User login
What’s hot in knee OA rehab research
TORONTO – Emerging evidence indicates that patients with knee osteoarthritis who engage in high-intensity interval training obtain significantly greater improvement in physical function than with conventionally prescribed moderate-intensity exercise, Monica R. Maly, PhD, said at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
This was one of the key conclusions she and her coworkers drew from their analysis of the past year’s published research on diet and exercise interventions to improve outcomes in patients with OA, where obesity and physical inactivity figure prominently as modifiable lifestyle factors.
Another finding: Exercise interventions are where all the action is at present in the field of lifestyle-modification research aimed at achieving better health-related quality of life and other positive outcomes in OA. Dietary interventions are simply not a hot research topic. Indeed, her review of the past year’s literature included 38 randomized, controlled trials (RCTs) and 15 meta-analyses and systematic reviews – and all 38 RCTs addressed exercise interventions.
“It’s interesting to note that we found no new RCT data on diet to modify obesity in OA in the past year,” Dr. Maly said at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Additionally, 32 of the 38 RCTs devoted to exercise interventions for OA focused specifically on knee OA, noted Dr. Maly of the department of kinesiology at the University of Waterloo (Ont.).
Aerobic exercise dosage and intensity
Australian investigators conducted a pilot randomized trial of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) versus more conventional moderate-intensity exercise to improve health-related quality of life and physical function in 27 patients with knee OA. The exercise programs involved unsupervised home-based cycling, with participants requested to do four roughly 25-minute sessions per week for 8 weeks.
The two exercise intensity groups showed similar gains in health-related quality of life as assessed by the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC). However, the HIIT group showed significantly greater improvement in physical function as measured on the Timed Up and Go test (PeerJ. 2018 May 9;6:e4738).
Dr. Maly noted that adherence to the home-based exercise programs was a challenge: Only 17 of the 27 patients completed the 8-week Australian study, for a 37% dropout rate. However, most study withdrawals were because of family-related issues, illness, or injuries unrelated to cycling, with no signal that HIIT placed knee OA patients at higher injury risk.
Other investigators performed a systematic review of 45 studies in an effort to generate evidence-based guidance about the optimal exercise dosing in order to improve outcomes in knee OA patients. They concluded that programs comprising 24 therapeutic exercise sessions over the course of 8-12 weeks resulted in the largest improvements in measures of pain and physical function. And, importantly, one exercise session per week conferred no benefits (J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2018 Mar;48[3]:146-61).
“Frequency probably matters,” Dr. Maly observed.
Patients and their physicians often wonder if long-term, land-based exercise might have deleterious impacts on joint structure in patients with knee OA. Reassurance on this score was provided by a recent meta-analysis of RCTs that concluded, on the basis of moderate-strength evidence, that exercise therapy of longer than 6 months duration had no adverse effect on tibiofemoral radiographic disease severity, compared with no exercise. Nor was there evidence of a long-term-exercise–associated deterioration of tibiofemoral cartilage morphology or worsening of synovitis or effusion. Plus, the meta-analysis provided limited evidence to suggest long-term exercise had a protective effect on the composition of patellar cartilage (Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019 Jun;48[6]:941-9).
“While there was a little bit of evidence suggesting that long-term exercise could worsen bone marrow lesions, really there was no other evidence that it could change the structure of a joint,” according to Dr. Maly.
Internet-based exercise training
Using the Internet to deliver an individually tailored exercise-training program for patients with symptomatic knee OA might sound like an efficient strategy, but in fact it proved fruitless in a large randomized trial. The 350 participants were assigned to an 8-visit, 4-month program of physical therapy, a wait-list control group, or an internet-based program that delivered tailored exercises and video demonstrations with no face-to-face contact. The bottom line is that improvement in WOMAC scores didn’t differ significantly between the three groups when evaluated at 4 and 12 months (Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018 Mar;26[3]:383-96).
“When we deliver exercise with the use of technology, it may require some support, including face to face,” Dr. Maly concluded from the study results.
Strength training
High-intensity resistance training such as weight lifting aimed at strengthening the quadriceps and other large muscles is often eschewed in patients with knee OA because of concern about possible damage to their already damaged joints. Intriguingly, Brazilian investigators may have found a workaround. They randomized 48 women with knee OA to 12 weeks of either supervised low-intensity resistance training performed with partial blood-flow restriction using an air cuff, to low-intensity resistance training alone, or to high-intensity resistance training. The low-intensity resistance workouts involved exercises such as leg presses and knee extensions performed at 30% of maximum effort.
The low-intensity resistance training performed with blood-flow restriction and the high-intensity strength training programs proved similarly effective in improving quadriceps muscle mass, muscle strength, and physical function to a significantly greater extent than with low-intensity resistance training alone. Moreover, low-intensity resistance training with blood-flow restriction also resulted in a significant improvement in pain scores. That finding, coupled with the fact that 4 of the 16 patients in the high-intensity resistance training group dropped out of the trial because of exercise-induced knee pain, suggests that low-intensity strength training carried out with partial blood-flow restriction may have a bright future (Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018 May;50[5]:897-905).
Exercise plus diet-induced weight loss
How does the combination of dietary weight loss plus exercise stack up against diet alone in terms of benefits on pain and physical function in obese patients with knee OA? A systematic review and meta-analysis of nine RCTs aimed at answering that question concluded that diet-alone strategies are less effective. Both the diet-plus-exercise and diet-only interventions resulted in comparably moderate improvement in physical function. However, diet-only treatments didn’t reduce pain, whereas diet-plus-exercise interventions achieved moderate pain relief (Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019 Apr;48[5]:765-77).
Dr. Maly reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding her presentation.
TORONTO – Emerging evidence indicates that patients with knee osteoarthritis who engage in high-intensity interval training obtain significantly greater improvement in physical function than with conventionally prescribed moderate-intensity exercise, Monica R. Maly, PhD, said at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
This was one of the key conclusions she and her coworkers drew from their analysis of the past year’s published research on diet and exercise interventions to improve outcomes in patients with OA, where obesity and physical inactivity figure prominently as modifiable lifestyle factors.
Another finding: Exercise interventions are where all the action is at present in the field of lifestyle-modification research aimed at achieving better health-related quality of life and other positive outcomes in OA. Dietary interventions are simply not a hot research topic. Indeed, her review of the past year’s literature included 38 randomized, controlled trials (RCTs) and 15 meta-analyses and systematic reviews – and all 38 RCTs addressed exercise interventions.
“It’s interesting to note that we found no new RCT data on diet to modify obesity in OA in the past year,” Dr. Maly said at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Additionally, 32 of the 38 RCTs devoted to exercise interventions for OA focused specifically on knee OA, noted Dr. Maly of the department of kinesiology at the University of Waterloo (Ont.).
Aerobic exercise dosage and intensity
Australian investigators conducted a pilot randomized trial of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) versus more conventional moderate-intensity exercise to improve health-related quality of life and physical function in 27 patients with knee OA. The exercise programs involved unsupervised home-based cycling, with participants requested to do four roughly 25-minute sessions per week for 8 weeks.
The two exercise intensity groups showed similar gains in health-related quality of life as assessed by the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC). However, the HIIT group showed significantly greater improvement in physical function as measured on the Timed Up and Go test (PeerJ. 2018 May 9;6:e4738).
Dr. Maly noted that adherence to the home-based exercise programs was a challenge: Only 17 of the 27 patients completed the 8-week Australian study, for a 37% dropout rate. However, most study withdrawals were because of family-related issues, illness, or injuries unrelated to cycling, with no signal that HIIT placed knee OA patients at higher injury risk.
Other investigators performed a systematic review of 45 studies in an effort to generate evidence-based guidance about the optimal exercise dosing in order to improve outcomes in knee OA patients. They concluded that programs comprising 24 therapeutic exercise sessions over the course of 8-12 weeks resulted in the largest improvements in measures of pain and physical function. And, importantly, one exercise session per week conferred no benefits (J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2018 Mar;48[3]:146-61).
“Frequency probably matters,” Dr. Maly observed.
Patients and their physicians often wonder if long-term, land-based exercise might have deleterious impacts on joint structure in patients with knee OA. Reassurance on this score was provided by a recent meta-analysis of RCTs that concluded, on the basis of moderate-strength evidence, that exercise therapy of longer than 6 months duration had no adverse effect on tibiofemoral radiographic disease severity, compared with no exercise. Nor was there evidence of a long-term-exercise–associated deterioration of tibiofemoral cartilage morphology or worsening of synovitis or effusion. Plus, the meta-analysis provided limited evidence to suggest long-term exercise had a protective effect on the composition of patellar cartilage (Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019 Jun;48[6]:941-9).
“While there was a little bit of evidence suggesting that long-term exercise could worsen bone marrow lesions, really there was no other evidence that it could change the structure of a joint,” according to Dr. Maly.
Internet-based exercise training
Using the Internet to deliver an individually tailored exercise-training program for patients with symptomatic knee OA might sound like an efficient strategy, but in fact it proved fruitless in a large randomized trial. The 350 participants were assigned to an 8-visit, 4-month program of physical therapy, a wait-list control group, or an internet-based program that delivered tailored exercises and video demonstrations with no face-to-face contact. The bottom line is that improvement in WOMAC scores didn’t differ significantly between the three groups when evaluated at 4 and 12 months (Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018 Mar;26[3]:383-96).
“When we deliver exercise with the use of technology, it may require some support, including face to face,” Dr. Maly concluded from the study results.
Strength training
High-intensity resistance training such as weight lifting aimed at strengthening the quadriceps and other large muscles is often eschewed in patients with knee OA because of concern about possible damage to their already damaged joints. Intriguingly, Brazilian investigators may have found a workaround. They randomized 48 women with knee OA to 12 weeks of either supervised low-intensity resistance training performed with partial blood-flow restriction using an air cuff, to low-intensity resistance training alone, or to high-intensity resistance training. The low-intensity resistance workouts involved exercises such as leg presses and knee extensions performed at 30% of maximum effort.
The low-intensity resistance training performed with blood-flow restriction and the high-intensity strength training programs proved similarly effective in improving quadriceps muscle mass, muscle strength, and physical function to a significantly greater extent than with low-intensity resistance training alone. Moreover, low-intensity resistance training with blood-flow restriction also resulted in a significant improvement in pain scores. That finding, coupled with the fact that 4 of the 16 patients in the high-intensity resistance training group dropped out of the trial because of exercise-induced knee pain, suggests that low-intensity strength training carried out with partial blood-flow restriction may have a bright future (Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018 May;50[5]:897-905).
Exercise plus diet-induced weight loss
How does the combination of dietary weight loss plus exercise stack up against diet alone in terms of benefits on pain and physical function in obese patients with knee OA? A systematic review and meta-analysis of nine RCTs aimed at answering that question concluded that diet-alone strategies are less effective. Both the diet-plus-exercise and diet-only interventions resulted in comparably moderate improvement in physical function. However, diet-only treatments didn’t reduce pain, whereas diet-plus-exercise interventions achieved moderate pain relief (Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019 Apr;48[5]:765-77).
Dr. Maly reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding her presentation.
TORONTO – Emerging evidence indicates that patients with knee osteoarthritis who engage in high-intensity interval training obtain significantly greater improvement in physical function than with conventionally prescribed moderate-intensity exercise, Monica R. Maly, PhD, said at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
This was one of the key conclusions she and her coworkers drew from their analysis of the past year’s published research on diet and exercise interventions to improve outcomes in patients with OA, where obesity and physical inactivity figure prominently as modifiable lifestyle factors.
Another finding: Exercise interventions are where all the action is at present in the field of lifestyle-modification research aimed at achieving better health-related quality of life and other positive outcomes in OA. Dietary interventions are simply not a hot research topic. Indeed, her review of the past year’s literature included 38 randomized, controlled trials (RCTs) and 15 meta-analyses and systematic reviews – and all 38 RCTs addressed exercise interventions.
“It’s interesting to note that we found no new RCT data on diet to modify obesity in OA in the past year,” Dr. Maly said at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Additionally, 32 of the 38 RCTs devoted to exercise interventions for OA focused specifically on knee OA, noted Dr. Maly of the department of kinesiology at the University of Waterloo (Ont.).
Aerobic exercise dosage and intensity
Australian investigators conducted a pilot randomized trial of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) versus more conventional moderate-intensity exercise to improve health-related quality of life and physical function in 27 patients with knee OA. The exercise programs involved unsupervised home-based cycling, with participants requested to do four roughly 25-minute sessions per week for 8 weeks.
The two exercise intensity groups showed similar gains in health-related quality of life as assessed by the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC). However, the HIIT group showed significantly greater improvement in physical function as measured on the Timed Up and Go test (PeerJ. 2018 May 9;6:e4738).
Dr. Maly noted that adherence to the home-based exercise programs was a challenge: Only 17 of the 27 patients completed the 8-week Australian study, for a 37% dropout rate. However, most study withdrawals were because of family-related issues, illness, or injuries unrelated to cycling, with no signal that HIIT placed knee OA patients at higher injury risk.
Other investigators performed a systematic review of 45 studies in an effort to generate evidence-based guidance about the optimal exercise dosing in order to improve outcomes in knee OA patients. They concluded that programs comprising 24 therapeutic exercise sessions over the course of 8-12 weeks resulted in the largest improvements in measures of pain and physical function. And, importantly, one exercise session per week conferred no benefits (J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2018 Mar;48[3]:146-61).
“Frequency probably matters,” Dr. Maly observed.
Patients and their physicians often wonder if long-term, land-based exercise might have deleterious impacts on joint structure in patients with knee OA. Reassurance on this score was provided by a recent meta-analysis of RCTs that concluded, on the basis of moderate-strength evidence, that exercise therapy of longer than 6 months duration had no adverse effect on tibiofemoral radiographic disease severity, compared with no exercise. Nor was there evidence of a long-term-exercise–associated deterioration of tibiofemoral cartilage morphology or worsening of synovitis or effusion. Plus, the meta-analysis provided limited evidence to suggest long-term exercise had a protective effect on the composition of patellar cartilage (Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019 Jun;48[6]:941-9).
“While there was a little bit of evidence suggesting that long-term exercise could worsen bone marrow lesions, really there was no other evidence that it could change the structure of a joint,” according to Dr. Maly.
Internet-based exercise training
Using the Internet to deliver an individually tailored exercise-training program for patients with symptomatic knee OA might sound like an efficient strategy, but in fact it proved fruitless in a large randomized trial. The 350 participants were assigned to an 8-visit, 4-month program of physical therapy, a wait-list control group, or an internet-based program that delivered tailored exercises and video demonstrations with no face-to-face contact. The bottom line is that improvement in WOMAC scores didn’t differ significantly between the three groups when evaluated at 4 and 12 months (Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018 Mar;26[3]:383-96).
“When we deliver exercise with the use of technology, it may require some support, including face to face,” Dr. Maly concluded from the study results.
Strength training
High-intensity resistance training such as weight lifting aimed at strengthening the quadriceps and other large muscles is often eschewed in patients with knee OA because of concern about possible damage to their already damaged joints. Intriguingly, Brazilian investigators may have found a workaround. They randomized 48 women with knee OA to 12 weeks of either supervised low-intensity resistance training performed with partial blood-flow restriction using an air cuff, to low-intensity resistance training alone, or to high-intensity resistance training. The low-intensity resistance workouts involved exercises such as leg presses and knee extensions performed at 30% of maximum effort.
The low-intensity resistance training performed with blood-flow restriction and the high-intensity strength training programs proved similarly effective in improving quadriceps muscle mass, muscle strength, and physical function to a significantly greater extent than with low-intensity resistance training alone. Moreover, low-intensity resistance training with blood-flow restriction also resulted in a significant improvement in pain scores. That finding, coupled with the fact that 4 of the 16 patients in the high-intensity resistance training group dropped out of the trial because of exercise-induced knee pain, suggests that low-intensity strength training carried out with partial blood-flow restriction may have a bright future (Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018 May;50[5]:897-905).
Exercise plus diet-induced weight loss
How does the combination of dietary weight loss plus exercise stack up against diet alone in terms of benefits on pain and physical function in obese patients with knee OA? A systematic review and meta-analysis of nine RCTs aimed at answering that question concluded that diet-alone strategies are less effective. Both the diet-plus-exercise and diet-only interventions resulted in comparably moderate improvement in physical function. However, diet-only treatments didn’t reduce pain, whereas diet-plus-exercise interventions achieved moderate pain relief (Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019 Apr;48[5]:765-77).
Dr. Maly reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding her presentation.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM OARSI 2019
Occupational therapy program helps thumb OA
TORONTO – A multimodal occupational therapy intervention in patients with thumb base osteoarthritis brought clinically meaningful improvements in pain, grip strength, and function, at least short term, in a Norwegian multicenter randomized clinical trial, Anne Therese Tveter reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
OA of the thumb base – that is, the carpometacarpal joint – causes more pain and dysfunction than disease involvement at many other sites because of the evolutionary importance of the opposable thumb. Current guidelines recommend conservative therapies as first line for hand OA; however, there is a dearth of high-quality evidence for multimodal occupational therapy in the special setting of thumb-base OA. This was the impetus for a randomized trial of 170 consecutive patients with thumb OA who presented to three Norwegian rheumatology departments for surgical consultation, explained Ms. Tveter, a physiotherapist at the Norwegian National Advisory Unit on Rehabilitation in Rheumatology at Diakonhjemmet Hospital in Oslo.
Participants were randomized to a 3-month, multimodal self-management intervention. It included education about OA; ergonomic principles; the importance of using separate orthoses as much as possible both day and night to stabilize the joint, improve performance, and relieve pain; and – at the heart of the program – instruction in hand exercises to enhance joint mobility, strength, and stability, as well as hand-stretching exercises. The exercises were to be done at home three times per week. Also, the active intervention group received five common assistive devices to help them in household tasks, such as opening jars. The control group received usual care, which was basically information about hand OA, she said at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Ms. Tveter presented an interim analysis focused on the 3-month outcomes. At 4 months, participants underwent surgical consultation. The study will continue for 2 years, with endpoints including the impact of the occupational therapy intervention on need for joint surgery, as well as long-term pain and function measures.
At baseline, most patients reported mild pain, with a median score of 3 on a 10-point numeric rating scale, and moderate disability. Baseline grip and pinch strength was 60%-65% of normal. The 3-month outcomes included pain at rest and during pinch- and grip-strength testing, range of motion through palmar abduction and abduction in the carpometacarpal joint, and self-reported function as measured using the validated MAP-Hand and QuickDASH physiotherapy measures. Adherence to the program was assessed by review of patient diaries.
At 3 months of follow-up, the active-intervention group showed significant improvements in all measures of pain and function except for the flexion deficit, which was minimal to begin with. In contrast, the control group showed no improvements and a trend towards deterioration in pain and function.
Specifically, the intervention group averaged a 1.4-point reduction in pain at rest on a self-reported 10-point scale, a 1.1-point improvement in pain following a grip strength test, and a 0.8-point improvement in pain following a pinch test. On the MAP-Hand self-reported test of function, the intervention group showed a 0.18-point improvement from a baseline of 2 on the 1-4 scale, coupled with an 8.1-point improvement on the QuickDASH, which is scored 0-100.
Adherence to the program was deemed acceptable: 82% of patients reported doing their hand exercises at least twice per week for at least 8 of the 12 weeks, 61% used their day orthotic devices at least 4 days per week for 8 weeks, 54% used the night orthoses at least 5 nights per week for 8 weeks, and 69% utilized at least three of the five home-assist devices. In total, 64% of patients adhered to at least three of the four program components.
Asked for the rationale in requesting that patients do their home exercises three times per week instead of daily, Ms. Tveter replied that three times per week is more realistic and is consistent with major guidelines.
“It would be nice to exercise every day. I don’t think it would be possible to get adherence to that,” she said.
She reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, funded by scientific research grants from the Norwegian government.
TORONTO – A multimodal occupational therapy intervention in patients with thumb base osteoarthritis brought clinically meaningful improvements in pain, grip strength, and function, at least short term, in a Norwegian multicenter randomized clinical trial, Anne Therese Tveter reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
OA of the thumb base – that is, the carpometacarpal joint – causes more pain and dysfunction than disease involvement at many other sites because of the evolutionary importance of the opposable thumb. Current guidelines recommend conservative therapies as first line for hand OA; however, there is a dearth of high-quality evidence for multimodal occupational therapy in the special setting of thumb-base OA. This was the impetus for a randomized trial of 170 consecutive patients with thumb OA who presented to three Norwegian rheumatology departments for surgical consultation, explained Ms. Tveter, a physiotherapist at the Norwegian National Advisory Unit on Rehabilitation in Rheumatology at Diakonhjemmet Hospital in Oslo.
Participants were randomized to a 3-month, multimodal self-management intervention. It included education about OA; ergonomic principles; the importance of using separate orthoses as much as possible both day and night to stabilize the joint, improve performance, and relieve pain; and – at the heart of the program – instruction in hand exercises to enhance joint mobility, strength, and stability, as well as hand-stretching exercises. The exercises were to be done at home three times per week. Also, the active intervention group received five common assistive devices to help them in household tasks, such as opening jars. The control group received usual care, which was basically information about hand OA, she said at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Ms. Tveter presented an interim analysis focused on the 3-month outcomes. At 4 months, participants underwent surgical consultation. The study will continue for 2 years, with endpoints including the impact of the occupational therapy intervention on need for joint surgery, as well as long-term pain and function measures.
At baseline, most patients reported mild pain, with a median score of 3 on a 10-point numeric rating scale, and moderate disability. Baseline grip and pinch strength was 60%-65% of normal. The 3-month outcomes included pain at rest and during pinch- and grip-strength testing, range of motion through palmar abduction and abduction in the carpometacarpal joint, and self-reported function as measured using the validated MAP-Hand and QuickDASH physiotherapy measures. Adherence to the program was assessed by review of patient diaries.
At 3 months of follow-up, the active-intervention group showed significant improvements in all measures of pain and function except for the flexion deficit, which was minimal to begin with. In contrast, the control group showed no improvements and a trend towards deterioration in pain and function.
Specifically, the intervention group averaged a 1.4-point reduction in pain at rest on a self-reported 10-point scale, a 1.1-point improvement in pain following a grip strength test, and a 0.8-point improvement in pain following a pinch test. On the MAP-Hand self-reported test of function, the intervention group showed a 0.18-point improvement from a baseline of 2 on the 1-4 scale, coupled with an 8.1-point improvement on the QuickDASH, which is scored 0-100.
Adherence to the program was deemed acceptable: 82% of patients reported doing their hand exercises at least twice per week for at least 8 of the 12 weeks, 61% used their day orthotic devices at least 4 days per week for 8 weeks, 54% used the night orthoses at least 5 nights per week for 8 weeks, and 69% utilized at least three of the five home-assist devices. In total, 64% of patients adhered to at least three of the four program components.
Asked for the rationale in requesting that patients do their home exercises three times per week instead of daily, Ms. Tveter replied that three times per week is more realistic and is consistent with major guidelines.
“It would be nice to exercise every day. I don’t think it would be possible to get adherence to that,” she said.
She reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, funded by scientific research grants from the Norwegian government.
TORONTO – A multimodal occupational therapy intervention in patients with thumb base osteoarthritis brought clinically meaningful improvements in pain, grip strength, and function, at least short term, in a Norwegian multicenter randomized clinical trial, Anne Therese Tveter reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
OA of the thumb base – that is, the carpometacarpal joint – causes more pain and dysfunction than disease involvement at many other sites because of the evolutionary importance of the opposable thumb. Current guidelines recommend conservative therapies as first line for hand OA; however, there is a dearth of high-quality evidence for multimodal occupational therapy in the special setting of thumb-base OA. This was the impetus for a randomized trial of 170 consecutive patients with thumb OA who presented to three Norwegian rheumatology departments for surgical consultation, explained Ms. Tveter, a physiotherapist at the Norwegian National Advisory Unit on Rehabilitation in Rheumatology at Diakonhjemmet Hospital in Oslo.
Participants were randomized to a 3-month, multimodal self-management intervention. It included education about OA; ergonomic principles; the importance of using separate orthoses as much as possible both day and night to stabilize the joint, improve performance, and relieve pain; and – at the heart of the program – instruction in hand exercises to enhance joint mobility, strength, and stability, as well as hand-stretching exercises. The exercises were to be done at home three times per week. Also, the active intervention group received five common assistive devices to help them in household tasks, such as opening jars. The control group received usual care, which was basically information about hand OA, she said at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Ms. Tveter presented an interim analysis focused on the 3-month outcomes. At 4 months, participants underwent surgical consultation. The study will continue for 2 years, with endpoints including the impact of the occupational therapy intervention on need for joint surgery, as well as long-term pain and function measures.
At baseline, most patients reported mild pain, with a median score of 3 on a 10-point numeric rating scale, and moderate disability. Baseline grip and pinch strength was 60%-65% of normal. The 3-month outcomes included pain at rest and during pinch- and grip-strength testing, range of motion through palmar abduction and abduction in the carpometacarpal joint, and self-reported function as measured using the validated MAP-Hand and QuickDASH physiotherapy measures. Adherence to the program was assessed by review of patient diaries.
At 3 months of follow-up, the active-intervention group showed significant improvements in all measures of pain and function except for the flexion deficit, which was minimal to begin with. In contrast, the control group showed no improvements and a trend towards deterioration in pain and function.
Specifically, the intervention group averaged a 1.4-point reduction in pain at rest on a self-reported 10-point scale, a 1.1-point improvement in pain following a grip strength test, and a 0.8-point improvement in pain following a pinch test. On the MAP-Hand self-reported test of function, the intervention group showed a 0.18-point improvement from a baseline of 2 on the 1-4 scale, coupled with an 8.1-point improvement on the QuickDASH, which is scored 0-100.
Adherence to the program was deemed acceptable: 82% of patients reported doing their hand exercises at least twice per week for at least 8 of the 12 weeks, 61% used their day orthotic devices at least 4 days per week for 8 weeks, 54% used the night orthoses at least 5 nights per week for 8 weeks, and 69% utilized at least three of the five home-assist devices. In total, 64% of patients adhered to at least three of the four program components.
Asked for the rationale in requesting that patients do their home exercises three times per week instead of daily, Ms. Tveter replied that three times per week is more realistic and is consistent with major guidelines.
“It would be nice to exercise every day. I don’t think it would be possible to get adherence to that,” she said.
She reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, funded by scientific research grants from the Norwegian government.
REPORTING FROM OARSI 2019
Key clinical point: A multimodal occupational therapy intervention brought significant improvements in pain and function in patients with thumb-base OA.
Major finding: The intervention resulted in a mean 1.4-point decrease in self-reported pain at rest from a baseline of 3 on a 10-point scale, while most usual care controls showed a modest trend for worsening.
Study details: This was an interim 3-month report from a 2-year, randomized, multicenter trial including 170 consecutive patients who presented for surgical consultation regarding their thumb base OA.
Disclosures: The presenter reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, funded by Norwegian governmental scientific research grants.
Liposomal steroid brings durable pain relief in knee OA
TORONTO – A single intra-articular injection of a novel, sustained-release liposomal formulation of dexamethasone in patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis brought at least 6 months of pain control in a multicenter, phase 2a trial, David Hunter, MD, reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
This is a product that could fill a significant unmet medical need. Current therapies for knee OA have modest efficacy, and the injectable ones provide only 2-4 weeks of benefit. The ability to obtain significant pain relief with just a couple of intra-articular injections per year would be an important therapeutic advance, observed Dr. Hunter, professor of medicine at the University of Sydney.
He presented a 24-week study of 75 patients with symptomatic knee OA randomized at 13 sites in Australia and Taiwan to a single intra-articular injection of either 12 or 18 mg of the liposomal dexamethasone or to normal saline. One knee per patient was treated.
The primary outcome was the change in the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain score from baseline to week 12. The 12-mg formulation of steroid significantly outperformed placebo at that time point as well as at all others. From a mean baseline WOMAC pain score of 1.49 on the 0-4 scale, patients in the 12-mg group averaged reductions of 0.83 points at 12 weeks, 0.85 at both weeks 16 and 20, and 0.87 at week 24. A statistically significant between-group difference was seen as early as day 3 after injection.
More than half (52%) of recipients of the 12-mg dose of liposomal dexamethasone, a product known for now simply as TLC599, maintained at least 30% pain relief at all visits through the study close at 24 weeks, as did 22% of controls, the rheumatologist reported at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
The 12-mg injection also proved superior to placebo for the secondary endpoint of change in WOMAC function score. From a mean baseline score of 1.53, recipients of the 12-mg dose had improvements ranging from 0.82 points at week 12 to 0.85 points at week 24.
Of note, total acetaminophen intake over the course of the trial in the 12-mg steroid group was less than one-third of that in controls.
The 18-mg dose didn’t result in significantly greater reduction in pain scores than placebo. This is because dexamethasone release in the higher-dose formulation as presently constituted turned out to be less efficient, Dr. Hunter explained.
The safety profile was closely similar in all three study arms.
In phase 3 clinical trials, TLC599 will be compared with standard intra-articular triamcinolone, according to the rheumatologist.
He reported serving as a consultant to the Taiwan Liposome Company, which sponsored the phase 2a study, as well as to a handful of other pharmaceutical companies.
TORONTO – A single intra-articular injection of a novel, sustained-release liposomal formulation of dexamethasone in patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis brought at least 6 months of pain control in a multicenter, phase 2a trial, David Hunter, MD, reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
This is a product that could fill a significant unmet medical need. Current therapies for knee OA have modest efficacy, and the injectable ones provide only 2-4 weeks of benefit. The ability to obtain significant pain relief with just a couple of intra-articular injections per year would be an important therapeutic advance, observed Dr. Hunter, professor of medicine at the University of Sydney.
He presented a 24-week study of 75 patients with symptomatic knee OA randomized at 13 sites in Australia and Taiwan to a single intra-articular injection of either 12 or 18 mg of the liposomal dexamethasone or to normal saline. One knee per patient was treated.
The primary outcome was the change in the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain score from baseline to week 12. The 12-mg formulation of steroid significantly outperformed placebo at that time point as well as at all others. From a mean baseline WOMAC pain score of 1.49 on the 0-4 scale, patients in the 12-mg group averaged reductions of 0.83 points at 12 weeks, 0.85 at both weeks 16 and 20, and 0.87 at week 24. A statistically significant between-group difference was seen as early as day 3 after injection.
More than half (52%) of recipients of the 12-mg dose of liposomal dexamethasone, a product known for now simply as TLC599, maintained at least 30% pain relief at all visits through the study close at 24 weeks, as did 22% of controls, the rheumatologist reported at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
The 12-mg injection also proved superior to placebo for the secondary endpoint of change in WOMAC function score. From a mean baseline score of 1.53, recipients of the 12-mg dose had improvements ranging from 0.82 points at week 12 to 0.85 points at week 24.
Of note, total acetaminophen intake over the course of the trial in the 12-mg steroid group was less than one-third of that in controls.
The 18-mg dose didn’t result in significantly greater reduction in pain scores than placebo. This is because dexamethasone release in the higher-dose formulation as presently constituted turned out to be less efficient, Dr. Hunter explained.
The safety profile was closely similar in all three study arms.
In phase 3 clinical trials, TLC599 will be compared with standard intra-articular triamcinolone, according to the rheumatologist.
He reported serving as a consultant to the Taiwan Liposome Company, which sponsored the phase 2a study, as well as to a handful of other pharmaceutical companies.
TORONTO – A single intra-articular injection of a novel, sustained-release liposomal formulation of dexamethasone in patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis brought at least 6 months of pain control in a multicenter, phase 2a trial, David Hunter, MD, reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
This is a product that could fill a significant unmet medical need. Current therapies for knee OA have modest efficacy, and the injectable ones provide only 2-4 weeks of benefit. The ability to obtain significant pain relief with just a couple of intra-articular injections per year would be an important therapeutic advance, observed Dr. Hunter, professor of medicine at the University of Sydney.
He presented a 24-week study of 75 patients with symptomatic knee OA randomized at 13 sites in Australia and Taiwan to a single intra-articular injection of either 12 or 18 mg of the liposomal dexamethasone or to normal saline. One knee per patient was treated.
The primary outcome was the change in the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain score from baseline to week 12. The 12-mg formulation of steroid significantly outperformed placebo at that time point as well as at all others. From a mean baseline WOMAC pain score of 1.49 on the 0-4 scale, patients in the 12-mg group averaged reductions of 0.83 points at 12 weeks, 0.85 at both weeks 16 and 20, and 0.87 at week 24. A statistically significant between-group difference was seen as early as day 3 after injection.
More than half (52%) of recipients of the 12-mg dose of liposomal dexamethasone, a product known for now simply as TLC599, maintained at least 30% pain relief at all visits through the study close at 24 weeks, as did 22% of controls, the rheumatologist reported at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
The 12-mg injection also proved superior to placebo for the secondary endpoint of change in WOMAC function score. From a mean baseline score of 1.53, recipients of the 12-mg dose had improvements ranging from 0.82 points at week 12 to 0.85 points at week 24.
Of note, total acetaminophen intake over the course of the trial in the 12-mg steroid group was less than one-third of that in controls.
The 18-mg dose didn’t result in significantly greater reduction in pain scores than placebo. This is because dexamethasone release in the higher-dose formulation as presently constituted turned out to be less efficient, Dr. Hunter explained.
The safety profile was closely similar in all three study arms.
In phase 3 clinical trials, TLC599 will be compared with standard intra-articular triamcinolone, according to the rheumatologist.
He reported serving as a consultant to the Taiwan Liposome Company, which sponsored the phase 2a study, as well as to a handful of other pharmaceutical companies.
REPORTING FROM OARSI 2019
What’s up in the osteoarthritis drug pipeline
TORONTO – Philip G. Conaghan, MBBS, PhD, observed at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
“Not only have things not improved during my time in osteoarthritis-land, they’ve gotten worse. We’ve lost therapies,” said Dr. Conaghan, professor of musculoskeletal medicine at the University of Leeds (England) and director of the Leeds Institute of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Medicine.
Specifically, opioids are now shunned because of the ongoing epidemic of addiction and a belated recognition that opioids are not a good option for pain relief in OA patients who want to have active lives. And acetaminophen has fallen by the wayside in light of recent evidence of lack of effectiveness: “It’s what our patients have been telling us for a long period of time,” he noted at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
But change is in the air.
“I think we’ve got some things coming that look promising. What do I think will be the fastest to get to market? The peripheral nerve modulators look to me like the ones closest to going forward,” according to the rheumatologist, who provided an overview of the OA drug development pipeline, organized by treatment target.
Nerves
“Nerves as a treatment target in OA is a hot area. We’ve seen quite a slew of products recently looking at this. I think it’s a really fascinating area to play in: looking at how we modulate peripheral nociceptive pain,” Dr. Conaghan continued.
Tanezumab, an inhibitor of nerve growth factor, demonstrated very good pain relief and improvement in physical function in a phase 3 trial, although the occurrence of rapidly progressive OA in a subset of patients has bedeviled the drug development program. The hope is that a new subcutaneous drug delivery system coupled with careful patient pretreatment screening will mitigate the problem.
Tanezumab’s efficacy has contributed to a new understanding of the nature of pain in OA.
“I know I’m going to upset some people, but if you think central sensitization is the biggest driver of pain, I’d have to argue that the tanezumab program is the biggest single argument against that, since tanezumab is a large monoclonal antibody that doesn’t cross the blood-brain barrier and yet it has some of the best pain responses that we’ve seen,” Dr. Conaghan said.
Another peripheral nerve modulator, known for now as CNTX-4975, exhibited dose-dependent improvement in knee OA pain in the 175-patient, phase 2b TRIUMPH trial (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Mar 19. doi: 10.1002/art.40894). CNTX-4975, which is delivered by intra-articular injection, is a synthetic form of capsaicin specific to pain nociceptors within the joint. Other sensory fibers remain unaffected.
Cartilage
Sprifermin, a recombinant human fibroblast growth factor 18 given by intra-articular injection, stimulates chondrocyte growth and decreases type 1 collagen expression. At year 2 in the ongoing 549-patient, 5-year, phase 2 FORWARD study, a dose-dependent increase in cartilage thickness at the tibiofemoral joint became apparent in sprifermin-treated patients, compared with those on placebo. This cartilage rebuilding effect was maintained at year 3, Dr. Conaghan said.
Bone
At the OARSI meeting, Dr. Conaghan and coinvestigators presented the results of a 6-month, open-label extension of their previously reported 6-month, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study of MIV-711, a potent selective reversible inhibitor of cathepsin K. The disease-modifying effects of MIV-711 seen in the first 6 months of the study, based on MRI-based measurements of changes in three-dimensional bone shape and cartilage thickness, were maintained in the second 6 months. Notably, MIV-711 slowed the rate of increase in bone area in the medial femur region and reduced loss of cartilage thickness relative to placebo. MIV-711 has also been shown to achieve a rapid and sustained reduction in the bone turnover biomarkers CTX-1 and -2, providing a rational mechanism to explain the drug’s observed structural benefits.
“So we’ve now got two agents – sprifermin for cartilage and MIV-711 for bone – showing that it’s possible to get some structural change, but no symptomatic benefit within the period of those trials,” the rheumatologist noted.
Wnt pathway inhibition
Samumed has launched a phase 3 clinical trials program, known as STRIDES, for lorecivivint, the company’s investigational small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway. In phase 2 studies, including one led by Dr. Conaghan, intra-articular injection of lorecivivint, previously known as SMO4690, improved pain and physical function as well as medial joint space width. The drug’s potential effects on multiple tissues offers the promise of providing both symptomatic improvement and modification of the course of structural disease progression.
Inflammation
Lutikizumab, an anti–interleukin-1 alpha/beta immunoglobulin, proved to be a disappointment in a recent phase 2, placebo-controlled trial carried out in 350 patients with knee OA and synovitis. The IL-1 inhibitor had no benefit on synovitis, joint space narrowing, or cartilage thickness. Nor was it significantly better than placebo for pain reduction (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Jul;71[7]:1056-69).
Anti–tumor necrosis factor agents haven’t exactly set the OA world on fire, either.
“In rheumatoid arthritis we know they’re stupendously effective, but the data from a number of trials in OA show they’re not so effective on symptoms and signs,” Dr. Conaghan said.
Colchicine and hydroxychloroquine are other anti-inflammatory agents which, while in theory might be helpful, have in actuality shown no benefit for OA symptoms in controlled clinical trials and are now considered dead ends.
On the other hand, the sustained delivery of intra-articular corticosteroids through the use of microsphere technology is advancing smartly through the developmental pipeline. Dr. Conaghan was first author of a multicenter, double-blind, phase 3 trial of FX006, a sustained-release formulation of triamcinolone acetonide, which showed that a single intra-articular injection provided at least 3 months of pain relief in knee OA patients, along with reduced systemic drug exposure, compared with standard intra-articular corticosteroids (J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018 Apr 18;100[8]:666-77).
FX006 also performed well in another phase 3 trial, this one featuring repeated dosing on a flexible schedule based upon patient response (Rheumatol Ther. 2019 Mar;6[1]:109-24).
Reassuringly, this slow-release corticosteroid doesn’t appear to worsen glycemic control in knee OA patients with type 2 diabetes (Rheumatology [Oxford]. 2018 Dec 1;57[12]:2235-41).
“This is the start of a revolution in nanotechnology and the ability to slowly deliver a variety of drugs within the joint,” Dr. Conaghan predicted.
Although he was tasked at OARSI 2019 with providing an overview of the OA pharmacologic pipeline, he stressed that in his clinical practice, as opposed to his work as a clinical trialist, he functions more like a physical therapist.
“I actually spend my whole time in the OA clinic being a physical therapist and trying to get people strong, because that does work and it has no side effects. It’s just that nobody does it. We have a real adherence problem,” he said. “My favorite thought is this: keep people strong. If a patient can’t get out of a chair easily or can’t undo a jar, then they’ve got a problem.”
Dr. Conaghan reported receiving research funding from and serving as a consultant to many of the companies developing novel drug treatments for OA.
TORONTO – Philip G. Conaghan, MBBS, PhD, observed at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
“Not only have things not improved during my time in osteoarthritis-land, they’ve gotten worse. We’ve lost therapies,” said Dr. Conaghan, professor of musculoskeletal medicine at the University of Leeds (England) and director of the Leeds Institute of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Medicine.
Specifically, opioids are now shunned because of the ongoing epidemic of addiction and a belated recognition that opioids are not a good option for pain relief in OA patients who want to have active lives. And acetaminophen has fallen by the wayside in light of recent evidence of lack of effectiveness: “It’s what our patients have been telling us for a long period of time,” he noted at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
But change is in the air.
“I think we’ve got some things coming that look promising. What do I think will be the fastest to get to market? The peripheral nerve modulators look to me like the ones closest to going forward,” according to the rheumatologist, who provided an overview of the OA drug development pipeline, organized by treatment target.
Nerves
“Nerves as a treatment target in OA is a hot area. We’ve seen quite a slew of products recently looking at this. I think it’s a really fascinating area to play in: looking at how we modulate peripheral nociceptive pain,” Dr. Conaghan continued.
Tanezumab, an inhibitor of nerve growth factor, demonstrated very good pain relief and improvement in physical function in a phase 3 trial, although the occurrence of rapidly progressive OA in a subset of patients has bedeviled the drug development program. The hope is that a new subcutaneous drug delivery system coupled with careful patient pretreatment screening will mitigate the problem.
Tanezumab’s efficacy has contributed to a new understanding of the nature of pain in OA.
“I know I’m going to upset some people, but if you think central sensitization is the biggest driver of pain, I’d have to argue that the tanezumab program is the biggest single argument against that, since tanezumab is a large monoclonal antibody that doesn’t cross the blood-brain barrier and yet it has some of the best pain responses that we’ve seen,” Dr. Conaghan said.
Another peripheral nerve modulator, known for now as CNTX-4975, exhibited dose-dependent improvement in knee OA pain in the 175-patient, phase 2b TRIUMPH trial (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Mar 19. doi: 10.1002/art.40894). CNTX-4975, which is delivered by intra-articular injection, is a synthetic form of capsaicin specific to pain nociceptors within the joint. Other sensory fibers remain unaffected.
Cartilage
Sprifermin, a recombinant human fibroblast growth factor 18 given by intra-articular injection, stimulates chondrocyte growth and decreases type 1 collagen expression. At year 2 in the ongoing 549-patient, 5-year, phase 2 FORWARD study, a dose-dependent increase in cartilage thickness at the tibiofemoral joint became apparent in sprifermin-treated patients, compared with those on placebo. This cartilage rebuilding effect was maintained at year 3, Dr. Conaghan said.
Bone
At the OARSI meeting, Dr. Conaghan and coinvestigators presented the results of a 6-month, open-label extension of their previously reported 6-month, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study of MIV-711, a potent selective reversible inhibitor of cathepsin K. The disease-modifying effects of MIV-711 seen in the first 6 months of the study, based on MRI-based measurements of changes in three-dimensional bone shape and cartilage thickness, were maintained in the second 6 months. Notably, MIV-711 slowed the rate of increase in bone area in the medial femur region and reduced loss of cartilage thickness relative to placebo. MIV-711 has also been shown to achieve a rapid and sustained reduction in the bone turnover biomarkers CTX-1 and -2, providing a rational mechanism to explain the drug’s observed structural benefits.
“So we’ve now got two agents – sprifermin for cartilage and MIV-711 for bone – showing that it’s possible to get some structural change, but no symptomatic benefit within the period of those trials,” the rheumatologist noted.
Wnt pathway inhibition
Samumed has launched a phase 3 clinical trials program, known as STRIDES, for lorecivivint, the company’s investigational small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway. In phase 2 studies, including one led by Dr. Conaghan, intra-articular injection of lorecivivint, previously known as SMO4690, improved pain and physical function as well as medial joint space width. The drug’s potential effects on multiple tissues offers the promise of providing both symptomatic improvement and modification of the course of structural disease progression.
Inflammation
Lutikizumab, an anti–interleukin-1 alpha/beta immunoglobulin, proved to be a disappointment in a recent phase 2, placebo-controlled trial carried out in 350 patients with knee OA and synovitis. The IL-1 inhibitor had no benefit on synovitis, joint space narrowing, or cartilage thickness. Nor was it significantly better than placebo for pain reduction (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Jul;71[7]:1056-69).
Anti–tumor necrosis factor agents haven’t exactly set the OA world on fire, either.
“In rheumatoid arthritis we know they’re stupendously effective, but the data from a number of trials in OA show they’re not so effective on symptoms and signs,” Dr. Conaghan said.
Colchicine and hydroxychloroquine are other anti-inflammatory agents which, while in theory might be helpful, have in actuality shown no benefit for OA symptoms in controlled clinical trials and are now considered dead ends.
On the other hand, the sustained delivery of intra-articular corticosteroids through the use of microsphere technology is advancing smartly through the developmental pipeline. Dr. Conaghan was first author of a multicenter, double-blind, phase 3 trial of FX006, a sustained-release formulation of triamcinolone acetonide, which showed that a single intra-articular injection provided at least 3 months of pain relief in knee OA patients, along with reduced systemic drug exposure, compared with standard intra-articular corticosteroids (J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018 Apr 18;100[8]:666-77).
FX006 also performed well in another phase 3 trial, this one featuring repeated dosing on a flexible schedule based upon patient response (Rheumatol Ther. 2019 Mar;6[1]:109-24).
Reassuringly, this slow-release corticosteroid doesn’t appear to worsen glycemic control in knee OA patients with type 2 diabetes (Rheumatology [Oxford]. 2018 Dec 1;57[12]:2235-41).
“This is the start of a revolution in nanotechnology and the ability to slowly deliver a variety of drugs within the joint,” Dr. Conaghan predicted.
Although he was tasked at OARSI 2019 with providing an overview of the OA pharmacologic pipeline, he stressed that in his clinical practice, as opposed to his work as a clinical trialist, he functions more like a physical therapist.
“I actually spend my whole time in the OA clinic being a physical therapist and trying to get people strong, because that does work and it has no side effects. It’s just that nobody does it. We have a real adherence problem,” he said. “My favorite thought is this: keep people strong. If a patient can’t get out of a chair easily or can’t undo a jar, then they’ve got a problem.”
Dr. Conaghan reported receiving research funding from and serving as a consultant to many of the companies developing novel drug treatments for OA.
TORONTO – Philip G. Conaghan, MBBS, PhD, observed at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
“Not only have things not improved during my time in osteoarthritis-land, they’ve gotten worse. We’ve lost therapies,” said Dr. Conaghan, professor of musculoskeletal medicine at the University of Leeds (England) and director of the Leeds Institute of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Medicine.
Specifically, opioids are now shunned because of the ongoing epidemic of addiction and a belated recognition that opioids are not a good option for pain relief in OA patients who want to have active lives. And acetaminophen has fallen by the wayside in light of recent evidence of lack of effectiveness: “It’s what our patients have been telling us for a long period of time,” he noted at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
But change is in the air.
“I think we’ve got some things coming that look promising. What do I think will be the fastest to get to market? The peripheral nerve modulators look to me like the ones closest to going forward,” according to the rheumatologist, who provided an overview of the OA drug development pipeline, organized by treatment target.
Nerves
“Nerves as a treatment target in OA is a hot area. We’ve seen quite a slew of products recently looking at this. I think it’s a really fascinating area to play in: looking at how we modulate peripheral nociceptive pain,” Dr. Conaghan continued.
Tanezumab, an inhibitor of nerve growth factor, demonstrated very good pain relief and improvement in physical function in a phase 3 trial, although the occurrence of rapidly progressive OA in a subset of patients has bedeviled the drug development program. The hope is that a new subcutaneous drug delivery system coupled with careful patient pretreatment screening will mitigate the problem.
Tanezumab’s efficacy has contributed to a new understanding of the nature of pain in OA.
“I know I’m going to upset some people, but if you think central sensitization is the biggest driver of pain, I’d have to argue that the tanezumab program is the biggest single argument against that, since tanezumab is a large monoclonal antibody that doesn’t cross the blood-brain barrier and yet it has some of the best pain responses that we’ve seen,” Dr. Conaghan said.
Another peripheral nerve modulator, known for now as CNTX-4975, exhibited dose-dependent improvement in knee OA pain in the 175-patient, phase 2b TRIUMPH trial (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Mar 19. doi: 10.1002/art.40894). CNTX-4975, which is delivered by intra-articular injection, is a synthetic form of capsaicin specific to pain nociceptors within the joint. Other sensory fibers remain unaffected.
Cartilage
Sprifermin, a recombinant human fibroblast growth factor 18 given by intra-articular injection, stimulates chondrocyte growth and decreases type 1 collagen expression. At year 2 in the ongoing 549-patient, 5-year, phase 2 FORWARD study, a dose-dependent increase in cartilage thickness at the tibiofemoral joint became apparent in sprifermin-treated patients, compared with those on placebo. This cartilage rebuilding effect was maintained at year 3, Dr. Conaghan said.
Bone
At the OARSI meeting, Dr. Conaghan and coinvestigators presented the results of a 6-month, open-label extension of their previously reported 6-month, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study of MIV-711, a potent selective reversible inhibitor of cathepsin K. The disease-modifying effects of MIV-711 seen in the first 6 months of the study, based on MRI-based measurements of changes in three-dimensional bone shape and cartilage thickness, were maintained in the second 6 months. Notably, MIV-711 slowed the rate of increase in bone area in the medial femur region and reduced loss of cartilage thickness relative to placebo. MIV-711 has also been shown to achieve a rapid and sustained reduction in the bone turnover biomarkers CTX-1 and -2, providing a rational mechanism to explain the drug’s observed structural benefits.
“So we’ve now got two agents – sprifermin for cartilage and MIV-711 for bone – showing that it’s possible to get some structural change, but no symptomatic benefit within the period of those trials,” the rheumatologist noted.
Wnt pathway inhibition
Samumed has launched a phase 3 clinical trials program, known as STRIDES, for lorecivivint, the company’s investigational small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway. In phase 2 studies, including one led by Dr. Conaghan, intra-articular injection of lorecivivint, previously known as SMO4690, improved pain and physical function as well as medial joint space width. The drug’s potential effects on multiple tissues offers the promise of providing both symptomatic improvement and modification of the course of structural disease progression.
Inflammation
Lutikizumab, an anti–interleukin-1 alpha/beta immunoglobulin, proved to be a disappointment in a recent phase 2, placebo-controlled trial carried out in 350 patients with knee OA and synovitis. The IL-1 inhibitor had no benefit on synovitis, joint space narrowing, or cartilage thickness. Nor was it significantly better than placebo for pain reduction (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Jul;71[7]:1056-69).
Anti–tumor necrosis factor agents haven’t exactly set the OA world on fire, either.
“In rheumatoid arthritis we know they’re stupendously effective, but the data from a number of trials in OA show they’re not so effective on symptoms and signs,” Dr. Conaghan said.
Colchicine and hydroxychloroquine are other anti-inflammatory agents which, while in theory might be helpful, have in actuality shown no benefit for OA symptoms in controlled clinical trials and are now considered dead ends.
On the other hand, the sustained delivery of intra-articular corticosteroids through the use of microsphere technology is advancing smartly through the developmental pipeline. Dr. Conaghan was first author of a multicenter, double-blind, phase 3 trial of FX006, a sustained-release formulation of triamcinolone acetonide, which showed that a single intra-articular injection provided at least 3 months of pain relief in knee OA patients, along with reduced systemic drug exposure, compared with standard intra-articular corticosteroids (J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018 Apr 18;100[8]:666-77).
FX006 also performed well in another phase 3 trial, this one featuring repeated dosing on a flexible schedule based upon patient response (Rheumatol Ther. 2019 Mar;6[1]:109-24).
Reassuringly, this slow-release corticosteroid doesn’t appear to worsen glycemic control in knee OA patients with type 2 diabetes (Rheumatology [Oxford]. 2018 Dec 1;57[12]:2235-41).
“This is the start of a revolution in nanotechnology and the ability to slowly deliver a variety of drugs within the joint,” Dr. Conaghan predicted.
Although he was tasked at OARSI 2019 with providing an overview of the OA pharmacologic pipeline, he stressed that in his clinical practice, as opposed to his work as a clinical trialist, he functions more like a physical therapist.
“I actually spend my whole time in the OA clinic being a physical therapist and trying to get people strong, because that does work and it has no side effects. It’s just that nobody does it. We have a real adherence problem,” he said. “My favorite thought is this: keep people strong. If a patient can’t get out of a chair easily or can’t undo a jar, then they’ve got a problem.”
Dr. Conaghan reported receiving research funding from and serving as a consultant to many of the companies developing novel drug treatments for OA.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM OARSI 2019
How common is accelerated knee OA?
TORONTO – Accelerated knee osteoarthritis – a particularly noxious form of the joint disease – occurred in more than one in seven women who developed knee osteoarthritis in the prospective, long-term Chingford Cohort Study, Jeffrey B. Driban, PhD, reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
This finding from a unique prospective study of 1,003 middle-aged U.K. women who were followed for the development of knee osteoarthritis (OA) for 15 years is important because the participants represented a typical community-based population sample. And yet the Chingford results are consistent with and confirmatory of those found earlier in the Osteoarthritis Initiative, a U.S. cohort study of nearly 4,800 individuals, even though the Osteoarthritis Initiative featured a population enriched with established risk factors for knee OA, Dr. Driban explained at the meeting, sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
In Chingford, accelerated knee OA accounted for 15% of all incident cases of knee OA during follow-up, and for 17% of all newly affected knees, whereas 20% of incident knee OA in the Osteoarthritis Initiative was accelerated knee OA, noted Dr. Driban of Tufts University, Boston.
Accelerated knee OA is defined by rapidly progressive structural damage. Affected individuals streak from no radiographic evidence of knee OA to advanced-stage disease marked by a Kellgren-Lawrence score of 3 or more within 4 years, whereas the typical form of knee OA follows a more gradual course. Also, accelerated knee OA features greater pain and disability.
In the Chingford study, the cumulative incidence of accelerated knee OA was 3.9%, while typical knee OA occurred in 21.7% of women. During years 6-15 of follow-up, 21% of women with accelerated knee OA underwent total knee replacement, compared with 2% of those with typical knee OA and 0.9% of women without knee OA.
Dr. Driban reported having no financial conflicts regarding his analysis of the Chingford Cohort Study and the Osteoarthritis Initiative, supported by Arthritis Research UK and the National Institutes of Health, respectively.
SOURCE: Driban JB et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Apr;27[suppl 1]:S250-S251, Abstract 352.
TORONTO – Accelerated knee osteoarthritis – a particularly noxious form of the joint disease – occurred in more than one in seven women who developed knee osteoarthritis in the prospective, long-term Chingford Cohort Study, Jeffrey B. Driban, PhD, reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
This finding from a unique prospective study of 1,003 middle-aged U.K. women who were followed for the development of knee osteoarthritis (OA) for 15 years is important because the participants represented a typical community-based population sample. And yet the Chingford results are consistent with and confirmatory of those found earlier in the Osteoarthritis Initiative, a U.S. cohort study of nearly 4,800 individuals, even though the Osteoarthritis Initiative featured a population enriched with established risk factors for knee OA, Dr. Driban explained at the meeting, sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
In Chingford, accelerated knee OA accounted for 15% of all incident cases of knee OA during follow-up, and for 17% of all newly affected knees, whereas 20% of incident knee OA in the Osteoarthritis Initiative was accelerated knee OA, noted Dr. Driban of Tufts University, Boston.
Accelerated knee OA is defined by rapidly progressive structural damage. Affected individuals streak from no radiographic evidence of knee OA to advanced-stage disease marked by a Kellgren-Lawrence score of 3 or more within 4 years, whereas the typical form of knee OA follows a more gradual course. Also, accelerated knee OA features greater pain and disability.
In the Chingford study, the cumulative incidence of accelerated knee OA was 3.9%, while typical knee OA occurred in 21.7% of women. During years 6-15 of follow-up, 21% of women with accelerated knee OA underwent total knee replacement, compared with 2% of those with typical knee OA and 0.9% of women without knee OA.
Dr. Driban reported having no financial conflicts regarding his analysis of the Chingford Cohort Study and the Osteoarthritis Initiative, supported by Arthritis Research UK and the National Institutes of Health, respectively.
SOURCE: Driban JB et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Apr;27[suppl 1]:S250-S251, Abstract 352.
TORONTO – Accelerated knee osteoarthritis – a particularly noxious form of the joint disease – occurred in more than one in seven women who developed knee osteoarthritis in the prospective, long-term Chingford Cohort Study, Jeffrey B. Driban, PhD, reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
This finding from a unique prospective study of 1,003 middle-aged U.K. women who were followed for the development of knee osteoarthritis (OA) for 15 years is important because the participants represented a typical community-based population sample. And yet the Chingford results are consistent with and confirmatory of those found earlier in the Osteoarthritis Initiative, a U.S. cohort study of nearly 4,800 individuals, even though the Osteoarthritis Initiative featured a population enriched with established risk factors for knee OA, Dr. Driban explained at the meeting, sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
In Chingford, accelerated knee OA accounted for 15% of all incident cases of knee OA during follow-up, and for 17% of all newly affected knees, whereas 20% of incident knee OA in the Osteoarthritis Initiative was accelerated knee OA, noted Dr. Driban of Tufts University, Boston.
Accelerated knee OA is defined by rapidly progressive structural damage. Affected individuals streak from no radiographic evidence of knee OA to advanced-stage disease marked by a Kellgren-Lawrence score of 3 or more within 4 years, whereas the typical form of knee OA follows a more gradual course. Also, accelerated knee OA features greater pain and disability.
In the Chingford study, the cumulative incidence of accelerated knee OA was 3.9%, while typical knee OA occurred in 21.7% of women. During years 6-15 of follow-up, 21% of women with accelerated knee OA underwent total knee replacement, compared with 2% of those with typical knee OA and 0.9% of women without knee OA.
Dr. Driban reported having no financial conflicts regarding his analysis of the Chingford Cohort Study and the Osteoarthritis Initiative, supported by Arthritis Research UK and the National Institutes of Health, respectively.
SOURCE: Driban JB et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Apr;27[suppl 1]:S250-S251, Abstract 352.
REPORTING FROM OARSI 2019
Foot OA: Forgotten no longer
TORONTO – Foot osteoarthritis has been a relatively neglected topic by researchers – but that’s finally changing, Michelle Marshall, PhD, observed at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
She was a coinvestigator in the groundbreaking Clinical Assessment of the Foot (CASF), a large prospective study that has brought new insights into the prevalence of foot osteoarthritis (OA), its risk factors, the sizable disease burden, and foot OA’s diverse phenotypes. She shared study highlights at the meeting, which was sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Elsewhere at OARSI 2019, Lucy S. Gates, PhD, presented the eagerly awaited results of the Chingford 1000 Women Study of the progression pattern of symptomatic radiographic OA of the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ). With 19 years of follow-up, Chingford is far and away the largest and longest longitudinal study of first MTP joint OA.
The prospective, population-based, observational cohort CASF study was carried out by Dr. Marshall and her coinvestigators at Keele University in Staffordshire, England. They surveyed Staffordshire residents aged 50 and older regarding whether they had experienced foot pain within the last 12 months. Those who answered affirmatively were invited to come in for a more detailed assessment and get weight-bearing x-rays of both feet. Among the 557 symptomatic participants with foot x-rays, the prevalence of radiographic OA of the foot was 16.7%, or roughly one in six – underscoring that it’s a common condition. The first MTP joint was the most commonly affected site, with a prevalence of 7.8%, followed by the second cuneometatarsal joint (CMJ) at 6.8%, the talonavicular joint (TNJ) at 5.2%, the navicular first cuneiform joint (NCJ) at 5.2%, and the first CMJ at 3.9%. Three-quarters of those who had symptomatic radiographic foot OA reported disabling symptoms, an established risk factor for falls (Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Jan;74[1]:156-63).
With an eye toward identification of potential distinct phenotypes of foot OA, the CASF investigators conducted a separate analysis of those study participants with symptomatic radiographic midfoot OA – that is, OA of the TNJ, NCJ, and/or first or second CMJs, but not the first MTP joint. The prevalence in the Staffordshire population over age 50 with a history of foot pain was 12%. Independent risk factors for midfoot OA included obesity, with an adjusted odds ratio of 2.0; pain in other weight-bearing lower limb joints, with an adjusted odds ratio of 8.5; diabetes, odds ratio of 1.9; and previous foot injury, with an associated 1.6-fold increased risk. Midfoot OA was most prevalent in women older than 75 years; however, contrary to the conventional wisdom, a history of frequently wearing high-heeled shoes posed no increased risk.
The burden associated with midfoot OA was reflected in affected individuals’ frequent use of health care resources: During the past year, 46% of them had consulted their primary care physicians about their foot pain, 48% had been to a podiatrist, and 19% had seen a physical therapist (Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Jul 13;17:178. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0693-3).
In a separate analysis, the investigators compiled additional evidence from CASF pointing to the existence of two phenotypes of foot OA: isolated first MTP OA and polyarticular foot OA, with distinct risk factors and symptom profiles (Arthritis Care Res [Hoboken]. 2016 Feb;68[2]:217-27).
“We found that OA affected both feet significantly more than was expected by chance, and we identified strong symmetrical patterns. This mirrors findings in hand OA and implies involvement of systemic components within a foot,” Dr. Marshall said.
The course of foot OA
During 18 months of prospective follow-up in CASF, subjects with isolated first MTP joint or polyarticular foot OA showed no clinically meaningful change in symptoms (Arthritis Care Res [Hoboken]. 2018 Jul;70[7]:1107-12).
But that finding may have been a function of the relatively brief follow-up, as the Chingford 1000 Women Study, with its 19 years of prospective follow-up, told a different story. Dr. Gates, of the University of Southampton (England), reported that among the 193 patients with foot x-rays at both baseline and follow-up, by which point they averaged nearly 76 years in age, 33.2% had OA of the first MTP joint of either foot at baseline as defined by at least a grade 2 score on the LaTrobe foot atlas, and 13% had prevalent involvement of both feet. During 19 years of follow-up of the women from Chingford, an area in northeast London, the incidence of new-onset radiographic first MTP joint OA was 7% in the left foot and 17% in the right. Meanwhile, progression to grade 3 radiographic OA occurred in the left foot of 28% of those with grade 2 disease at baseline and in 35% of those with baseline first MTP joint OA of the right foot. Twenty-eight percent of patients with unilateral first MTP joint OA at baseline progressed to bilateral involvement within 19 years.
Dr. Gates reported having no financial conflicts regarding the Chingford study, funded primarily by Arthritis Research UK, which merged with Arthritis Care in 2018 to form Versus Arthritis.
Similarly, Dr. Marshall reported no financial conflicts regarding CASF, also funded by Arthritis Research UK.
SOURCES: Marshall M. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Apr;27[suppl 1]:S16, Abstract I-8 and Magnusson K et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Apr;27[suppl 1]:S260-S261, Abstract 367.
TORONTO – Foot osteoarthritis has been a relatively neglected topic by researchers – but that’s finally changing, Michelle Marshall, PhD, observed at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
She was a coinvestigator in the groundbreaking Clinical Assessment of the Foot (CASF), a large prospective study that has brought new insights into the prevalence of foot osteoarthritis (OA), its risk factors, the sizable disease burden, and foot OA’s diverse phenotypes. She shared study highlights at the meeting, which was sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Elsewhere at OARSI 2019, Lucy S. Gates, PhD, presented the eagerly awaited results of the Chingford 1000 Women Study of the progression pattern of symptomatic radiographic OA of the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ). With 19 years of follow-up, Chingford is far and away the largest and longest longitudinal study of first MTP joint OA.
The prospective, population-based, observational cohort CASF study was carried out by Dr. Marshall and her coinvestigators at Keele University in Staffordshire, England. They surveyed Staffordshire residents aged 50 and older regarding whether they had experienced foot pain within the last 12 months. Those who answered affirmatively were invited to come in for a more detailed assessment and get weight-bearing x-rays of both feet. Among the 557 symptomatic participants with foot x-rays, the prevalence of radiographic OA of the foot was 16.7%, or roughly one in six – underscoring that it’s a common condition. The first MTP joint was the most commonly affected site, with a prevalence of 7.8%, followed by the second cuneometatarsal joint (CMJ) at 6.8%, the talonavicular joint (TNJ) at 5.2%, the navicular first cuneiform joint (NCJ) at 5.2%, and the first CMJ at 3.9%. Three-quarters of those who had symptomatic radiographic foot OA reported disabling symptoms, an established risk factor for falls (Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Jan;74[1]:156-63).
With an eye toward identification of potential distinct phenotypes of foot OA, the CASF investigators conducted a separate analysis of those study participants with symptomatic radiographic midfoot OA – that is, OA of the TNJ, NCJ, and/or first or second CMJs, but not the first MTP joint. The prevalence in the Staffordshire population over age 50 with a history of foot pain was 12%. Independent risk factors for midfoot OA included obesity, with an adjusted odds ratio of 2.0; pain in other weight-bearing lower limb joints, with an adjusted odds ratio of 8.5; diabetes, odds ratio of 1.9; and previous foot injury, with an associated 1.6-fold increased risk. Midfoot OA was most prevalent in women older than 75 years; however, contrary to the conventional wisdom, a history of frequently wearing high-heeled shoes posed no increased risk.
The burden associated with midfoot OA was reflected in affected individuals’ frequent use of health care resources: During the past year, 46% of them had consulted their primary care physicians about their foot pain, 48% had been to a podiatrist, and 19% had seen a physical therapist (Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Jul 13;17:178. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0693-3).
In a separate analysis, the investigators compiled additional evidence from CASF pointing to the existence of two phenotypes of foot OA: isolated first MTP OA and polyarticular foot OA, with distinct risk factors and symptom profiles (Arthritis Care Res [Hoboken]. 2016 Feb;68[2]:217-27).
“We found that OA affected both feet significantly more than was expected by chance, and we identified strong symmetrical patterns. This mirrors findings in hand OA and implies involvement of systemic components within a foot,” Dr. Marshall said.
The course of foot OA
During 18 months of prospective follow-up in CASF, subjects with isolated first MTP joint or polyarticular foot OA showed no clinically meaningful change in symptoms (Arthritis Care Res [Hoboken]. 2018 Jul;70[7]:1107-12).
But that finding may have been a function of the relatively brief follow-up, as the Chingford 1000 Women Study, with its 19 years of prospective follow-up, told a different story. Dr. Gates, of the University of Southampton (England), reported that among the 193 patients with foot x-rays at both baseline and follow-up, by which point they averaged nearly 76 years in age, 33.2% had OA of the first MTP joint of either foot at baseline as defined by at least a grade 2 score on the LaTrobe foot atlas, and 13% had prevalent involvement of both feet. During 19 years of follow-up of the women from Chingford, an area in northeast London, the incidence of new-onset radiographic first MTP joint OA was 7% in the left foot and 17% in the right. Meanwhile, progression to grade 3 radiographic OA occurred in the left foot of 28% of those with grade 2 disease at baseline and in 35% of those with baseline first MTP joint OA of the right foot. Twenty-eight percent of patients with unilateral first MTP joint OA at baseline progressed to bilateral involvement within 19 years.
Dr. Gates reported having no financial conflicts regarding the Chingford study, funded primarily by Arthritis Research UK, which merged with Arthritis Care in 2018 to form Versus Arthritis.
Similarly, Dr. Marshall reported no financial conflicts regarding CASF, also funded by Arthritis Research UK.
SOURCES: Marshall M. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Apr;27[suppl 1]:S16, Abstract I-8 and Magnusson K et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Apr;27[suppl 1]:S260-S261, Abstract 367.
TORONTO – Foot osteoarthritis has been a relatively neglected topic by researchers – but that’s finally changing, Michelle Marshall, PhD, observed at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
She was a coinvestigator in the groundbreaking Clinical Assessment of the Foot (CASF), a large prospective study that has brought new insights into the prevalence of foot osteoarthritis (OA), its risk factors, the sizable disease burden, and foot OA’s diverse phenotypes. She shared study highlights at the meeting, which was sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Elsewhere at OARSI 2019, Lucy S. Gates, PhD, presented the eagerly awaited results of the Chingford 1000 Women Study of the progression pattern of symptomatic radiographic OA of the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ). With 19 years of follow-up, Chingford is far and away the largest and longest longitudinal study of first MTP joint OA.
The prospective, population-based, observational cohort CASF study was carried out by Dr. Marshall and her coinvestigators at Keele University in Staffordshire, England. They surveyed Staffordshire residents aged 50 and older regarding whether they had experienced foot pain within the last 12 months. Those who answered affirmatively were invited to come in for a more detailed assessment and get weight-bearing x-rays of both feet. Among the 557 symptomatic participants with foot x-rays, the prevalence of radiographic OA of the foot was 16.7%, or roughly one in six – underscoring that it’s a common condition. The first MTP joint was the most commonly affected site, with a prevalence of 7.8%, followed by the second cuneometatarsal joint (CMJ) at 6.8%, the talonavicular joint (TNJ) at 5.2%, the navicular first cuneiform joint (NCJ) at 5.2%, and the first CMJ at 3.9%. Three-quarters of those who had symptomatic radiographic foot OA reported disabling symptoms, an established risk factor for falls (Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Jan;74[1]:156-63).
With an eye toward identification of potential distinct phenotypes of foot OA, the CASF investigators conducted a separate analysis of those study participants with symptomatic radiographic midfoot OA – that is, OA of the TNJ, NCJ, and/or first or second CMJs, but not the first MTP joint. The prevalence in the Staffordshire population over age 50 with a history of foot pain was 12%. Independent risk factors for midfoot OA included obesity, with an adjusted odds ratio of 2.0; pain in other weight-bearing lower limb joints, with an adjusted odds ratio of 8.5; diabetes, odds ratio of 1.9; and previous foot injury, with an associated 1.6-fold increased risk. Midfoot OA was most prevalent in women older than 75 years; however, contrary to the conventional wisdom, a history of frequently wearing high-heeled shoes posed no increased risk.
The burden associated with midfoot OA was reflected in affected individuals’ frequent use of health care resources: During the past year, 46% of them had consulted their primary care physicians about their foot pain, 48% had been to a podiatrist, and 19% had seen a physical therapist (Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Jul 13;17:178. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0693-3).
In a separate analysis, the investigators compiled additional evidence from CASF pointing to the existence of two phenotypes of foot OA: isolated first MTP OA and polyarticular foot OA, with distinct risk factors and symptom profiles (Arthritis Care Res [Hoboken]. 2016 Feb;68[2]:217-27).
“We found that OA affected both feet significantly more than was expected by chance, and we identified strong symmetrical patterns. This mirrors findings in hand OA and implies involvement of systemic components within a foot,” Dr. Marshall said.
The course of foot OA
During 18 months of prospective follow-up in CASF, subjects with isolated first MTP joint or polyarticular foot OA showed no clinically meaningful change in symptoms (Arthritis Care Res [Hoboken]. 2018 Jul;70[7]:1107-12).
But that finding may have been a function of the relatively brief follow-up, as the Chingford 1000 Women Study, with its 19 years of prospective follow-up, told a different story. Dr. Gates, of the University of Southampton (England), reported that among the 193 patients with foot x-rays at both baseline and follow-up, by which point they averaged nearly 76 years in age, 33.2% had OA of the first MTP joint of either foot at baseline as defined by at least a grade 2 score on the LaTrobe foot atlas, and 13% had prevalent involvement of both feet. During 19 years of follow-up of the women from Chingford, an area in northeast London, the incidence of new-onset radiographic first MTP joint OA was 7% in the left foot and 17% in the right. Meanwhile, progression to grade 3 radiographic OA occurred in the left foot of 28% of those with grade 2 disease at baseline and in 35% of those with baseline first MTP joint OA of the right foot. Twenty-eight percent of patients with unilateral first MTP joint OA at baseline progressed to bilateral involvement within 19 years.
Dr. Gates reported having no financial conflicts regarding the Chingford study, funded primarily by Arthritis Research UK, which merged with Arthritis Care in 2018 to form Versus Arthritis.
Similarly, Dr. Marshall reported no financial conflicts regarding CASF, also funded by Arthritis Research UK.
SOURCES: Marshall M. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Apr;27[suppl 1]:S16, Abstract I-8 and Magnusson K et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Apr;27[suppl 1]:S260-S261, Abstract 367.
REPORTING FROM OARSI 2019
Swedish OA self-management program earns high marks
TORONTO – A in an observational registry study of 47,035 participants, Therese S. Jönsson reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
“The BOA [Better management of patients with Osteoarthritis] program is feasible and demonstrates positive results in a large clinical context. Our results indicate that offering this intervention as the first-line treatment for patients with hip and knee osteoarthritis may reduce the burden of disease,” she said at the meeting, sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Indeed, the results of the Swedish BOA program for nonsurgical treatment of OA played an influential role in the new draft of OARSI guidelines for management of knee osteoarthritis. The program could serve as a template for implementation of a similar approach in other health care settings. The BOA program has been rolled out to more than 700 Swedish primary care practice sites, according to Ms. Jönsson, a PhD student at Lund (Sweden) University.
The program was created to meet a defined national goal that, as early as possible in the course of the disease, every Swedish patient with knee or hip OA should receive education about their disease and the importance of exercise as a means of improving their quality of life. The impetus for BOA was a widespread concern that, in Sweden and elsewhere, far too many OA patients were being referred for joint surgery without ever having tried the evidence-based core nonsurgical treatments.
The BOA intervention
Following patient referral by a primary care physician, the Swedish BOA program starts off with individual assessment and biomechanical testing by a physical therapist. This is followed by two small-group education sessions of about 90 minutes led by a physical therapist or occupational therapist. Session one includes information about the pathology of OA, risk factors, symptoms, and the available treatments. Session two focuses on coping skills, self-management strategies to reduce pain and symptoms, the central role of exercise as a core treatment in OA, and ways to incorporate physical activity into daily living.
Then comes a decision point. Having listened to a motivational message extolling the benefits of exercise as a means of empowering self-management of their chronic disease, participants next have three choices: They can attend supervised group exercise classes twice weekly for 6 weeks to kick-start a more physically active lifestyle, they can start an individually adapted home exercise program, or they can decline exercise.
Giving patients a choice in this matter is a strategy rooted in the psychological concept of motivational stages of change, which recognizes that some patients with a chronic illness whose course is modifiable through lifestyle change are initially in a precontemplation stage of change. And pushing them hard at that point is counterproductive. The home exercise option, which permits patients to take a low-and-slow approach to exercise, is based upon the BOA program developers’ stated philosophy that 5 minutes of exercise daily, performed as part of everyday life, has a bigger impact upon function than does a 30-minute exercise program that’s abandoned after a few weeks. The goal of the BOA program is for patients to eventually build up to at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
The results
Roughly 15% of patients enrolled in the registry declined the exercise option. Ms. Jönsson’s analysis focused on those who opted to participate in an exercise program, 40% of whom selected the home exercise option. This analysis included 30,682 patients with knee OA and 16,363 with hip OA. They returned to the physical therapist for a face-to-face reassessment after 3 months, and they completed a mailed outcome-oriented questionnaire at 12 months.
The BOA intervention was more effective in reducing pain in the knee OA group than in those with hip OA. A statistically significant reduction in self-assessed pain scores on a 0-10 scale was seen in both the knee and hip OA groups at 3 and 12 months; however, only the knee OA patients achieved a clinically important decrease in pain, defined as at least a 15% drop in pain scores. Their pain scores improved from 5.24 at baseline to 4.07 at 3 months and 4.23 at 12 months. In the hip OA patients, pain scores went from 5.39 at baseline to 4.56 at 3 months and 4.7 at 12 months.
However, at 3 and 12 months, significantly fewer patients in both the hip and knee OA groups reported experiencing pain more than once per week, compared with baseline. They also took fewer pain-killing medications, reported less avoidance behavior involving fear of movement, were less willing to undergo joint surgery, and scored significantly higher on the five-level EQ-5D quality-of-life measure than at baseline. Moreover, fewer patients were on sick leave at the 12-month follow-up than at baseline, an outcome that wasn’t assessed at 3 months.
Adherence to the group exercise classes was “quite low,” according to Ms. Jönsson, and poor adherence was reflected in smaller reductions in pain scores. Only 30% of patients who elected the supervised group exercise option attended 10 of the 12 sessions, she noted.
Ms. Jönsson reported having no financial conflicts regarding her study. The BOA program is funded by the Swedish government.
SOURCE: Jönsson TS et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Apr;27(suppl 1):S497, Abstract 717.
TORONTO – A in an observational registry study of 47,035 participants, Therese S. Jönsson reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
“The BOA [Better management of patients with Osteoarthritis] program is feasible and demonstrates positive results in a large clinical context. Our results indicate that offering this intervention as the first-line treatment for patients with hip and knee osteoarthritis may reduce the burden of disease,” she said at the meeting, sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Indeed, the results of the Swedish BOA program for nonsurgical treatment of OA played an influential role in the new draft of OARSI guidelines for management of knee osteoarthritis. The program could serve as a template for implementation of a similar approach in other health care settings. The BOA program has been rolled out to more than 700 Swedish primary care practice sites, according to Ms. Jönsson, a PhD student at Lund (Sweden) University.
The program was created to meet a defined national goal that, as early as possible in the course of the disease, every Swedish patient with knee or hip OA should receive education about their disease and the importance of exercise as a means of improving their quality of life. The impetus for BOA was a widespread concern that, in Sweden and elsewhere, far too many OA patients were being referred for joint surgery without ever having tried the evidence-based core nonsurgical treatments.
The BOA intervention
Following patient referral by a primary care physician, the Swedish BOA program starts off with individual assessment and biomechanical testing by a physical therapist. This is followed by two small-group education sessions of about 90 minutes led by a physical therapist or occupational therapist. Session one includes information about the pathology of OA, risk factors, symptoms, and the available treatments. Session two focuses on coping skills, self-management strategies to reduce pain and symptoms, the central role of exercise as a core treatment in OA, and ways to incorporate physical activity into daily living.
Then comes a decision point. Having listened to a motivational message extolling the benefits of exercise as a means of empowering self-management of their chronic disease, participants next have three choices: They can attend supervised group exercise classes twice weekly for 6 weeks to kick-start a more physically active lifestyle, they can start an individually adapted home exercise program, or they can decline exercise.
Giving patients a choice in this matter is a strategy rooted in the psychological concept of motivational stages of change, which recognizes that some patients with a chronic illness whose course is modifiable through lifestyle change are initially in a precontemplation stage of change. And pushing them hard at that point is counterproductive. The home exercise option, which permits patients to take a low-and-slow approach to exercise, is based upon the BOA program developers’ stated philosophy that 5 minutes of exercise daily, performed as part of everyday life, has a bigger impact upon function than does a 30-minute exercise program that’s abandoned after a few weeks. The goal of the BOA program is for patients to eventually build up to at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
The results
Roughly 15% of patients enrolled in the registry declined the exercise option. Ms. Jönsson’s analysis focused on those who opted to participate in an exercise program, 40% of whom selected the home exercise option. This analysis included 30,682 patients with knee OA and 16,363 with hip OA. They returned to the physical therapist for a face-to-face reassessment after 3 months, and they completed a mailed outcome-oriented questionnaire at 12 months.
The BOA intervention was more effective in reducing pain in the knee OA group than in those with hip OA. A statistically significant reduction in self-assessed pain scores on a 0-10 scale was seen in both the knee and hip OA groups at 3 and 12 months; however, only the knee OA patients achieved a clinically important decrease in pain, defined as at least a 15% drop in pain scores. Their pain scores improved from 5.24 at baseline to 4.07 at 3 months and 4.23 at 12 months. In the hip OA patients, pain scores went from 5.39 at baseline to 4.56 at 3 months and 4.7 at 12 months.
However, at 3 and 12 months, significantly fewer patients in both the hip and knee OA groups reported experiencing pain more than once per week, compared with baseline. They also took fewer pain-killing medications, reported less avoidance behavior involving fear of movement, were less willing to undergo joint surgery, and scored significantly higher on the five-level EQ-5D quality-of-life measure than at baseline. Moreover, fewer patients were on sick leave at the 12-month follow-up than at baseline, an outcome that wasn’t assessed at 3 months.
Adherence to the group exercise classes was “quite low,” according to Ms. Jönsson, and poor adherence was reflected in smaller reductions in pain scores. Only 30% of patients who elected the supervised group exercise option attended 10 of the 12 sessions, she noted.
Ms. Jönsson reported having no financial conflicts regarding her study. The BOA program is funded by the Swedish government.
SOURCE: Jönsson TS et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Apr;27(suppl 1):S497, Abstract 717.
TORONTO – A in an observational registry study of 47,035 participants, Therese S. Jönsson reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
“The BOA [Better management of patients with Osteoarthritis] program is feasible and demonstrates positive results in a large clinical context. Our results indicate that offering this intervention as the first-line treatment for patients with hip and knee osteoarthritis may reduce the burden of disease,” she said at the meeting, sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Indeed, the results of the Swedish BOA program for nonsurgical treatment of OA played an influential role in the new draft of OARSI guidelines for management of knee osteoarthritis. The program could serve as a template for implementation of a similar approach in other health care settings. The BOA program has been rolled out to more than 700 Swedish primary care practice sites, according to Ms. Jönsson, a PhD student at Lund (Sweden) University.
The program was created to meet a defined national goal that, as early as possible in the course of the disease, every Swedish patient with knee or hip OA should receive education about their disease and the importance of exercise as a means of improving their quality of life. The impetus for BOA was a widespread concern that, in Sweden and elsewhere, far too many OA patients were being referred for joint surgery without ever having tried the evidence-based core nonsurgical treatments.
The BOA intervention
Following patient referral by a primary care physician, the Swedish BOA program starts off with individual assessment and biomechanical testing by a physical therapist. This is followed by two small-group education sessions of about 90 minutes led by a physical therapist or occupational therapist. Session one includes information about the pathology of OA, risk factors, symptoms, and the available treatments. Session two focuses on coping skills, self-management strategies to reduce pain and symptoms, the central role of exercise as a core treatment in OA, and ways to incorporate physical activity into daily living.
Then comes a decision point. Having listened to a motivational message extolling the benefits of exercise as a means of empowering self-management of their chronic disease, participants next have three choices: They can attend supervised group exercise classes twice weekly for 6 weeks to kick-start a more physically active lifestyle, they can start an individually adapted home exercise program, or they can decline exercise.
Giving patients a choice in this matter is a strategy rooted in the psychological concept of motivational stages of change, which recognizes that some patients with a chronic illness whose course is modifiable through lifestyle change are initially in a precontemplation stage of change. And pushing them hard at that point is counterproductive. The home exercise option, which permits patients to take a low-and-slow approach to exercise, is based upon the BOA program developers’ stated philosophy that 5 minutes of exercise daily, performed as part of everyday life, has a bigger impact upon function than does a 30-minute exercise program that’s abandoned after a few weeks. The goal of the BOA program is for patients to eventually build up to at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
The results
Roughly 15% of patients enrolled in the registry declined the exercise option. Ms. Jönsson’s analysis focused on those who opted to participate in an exercise program, 40% of whom selected the home exercise option. This analysis included 30,682 patients with knee OA and 16,363 with hip OA. They returned to the physical therapist for a face-to-face reassessment after 3 months, and they completed a mailed outcome-oriented questionnaire at 12 months.
The BOA intervention was more effective in reducing pain in the knee OA group than in those with hip OA. A statistically significant reduction in self-assessed pain scores on a 0-10 scale was seen in both the knee and hip OA groups at 3 and 12 months; however, only the knee OA patients achieved a clinically important decrease in pain, defined as at least a 15% drop in pain scores. Their pain scores improved from 5.24 at baseline to 4.07 at 3 months and 4.23 at 12 months. In the hip OA patients, pain scores went from 5.39 at baseline to 4.56 at 3 months and 4.7 at 12 months.
However, at 3 and 12 months, significantly fewer patients in both the hip and knee OA groups reported experiencing pain more than once per week, compared with baseline. They also took fewer pain-killing medications, reported less avoidance behavior involving fear of movement, were less willing to undergo joint surgery, and scored significantly higher on the five-level EQ-5D quality-of-life measure than at baseline. Moreover, fewer patients were on sick leave at the 12-month follow-up than at baseline, an outcome that wasn’t assessed at 3 months.
Adherence to the group exercise classes was “quite low,” according to Ms. Jönsson, and poor adherence was reflected in smaller reductions in pain scores. Only 30% of patients who elected the supervised group exercise option attended 10 of the 12 sessions, she noted.
Ms. Jönsson reported having no financial conflicts regarding her study. The BOA program is funded by the Swedish government.
SOURCE: Jönsson TS et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Apr;27(suppl 1):S497, Abstract 717.
REPORTING FROM OARSI 2019
OA is underrepresented in the medical literature
TORONTO – Osteoarthritis research doesn’t get nearly the respect it deserves in the medical literature, Elizabeth M. Badley, PhD, asserted at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
“Osteoarthritis is by far the most common type of arthritis. There are easily 10 times more people who have osteoarthritis than any other joint disease, but when you look at the literature, the situation is kind of reversed. Osteoarthritis is brushed off by society to a degree,” she said at the meeting, sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Dr. Bradley and colleagues performed a search of MEDLINE for 2007-2016, which turned up a total of 1,625 publications in 2016 on osteoarthritis, excluding those with an orthopedic surgery focus, compared with 10,904 results regarding the broader topic of joint diseases and 28,932 on musculoskeletal diseases.
The bottom line: “Progress is slow, and at this rate osteoarthritis will not be receiving the attention it deserves in our lifetime,” said Dr. Badley, of the department of epidemiology at the University of Toronto and a senior scientist at the Krembil Research Institute, also in Toronto.
The number of publications per year devoted to OA rose by a robust 88% during 2007-2016, while the number on OA not focused on orthopedic procedures grew by 65%. Both of these increases were greater than those for publications on musculoskeletal diseases and joint diseases overall, which were 41% and 51%, respectively. But the absolute number of OA publications was dwarfed by the numbers of those in the other search categories. For example, the number of publications on OA without an orthopedic surgery thrust was 985 in 2007, compared with 7,204 on joint diseases overall.
Among the striking findings of the investigators’ study of the medical literature was the disconnect between the amount of attention devoted to some of the joint-specific manifestations of OA and the actual prevalence of these conditions in the population. For example, the prevalence of hand OA in people living with OA was 52% according to the 2009 Survey on Living with Chronic Diseases in Canada, conducted by Statistics Canada, yet only 6.5% of the publications on OA in 2016 were devoted to hand/thumb OA. Similarly, the prevalence of spine OA was 52% among Canadians with OA, but only 4.3% of OA publications in 2016 focused on that topic. And while the number of publications devoted to elbow OA soared by a seemingly impressive 233% during the study period, the actual numbers were 3 publications in 2007 and 10 in 2016.
“Also, the average number of affected joints in people with osteoarthritis is four. Yet very, very few papers are about multijoint osteoarthritis. And when they do talk about multijoint osteoarthritis, they’re still only talking about hand/hip/knee. So we’re missing the bigger picture of osteoarthritis as a multijoint disease. We’re missing the spine, largely, as a part of osteoarthritis, and we’re missing the peripheral joints,” she said.
Dr. Badley reported having no financial conflicts regarding her study, conducted free of commercial support.
SOURCE: Badley EM et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Apr;27(Suppl 1):S278, Abstract 393.
TORONTO – Osteoarthritis research doesn’t get nearly the respect it deserves in the medical literature, Elizabeth M. Badley, PhD, asserted at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
“Osteoarthritis is by far the most common type of arthritis. There are easily 10 times more people who have osteoarthritis than any other joint disease, but when you look at the literature, the situation is kind of reversed. Osteoarthritis is brushed off by society to a degree,” she said at the meeting, sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Dr. Bradley and colleagues performed a search of MEDLINE for 2007-2016, which turned up a total of 1,625 publications in 2016 on osteoarthritis, excluding those with an orthopedic surgery focus, compared with 10,904 results regarding the broader topic of joint diseases and 28,932 on musculoskeletal diseases.
The bottom line: “Progress is slow, and at this rate osteoarthritis will not be receiving the attention it deserves in our lifetime,” said Dr. Badley, of the department of epidemiology at the University of Toronto and a senior scientist at the Krembil Research Institute, also in Toronto.
The number of publications per year devoted to OA rose by a robust 88% during 2007-2016, while the number on OA not focused on orthopedic procedures grew by 65%. Both of these increases were greater than those for publications on musculoskeletal diseases and joint diseases overall, which were 41% and 51%, respectively. But the absolute number of OA publications was dwarfed by the numbers of those in the other search categories. For example, the number of publications on OA without an orthopedic surgery thrust was 985 in 2007, compared with 7,204 on joint diseases overall.
Among the striking findings of the investigators’ study of the medical literature was the disconnect between the amount of attention devoted to some of the joint-specific manifestations of OA and the actual prevalence of these conditions in the population. For example, the prevalence of hand OA in people living with OA was 52% according to the 2009 Survey on Living with Chronic Diseases in Canada, conducted by Statistics Canada, yet only 6.5% of the publications on OA in 2016 were devoted to hand/thumb OA. Similarly, the prevalence of spine OA was 52% among Canadians with OA, but only 4.3% of OA publications in 2016 focused on that topic. And while the number of publications devoted to elbow OA soared by a seemingly impressive 233% during the study period, the actual numbers were 3 publications in 2007 and 10 in 2016.
“Also, the average number of affected joints in people with osteoarthritis is four. Yet very, very few papers are about multijoint osteoarthritis. And when they do talk about multijoint osteoarthritis, they’re still only talking about hand/hip/knee. So we’re missing the bigger picture of osteoarthritis as a multijoint disease. We’re missing the spine, largely, as a part of osteoarthritis, and we’re missing the peripheral joints,” she said.
Dr. Badley reported having no financial conflicts regarding her study, conducted free of commercial support.
SOURCE: Badley EM et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Apr;27(Suppl 1):S278, Abstract 393.
TORONTO – Osteoarthritis research doesn’t get nearly the respect it deserves in the medical literature, Elizabeth M. Badley, PhD, asserted at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
“Osteoarthritis is by far the most common type of arthritis. There are easily 10 times more people who have osteoarthritis than any other joint disease, but when you look at the literature, the situation is kind of reversed. Osteoarthritis is brushed off by society to a degree,” she said at the meeting, sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Dr. Bradley and colleagues performed a search of MEDLINE for 2007-2016, which turned up a total of 1,625 publications in 2016 on osteoarthritis, excluding those with an orthopedic surgery focus, compared with 10,904 results regarding the broader topic of joint diseases and 28,932 on musculoskeletal diseases.
The bottom line: “Progress is slow, and at this rate osteoarthritis will not be receiving the attention it deserves in our lifetime,” said Dr. Badley, of the department of epidemiology at the University of Toronto and a senior scientist at the Krembil Research Institute, also in Toronto.
The number of publications per year devoted to OA rose by a robust 88% during 2007-2016, while the number on OA not focused on orthopedic procedures grew by 65%. Both of these increases were greater than those for publications on musculoskeletal diseases and joint diseases overall, which were 41% and 51%, respectively. But the absolute number of OA publications was dwarfed by the numbers of those in the other search categories. For example, the number of publications on OA without an orthopedic surgery thrust was 985 in 2007, compared with 7,204 on joint diseases overall.
Among the striking findings of the investigators’ study of the medical literature was the disconnect between the amount of attention devoted to some of the joint-specific manifestations of OA and the actual prevalence of these conditions in the population. For example, the prevalence of hand OA in people living with OA was 52% according to the 2009 Survey on Living with Chronic Diseases in Canada, conducted by Statistics Canada, yet only 6.5% of the publications on OA in 2016 were devoted to hand/thumb OA. Similarly, the prevalence of spine OA was 52% among Canadians with OA, but only 4.3% of OA publications in 2016 focused on that topic. And while the number of publications devoted to elbow OA soared by a seemingly impressive 233% during the study period, the actual numbers were 3 publications in 2007 and 10 in 2016.
“Also, the average number of affected joints in people with osteoarthritis is four. Yet very, very few papers are about multijoint osteoarthritis. And when they do talk about multijoint osteoarthritis, they’re still only talking about hand/hip/knee. So we’re missing the bigger picture of osteoarthritis as a multijoint disease. We’re missing the spine, largely, as a part of osteoarthritis, and we’re missing the peripheral joints,” she said.
Dr. Badley reported having no financial conflicts regarding her study, conducted free of commercial support.
SOURCE: Badley EM et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Apr;27(Suppl 1):S278, Abstract 393.
REPORTING FROM OARSI 2019
Pain coping skills training doesn’t improve knee arthroplasty outcomes
TORONTO – A high level of pain catastrophizing prior to scheduled knee arthroplasty is not, as previously thought, a harbinger of poor outcomes, and affected patients don’t benefit from cognitive-behavioral therapy–based training in pain coping skills, Daniel L. Riddle, PhD, reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
“The take-home message for us is knee arthroplasty is incredibly effective and there really is no reason to do pain coping skills training in these high–pain catastrophizing patients because the great majority of them have such good outcomes,” said Dr. Riddle, professor of physical therapy at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond.
“The other clear message from our trial is that, when you have pain-catastrophizing patients and you lower their pain, their catastrophizing is also lowered. So pain catastrophizing is clearly a response to pain and not a personality trait per se,” he said at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
He presented the results of a 402-patient, randomized, three-arm, single-blind trial conducted at five U.S. medical centers. All participants were scheduled for knee arthroplasty for osteoarthritis, and all had moderate- to high-level pain catastrophizing as reflected in the group’s average Pain Catastrophizing Score of 30. They were assigned to an arthritis education active control group, usual care, or an intervention developed specifically for this study: a cognitive-behavioral therapy–based training program for pain coping skills. Similar pain coping skills training interventions have been shown to be beneficial in patients with medically treated knee OA but hadn’t previously been evaluated in surgically treated patients. The primary study endpoint was change in the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) Pain Scale at 2, 6, and 12 months after surgery.
The improvement in WOMAC pain in the three study arms was virtually superimposable, going from an average pain score of about 12 preoperatively to 2 postoperatively.
“This was a clear no-effect trial,” Dr. Riddle observed. “These are patients we thought to be at increased risk for poor outcome, but indeed they’re not.”
Pain Catastrophizing Scores improved from 30 preoperatively to roughly 7 at 1 year. “We’ve never seen pain catastrophizing improvements of this magnitude,” the researcher commented.
The study participants typically had a large number of chronically painful areas, but only minimal change in pain scores occurred except in the surgically treated knee.
Of note, even with the impressively large improvements in knee pain, function, and other secondary endpoints in the study group as a whole, roughly 20% of study participants experienced essentially no improvement in their function-limiting knee pain during the first year after arthroplasty. These nonresponders were spread equally across all three study arms. Further research will be needed to develop interventions to help this challenging patient subgroup.
The pain coping skills training consisted of 8 weekly sessions, each an hour long, which began prior to surgery and continued afterward. The intervention was delivered by physical therapists who had been trained by pain psychologists with expertise in cognitive-behavioral therapy. The intervention was delivered by telephone and in face-to-face sessions. The trainers were tracked over the course of the study to make sure that the structured intervention was delivered as planned.
Dr. Riddle reported having no financial conflicts regarding the National Institutes of Health-funded study, the full details of which have been published (J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019 Feb 6;101[3]:218-227).
TORONTO – A high level of pain catastrophizing prior to scheduled knee arthroplasty is not, as previously thought, a harbinger of poor outcomes, and affected patients don’t benefit from cognitive-behavioral therapy–based training in pain coping skills, Daniel L. Riddle, PhD, reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
“The take-home message for us is knee arthroplasty is incredibly effective and there really is no reason to do pain coping skills training in these high–pain catastrophizing patients because the great majority of them have such good outcomes,” said Dr. Riddle, professor of physical therapy at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond.
“The other clear message from our trial is that, when you have pain-catastrophizing patients and you lower their pain, their catastrophizing is also lowered. So pain catastrophizing is clearly a response to pain and not a personality trait per se,” he said at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
He presented the results of a 402-patient, randomized, three-arm, single-blind trial conducted at five U.S. medical centers. All participants were scheduled for knee arthroplasty for osteoarthritis, and all had moderate- to high-level pain catastrophizing as reflected in the group’s average Pain Catastrophizing Score of 30. They were assigned to an arthritis education active control group, usual care, or an intervention developed specifically for this study: a cognitive-behavioral therapy–based training program for pain coping skills. Similar pain coping skills training interventions have been shown to be beneficial in patients with medically treated knee OA but hadn’t previously been evaluated in surgically treated patients. The primary study endpoint was change in the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) Pain Scale at 2, 6, and 12 months after surgery.
The improvement in WOMAC pain in the three study arms was virtually superimposable, going from an average pain score of about 12 preoperatively to 2 postoperatively.
“This was a clear no-effect trial,” Dr. Riddle observed. “These are patients we thought to be at increased risk for poor outcome, but indeed they’re not.”
Pain Catastrophizing Scores improved from 30 preoperatively to roughly 7 at 1 year. “We’ve never seen pain catastrophizing improvements of this magnitude,” the researcher commented.
The study participants typically had a large number of chronically painful areas, but only minimal change in pain scores occurred except in the surgically treated knee.
Of note, even with the impressively large improvements in knee pain, function, and other secondary endpoints in the study group as a whole, roughly 20% of study participants experienced essentially no improvement in their function-limiting knee pain during the first year after arthroplasty. These nonresponders were spread equally across all three study arms. Further research will be needed to develop interventions to help this challenging patient subgroup.
The pain coping skills training consisted of 8 weekly sessions, each an hour long, which began prior to surgery and continued afterward. The intervention was delivered by physical therapists who had been trained by pain psychologists with expertise in cognitive-behavioral therapy. The intervention was delivered by telephone and in face-to-face sessions. The trainers were tracked over the course of the study to make sure that the structured intervention was delivered as planned.
Dr. Riddle reported having no financial conflicts regarding the National Institutes of Health-funded study, the full details of which have been published (J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019 Feb 6;101[3]:218-227).
TORONTO – A high level of pain catastrophizing prior to scheduled knee arthroplasty is not, as previously thought, a harbinger of poor outcomes, and affected patients don’t benefit from cognitive-behavioral therapy–based training in pain coping skills, Daniel L. Riddle, PhD, reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
“The take-home message for us is knee arthroplasty is incredibly effective and there really is no reason to do pain coping skills training in these high–pain catastrophizing patients because the great majority of them have such good outcomes,” said Dr. Riddle, professor of physical therapy at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond.
“The other clear message from our trial is that, when you have pain-catastrophizing patients and you lower their pain, their catastrophizing is also lowered. So pain catastrophizing is clearly a response to pain and not a personality trait per se,” he said at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
He presented the results of a 402-patient, randomized, three-arm, single-blind trial conducted at five U.S. medical centers. All participants were scheduled for knee arthroplasty for osteoarthritis, and all had moderate- to high-level pain catastrophizing as reflected in the group’s average Pain Catastrophizing Score of 30. They were assigned to an arthritis education active control group, usual care, or an intervention developed specifically for this study: a cognitive-behavioral therapy–based training program for pain coping skills. Similar pain coping skills training interventions have been shown to be beneficial in patients with medically treated knee OA but hadn’t previously been evaluated in surgically treated patients. The primary study endpoint was change in the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) Pain Scale at 2, 6, and 12 months after surgery.
The improvement in WOMAC pain in the three study arms was virtually superimposable, going from an average pain score of about 12 preoperatively to 2 postoperatively.
“This was a clear no-effect trial,” Dr. Riddle observed. “These are patients we thought to be at increased risk for poor outcome, but indeed they’re not.”
Pain Catastrophizing Scores improved from 30 preoperatively to roughly 7 at 1 year. “We’ve never seen pain catastrophizing improvements of this magnitude,” the researcher commented.
The study participants typically had a large number of chronically painful areas, but only minimal change in pain scores occurred except in the surgically treated knee.
Of note, even with the impressively large improvements in knee pain, function, and other secondary endpoints in the study group as a whole, roughly 20% of study participants experienced essentially no improvement in their function-limiting knee pain during the first year after arthroplasty. These nonresponders were spread equally across all three study arms. Further research will be needed to develop interventions to help this challenging patient subgroup.
The pain coping skills training consisted of 8 weekly sessions, each an hour long, which began prior to surgery and continued afterward. The intervention was delivered by physical therapists who had been trained by pain psychologists with expertise in cognitive-behavioral therapy. The intervention was delivered by telephone and in face-to-face sessions. The trainers were tracked over the course of the study to make sure that the structured intervention was delivered as planned.
Dr. Riddle reported having no financial conflicts regarding the National Institutes of Health-funded study, the full details of which have been published (J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019 Feb 6;101[3]:218-227).
REPORTING FROM OARSI 2019
Methotrexate significantly reduced knee OA pain
TORONTO – Philip G. Conaghan, MD, PhD, reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
There is, however, an asterisk attached to these findings. “Despite a moderate standard effect size, the treatment effect was smaller than some of the thresholds for what is considered clinically meaningful,” he noted at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
That being said, the rheumatologist is convinced further investigation of methotrexate in osteoarthritis is warranted.
“I have to say that, unlike our earlier hydroxychloroquine trial, which was robustly negative with nothing more to say, I think there is a signal in this study. I need to understand the results of this trial better to understand if there is a subgroup we could treat with methotrexate. It’s a cheap drug, it’s readily available, and we’ve got a lot of experience with it,” noted Dr. Conaghan, professor of musculoskeletal medicine at the University of Leeds (England) and director of the Leeds Institute of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Medicine.
The rationale for the 15-center PROMOTE trial is that synovitis is common in OA. Synovitis is associated with pain, methotrexate is the gold-standard treatment for synovitis in inflammatory forms of arthritis, and current treatments for OA are, to say the least, severely limited. Also, an earlier 30-patient, open-label pilot study of methotrexate in patients with painful knee OA conducted by Dr. Conaghan and coworkers suggested the drug was promising (Rheumatology [Oxford]. 2013 May;52[5]:888-92).
PROMOTE included 134 patients with symptomatic and radiographic knee OA who were randomized in double-blind fashion to 6 months of oral methotrexate at 10 mg titrated to a target dose of 25 mg/week or to placebo. All patients also received usual care with oral NSAIDs and/or acetaminophen. Their mean baseline knee pain on a 0-10 numeric rating scale was 6.6.
The primary endpoint, assessed at 6 months, was the difference between the two study arms in average knee pain during the previous week on a 0-10 scale. The score was 5.1 in the methotrexate group and 6.2 in the placebo arm, for a baseline-adjusted treatment difference of 0.83 points, which works out to a standard effect size of 0.36. When the data were reanalyzed after excluding the 15 patients who missed more than four doses of medication within any 3-month period, the between-group difference in pain scores increased to 0.95 points in favor of the methotrexate group.
A significant difference in favor of the methotrexate group was documented in the OARSI-OMERACT response rate at 6 months: 45% in the methotrexate group and 26% in the controls. Some secondary endpoints were positive as well, with statistically significant differences seen at 6 months in Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) stiffness, WOMAC physical function, and several other endpoints. But there were no significant differences in WOMAC pain, SF-12 physical component or SF-12 mental component scores, or in an OA quality of life measure.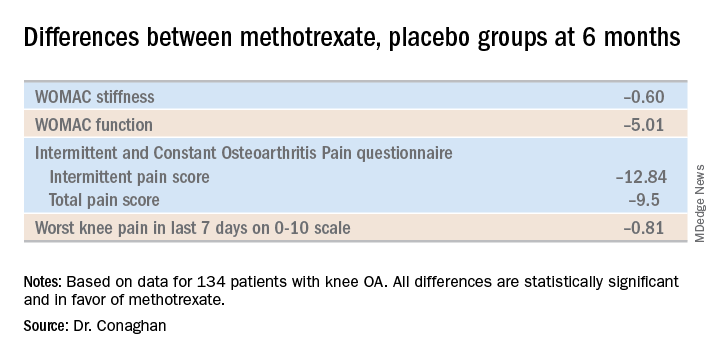
The mean dose of methotrexate used in the study was about 17 mg/week. Dr. Conaghan said that if he could do the trial over again, he would have used subcutaneous methotrexate.
“It’s a more reliable way of getting a dose into people and probably of getting a slightly higher dose into people. In the rheumatoid arthritis world, we use a lot more subcutaneous methotrexate now than we did 10 years ago because it gets around a lot of the minor side effects and helps compliance,” he said.
One audience member suggested that one potentially useful way to zero in on a subgroup of knee OA patients likely to derive the most benefit from methotrexate would be to have screened potential study participants for comorbid fibromyalgia and exclude those with the disorder. Dr. Conaghan replied that the PROMOTE investigators did gather data on participants’ pain at sites other than the knee. That data can be used to identify those at increased likelihood of fibromyalgia, and he agreed that’s worth looking into.
Dr. Conaghan reported having no financial conflicts regarding PROMOTE, which was funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health Research and Versus Arthritis.
SOURCE: Conaghan PG et al. OARSI 2019, Abstract 86.
TORONTO – Philip G. Conaghan, MD, PhD, reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
There is, however, an asterisk attached to these findings. “Despite a moderate standard effect size, the treatment effect was smaller than some of the thresholds for what is considered clinically meaningful,” he noted at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
That being said, the rheumatologist is convinced further investigation of methotrexate in osteoarthritis is warranted.
“I have to say that, unlike our earlier hydroxychloroquine trial, which was robustly negative with nothing more to say, I think there is a signal in this study. I need to understand the results of this trial better to understand if there is a subgroup we could treat with methotrexate. It’s a cheap drug, it’s readily available, and we’ve got a lot of experience with it,” noted Dr. Conaghan, professor of musculoskeletal medicine at the University of Leeds (England) and director of the Leeds Institute of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Medicine.
The rationale for the 15-center PROMOTE trial is that synovitis is common in OA. Synovitis is associated with pain, methotrexate is the gold-standard treatment for synovitis in inflammatory forms of arthritis, and current treatments for OA are, to say the least, severely limited. Also, an earlier 30-patient, open-label pilot study of methotrexate in patients with painful knee OA conducted by Dr. Conaghan and coworkers suggested the drug was promising (Rheumatology [Oxford]. 2013 May;52[5]:888-92).
PROMOTE included 134 patients with symptomatic and radiographic knee OA who were randomized in double-blind fashion to 6 months of oral methotrexate at 10 mg titrated to a target dose of 25 mg/week or to placebo. All patients also received usual care with oral NSAIDs and/or acetaminophen. Their mean baseline knee pain on a 0-10 numeric rating scale was 6.6.
The primary endpoint, assessed at 6 months, was the difference between the two study arms in average knee pain during the previous week on a 0-10 scale. The score was 5.1 in the methotrexate group and 6.2 in the placebo arm, for a baseline-adjusted treatment difference of 0.83 points, which works out to a standard effect size of 0.36. When the data were reanalyzed after excluding the 15 patients who missed more than four doses of medication within any 3-month period, the between-group difference in pain scores increased to 0.95 points in favor of the methotrexate group.
A significant difference in favor of the methotrexate group was documented in the OARSI-OMERACT response rate at 6 months: 45% in the methotrexate group and 26% in the controls. Some secondary endpoints were positive as well, with statistically significant differences seen at 6 months in Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) stiffness, WOMAC physical function, and several other endpoints. But there were no significant differences in WOMAC pain, SF-12 physical component or SF-12 mental component scores, or in an OA quality of life measure.
The mean dose of methotrexate used in the study was about 17 mg/week. Dr. Conaghan said that if he could do the trial over again, he would have used subcutaneous methotrexate.
“It’s a more reliable way of getting a dose into people and probably of getting a slightly higher dose into people. In the rheumatoid arthritis world, we use a lot more subcutaneous methotrexate now than we did 10 years ago because it gets around a lot of the minor side effects and helps compliance,” he said.
One audience member suggested that one potentially useful way to zero in on a subgroup of knee OA patients likely to derive the most benefit from methotrexate would be to have screened potential study participants for comorbid fibromyalgia and exclude those with the disorder. Dr. Conaghan replied that the PROMOTE investigators did gather data on participants’ pain at sites other than the knee. That data can be used to identify those at increased likelihood of fibromyalgia, and he agreed that’s worth looking into.
Dr. Conaghan reported having no financial conflicts regarding PROMOTE, which was funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health Research and Versus Arthritis.
SOURCE: Conaghan PG et al. OARSI 2019, Abstract 86.
TORONTO – Philip G. Conaghan, MD, PhD, reported at the OARSI 2019 World Congress.
There is, however, an asterisk attached to these findings. “Despite a moderate standard effect size, the treatment effect was smaller than some of the thresholds for what is considered clinically meaningful,” he noted at the meeting sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
That being said, the rheumatologist is convinced further investigation of methotrexate in osteoarthritis is warranted.
“I have to say that, unlike our earlier hydroxychloroquine trial, which was robustly negative with nothing more to say, I think there is a signal in this study. I need to understand the results of this trial better to understand if there is a subgroup we could treat with methotrexate. It’s a cheap drug, it’s readily available, and we’ve got a lot of experience with it,” noted Dr. Conaghan, professor of musculoskeletal medicine at the University of Leeds (England) and director of the Leeds Institute of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Medicine.
The rationale for the 15-center PROMOTE trial is that synovitis is common in OA. Synovitis is associated with pain, methotrexate is the gold-standard treatment for synovitis in inflammatory forms of arthritis, and current treatments for OA are, to say the least, severely limited. Also, an earlier 30-patient, open-label pilot study of methotrexate in patients with painful knee OA conducted by Dr. Conaghan and coworkers suggested the drug was promising (Rheumatology [Oxford]. 2013 May;52[5]:888-92).
PROMOTE included 134 patients with symptomatic and radiographic knee OA who were randomized in double-blind fashion to 6 months of oral methotrexate at 10 mg titrated to a target dose of 25 mg/week or to placebo. All patients also received usual care with oral NSAIDs and/or acetaminophen. Their mean baseline knee pain on a 0-10 numeric rating scale was 6.6.
The primary endpoint, assessed at 6 months, was the difference between the two study arms in average knee pain during the previous week on a 0-10 scale. The score was 5.1 in the methotrexate group and 6.2 in the placebo arm, for a baseline-adjusted treatment difference of 0.83 points, which works out to a standard effect size of 0.36. When the data were reanalyzed after excluding the 15 patients who missed more than four doses of medication within any 3-month period, the between-group difference in pain scores increased to 0.95 points in favor of the methotrexate group.
A significant difference in favor of the methotrexate group was documented in the OARSI-OMERACT response rate at 6 months: 45% in the methotrexate group and 26% in the controls. Some secondary endpoints were positive as well, with statistically significant differences seen at 6 months in Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) stiffness, WOMAC physical function, and several other endpoints. But there were no significant differences in WOMAC pain, SF-12 physical component or SF-12 mental component scores, or in an OA quality of life measure.
The mean dose of methotrexate used in the study was about 17 mg/week. Dr. Conaghan said that if he could do the trial over again, he would have used subcutaneous methotrexate.
“It’s a more reliable way of getting a dose into people and probably of getting a slightly higher dose into people. In the rheumatoid arthritis world, we use a lot more subcutaneous methotrexate now than we did 10 years ago because it gets around a lot of the minor side effects and helps compliance,” he said.
One audience member suggested that one potentially useful way to zero in on a subgroup of knee OA patients likely to derive the most benefit from methotrexate would be to have screened potential study participants for comorbid fibromyalgia and exclude those with the disorder. Dr. Conaghan replied that the PROMOTE investigators did gather data on participants’ pain at sites other than the knee. That data can be used to identify those at increased likelihood of fibromyalgia, and he agreed that’s worth looking into.
Dr. Conaghan reported having no financial conflicts regarding PROMOTE, which was funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health Research and Versus Arthritis.
SOURCE: Conaghan PG et al. OARSI 2019, Abstract 86.
REPORTING FROM OARSI 2019



















