Risks, contraindications, and breastfeeding impact
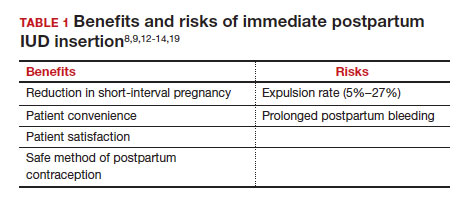
What are the risks of immediate postpartum IUD placement? The highest risk of IUD placement in the immediate postpartum period appears to be expulsion (TABLE 1). In a meta-analysis conducted in 2022, which looked at 11 studies of immediate IUD insertion, the rates of expulsion were between 5% and 27%.3,8,12,13 Results of a study by Cohen and colleagues demonstrated that most expulsions occurred within the first 12 weeks following delivery; of those expulsions that occurred, only 11% went unrecognized.13 Immediate postpartum IUD insertion does not increase the IUD-associated risks of perforation, infection, or immediate postpartum bleeding (although prolonged bleeding may be more common).12
Are there contraindications to placing an IUD immediately postpartum? The main contraindication to immediate postpartum IUD use is peripartum infection, including Triple I, endomyometritis, and puerperal sepsis. Other contraindications include retained placenta requiring manual or surgical removal, uterine anomalies, and other medical contraindications to IUD use as recommended by the US Medical Eligibility Criteria.14
Does immediate IUD placement affect breastfeeding? There is theoretical risk of decreased milk supply or difficulty breastfeeding with initiation of progestin-only methods of contraception in the immediate postpartum period, as the rapid fall in progesterone levels initiates lactogenesis. However, progestin-only methods appear to have limited effect on initiation and continuation of breastfeeding in the immediate postpartum period.15
There were 2 secondary analyses of a pair of RCTs comparing immediate and delayed postpartum IUD use. Results from Levi and colleagues demonstrated no difference between immediate and interval IUD placement groups in the proportion of women who were breastfeeding at 6, 12, and 24 weeks.16 Chen and colleagues’ study was smaller; researchers found that women with interval IUD placement were more likely to be exclusively breastfeeding and continuing to breastfeed at 6 months compared with the immediate postpartum group.17
To better characterize the impact of progestin implants, in a recent meta-analysis, authors examined the use of subcutaneous levonorgestrel rods and found no difference in breastfeeding initiation and continuation rates between women who had them placed immediately versus 6 ̶ 8 weeks postpartum.12
Benefits of immediate postpartum IUD placement
One benefit of immediate postpartum IUD insertion is a reduction in short-interval pregnancies. In a study by Cohen and colleagues13 of young women aged 13 to 22 years choosing immediate postpartum IUDs (82) or implants (162), the authors found that 61% of women retained their IUDs at 12 months postpartum. Because few requested IUD removal over that time frame, the discontinuation rate at 1 year was primarily due to expulsions. Pregnancy rates at 1 year were 7.6% in the IUD group and 1.5% in the implant group. However, the 7.6% rate in the IUD group was lower than in previously studied adolescent control groups: 18.6% of control adolescents (38 of 204) using a contraceptive form other than a postpartum etonogestrel implant had repeat pregnancy at 1 year.13,18
Not only are patients who receive immediate postpartum IUDs more likely to receive them and continue their use, but they are also satisfied with the experience of receiving the IUD and with the method of contraception. A small mixed methods study of 66 patients demonstrated that women were interested in obtaining immediate postpartum contraception to avoid some of the logistical and financial challenges of returning for a postpartum visit. They also felt that the IUD placement was less painful than expected, and they didn’t feel that the insertion process imposed on their birth experience. Many described relief to know that they had a safe and effective contraceptive method upon leaving the hospital.19 Other studies have shown that even among women who expel an IUD following immediate postpartum placement, many choose to replace it in order to continue it as a contraceptive method.8,9,13
Continue to: Instructions for placement...