The Diagnosis: Lichen Aureus
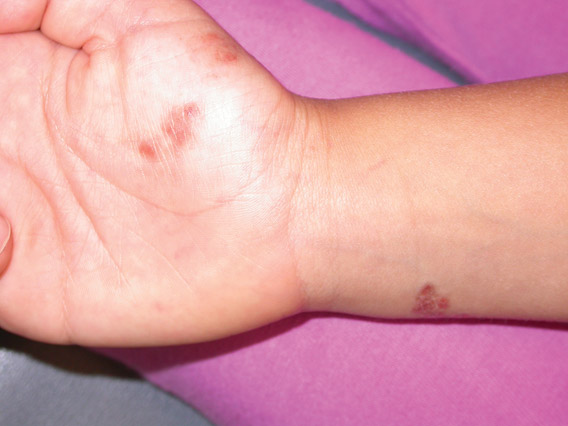
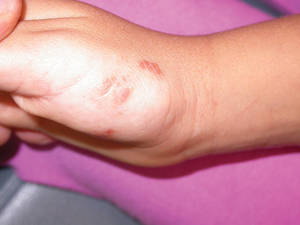
Lichen aureus (LA) is classified as a pigmented purpuric dermatosis (PPD), a collection of conditions that are characterized by petechiae, pigmentation, and occasionally telangiectasia without a causative underlying disorder. As in our case, the lesions of LA are usually asymptomatic. They appear as circumscribed areas of discrete or confluent macules and papules that can range in color from gold or copper to purple (Figure 1). The lesions typically occur unilaterally on the lower extremities but can occur on all body regions. The etiology is unknown, but explanations such as venous insufficiency,1 contact allergens,2 and drugs3,4 have been proposed. Unlike other PPDs, LA tends to occur abruptly and then either stabilizes or progresses slowly over years. Studies have reported resolution in 2 to 7 years.5 The average age of onset is in the 20s and 30s, with pediatric cases accounting for only 17%.6 Pediatric cases are more likely to be self-limited and occur in uncommon sites such as the trunk and arms.7
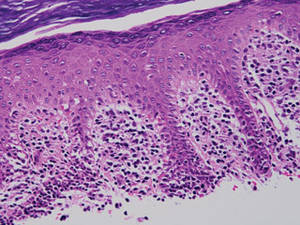
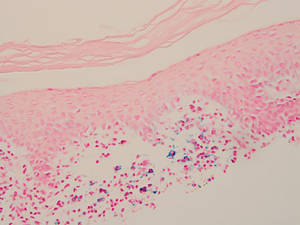
Lichen aureus is characterized histopathologically by a dense, bandlike, dermal inflammatory infiltrate (Figure 2). Additionally, there is variable exocytosis of lymphocytes and marked accumulation of siderotic macrophages (Figure 3). These qualities in the proper clinical setting help differentiate LA from other PPDs that share findings of capillaritis, hemosiderin deposition, and erythrocyte extravasation near dermal vessels. An iron stain assists in the diagnosis of LA (Figure 3), as it differentiates the disease from other lichenoid conditions such as lichen planus. Zaballos et al8 also demonstrated a role for dermoscopy to clinically differentiate LA from other similar-appearing lesions such as lichen planus.
The lesions of LA are benign. Because the predominantly T-cell infiltrate is monoclonal in approximately 50% of cases,2,9-11 authors have suggested the possibility of progression to cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.9,12 Guitart and Magro13 classified LA as a T-cell lymphoid dyscrasia with potential for progression. Despite these reports, the general consensus is that LA is a benign, self-limiting condition. The benign nature of LA is supported by Fink-Puches et al2 who followed 23 patients for a mean 102.1 months and did not observe a single case of progression to malignancy.
There have been many treatment regimens attempted for patients with LA. Topical corticosteroids have not been found to be beneficial14; however, there have been isolated cases reporting its efficacy in children.7,15 Other medications that have been effective in small trials include psoralen plus UVA,16 topical pimecrolimus,5 calcium dobesilate,17 and combination therapy with pentoxifylline and prostacyclin.18 Despite some reported benefit, the use of potent immunomodulating medications is not indicated due to the benign nature of the disease. Alternative supplements including oral bioflavonoids and ascorbic acid have also been explored with modest benefit.19