Dermpath Diagnosis
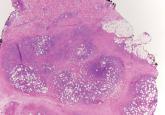
Subcutaneous Panniculitislike T-Cell Lymphoma
Subcutaneous panniculitislike T-cell lymphoma is a cutaneous lymphoma of α and β phenotype cytotoxic T cells in which the neoplastic cells are...
All from the Department of Pathology and Molecular Medicine, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. Drs. Salama and Alowami also are from St. Joseph’s Healthcare, Hamilton.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Ryan Yu, MD, McMaster University, HSC-2N22B, 1280 Main St W, Hamilton, ON 8S 4K1, Canada (ryan.yu@medportal.ca).

A fibrous papule is a common benign lesion that usually presents in adults on the face, especially on the lower portion of the nose. The differential diagnosis includes balloon cell malignant melanoma, balloon cell nevus, clear cell hidradenoma, and cutaneous metastasis of clear cell (conventional) renal cell carcinoma.
A fibrous papule is a common benign lesion that usually presents in adults on the face, especially on the lower portion of the nose. It typically presents as a small (2–5 mm), asymptomatic, flesh-colored, dome-shaped lesion that is firm and nontender. Several histopathologic variants of fibrous papules have been described, including clear cell, granular, epithelioid, hypercellular, pleomorphic, pigmented, and inflammatory.1 Clear cell fibrous papules are exceedingly rare. On microscopic examination the epidermis may be normal or show some degree of hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis, erosion, ulceration, or crust. The basal layer may show an increase of melanin. The dermis is expanded by a proliferation of clear cells arranged in sheets, clusters, or as single cells (Figure 1). The clear cells show variation in size and shape. The nuclei are small and round without pleomorphism, hyperchromasia, or mitoses. The nuclei may be centrally located or eccentrically displaced by a large intracytoplasmic vacuole (Figure 2). Some clear cells may exhibit finely vacuolated cytoplasm with nuclear scalloping. The surrounding stroma usually consists of sclerotic collagen and dilated blood vessels (Figure 3). Extravasated red blood cells may be present focally. Patchy lymphocytic infiltrates may be found in the stroma at the periphery of the lesion. Periodic acid–Schiff and mucicarmine staining of the clear cells is negative. On immunohistochemistry, the clear cells are diffusely positive for vimentin and negative for cytokeratin AE1/AE3, epithelial membrane antigen, carcinoembryonic antigen, and HMB-45 (human melanoma black 45).2,3 The clear cells often are positive for CD68, factor XIIIa, and NKI/C3 (anti-CD63) but also may be negative. The S-100 protein often is negative but may be focally positive.
The differential diagnosis for clear cell fibrous papules is broad but reasonably includes balloon cell nevus, clear cell hidradenoma, and cutaneous metastasis of clear cell (conventional) renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). Balloon cell malignant melanoma is not considered strongly in the differential diagnosis because it usually exhibits invasive growth, cytologic atypia, and mitoses, all of which are not characteristic morphologic features of clear cell fibrous papules.
A balloon cell nevus may be difficult to distinguish from a clear cell fibrous papule on routine hematoxylin and eosin staining (Figure 4); however, the nuclei of a balloon cell nevus tend to be more rounded and centrally located. Any junctional nesting or nests of conventional nevus cells in the dermis also help differentiate a balloon cell nevus from a clear cell fibrous papule. Diffusely positive immunostaining for S-100 protein also is indicative of a balloon cell nevus.
Clear cell hidradenoma consists predominantly of cells with clear cytoplasm and small dark nuclei that may closely mimic a clear cell fibrous papule (Figure 5) but often shows a second population of cells with more vesicular nuclei and dark eosinophilic cytoplasm. Cystic spaces containing hyaline material and foci of squamoid change are common, along with occasional tubular lumina that may be prominent or inconspicuous. Further, the tumor cells of clear cell hidradenoma show positive immunostaining for epithelial markers (eg, cytokeratin AE1/AE3, CAM5.2).
Cutaneous metastasis of ccRCC is rare and usually presents clinically as a larger lesion than a clear cell fibrous papule. The cells of ccRCC have moderate to abundant clear cytoplasm and nuclei with varying degrees of pleomorphism (Figure 6). Periodic acid–Schiff staining demonstrates intracytoplasmic glycogen. The stroma is abundantly vascular and extravasated blood cells are frequently observed. On immunohistochemistry, the tumor cells of ccRCC stain positively for cytokeratin AE1/AE3, CAM5.2, epithelial membrane antigen, CD10, and vimentin.

Subcutaneous panniculitislike T-cell lymphoma is a cutaneous lymphoma of α and β phenotype cytotoxic T cells in which the neoplastic cells are...
Pretibial myxedema is a cutaneous mucinosis associated with thyroid dysfunction. The differential diagnosis includes nephrogenic systemic fibrosis...

Lipidized dermatofibromas most commonly are found on the ankles, which has led some authors to refer to these lesions as ankle-type fibrous...
