Dermpath Diagnosis

Lipidized Dermatofibroma
Lipidized dermatofibromas most commonly are found on the ankles, which has led some authors to refer to these lesions as ankle-type fibrous...
Dr. Kaminska-Winciorek is from the Department of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Onco-Hematology, The Maria Sklodowska-Curie Memorial Cancer Center and Institute of Oncology Gliwice Branch, Poland. Dr. Antosz is from Regional Specialist Hospital, Tychy, Poland. Dr. Spiewak is from the Department of Experimental Dermatology and Cosmetology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jagiellonian University Medical College, Krakow, Poland.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Grazyna Kaminska-Winciorek, MD, PhD, The Department of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Onco-Hematology, The Maria Sklodowska-Curie Memorial Cancer Center and Institute of Oncology Gliwice Branch, 44-101 Gliwice, Wybrzeze Armii Krajowej 15, Poland (dermatolog.pl@gmail.com).

Practice Points
To the Editor:
Dermatofibroma is a common cutaneous lesion that most frequently affects young or middle-aged adults, especially women.1 Clinically, it appears as a firm, pink or brown nodule. It may be painful or show a tendency for scarring. The pathognomonic feature of dermatofibroma, regarded as a fibrohistiocytic tumor, is the so-called button sign caused by skin depression following pressure. We present a unique case of elongated dermatofibroma with a linear, white, scarlike patch with a brownish pigmented network and globules.
A 40-year-old woman presented with a linear elongated lesion localized to the right side of the infrascapular region of 10 years’ duration. The lesion initially was a small brownish plaque. There was no history of trauma or scratching. Over the next 10 years, the lesion slowly progressed, finally becoming a linear, atrophic, brownish plaque that was 2.5-cm long (Figure 1). The button sign was positive. On dermoscopy the central, elongated, white patch was visualized not as a typical round patch but as a scarlike white line (Figure 2A) surrounded by a brownish network that was especially pronounced in the distal parts of the lesion. In the upper part of the lesion, multiple marginally disseminated, dark brown dots were present. Brownish globules within the linear white patch also were observed in the lower central part. Figure 2B presents a dermoscopic picture of the linear variant of dermatofibroma. For cosmetic reasons, the patient underwent total surgical excision of the lesion. Histopathology revealed distinct characteristics of dermatofibroma (Figures 3A and 3B).
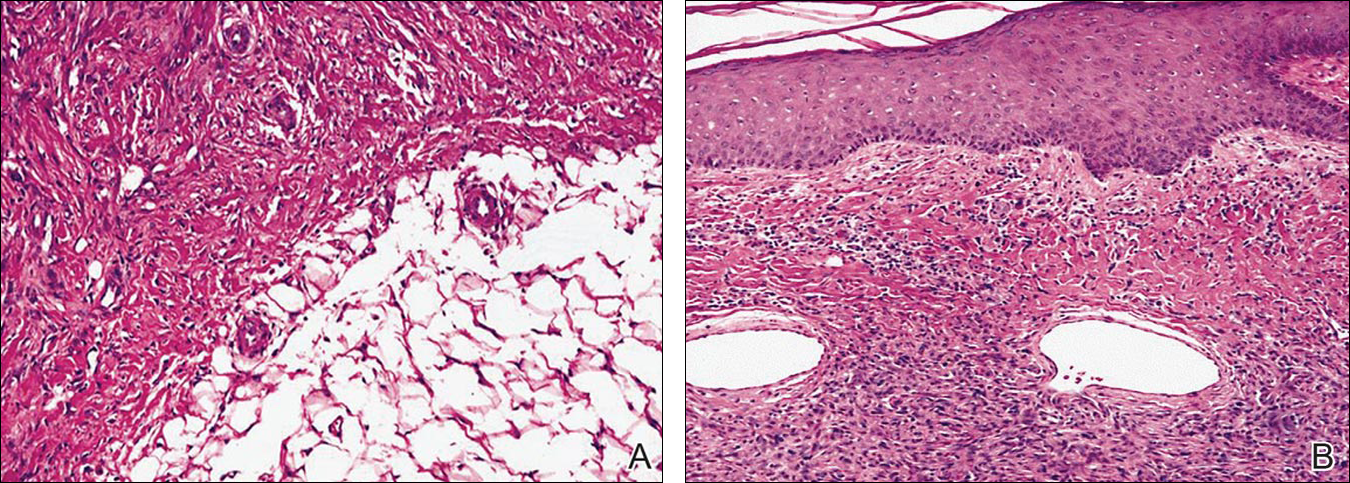
Figure 3. Histopathology revealed dermatofibroma (A and B)(both H&E, original magnifications ×40 and ×100). A storiform pattern of spindled and bland fibroblasts and histiocytelike cells in the mid dermis and subcutaneous tissue were seen with infiltrative margins but sparing the epidermis. Spindle cells had scant cytoplasm and thin elongated nuclei with pointed ends. Nuclei almost touched each other, unlike smooth muscle lesions.

Lipidized dermatofibromas most commonly are found on the ankles, which has led some authors to refer to these lesions as ankle-type fibrous...
No abstract available.
