all ages, ethnicities, and genders. Cocaine can be smoked, snorted, or injected. In nearly all reported cases, patients characteristically present with hemorrhagic bullae of the bilateral ear helix, cheeks, or nasal tip. Any body site can be affected with retiform purpura or necrotic bullae. Along with skin lesions, arthralgia is commonly reported, as are constitutional symptoms (eg, fever, night sweats, weight loss, malaise)4; oral mucosal involvement also has been reported.5 Laboratory investigation can reveal neutropenia, positive antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCAs) in the perinuclear or cytoplasmic pattern, positive proteinase 3, and negative or mildly elevated antimyeloperoxidase.3-5 Acute renal injury and pulmonary hemorrhage are other potentially serious copmlications.4 Antihuman neutrophil elastase antibody testing can help distinguish levamisole-induced vasculopathy from other forms of immune-mediated vasculitis and will be negative in immune-mediated vasculitides such as Churg-Strauss syndrome (allergic granulomatosis), Wegener granulomatosis (granulomatosis with polyangiitis), and polyarteritis nodosa.6 On histology, microvascular thrombosis or leukocytoclastic vasculitis can both, or individually, be seen. Epidermal necrosis, dermal hemorrhage, and endothelial hyperplasia have all been noted in skin biopsied from necrotic bullae.
|
Levamisole’s short half-life (approximately 5–6 hours) makes it difficult to detect on routine blood draws. An astute physician suspecting this diagnosis on initial presentation can ask for levamisole detection on urine toxicology screening.7 Urine samples also can be sent for testing with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, though this test may only be available at major research centers.8
Differential diagnosis of levamisole toxicity includes different types of vasculitides such as cryoglobulinemia (positive serum IgM and IgG cryoglobulins; possible hepatitis C infection), Wegener granulomatosis (cytoplasmic ANCA positive; associated with upper and lower respiratory tract inflammation, glomerulonephritis), Churg-Strauss syndrome (perinuclear ANCA positive; associated with asthma and eosinophilia), and polyarteritis nodosa (medium vessel involvement only; associated with livedo reticularis, subcutaneous nodules, ulcers).9 Necrotic lesions also may raise the possibility of warfarin necrosis, heparin necrosis, or cholesterol emboli. Cholesterol embolism most frequently presents with small vessel vasculitis and necrosis of distal extremities such as the toes. With large areas of skin involvement and bullae, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis also should be considered.9
Definitive treatment of this condition requires complete and immediate cessation of cocaine use. Levamisole also has been found as a contaminant in heroin.1 Thus, it may be prudent to recommend heroin avoidance to the patient to prevent recurrences. Management of acute levamisole-induced vasculopathy is primarily symptomatic. Some patients with severe neutropenia at risk for infection have been treated with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, while others have only required pain control, usually with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.10 Oral prednisone and colchicine also have been used with reported success.5
Given the increasing incidence of levamisole toxicity and public health implications, clinicians should be aware of this association and the classic clinical and laboratory findings.