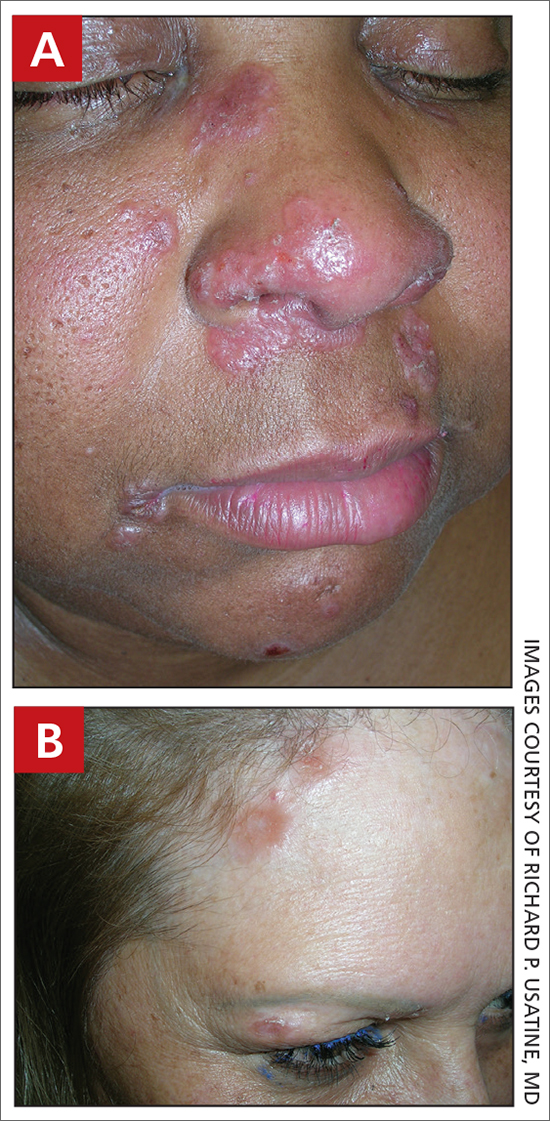
THE COMPARISON
A Pink, elevated, granulomatous, indurated plaques on the face, including the nasal alae, of a 52-year-old woman with a darker skin tone.
B Orange and pink, elevated, granulomatous, indurated plaques on the face of a 55-year-old woman with a lighter skin tone.
Sarcoidosis is a granulomatous disease that may affect the skin in addition to multiple body organ systems, including the lungs. Bilateral hilar adenopathy on a chest radiograph is the most common finding. Sarcoidosis also has a variety of cutaneous manifestations. Early diagnosis is vital, as patients with sarcoidosis and pulmonary fibrosis have a shortened life span compared to the overall population.1 With a growing skin of color population, it is important to recognize sarcoidosis as soon as possible.2
Epidemiology
People of African descent have the highest sarcoidosis prevalence in the United States.3 In the United States, the incidence of sarcoidosis in Black individuals peaks in the fourth decade of life. A 5-year study in a US health maintenance organization found that the age-adjusted annual incidence was 10.9 per 100,000 cases among Whites and 35.5 per 100,000 cases among Blacks.4
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones:
• Papules are seen in sarcoidosis, primarily on the face, and may start as orange hued or yellow-brown and then become brown-red or pink to violaceous before involuting into faint macules.5-7
• When round or oval sarcoid plaques appear, they often are more erythematous.
• In skin of color, plaques may become hypopigmented.8
• Erythema nodosum, the most common nonspecific cutaneous lesion seen in sarcoidosis, is less commonly seen in those of African and Asian descent.9-11 This is in contrast to distinctive forms of specific sarcoid skin lesions such as lupus pernio and scar sarcoidosis, as well as papules and plaques and minor forms of specific sarcoid skin lesions including subcutaneous nodules; hypopigmented macules; psoriasiform lesions; and ulcerative, localized erythrodermic, ichthyosiform, scalp, and nail lesions.
• Lupus pernio is a cutaneous manifestation of sarcoidosis that appears on the face. It looks similar to lupus erythematosus and occurs most commonly in women of African descent.8,12
• Hypopigmented lesions are more common in those with darker skin tones.9
• Ulcerative lesions are more common in those of African descent and women.13
• Scalp sarcoidosis is more common in patients of African descent.14
• Sarcoidosis may develop at sites of trauma, such as scars and tattoos.15-17
Worth noting
The cutaneous lesions seen in sarcoidosis may be emotionally devastating and disfiguring. Due to the variety of clinical manifestations, sarcoidosis may be misdiagnosed, leading to delays in treatment.18
Health disparity highlight
Patients older than 40 years presenting with sarcoidosis and those of African descent have a worse prognosis.19 Despite adjustment for race, ethnic group, age, and sex, patients with low income and financial barriers present with more severe sarcoidosis.20