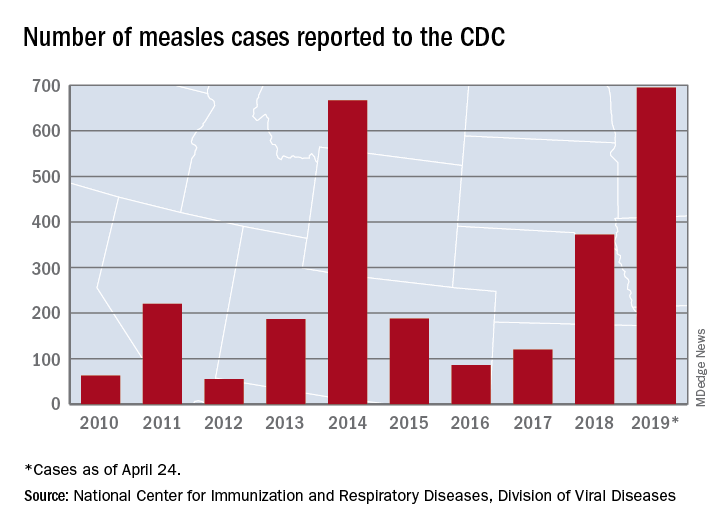
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
As of Wednesday, April 24, the case count for measles is 695, which eclipses the mark of 667 cases that had been the highest since the disease was declared to be eliminated from this country in 2000, the CDC reported.
“The high number of cases in 2019 is primarily the result of a few large outbreaks – one in Washington State and two large outbreaks in New York that started in late 2018. The outbreaks in New York City and New York State are among the largest and longest lasting since measles elimination in 2000. The longer these outbreaks continue, the greater the chance measles will again get a sustained foothold in the United States,” according to a written statement by the CDC.
Although these outbreaks began when the virus was brought into this country by unvaccinated travelers from other countries where there is widespread transmission, “a significant factor contributing to the outbreaks in New York is misinformation in the communities about the safety of the measles/mumps/rubella vaccine. Some organizations are deliberately targeting these communities with inaccurate and misleading information about vaccines,” according to the statement.
“Measles is not a harmless childhood illness, but a highly contagious, potentially life-threatening disease,” Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar said in a separate statement. “We have the ability to safely protect our children and our communities. Vaccines are a safe, highly effective public health solution that can prevent this disease. The measles vaccines are among the most extensively studied medical products we have, and their safety has been firmly established over many years in some of the largest vaccine studies ever undertaken. With a safe and effective vaccine that protects against measles, the suffering we are seeing is avoidable.”