Methods
Setting
The study was performed at Anne Arundel Medical Center (AAMC), a 384-bed community hospital in Annapolis, Maryland, that serves a region of over 1 million people. Approximately 26,000 adult patients are discharged annually. During the study, more than 90% of internal medicine service inpatients were cared for by one of 2 hospitalist groups: a hospital-employed group (“conventional” group, Anne Arundel Medical Group) and a contracted hospitalist group (“expanded PA” group, Physicians Inpatient Care Specialists). The conventional group’s providers received a small incentive for Core Measures compliance for patients with stroke, myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure and pneumonia. The expanded PA group received a flat fee for providing hospitalist services and the group’s providers received a small incentive for productivity from their employer. The study was deemed exempt by the AAMC institutional review board.
Staffing Models, Patient Allocation, and Assignment
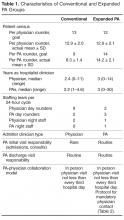
The expanded PA group used 3 physicians and 3 PAs daily for rounding; another PA was responsible for day shift admitting work. Day shift rounding PAs were expected to see 14 patients daily. Night admissions were covered by their own nocturnist physician and PA ( Table 1 ). The conventional group used 9 physicians and 2 PAs for rounding; day shift admissions were done by a physician. This group’s rounding PAs were expected to see 9 patients daily. Night admissions were covered by their own 2 nocturnist physicians.Admitted patients were designated to be admitted to one group or the other on the basis of standing arrangements with the patients’ primary care providers. Consultative referrals could also be made from subspecialists, who had discretion as to which group they wished to use.
Each morning, following sign-out report from the night team, each team of day providers determined which patients would be seen by which of their providers. Patients still on service from the previous day would be seen by the same provider again whenever possible in order to maintain continuity. Each individual provider had their own patients for the day who they rounded on independently and were responsible for. Physician involvement with patients seen primarily by PAs occurred as described below. Physicians in both groups were expected to take primary rounding responsibility for patients who were more acute or more complex based on morning sign-out report; there was no more formal mandate for patient allocation to particular provider type.