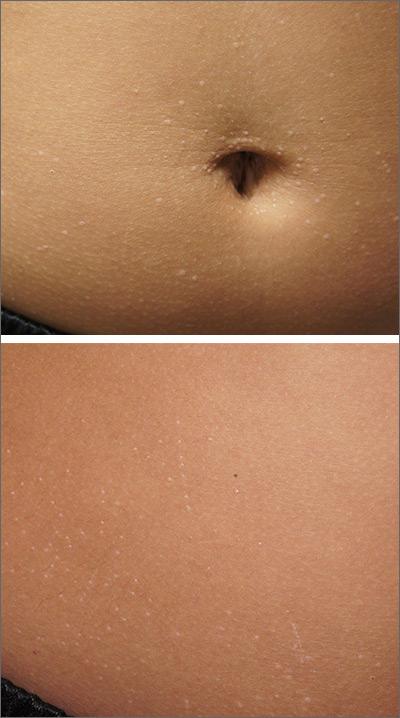
The miniscule papules arising suddenly on the trunk and genitals with linear arrays and clusters are clinically consistent with lichen nitidus, an uncommon eruption without a clear etiology.
Presentations may be focal or widespread and range from mildly itchy to asymptomatic. Children and young adults are most often affected. Linear arrays may appear in response to the trauma of scratching, which is termed the Koebner phenomenon. The differential diagnosis includes molluscum contagiosum, lichen planus, and lichen spinulosis. Usually these conditions can be distinguished clinically, but a biopsy would differentiate them, if needed. It’s worth noting, too, that lichen nitidus papules are monomorphic and lack the umbilication that is seen with molluscum contagiosum.
Cases of lichen nitidus clear up spontaneously, although usually months to years after diagnosis. Lichen nitidus is not contagious. Reassurance is, however, important as many patients may have experienced misdiagnosis and have concerns about sexual transmission because of the location of the papules on their genitals.
Treatment is often unnecessary. However, if itching is problematic, topical steroids and other topical antipruritics may be used. Topical hydrocortisone 2.5% cream or ointment for skin folds and genitals may be safely used, as well as topical triamcinolone 0.1% for the trunk and extremities. Pramoxine lotion (Sarna) is an over-the-counter nonsteroidal antipruritic. Oral nonsedating antihistamines can also be used as an adjunct.
This patient was reassured that the lesions were not contagious. Due to the itching, he was started on the pramoxine lotion twice daily, as needed, and the lesions cleared in about 6 months.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)