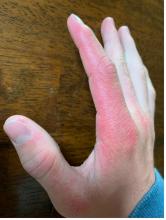
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune condition characterized by systemic and cutaneous manifestations. Systemic symptoms may include weight loss, fever, fatigue, arthralgia, or arthritis; patients are at risk of renal, cardiovascular, pulmonary, and neurologic complications of SLE.7 The most common cutaneous finding is malar rash, though there are myriad dermatologic manifestations that can occur associated with photosensitivity. Diagnosis is made based on history, physical, and laboratory testing. Treatment options include NSAIDs, oral glucocorticoids, antimalarial drugs, and immunosuppressants.7 Though our patient exhibited photosensitivity, he had none of the systemic findings associated with SLE, making this diagnosis unlikely.
Allergic contact dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, and may present as acute, subacute, or chronic dermatitis. The clinical findings vary based on chronicity. Acute ACD presents as pruritic erythematous papules and vesicles or bullae, similar to how it occurred in our patient, though our patient’s lesions were more tender than pruritic. Chronic ACD presents with erythematous lesions with pruritis, lichenification, scaling, and/or fissuring. Observing shapes or sharp demarcation of lesions may help with diagnosis. Patch testing is also useful in the diagnosis of ACD.
Treatment generally involves avoiding the offending agent with topical corticosteroids for symptom management.8
Polymorphous light eruption
Polymorphous light eruption (PLE) is a delayed, type IV hypersensitivity reaction to UV-induced antigens, though these antigens are unknown. PLE presents hours to days following solar or UV exposure and presents only in sun-exposed areas. Itching and burning are always present, but lesion morphology varies from erythema and papules to vesico-papules and blisters. Notably, PLE must be distinguished from drug photosensitivity through history. Treatment generally involves symptom management with topical steroids and sun protective measures for prevention.9 While PLE may present similarly to drug photosensitivity reactions, our patient’s use of a known phototoxic agent makes PLE a less likely diagnosis.
Ms. Appiah is a pediatric dermatology research associate and medical student at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Neither Dr. Matiz nor Ms. Appiah has any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Montgomery S et al. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40(1):57-63.
2. Blakely KM et al. Drug Saf. 2019;42(7):827-47.
3. Goetze S et al. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2017;30(2):76-80.
4. Odorici G et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34(4):e14978.
5. DeWane ME et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):267-81.
6. Waldman R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):283-96.
7. Kiriakidou M et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(11):ITC81-ITC96.
8. Nassau S et al. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(1):61-76.
9. Guarrera M. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;996:61-70.