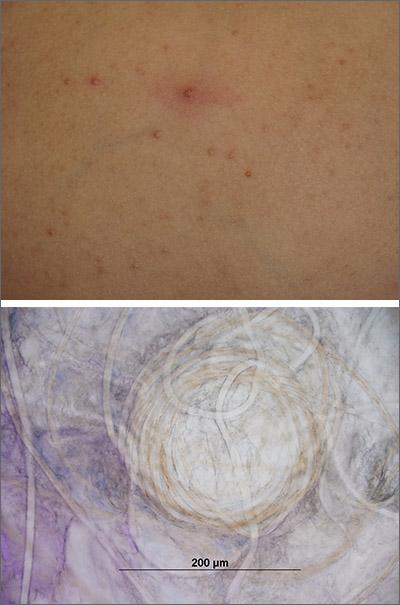
Potassium hydroxide preparation of expressed contents revealed no molluscum bodies, but rather, small-caliber, trapped, and coiled hairs consistent with eruptive vellus hair cysts (EVHCs).
Vellus hairs are fine, light-colored (nonterminal) hairs that normally are found on the face, trunk, and limbs. EVHCs are typically asymptomatic papules containing an entrapped vellus hair. They form from entrapment of the hair follicle just proximal to the infundibulum, leading to hair bulb atrophy and dilation of the follicle. EVHCs typically are dome-shaped, flesh-colored soft papules that are 2 to 3 mm in size.
Diagnostic confusion can arise with molluscum contagiosum because those lesions also tend to be umbilicated and flesh colored. EVHCs can appear at any age but are more common in the first 3 decades of life. Familial types exist, presenting earlier in life than sporadic types. The differential diagnosis includes molluscum contagiosum, folliculitis, and steatocystoma multiplex. Rare genodermatoses have been associated with EVHCs, including autosomal dominant familial keratin gene mutation, anhidrotic and hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia, and pachyonychia congenita.
Up to 25% of cases spontaneously resolve, so patients can be counseled to observe the lesions. Alternative options including topical emollients or various topical keratolytics, including ammonium lactate 20% once to twice daily, topical urea, or topical salicylic acid until the lesions are flat and smooth. Topical and systemic retinoids have been reported to have limited success. Individual lesions of concern may be removed surgically by excision, curettage, cryotherapy, or laser but will likely leave a minor scar.
The patient and his family were reassured of the benign nature of the lesions and instructed to treat the papules with topical ammonium lactate 20% twice daily until the next appointment in 12 weeks. At follow-up, many, but not all, of the lesions had resolved.
Text courtesy of Tristan Reynolds, DO, Maine Dartmouth Family Medicine Residency, and Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).