Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
One of the more baffling decisions the CDC made during this pandemic was when they reduced the duration of isolation after a positive COVID test from 10 days to 5 days and did not require a negative antigen test to end isolation.
Multiple studies had suggested, after all, that positive antigen tests, while not perfect, were a decent proxy for infectivity. And if the purpose of isolation is to keep other community members safe, why not use a readily available test to know when it might be safe to go out in public again?
Also, 5 days just wasn’t that much time. Many individuals are symptomatic long after that point. Many people test positive long after that point. What exactly is the point of the 5-day isolation period?
We got some hard numbers this week to show just how good (or bad) an arbitrary-seeming 5-day isolation period is, thanks to this study from JAMA Network Open, which gives us a low-end estimate for the proportion of people who remain positive on antigen tests, which is to say infectious, after an isolation period.
This study estimates the low end of postisolation infectivity because of the study population: student athletes at an NCAA Division I school, which may or may not be Stanford. These athletes tested positive for COVID after having at least one dose of vaccine from January to May 2022. School protocol was to put the students in isolation for 7 days, at which time they could “test out” with a negative antigen test.
Put simply, these were healthy people. They were young. They were athletes. They were vaccinated. If anyone is going to have a brief, easy COVID course, it would be them. And they are doing at least a week of isolation, not 5 days.
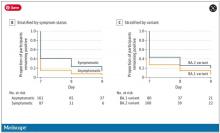
So – isolation for 7 days. Antigen testing on day 7. How many still tested positive? Of 248 individuals tested, 67 (27%) tested positive. One in four.
More than half of those positive on day 7 tested positive on day 8, and more than half of those tested positive again on day 9. By day 10, they were released from isolation without further testing.
So, right there .
There were some predictors of prolonged positivity.
Symptomatic athletes were much more likely to test positive than asymptomatic athletes.
And the particular variant seemed to matter as well. In this time period, BA.1 and BA.2 were dominant, and it was pretty clear that BA.2 persisted longer than BA.1.
This brings me back to my original question: What is the point of the 5-day isolation period? On the basis of this study, you could imagine a guideline based on symptoms: Stay home until you feel better. You could imagine a guideline based on testing: Stay home until you test negative. A guideline based on time alone just doesn’t comport with the data. The benefit of policies based on symptoms or testing are obvious; some people would be out of isolation even before 5 days. But the downside, of course, is that some people would be stuck in isolation for much longer.
Maybe we should just say it. At this point, you could even imagine there being no recommendation at all – no isolation period. Like, you just stay home if you feel like you should stay home. I’m not entirely sure that such a policy would necessarily result in a greater number of infectious people out in the community.
In any case, as the arbitrariness of this particular 5-day isolation policy becomes more clear, the policy itself may be living on borrowed time.