Lichen sclerosus
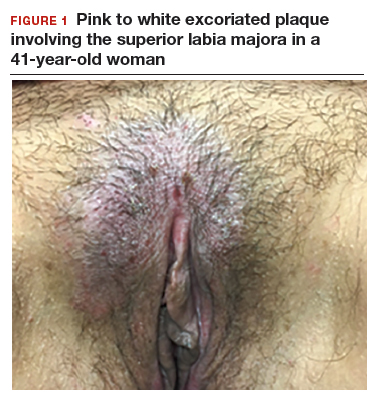
Lichen sclerosus is an inflammatory skin disease that primarily affects the genital and perianal skin of postmenopausal women. The mean age of onset is the mid- to late 50s; fewer than 15% of lichen sclerosus cases present in children.1,2 Case 1 represents presentation of vulvar lichen sclerosus in a premenopausal woman, which is uncommon.
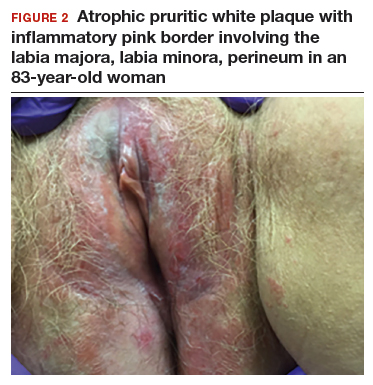
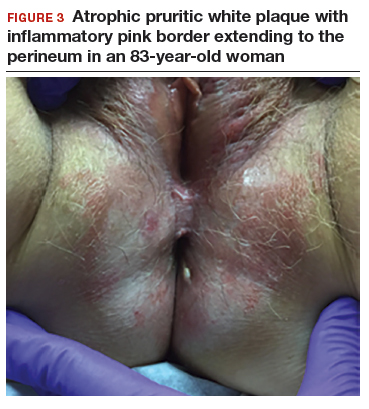
The classic presentation of lichen sclerosus is a well-defined white, atrophic plaque with a wrinkled surface appearance located on the vulva, perineum, and perianal skin. Less commonly, examination may reveal white papules and macules, pallor with overlying edema, or hyperpigmentation. Loss of labia minora tissue and phimosis of the clitoral hood also are often present in patients with untreated lichen sclerosus.
Additionally, secondary changes, such as erosions, fissuring, and blisters, can be seen on examination. The most frequent symptom associated with lichen sclerosus is intense itching of the affected area. Other symptoms include dyspareunia, dysuria, sexual dysfunction, and bleeding. Occasionally, lichen sclerosus is asymptomatic.1 Like other autoimmune conditions, lichen sclerosus may persist indefinitely, highlighting the importance of effective treatment.
How should we evaluate and treat patients with these symptoms?
Perform a skin biopsy and start treatment with very high–potency topical corticosteroid ointment daily for at least 6 weeks.
Skin biopsy. Definitive diagnosis of lichen sclerosus is made based on a skin biopsy. Because treatment can impact the interpretation of a skin biopsy, a biopsy is optimally performed prior to treatment initiation.
The patient in Case 1 underwent biopsy of the left labia majora. Results were consistent with early lichen sclerosus. The patient in Case 2 was reluctant to proceed with vulvar biopsy.
A biopsy specimen should be taken from the affected area that is most white in appearance.1
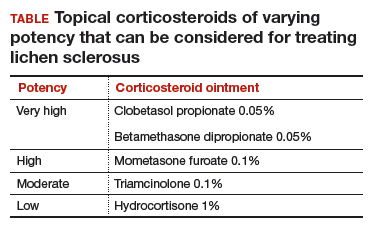
Topical treatment. To induce remission, twice-daily application of very high–potency topical corticosteroid ointment to the affected area for at least 6 weeks is recommended. Once the skin color and texture have normalized, the topical corticosteroid strength (and frequency of application) can slowly be reduced to the lowest potency/frequency at which the patient remains in remission. Examples of very high–, high-, moderate-, and low-potency corticosteroid ointments are listed in the TABLE.
Follow-up. Evaluate the patient every 3 months until the topical steroid potency remains stable and the skin appearance is normal.
Treat early, and aggressively, to prevent complications
Early diagnosis and aggressive intervention are important in managing this disease process. If diagnosis and treatment are delayed, significant scarring and deformation of the vulva can occur.1
Neoplastic transformation of lichen sclerosus into vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia and squamous cell carcinoma can occur (mean incidence, 2.8%). However, the literature reports significant variability in the incidence, ranging between 0% and 31%.3 Published reports support decreased scarring and future development of malignancies in patients who adhere to treatment recommendations.4
Symptoms resolved
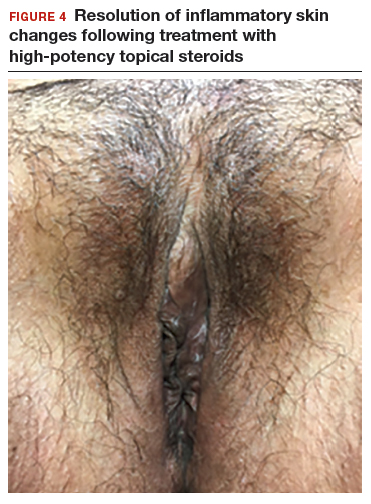
In both cases described here, the patients were treated with clobetasol 0.05% ointment twice daily for 6 weeks. Both women reported complete resolution of pruritus after treatment. As can be seen in the posttreatment photo of the patient described in Case 1, her vulvar inflammation resolved (FIGURE 4).
These cases represent the varied exam findings in patients experiencing vulvar pruritus with early (Case 1) versus more advanced (Case 2) lichen sclerosus. In addition, they underscore that appropriate evaluation and management of lichen sclerosus can produce excellent treatment results.