Magnesium Sulfate for Fetal Neuroprotection in Preterm Birth
Without a doubt, magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) given before anticipated preterm birth reduces the risk of cerebral palsy. It is a valuable tool for fetal neuroprotection at a time when there are no proven alternatives. Yet without the persistent research that occurred over more than 20 years, it may not have won the endorsement of the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecologists in 2010 and worked its way into routine practice.
Its history is worthy of reflection. It took years of observational trials (not all of which showed neuroprotective effects), six randomized controlled trials (none of which met their primary endpoint), three meta-analyses, and a Cochrane Database Systematic Review to arrive at the conclusion that antenatal magnesium sulfate therapy given to women at risk of preterm birth has definitive neuroprotective benefit.
This history also holds lessons for our specialty given the dearth of drugs approved for use in pregnancy and the recent withdrawal from the market of Makena — one of only nine drugs to ever be approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in pregnancy — after a second trial showed lack of benefit in preventing recurrent preterm birth. The story of MgSO4 tells us it’s acceptable to have major stumbling blocks: At one point, MgSO4 was considered to be not only not helpful, but harmful, causing neonatal death. Further research disproved this initial finding.
Moreover, the MgSO4 story is one that remains unfinished, as my laboratory and other researchers work to better understand its biologic plausibility and to discover additional neuroprotective agents for anticipated preterm birth that may further reduce the risk of cerebral palsy. This leading cause of chronic childhood disability is estimated by the United Cerebral Palsy Foundation to affect approximately 800,000 people in the United States.
Origins and Biologic Plausibility
The MgSO4 story is rooted in the late seventeenth century discovery by physician Nehemiah Grew that the compound was the key component of the then-famous medicinal spring waters in Epsom, England.1 MgSO4 was first used for eclampsia in 1906,2 and was first reported in the American literature for eclampsia in 1925.3 In 1959, its effect as a tocolytic agent was reported.4
More than 30 years later, in 1995, an observational study coauthored by Karin B. Nelson, MD, and Judith K. Grether, PhD of the National Institutes of Health, showed a reduced risk of cerebral palsy in very-low-birth-weight infants (VLBW).5 The report marked a turning point in research interest on neuroprotection for anticipated preterm birth.
The precise molecular mechanisms of action of MgSO4 for neuroprotection are still not well understood. However, research findings from the University of Maryland and other institutions have provided biologic plausibility for its use to prevent cerebral palsy. Our current thinking is that it involves the prevention of periventricular white matter injury and/or the prevention of oxidative stress and a neuronal injury mechanism called excitotoxicity.
Periventricular white matter injury involving injury to preoligodendrocytes before 32 weeks’ gestation is the most prevalent injury seen in cerebral palsy; preoligodendrocytes are precursors of myelinating oligodendrocytes, which constitute a major glial population in the white matter. Our research in a mouse model demonstrated that the intrauterine inflammation frequently associated with preterm birth can lead to neuronal injury as well as white matter damage, and that MgSO4 may ameliorate both.6,7
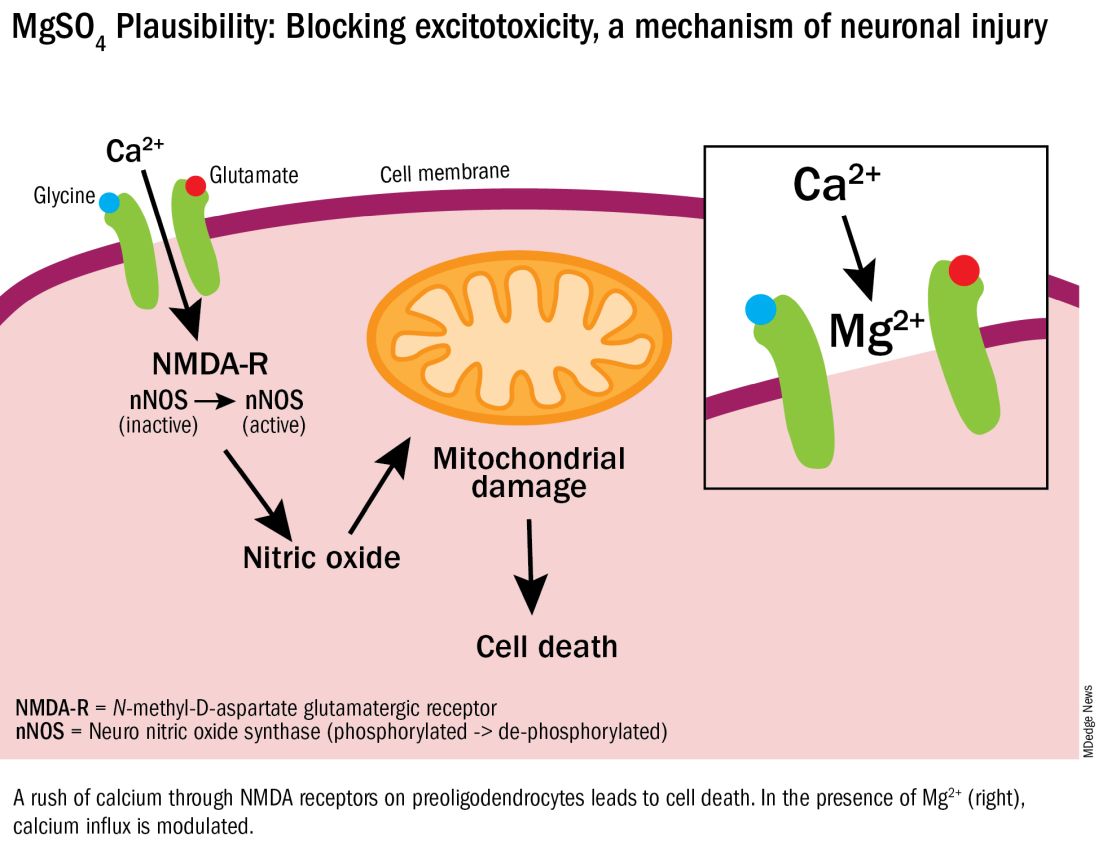
Excitotoxicity results from excessive stimulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamatergic receptors on preoligodendrocytes and a rush of calcium through the voltage-gated channels. This calcium influx leads to the production of nitric oxide, oxidative stress, and subsequent mitochondrial damage and cell death. As a bivalent ion, MgSO4 sits in the voltage-gated channels of the NMDA receptors and reduces glutamatergic signaling, thus serving as a calcium antagonist and modulating calcium influx (See Figure).
In vitro research in our laboratory has also shown that MgSO4 may dampen inflammatory reactions driven by intrauterine infections, which, like preterm birth, increase the risk of cerebral palsy and adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes.8 MgSO4 appears to do so by blocking the voltage-gated P2X7 receptor in umbilical vein endothelial cells, thus blocking endothelial secretion of the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)–1beta. Much more research is needed to determine whether MgSO4 could help prevent cerebral palsy through this mechanism.