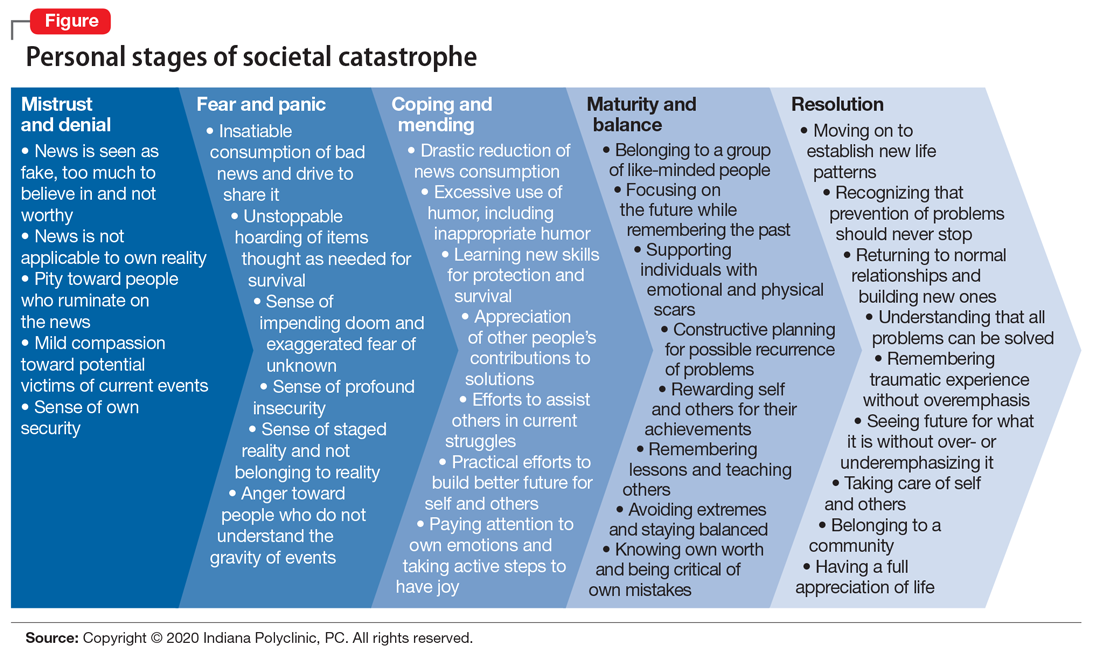
Unprecedented circumstances, extraordinary times, continental shift, life-altering experience—the descriptions of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic have been endless, and accurate. Every clinician who has cared for patients during these trying times has noticed new patterns in patient behavior. Psychiatrists are acutely aware of the emotional, behavioral, and cognitive methods that patients are using to protect themselves from the chaos around them, and the ways in which they process a societal catastrophe such as COVID-19 (Figure). Here are some new patterns I have noticed among my own patients.
Physical and emotional separation
I first noticed the changes in my patients’ behavior at the front desk, where they now spend less time talking with the staff. They bring their own pens for filling out the paperwork, avoid touching items around them, and try to keep social interactions brief and to the point. Patients have been more cooperative about scheduling and rescheduling their appointments. They have generally been nicer to the staff, frequently thanking us for the work we do, and verbalizing their support for health care professionals in general.
Patients have been more supportive of their family members and other patients in the clinic, with some noticeable exceptions, such as maintaining social distancing for their own comfort and safety. Some patients wear face masks not just for safety but also to separate themselves and hide their emotions from the world. This allows them to feel more emotionally secure when interacting with other people.
The use of telehealth has given many patients the security of not having to leave their home, and the decreased need for travel adds to their comfort.
Changes I didn’t expect
The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in some unexpected changes in my patients. Only a minority of my patients have expressed increased anxiety, while most have become less anxious overall on issues other than the pandemic. Many of my patients who have stressful jobs, especially teachers, say they feel more comfortable working from home and have less anxiety and depression because they are removed from their daily stressors. There also has been an increase in patients’ use of humor, including inappropriate humor, to defend against their fear of COVID-19.
Our clinic is a multidisciplinary facility that specializes in integrating mental and physical health treatments for pain, and for some patients, increased anxiety is clearly associated with an increase in pain. However, during the COVID-19 pandemic, patients have recognized this connection and verbalized their concerns. Some somatic patients have had a decrease in their physical symptoms, including chronic pain, because they see that the whole world is not well, which somehow helps to validate their concerns.
The changes in our patients’ psychological well-being will likely continue to morph as we enter a more stable period. The eventual resolution of the pandemic will bring further changes to our patients’ emotional lives. As we go through these times together, we will continue to uncover new ways that our patients will use to defend themselves against stress and adversities.