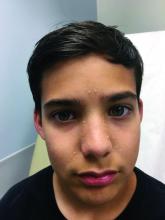
A shave biopsy of one of the lesions was performed that showed a proliferation of nests of basaloid cells on the dermis with palisading and rare vacuolated clear cell change. A rare ductal structure with luminal proteinaceous contents was noted. The findings were consistent with a trichoepithelioma.
Trichoepitheliomas are rare, benign, adnexal skin tumors that can start in early childhood or during puberty. The lesions are most commonly seen in girls as skin color papules on the face, and sometimes on the trunk and the neck. Trichoepitheliomas can appear as a benign single lesion nonfamilial form or as a familial form with multiple lesions.1 Brooke-Spiegler syndrome (BSS) is a rare autosomal dominant condition where affected individuals have multiple trichoepitheliomas, cylindromas, and spiradenomas. Depending on the predominant type of lesion, phenotypic variants include multiple familial trichoepithelioma type 1 and familial cylindromatosis.2 BSS is caused by mutations within CYLD, a tumor-suppressor gene located on chromosome 16q12-q13.3 Our patient presented only with trichoepitheliomas with no other lesions on the scalp, neck, or torso.
Multiple trichoepitheliomas also can be seen in other syndromes including Rombo syndrome, which is characterized by basal cell carcinomas, milia, hypotrichosis, distal vasodilation, and atrophoderma vermiculata; none seen in our patient. Bazex-Dupré-Christol syndrome is an X-linked dominant condition in which affected individuals can present with multiple trichoepitheliomas, as well as milia, hypotrichosis, follicular atrophoderma, and basal cell carcinomas.
The differential diagnosis of skin color papules on the central face on a child should include acne, flat warts, and angiofibromas seen in tuberous sclerosis. Our patient’s lesions were monomorphous, and there were no comedones, pustules, or inflammatory papules characteristic of acne.
He had warts on his hands which could make it suspicious for the face lesions to be verrucous in nature. Flat warts also present as skin color papules, but characteristically are flat, not round and shiny as our patient’s lesions were. Angiofibromas, as seen in individuals with tuberous sclerosis, also can start at an early age in the same location as trichoepitheliomas in BSS, but clinically the lesions are pinker and redder rather than the skin-color, round shape papules characteristic of trichoepitheliomas. Patients may have other findings suggestive of tuberous sclerosis including confetti hypopigmentation, ash leaf spots, shagreen patch, and a history of seizures or developmental delay – none of which were present in our patient. Children with basal cell nevus syndrome can present with skin color to shiny telangiectatic papules (basal cell carcinomas) that can be single or multiple on the face, chest, and back. The lesions usually are not seen in clusters around the nose and central face as seen in patients with BSS. Patients with basal cell nevus syndrome can develop jaw bone cysts, brain tumors (medulloblastoma), and fibromas on the heart or ovaries, palmar pits and be macrocephalic.4
Trichoepitheliomas usually are treated surgically but other nonsurgical removing techniques include laser resurfacing, curettage, and electrocautery.5 Malignant transformation can occur in 5%-10% of the individuals and should be managed by a multidisciplinary team. Topical treatment with sirolimus previously has been reported to be effective in young patients.6
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Matiz at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018 Jun;26(2):162-5.
2. Eur J Med Genet. 2015;58(5):271-8.
3. Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36(11):868-74.
4. Int J Dermatol. 2016 Apr;55(4):367-75.
5. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46(6):583-6.
6. Dermatol Ther. 2017 Mar. doi: 10.1111/dth.12458.