Shaving excision
The most conservative approach to resection of bowel endometriosis is shaving excision; this involves removing endometriotic tissue layer-by-layer until healthy, underlying tissue is encountered.2 With bowel endometriosis, the goal of shaving excision is to remove as much of the diseased tissue as possible while leaving behind the mucosal layer and a portion of the muscularis.2,15,16,36-38 This is the most conservative of the 3 surgical techniques and is associated with the lowest complication rate.2,14,15,36,37
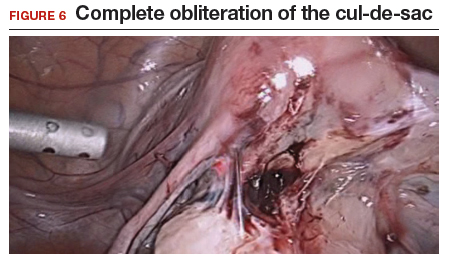
Our group reported on 185 women who underwent shaving excision for bowel endometriosis. At the time of surgery, 80 women had complete obliteration of the cul-de-sac (FIGURE 6). Of the study patients, 174 patients were available for follow-up, with 93% reporting moderate to complete pain relief.15
In a retrospective analysis of 3,298 surgeries for rectovaginal endometriosis in which shaving excision was used on all but 1% of patients, Donnez and colleagues reported a very low complication rate, with 1 case of rectal perforation, 1 case of fecal peritonitis, and 3 cases of ureteral injury.39
Roman and colleagues described the use of shaving excision for rectal endometriosis using plasma energy (n = 54) and laparoscopic scissors (n = 68).40 Only 4% of patients reported experiencing symptom recurrence, and the pregnancy rate was 65.4%, with 59% of those patients spontaneously conceiving. Two cases of rectal fistula were noted.
Disc resection
Laparoscopic disc excision has been described in the literature since the 1980s, and the technique involves the full-thickness removal of the diseased portion of the bowel, followed by closure of the remaining defect.2,12-14,28,29,31,41-45 To be appropriate for this technique, a lesion should involve only a portion of the bowel wall and, preferably, less than one-half of the bowel circumference.2,42 Disc excision results in excellent outcomes with fewer postoperative complications than segmental resection, but with more complications when compared to shaving excision.2,12,13,29,45,46
We reported on a series of 141 women with bowel endometriosis who underwent disc excision.2 At 1-month follow-up, 87% of patients experienced an improvement in their symptoms. No cases required conversion to laparotomy or were complicated by rectovaginal fistula formation, ureteral injury, bowel perforation, or pelvic abscess.2
Continue to: Segmental resection...