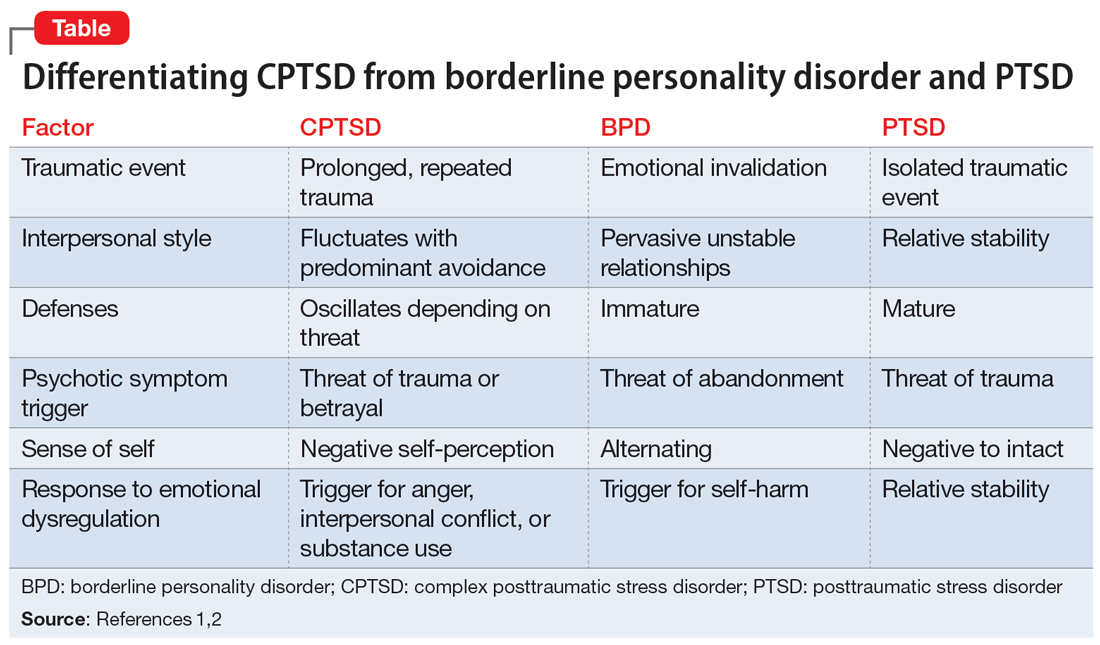
Complex posttraumatic stress disorder (CPTSD) is a condition characterized by classic trauma-related symptoms in addition to disturbances in self organization (DSO).1-3 DSO symptoms include negative self-concept, emotional dysregulation, and interpersonal problems. CPTSD differs from PTSD in that it includes symptoms of DSO, and differs from borderline personality disorder (BPD) in that it does not include extreme self-injurious behavior, a complete lack of sense of self, and avoidance of rejection or abandonment (Table1,2). The maladaptive traits of CPTSD are often the result of a chronic lack of safety in early childhood, particularly childhood sexual abuse (CSA). CSA may affect up to 20% of women and is defined by the CDC as “any completed or attempted sexual act, sexual contact with, or exploitation of a child by a caregiver.”4,5
Maternal lifetime trauma is more common among women who are in low-income minority groups and can lead to adverse birth outcomes in this vulnerable patient population.6 Recent research has found that trauma can increase cortisol levels during pregnancy, leading to increased placental permeability, inflammatory response, and longstanding alterations in the fetal hypothalamic-pituitary adrenal axis.6 A CPTSD diagnosis is of particular interest during the perinatal period because CPTSD is often a response to interpersonal trauma and attachment adversity, which can be reactivated during the perinatal period.7 CPTSD in survivors of CSA can be exacerbated due to feelings of disempowerment secondary to loss of bodily control throughout pregnancy, childbirth, breastfeeding, and obstetrical exams.5,8 Little is known about perinatal CPTSD, but we can extrapolate from trauma research that it is likely associated with the worsening of other maternal mental health conditions, suicidality, physical complaints, quality of life, maternal-child bonding outcomes, and low birth weight in offspring.5,9,10
Although there are no consensus guidelines on how to diagnose and treat CPTSD during the perinatal period, or how to promote family functioning thereafter, there are many opportunities for intervention. Mental health clinicians are in a particularly important position to care for women in the perinatal period, as collaborative work with obstetricians, pediatricians, and social services can have long-lasting effects.
In this article, we present cases of 3 CSA survivors who experienced worsening of CPTSD symptoms during the perinatal period and received psychiatric care via telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic. We also identify best practice approaches and highlight areas for future research.
Case descriptions
Case 1
Ms. A, age 33, is married, has 3 children, has asthma, and is vaccinated against COVID-19. Her psychiatric history includes self-reported dissociative identity disorder and bulimia nervosa. At 2 months postpartum following an unplanned yet desired pregnancy, Ms. A presents to the outpatient clinic after a violent episode toward her husband during sexual intercourse. Since the first trimester of her pregnancy, she has expressed increased anxiety and difficulty sleeping, hypervigilance, intimacy avoidance, and negative views of herself and the world, yet she denies persistent depressive, manic, or psychotic symptoms, other maladaptive personality traits, or substance use. She recalls experiencing similar symptoms during her 2 previous peripartum periods, and attributes it to worsening memories of sexual abuse during childhood. Ms. A has a history of psychiatric hospitalizations during adolescence and young adulthood for suicidal ideation. She had been treated with various medications, including chlorpromazine, lamotrigine, carbamazepine, and clonazepam, but self-discontinued these medications in 2016 because she felt they were ineffective. Since becoming a mother, she has consistently denied depressive symptoms or suicidal ideation, and intermittently engaged in interpersonal psychotherapy targeting her conflictual relationship with her husband and parenting struggles.
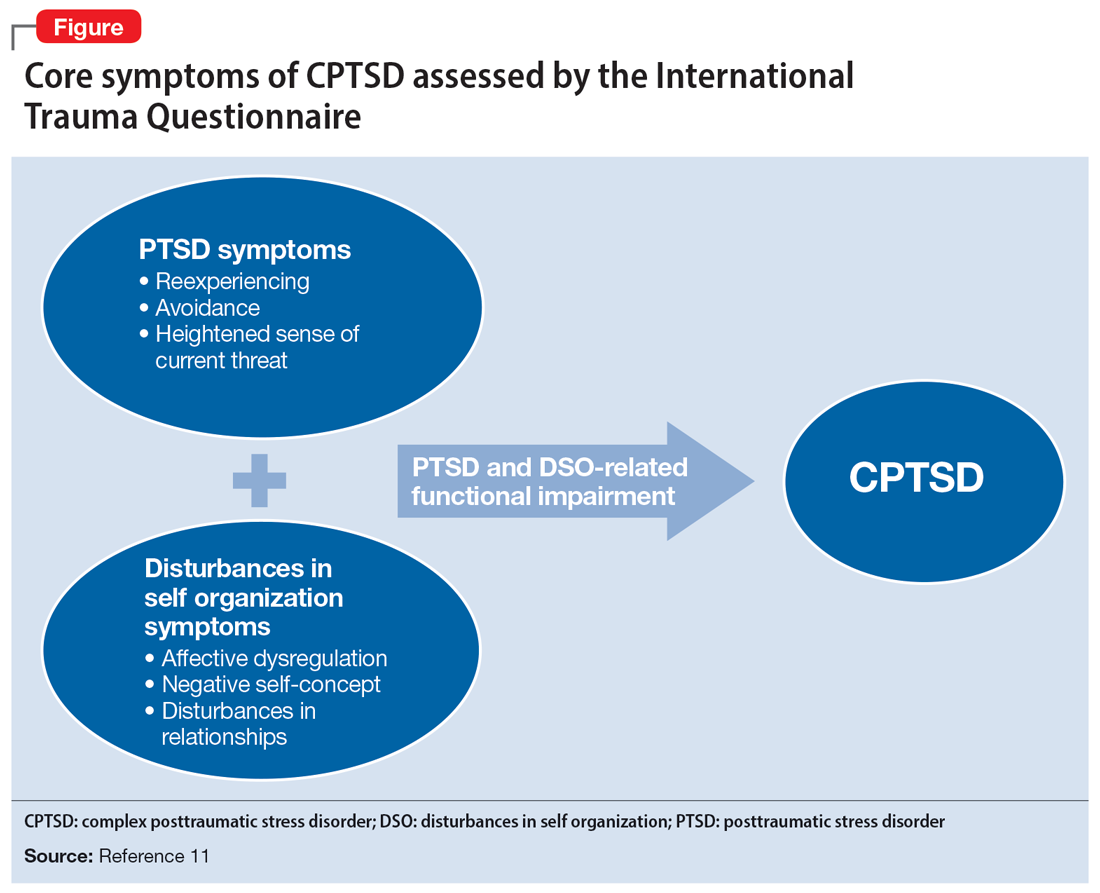
Ms. A underwent an induced vaginal delivery at 36 weeks gestation due to preeclampsia and had success with breastfeeding. While engaging in sexual activity for the first time postpartum, she dissociated and later learned she had forcefully grabbed her husband’s neck for several seconds but did not cause any longstanding physical damage. Upon learning of this episode, Ms. A’s psychiatrist asks her to complete the International Trauma Questionnaire (ITQ), a brief self-report measure developed for the assessment of the ICD-11 diagnosis of CPTSD (Figure11). Ms. A also completes the PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5), the Dissociative Experiences Scale, and the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS) to assist with assessing her symptoms.12-15 The psychiatrist uses ICD-11 criteria to diagnose Ms. A with CPTSD, given her functional impairment associated with both PTSD and DSO symptoms, which have acutely worsened during the perinatal period.
Ms. A initially engages in extensive trauma psychoeducation and supportive psychotherapy for 3 months. She later pursues prolonged exposure psychotherapy targeting intimacy, and after 6 months of treatment, improves her avoidance behaviors and marriage.
Continue to: Case 2