On hospital Day 6, she develops more severe symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy, with significant altered mental status and inattention. Ms. L is transferred to the ICU, intubated, and placed on the liver transplant list.
On hospital Day 9, she undergoes a liver transplantation.
The authors’ observations
Baseline laboratory testing should have been conducted prior to initiating valproic acid. As Ms. L’s symptoms worsened, better communication with her PCP and closer monitoring after starting valproic acid might have resulted in more immediate care. Early recognition of her symptoms and decompensation may have triggered earlier inpatient admission and/or transfer to a tertiary care facility for observation and treatment. Additionally, repeat laboratory testing and instructions on when to return to the ED should have been provided at Visit 1.
This case demonstrates the need for all clinicians who prescribe valproic acid to remain diligent about the accurate diagnosis of mood and behavioral symptoms, knowing when psychotropic medications are indicated, and carefully considering and discussing even rare, potentially life-threatening adverse effects of all medications with patients.
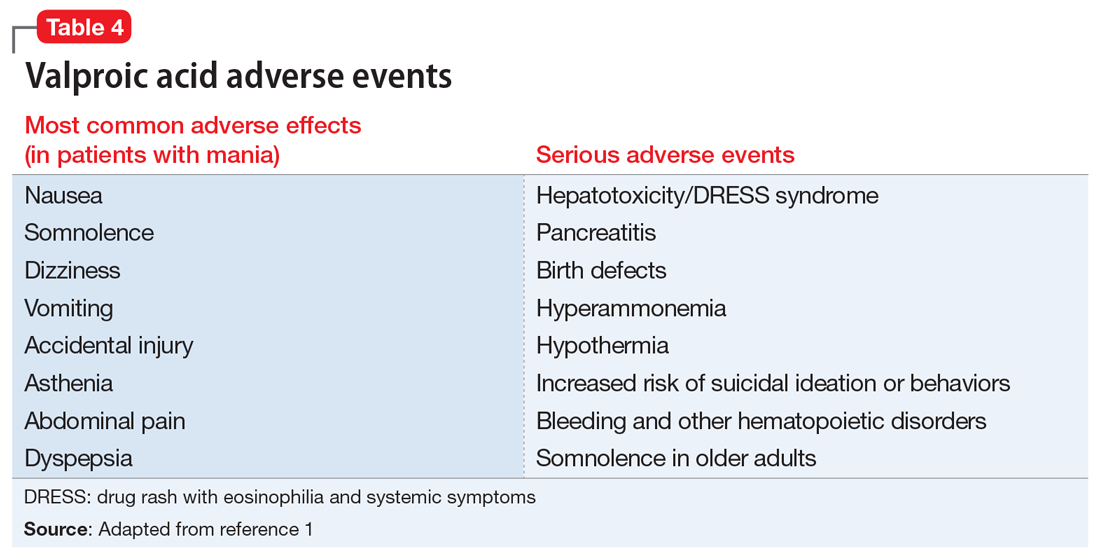
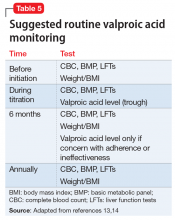
Although rare, after starting valproic acid, a patient may experience a rapid decompensation and life-threatening illness. Ideally, clinicians should closely monitor patients after initiating valproic acid (Table 41). Clinicians must have a clear knowledge of the recommended monitoring and indications for hospitalization and treatment when they note adverse effects such as elevated liver enzymes or transaminitis (Table 513,14). Even after stopping valproic acid, patients who have experienced adverse events should be closely monitored to ensure complete resolution.
Continue to: Consider patient-specific factors