Hysteroscopic versus laparoscopic procedures for permanent contraception
Bouillon K, Bertrand M, Bader G, et al. Association of hysteroscopic vs laparoscopic sterilization with procedural, gynecological, and medical outcomes. JAMA. 2018:319(4):375-387.
Antoun L, Smith P, Gupta J, et al. The feasibility, safety, and effectiveness of hysteroscopic sterilization compared with laparoscopic sterilization. Am J of Obstet Gynecol. 2017;217(5):570.e1-570.e6. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2017.07.011.
Jokinen E, Heino A, Karipohja T, et al. Safety and effectiveness of female tubal sterilisation by hysteroscopy, laparoscopy, or laparotomy: a register based study. BJOG. 2017;124(12):1851-1857.
In this section, we present 3 recent studies that evaluate pregnancy outcomes and complications including reoperation or second permanent contraception procedure rates.
Data from France measure up to 3-year differences in adverse outcomes
Bouillon and colleagues aimed to identify differences in adverse outcome rates between hysteroscopic and laparoscopic permanent contraceptive methods. Utilizing national hospital discharge data in France, the researchers conducted a large database study review of records from more than 105,000 women aged 30 to 54 years receiving hysteroscopic or laparoscopic permanent contraception between 2010 and 2014. The database contains details based on the ICD-10 codes for all public and private hospitals in France, representing approximately 75% of the total population. Procedures were performed at 831 hospitals in 26 regions.
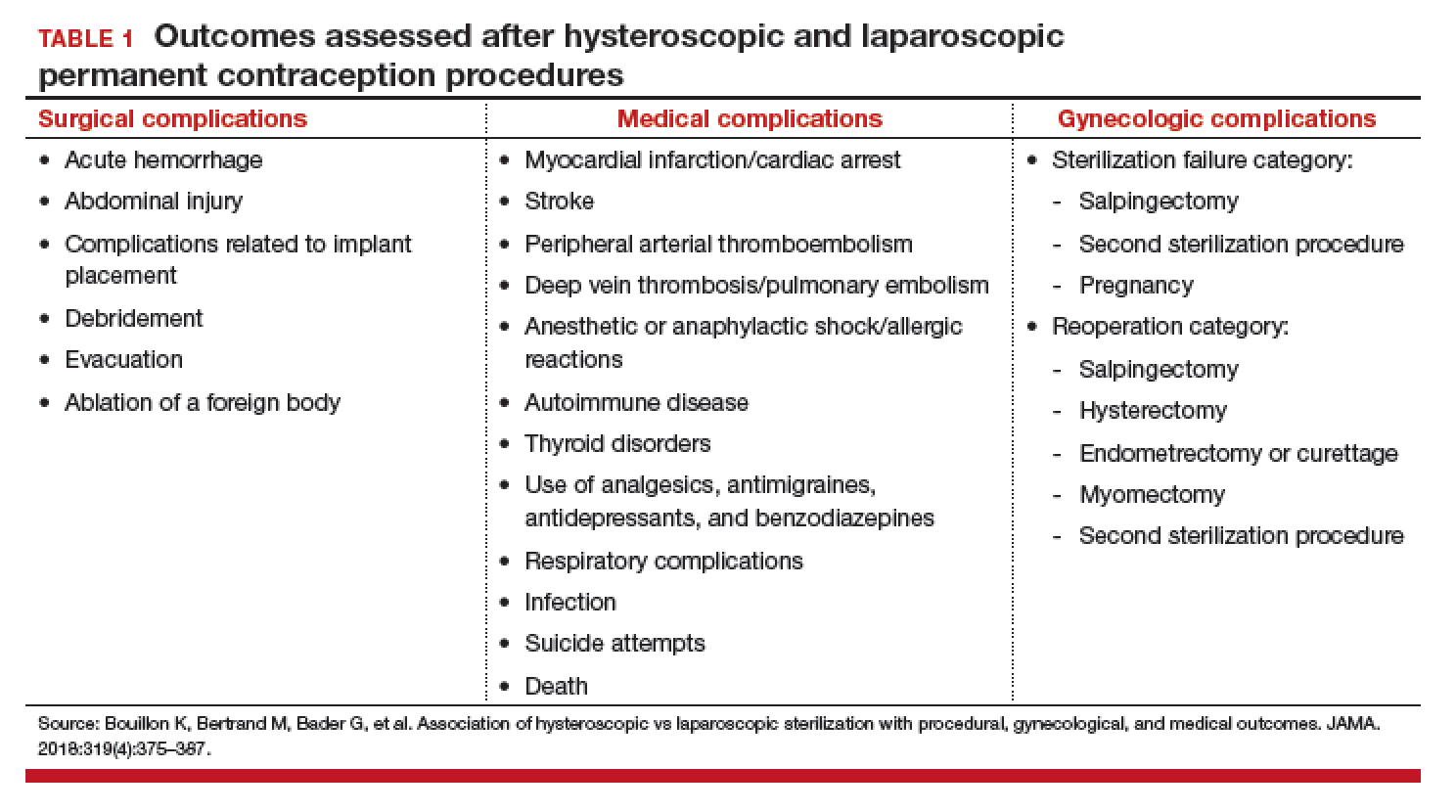
Adverse outcomes were divided into surgical, medical, and gynecologic complications (TABLE 1) and were assessed at 3 timepoints: at the time of procedure and at 1 and 3 years postprocedure.
Overall, 71,303 women (67.7%) underwent hysteroscopic permanent contraception procedures and 34,054 women (32.3%) underwent laparoscopic permanent contraception procedures. Immediate surgical and medical complications were significantly less common for women having hysteroscopic compared with laparoscopic procedures. Surgical complications at the time of the procedure occurred in 96 (0.13%) and 265 (0.78%) women, respectively (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 0.18; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.14-0.23). Medical complications at the time of procedure occurred in 41 (0.06%) and 39 (0.11%) women, respectively (aOR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.30-0.89).
However, gynecologic outcomes, including need for a second surgery to provide permanent contraception and overall failure rates (need for salpingectomy, a second permanent contraception procedure, or pregnancy) were significantly more common for women having hysteroscopic procedures. By 1 year after the procedure, 2,955 women (4.10%) who initially had a hysteroscopic procedure, and 56 women (0.16%) who had a laparoscopic procedure required a second permanent contraception surgery (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 25.99; 95% CI, 17.84-37.86). By the third year, additional procedures were performed in 3,230 (4.5%) and 97 (0.28%) women, respectively (aHR, 16.63; 95% CI, 12.50-22.20). Most (65%) of the repeat procedures were performed laparoscopically. Although pregnancy rates were significantly lower at 1 year among women who initially chose a hysteroscopic procedure (0.24% vs 0.41%; aHR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.53-0.92), the rates did not differ at 3 years (0.48% vs 0.57%, respectively; aHR, 1.04; 95% CI, 0.83-1.30).
Most importantly, overall procedure failure rates were significantly higher at 1 year in women initially choosing a hysteroscopic approach compared with laparoscopic approach (3,446 [4.83%] vs 235 [0.69%] women; aHR, 7.11; 95% CI, 5.92-8.54). This difference persisted through 3 years (4,098 [5.75%] vs 438 [1.29%] women, respectively; aHR, 4.66; 95% CI, 4.06-5.34).
UK data indicate high reoperation rate for hysteroscopic procedures
Antoun and colleagues aimed to compare pregnancy rates, radiologic imaging follow-up rates, reoperations, and 30-day adverse outcomes, between hysteroscopic and laparoscopic permanent contraception methods. Conducted at a single teaching hospital in the United Kingdom, this study included 3,497 women who underwent procedures between 2005 and 2015. The data were collected prospectively for the 1,085 women who underwent hysteroscopic procedures and retrospectively for 2,412 women who had laparoscopic permanent contraception procedures with the Filshie clip.
Over the 10-year study period, hysteroscopic permanent contraception increased from 14.2% (40 of 280) of procedures in 2005 to 40.5% (150 of 350) of procedures in 2015 (P<.001). Overall, 2,400 women (99.5%) underwent successful laparoscopic permanent contraception, compared with 992 women (91.4%) in the hysteroscopic group (OR, 18.8; 95% CI, 10.2-34.4).
In the hysteroscopic group, 958 women (97%) returned for confirmatory testing, of whom 902 (91% of women with successful placement) underwent satisfactory confirmatory testing. There were 93 (8.6%) unsuccessful placements that were due to inability to visualize ostia or tubal stenosis (n = 72 [77.4%]), patient intolerance to procedure (n = 15 [16.1%]), or device failure (n = 6 [6.5%]).
The odds for reoperation were 6 times greater in the hysteroscopic group by 1 year after surgery (22 [2%] vs 8 [0.3%] women; OR, 6.2; 95% CI, 2.8-14.0). However, the 1-year pregnancy risk was similar between the 2 groups, with 3 reported pregnancies after hysteroscopic permanent contraception and 5 reported pregnancies after laparoscopic permanent contraception (OR, 1.3; 95% CI, 0.3-5.6).
Finnish researchers also find high reoperation rate
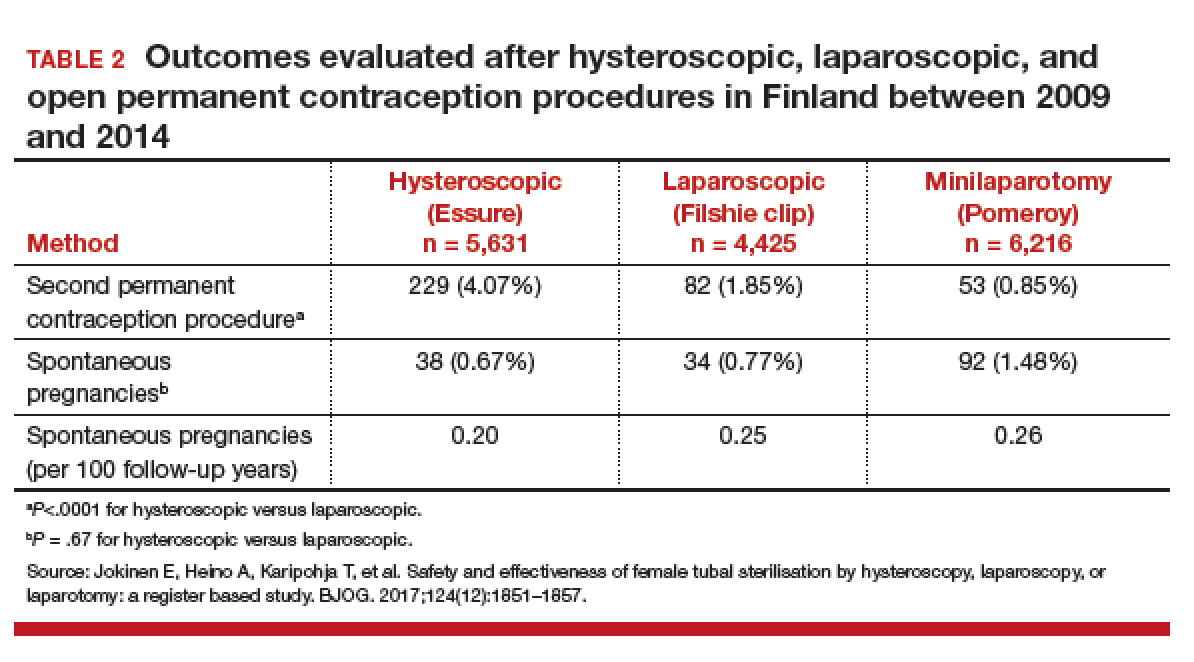
Jokinen and colleagues used linked national database registries in Finland to capture data on pregnancy rate and reoperations among 16,272 women who underwent permanent contraception procedures between 2009 and 2014. The authors compared outcomes following hysteroscopic (Essure), laparoscopic (Filshie clip), and postpartum minilaparotomy (Pomeroy) permanent contraception techniques. According to the investigators, the latter method was almost exclusively performed at the time of cesarean delivery. While there was no difference in pregnancy rates, second permanent contraception procedures were significantly greater in the hysteroscopic group compared with the laparoscopic group (TABLE 2).
At a glance, these studies suggest that pregnancy rates are similar between hysteroscopic and laparoscopic permanent contraceptive approaches. But, these low failure rates were only achieved after including women who required reoperation or a second permanent contraceptive procedure. All 3 European studies showed a high follow-up rate; as method failure was identified, additional procedures were offered and performed when desired. These rates are higher than typically reported in US studies. None of the studies included discussion about the proportion of women with failed procedures who declined a second permanent contraceptive surgery. Bouillon et al26 reported a slight improvement in perioperative safety for a hysteroscopic procedure compared with a laparoscopic procedure. While severity of complications was not reported, the risk of reoperation for laparoscopic procedures remained <1%. By contrast, based on the evidence presented here, hysteroscopic permanent contraceptive methods required a second procedure for 4% to 8% of women, most of whom underwent a laparoscopic procedure. Thus, the slight potential improvement in safety of hysteroscopic procedures does not offset the significantly lower efficacy of the method.