Practice Gap
In light of inflation, rising costs of procedures, and decreased reimbursements,1 there is an increased need to identify and utilize inexpensive multitasking tools that can serve the dermatologic surgeon from preoperative to postoperative care. The 70% isopropyl alcohol swab may be the dermatologist’s most cost-effective and versatile surgical tool.
The Technique
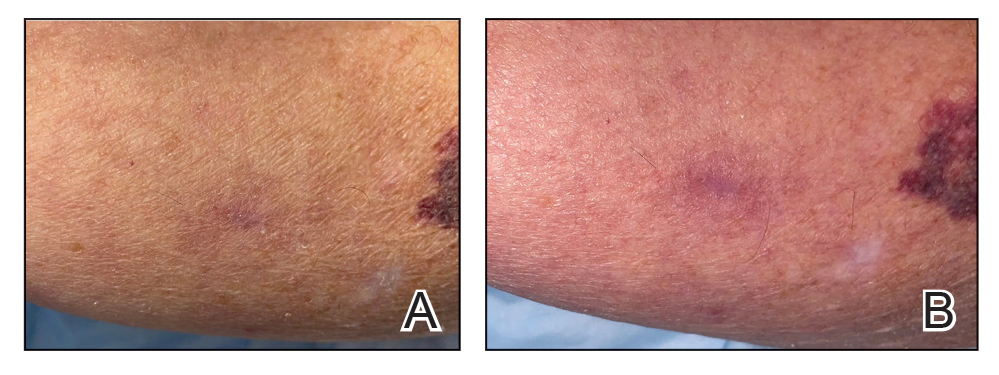
When assessing a lesion, alcohol swabs can remove scale, crust, or residue from personal care products to help reveal primary morphology. They aid in the diagnosis of porokeratosis by highlighting the cornoid lamella when used following application of gentian violet.2 The alcohol swab also can lay down a liquid interface to facilitate contact dermoscopy and improve visualization while also reducing the transmission of pathogens by the dermatoscope.3 Rubbing an area with an alcohol swab can induce vasodilation of scar tissue, which also may help localize a prior biopsy or surgical site (Figure).
Before a surgical site is marked, an initial cleanse with an alcohol swab serves to both remove debris and provide antisepsis ahead of the procedure. Additionally, the swab may improve adherence of skin markers by clearing excess lipid from the skin surface. Assessing the amount of debris and oil removed in the process can help determine a patient’s baseline level of hygiene, which can aid postoperative wound care planning. In extreme cases, use of an alcohol swab may help diagnose dermatitis neglecta or terra firma-forme dermatosis by completely removing any pigmentation.4
After surgery, the alcohol swab can remove skin marker(s) and blood and prepare the site for the surgical dressing. There also is some evidence to suggest that cleansing the surgical site with an alcohol swab as part of routine postoperative wound care may decrease incidence of surgical-site infection.5 At follow-up, the swab can remove crust and clean the skin before suture removal. If infection is suspected, the swab can cleanse skin before a wound culture is obtained to remove skin commensals and flora on the outer surface of the wound.
Practice Implications
The 70% isopropyl alcohol swab can assist the dermatologist in numerous tasks related to everyday procedures. It is readily available in every clinic and costs only a few cents.