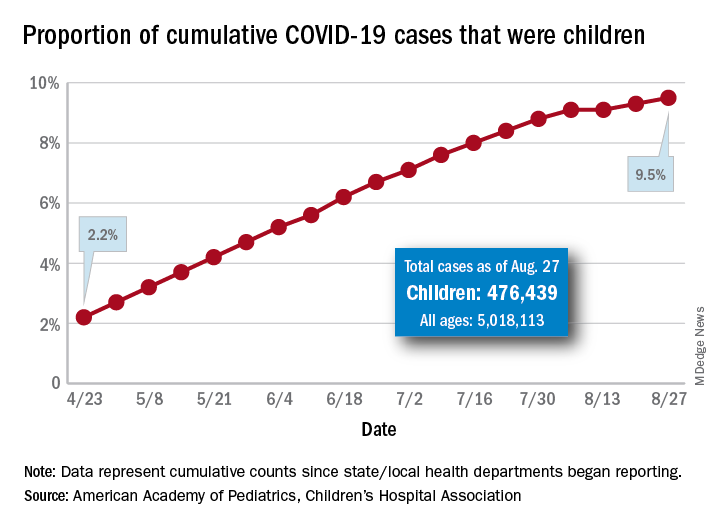
according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The new cases bring the cumulative number of infected children to over 476,000, and that figure represents 9.5% of the over 5 million COVID-19 cases reported among all ages, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly report. The cumulative number of children covers 49 states (New York is not reporting age distribution), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
From lowest to highest, the states occupying opposite ends of the cumulative proportion spectrum are New Jersey at 3.4% – New York City was lower with a 3.2% figure but is not a state – and Wyoming at 18.3%, the report showed.
Children represent more than 15% of all reported COVID-19 cases in five other states: Tennessee (17.1%), North Dakota (16.0%), Alaska (15.9%), New Mexico (15.7%), and Minnesota (15.1%). The states just above New Jersey are Florida (5.8%), Connecticut (5.9%), and Massachusetts (6.7%). Texas has a rate of 5.6% but has reported age for only 8% of confirmed cases, the AAP and CHA noted.
Children make up a much lower share of COVID-19 hospitalizations – 1.7% of the cumulative number for all ages – although that figure has been slowly rising over the course of the pandemic: it was 1.2% on July 9 and 0.9% on May 8. Arizona (4.1%) is the highest of the 22 states reporting age for hospitalizations and Hawaii (0.6%) is the lowest, based on the AAP/CHA data.
Mortality figures for children continue to be even lower. Nationwide, 0.07% of all COVID-19 deaths occurred in children, and 19 of the 43 states reporting age distributions have had no deaths yet. Pediatric deaths totaled 101 as of Aug. 27, the two groups reported.