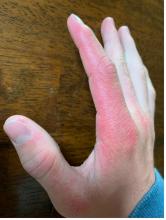
Photosensitivity due to doxycycline
As the patient’s rash presented in sun-exposed areas with both skin and nail changes, our patient was diagnosed with a phototoxic reaction to doxycycline, the oral antibiotic used to treat his acne.
Photosensitive cutaneous drug eruptions are reactions that occur after exposure to a medication and subsequent exposure to UV radiation or visible light. Reactions can be classified into two ways based on their mechanism of action: phototoxic or photoallergic.1 Phototoxic reactions are more common and are a result of direct keratinocyte damage and cellular necrosis. Many classes of medications may cause this adverse effect, but the tetracycline class of antibiotics is a common culprit.2 Photoallergic reactions are less common and are a result of a type IV immune reaction to the offending agent.1
Phototoxic reactions generally present shortly after sun or UV exposure with a photo-distributed eruption pattern.3 Commonly involved areas include the face, the neck, and the extensor surfaces of extremities, with sparing of relatively protected skin such as the upper eyelids and the skin folds.2 Erythema may initially develop in the exposed skin areas, followed by appearance of edema, vesicles, or bullae.1-3 The eruption may be painful and itchy, with some patients reporting severe pain.3
Doxycycline phototoxicity may also cause onycholysis of the nails.2 The reaction is dose dependent, with higher doses of medication leading to a higher likelihood of symptoms.1,2 It is also more prevalent in patients with Fitzpatrick skin type I and II. The usual UVA wavelength required to induce this reaction appears to be in the 320-400 nm range of the UV spectrum.4 By contrast, photoallergic reactions are dose independent, and require a sensitization period prior to the eruption.1 An eczematous eruption is most commonly seen with photoallergic reactions.3
Treatment of drug-induced photosensitivity reactions requires proper identification of the diagnosis and the offending agent, followed by cessation of the medication. If cessation is not possible, then lowering the dose can help to minimize worsening of the condition. However, for photoallergic reactions, the reaction is dose independent so switching to another tolerated agent is likely required. For persistent symptoms following medication withdrawal, topical or systemic steroids and oral antihistamine can help with symptom management.1 For patients with photo-onycholysis, treatment involves stopping the medication and waiting for the intact nail plate to grow.
Prevention is key in the management of photosensitivity reactions. Patients should be counseled about the increased risk of photosensitivity while on tetracycline medications and encouraged to engage in enhanced sun protection measures such as wearing sun protective hats and clothing, increasing use of sunscreen that provides mainly UVA but also UVB protection, and avoiding the sun during the midday when the UV index is highest.1-3
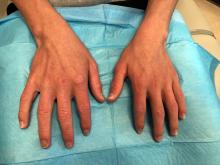
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune condition that presents with skin lesions as well as systemic findings such as myositis. The cutaneous findings are variable, but pathognomonic findings include Gottron papules of the hands, Gottron’s sign on the elbows, knees, and ankles, and the heliotrope rash of the face. Eighty percent of patients have myopathy presenting as muscle weakness, and commonly have elevated creatine kinase, aspartate transaminase, and alanine transaminase values.5 Diagnosis may be confirmed through skin or muscle biopsy, though antibody studies can also play a helpful role in diagnosis. Treatment is generally with oral corticosteroids or other immunosuppressants as well as sun protection.6 The rash seen in our patient could have been seen in patients with dermatomyositis, though it was not in the typical location on the knuckles (Gottron papules) as it also affected the lateral sides of the fingers.