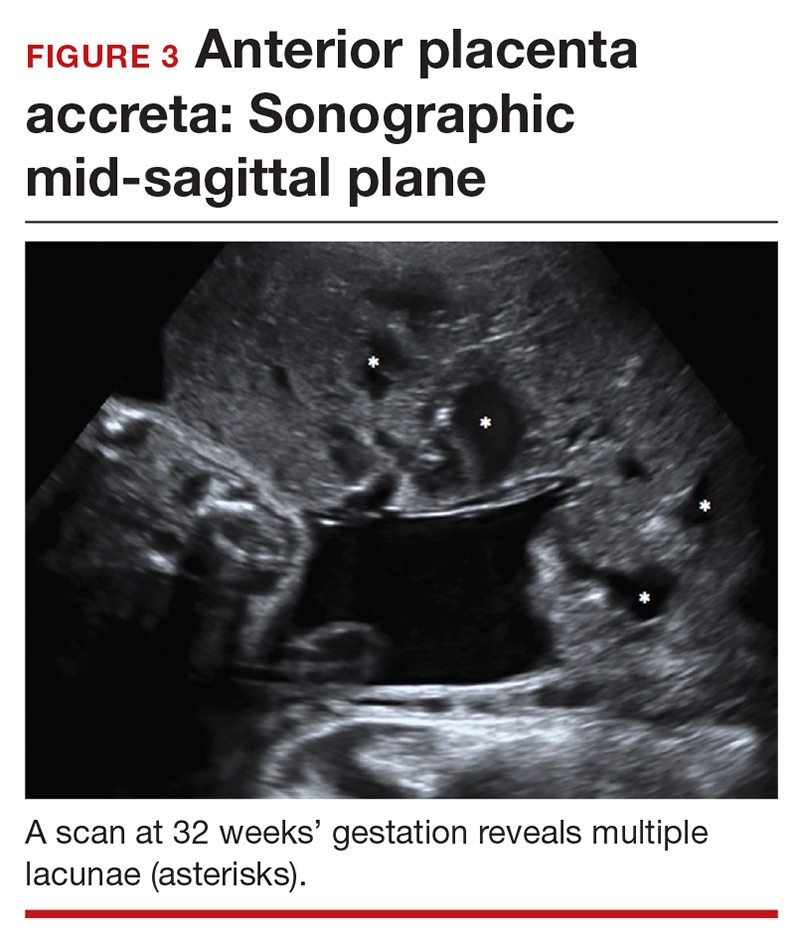
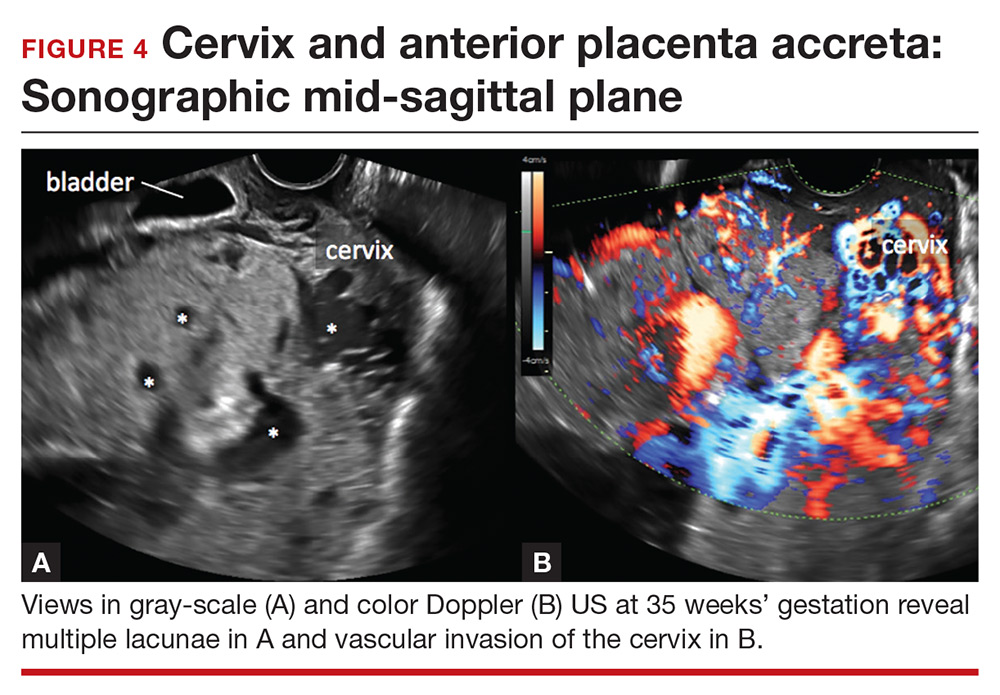
Lacunae. The finding of multiple hypoechoic vascular spaces within the placental parenchyma has been associated with PAS (FIGURES 3 and 4). The pathogenesis of this finding is probably related to alterations in placental tissue resulting from long-term exposure to pulsatile blood flow.11
Finberg and colleagues introduced a grading system for placental lacunae in 1992 that is still used:
- Grade 0: no lacunae seen
- Grade 1: 1 to 3 lacunae seen
- Grade 2: 4 to 6 lacunae seen
- Grade 3: multiple lacunae seen throughout the placenta.12
The sensitivity and specificity of lacunae as an independent marker for PAS have been reported to be 77% and 95%, respectively.13 Despite these findings, several studies report a range of sensitivity (73% to 100%) and negative predictive value (88% to 100%).14 Even in Finberg’s original work, 27% of cases of confirmed PAS had Grade 0 or Grade 1 placental lacunae and 11% of cases of placenta previa, without PAS, demonstrated Grade 2 lacunae.12 There is agreement, however, that, the more lacunae, the higher the risk of PAS.
Continue to: Other US markers for PAS