CHICAGO – Dulaglutide, an investigational once-weekly long-acting glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist, provided superior glycemic control compared with sitagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes in the phase III AWARD-5 trial.
In this 52-week, 1,098-patient randomized trial, both the 0.75- and 1.5-mg doses of once-weekly dulaglutide proved superior to oral sitagliptin (Januvia) at the standard dose of 100 mg/day in key efficacy endpoints. These outcomes included magnitude of hemoglobin A1c reduction, achievement of guideline-recommended HbA1c targets, and weight loss, Dr. Michael A. Nauck reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
Dulaglutide is a recombinant glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) fusion protein linking a human GLP-1 peptide analogue to a large protein that gives the medication a lengthy half-life of 5 days. Metabolism of dulaglutide is not renally dependent, making the drug a logical candidate for future study in type 2 diabetic patients with renal impairment, observed Dr. Nauck, head of the Bad Lauterberg (Germany) Diabetes Center.
AWARD-5: Dulaglutide vs. sitagliptin
The fifth Assessment of Weekly Administration of LY2189265 in Diabetes (AWARD-5) was one of three phase III clinical trials in the AWARD program presented at the meeting. In AWARD-1, the once-weekly injectable GLP-1 agonist demonstrated superior glycemic control compared with twice-daily exenatide (Byetta) in type 2 diabetic patients not adequately controlled with full-dose metformin and pioglitazone. AWARD-3 showed dulaglutide to be superior to metformin in patients with early type 2 diabetes.
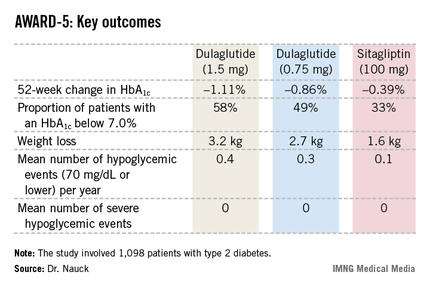
The 1,098 participants in AWARD-5 had a mean baseline HbA1c of 8.1% despite being on metformin and, in one-quarter of cases, an additional oral antidiabetic agent. They stayed on their previous oral medication during the trial. Their mean baseline body mass index was 31 kg/m2, and they averaged a 7-year history of diabetes.
The primary objective in AWARD-5 was to establish that dulaglutide was noninferior to sitagliptin in its ability to reduce HbA1c from baseline through 52 weeks. But in fact, Dr. Nauck reported, both doses of dulaglutide exceeded that standard and actually achieved statistically significant and clinically meaningful superiority to the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (see chart).
With regard to safety issues, the endocrinologist noted that hypoglycemia rates didn’t vary significantly between the study arms. No cases of pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer occurred in dulaglutide-treated patients. There were three cases of pancreatitis in the sitagliptin group.
Gastrointestinal side effects were common among recipients of the once-weekly GLP-1 agonist. The incidence of nausea was 17% in patients who received dulaglutide at 1.5 mg, 14% with 0.75 mg, and 5% with sitagliptin. Diarrhea occurred in 15% and 10% of patients on the high- and low-dose dulaglutide regimens, respectively, compared with 3% on sitagliptin. The incidence of vomiting was 13% with dulaglutide at 1.5 mg, 8% at 0.75 mg, and 2% with sitagliptin. However, the frequency of dulaglutide-related GI side effects dropped off markedly after the first 4-8 weeks, the side effects were mostly mild to moderate in nature, and very few patients dropped out of the study due to GI symptoms, according to Dr. Nauck.
AWARD-1: Dulaglutide vs. exenatide
In a separate presentation, Dr. Carol Wysham reported on 978 patients with type 2 diabetes in the 52-week, phase III AWARD-1 trial who were randomized to dulaglutide at 1.5 or 0.75 mg, the injectable GLP-1 agonist exenatide at 10 mcg twice daily, or placebo. Their baseline HbA1c was 8.07% despite being on metformin and pioglitazone.
The primary endpoint was change in HbA1c at 26 weeks. The reduction was significantly bigger in the two dulaglutide study arms than with exenatide: –1.51% compared with baseline in the dulaglutide 1.5-mg arm, –1.3% with dulaglutide 0.75 mg, –0.99% with exenatide, and –0.46% with placebo. The proportion of patients with an HbA1c of 6.5% or less at 26 weeks was 64% with dulaglutide 1.5 mg, 54% with the long-acting agent at 0.75 mg, 39% with sitagliptin, and 26% in placebo-treated controls.
These results held up at the 52-week mark as well. At that time, 71% of the dulaglutide 1.5-mg group had an HbA1c below 7.0%, as did 59% of patients on dulaglutide 0.75 mg and 49% on exenatide.
As in the other AWARD trials, most of the reduction in body weight and fasting plasma glucose in dulaglutide-treated patients occurred in the first 2 weeks of treatment. The early benefits were then maintained through 52 weeks, observed Dr. Wysham, an endocrinologist in Spokane, Wash.
AWARD-3: Dulaglutide vs. metformin
Dr. Guillermo E. Umpierrez presented the results of AWARD-3, which involved 807 patients with early type 2 diabetes as evidenced by their mean 2.6-year disease history. Their baseline HbA1c was 7.6% with diet and exercise alone or in combination with a single, low-dose, oral antidiabetic medication. Participants were randomized to dulaglutide at 1.5 or 0.75 mg or to metformin at 1,000 mg twice daily.