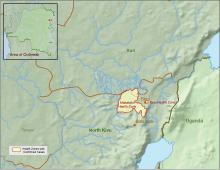
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has been working with the Ministry of Health of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) on a new Ebola outbreak reported on Aug, 1, 2018, in North Kivu province.
“For the current outbreak, CDC has deployed experienced Ebola experts to DRC and the World Health Organization [WHO] to provide guidance on coordination of outbreak response, laboratory testing, disease contact tracing, infection control, and health communication,” according to a CDC press release.
The CDC’s online response also provides a Traveler’s Health notice of Watch Level 1 for the DRC, which advises standard precautions and avoiding infected individuals, but not an advisory against travel.
The Ebola virus associated with the current outbreak is Zaire ebolavirus, according to genetic testing by scientists in the DRC. This is the same species that caused an outbreak earlier this year in Equateur province in northwestern DRC, although differences between the genes of the viruses suggest the two outbreaks are not linked, according to the CDC media announcement.
As of Aug. 12, 2018, the following statistics were reported by the WHO on the outbreak:
- Confirmed cases: 30
- Probable cases: 27
- Total cases: 57
- Deaths: 41 (14 confirmed, 27 probable)
The outbreak is of particular concern because of the instability of the area, which hampers relief and quarantine efforts. The outbreak is in a part of the country identified by the U.S. State Department as a “restricted travel” zone due to armed conflict and violence targeting civilians, according to the CDC.