Instructions for placement
1. Counsel appropriately. Thoroughly counsel patients regarding their options for postpartum contraception, with emphasis on the benefits, risks, and contraindications. Current recommendations to reduce the risk of expulsion are to place the IUD in the delivery room or operating room within 10 minutes of placental delivery.
2. Post ̶ vaginal delivery. Following vaginal delivery, remove the IUD from the inserter, cut the strings to 10 cm and, using either fingers to grasp the wings of the IUD or ring forceps, advance the IUD to the fundus. Ultrasound guidance may be used, but it does not appear to be helpful in preventing expulsion.20
3. Post ̶ cesarean delivery. Once the placenta is delivered, place the IUD using the inserter or a ring forceps at the fundus and guide the strings into the cervix, then close the hysterotomy.
ACOG does recommend formal trainingbefore placing postpartum IUDs. One resource they provide is a free online webinar (https://www.acog.org/education-and-events/webinars/long-acting-reversible-contra ception-overview-and-hands-on-practice-for-residents).3
CASE 1 Resolved
The patient was counseled in the office about her options, and she was most interested in immediate postpartum LNG-IUD placement. She went on to deliver a healthy baby vaginally at 39 weeks. Within 10 minutes of placental delivery, she received an LNG-IUD. She returned to the office 3 months later for STI screening; her examination revealed correct placement and no evidence of expulsion. She expressed that she was happy with her IUD and thankful that she was able to receive it immediately after the birth of her baby.
CASE 2 Nulliparous woman desires IUD for postpartum contraception
A 33-year-old nulliparous woman presents in the third trimester for a routine prenatal visit. She had used the LNG-IUD prior to getting pregnant and reports that she was very happy with it. She knows she wants to wait at least 2 years before trying to get pregnant again, and she would like to resume contraception as soon as it is reasonably safe to do so. She has read that it is possible to get an IUD immediately postpartum and asks about it as a possible option.
What barriers will she face in obtaining an immediate postpartum IUD?
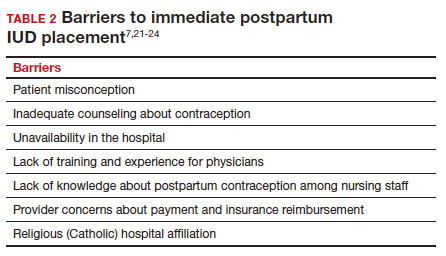
There are many barriers for patients who may be good candidates for immediate postpartum contraception (TABLE 2). Many patients are unaware that it is a safe option, and they often have concerns about such risks as infection, perforation, and effects on breastfeeding. Additionally, providers may not prioritize adequate counseling about postpartum contraception when they face time constraints and a need to counsel about other pregnancy-related topics during the prenatal visit schedule.7,21
System, hospital, and clinician barriers to immediate postpartum IUD use
Hospital implementation of a successful postpartum IUD program requires pharmacy, intrapartum and postpartum nursing staff, physicians, administration, and billing to be aligned. Hospital administration and pharmacists must stock IUDs in the pharmacy. Hospital nursing staff attitudes toward and knowledge of postpartum contraception can have profound influence on how they discuss safe and effective methods of postpartum contraception with patients who may not have received counseling during prenatal care.22 In a survey of 108 ACOG fellows, nearly 75% of ObGyn physicians did not offer immediate postpartum IUDs; lack of provider training, lack of IUD availability, and concern about cost and payment were found to be common reasons why.21 Additionally, Catholic-affiliated and rural institutions are less likely to offer it, whereas more urban, teaching hospitals are more likely to have programs in place.23 Prior to 2012, immediate postpartum IUD insertions and device costs were part of the global Medicaid obstetric fee in most states, and both hospital systems and individual providers were concerned about loss of revenue.23
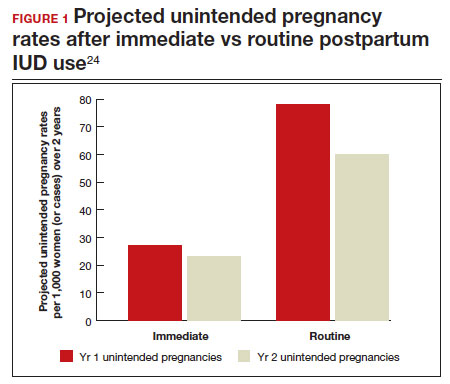
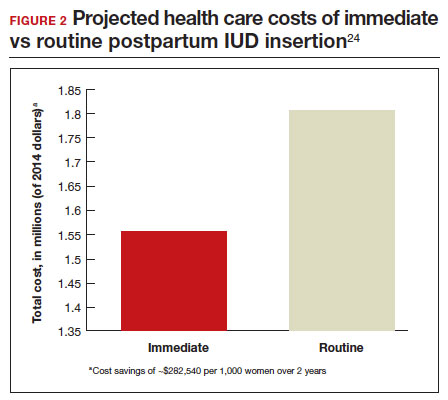
In 2015, Washington and colleagues published a decision analysis that examined the cost-effectiveness and cost savings associated with immediate postpartum IUD use. Accounting for expulsion rates, they found that immediate postpartum IUD placement can save $282,540 per 1,000 women over 2 years; additionally, immediate postpartum IUD use can prevent 88 unintended pregnancies per 1,000 women over 2 years.24 Not only do immediate postpartum IUDs have great potential to prevent individual patients from undesired short-interval pregnancies (FIGURE 1), but they can also save the system substantial health care dollars (FIGURE 2).
Overcoming barriers
Immediate postpartum IUD implementation is attainable with practice, policy, and institutional changes. Education and training programs geared toward providers and nursing staff can improve understanding of the benefits and risks of immediate postpartum IUD placement. Additionally, clinicians must provide comprehensive, nondirective counseling during the antepartum period, informing patients of all safe and effective options. Expulsion risks should be disclosed, as well as the benefit of not needing to return for a separate postpartum contraception appointment.
Since 2012, many state Medicaid agencies have decoupled reimbursement for inpatient postpartum IUD insertion from the delivery fee. By 2018, more than half of states adopted this practice. Commercial insurers have followed suit in some cases, and as such, both Medicaid and commercially insured patients have had increased access to immediate postpartum IUDs.23 This has translated into increased uptake of immediate postpartum IUDs among both Medicaid and commercially insured patients. Koch et al conducted a retrospective cohort study comparing IUD use in patients 1 year before and 1 year after the policy changes, and they found a 10-fold increase in use of immediate postpartum IUDs.25
While education, counseling, access, and changes in reimbursement may increase access in many hospital systems, some barriers, such as religious affiliation of the hospital system, may be impossible to overcome. A viable alternative to immediate postpartum IUD placement may be early postpartum IUD placement, which could allow patients to coordinate this procedure with 1- or 2-week return routine postpartum visits for CD recovery, mental health screenings, and/or well-baby visits. More data are necessary before recommending this universally, but Averbach and colleagues published a promising meta-analysis that demonstrated no complete expulsions in studies in which IUDs were placed between 2 and 4 weeks postpartum, and only a pooled partial expulsion rate (of immediate postpartum, early inpatient, early outpatient, and interval placement) of 3.7%.4
CASE 2 Resolved
Although the patient was interested in receiving a postpartum LNG-IUD immediately after her vaginal birth, she had to wait until her 6-week postpartum visit. The hospital did not stock IUDs for immediate postpartum IUD use, and her provider, having not been trained on immediate postpartum insertion, did not feel comfortable trying to place it in the immediate postpartum time frame. ●
- Immediate postpartum IUD insertion is a safe and effective method for postpartum contraception for many postpartum women.
- Immediate postpartum IUD insertion can result in increased uptake of postpartum contraception, a reduction in short interval pregnancies, and the opportunity for patients to plan their ideal family size.
- Patients should be thoroughly counseled about the safety of IUD placement and risks of expulsion associated with immediate postpartum placement.
- Successful programs for immediate postpartum IUD insertion incorporate training for providers on proper insertion techniques, education for nursing staff about safety and counseling, on-site IUD supply, and reimbursement that is decoupled from the payment for delivery.