TREATMENT Adjusting the medication regimen
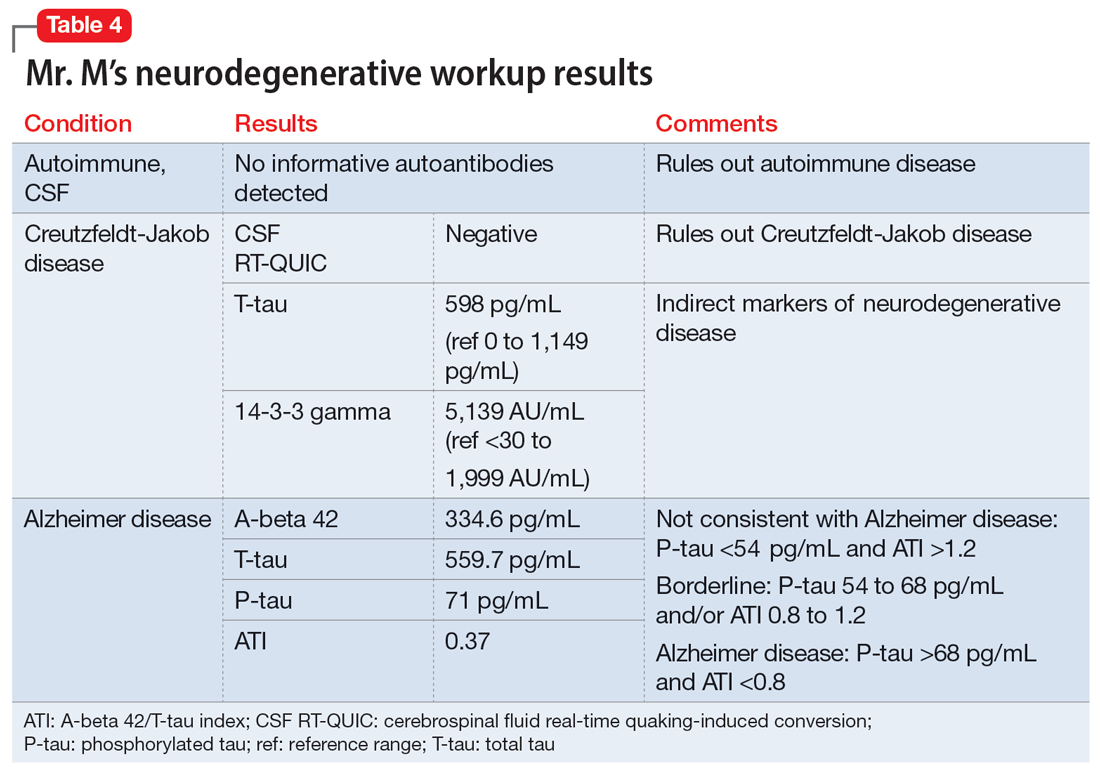
The neurologist completes additional examinations to rule out causes of rare neurodegenerative disorders, including CSF autoimmune disorders, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, and Alzheimer disease (AD) (Table 4). Mr. M continues to follow up with his outpatient psychiatrist and his medication regimen is adjusted. Aripiprazole and buspirone are discontinued, and duloxetine is titrated to 60 mg twice a day. During follow-up visits, Mr. M discusses his understanding of his neurologic condition. His concerns shift to his illness and prognosis. During these visits, he continues to deny suicidality.
The authors’ observations
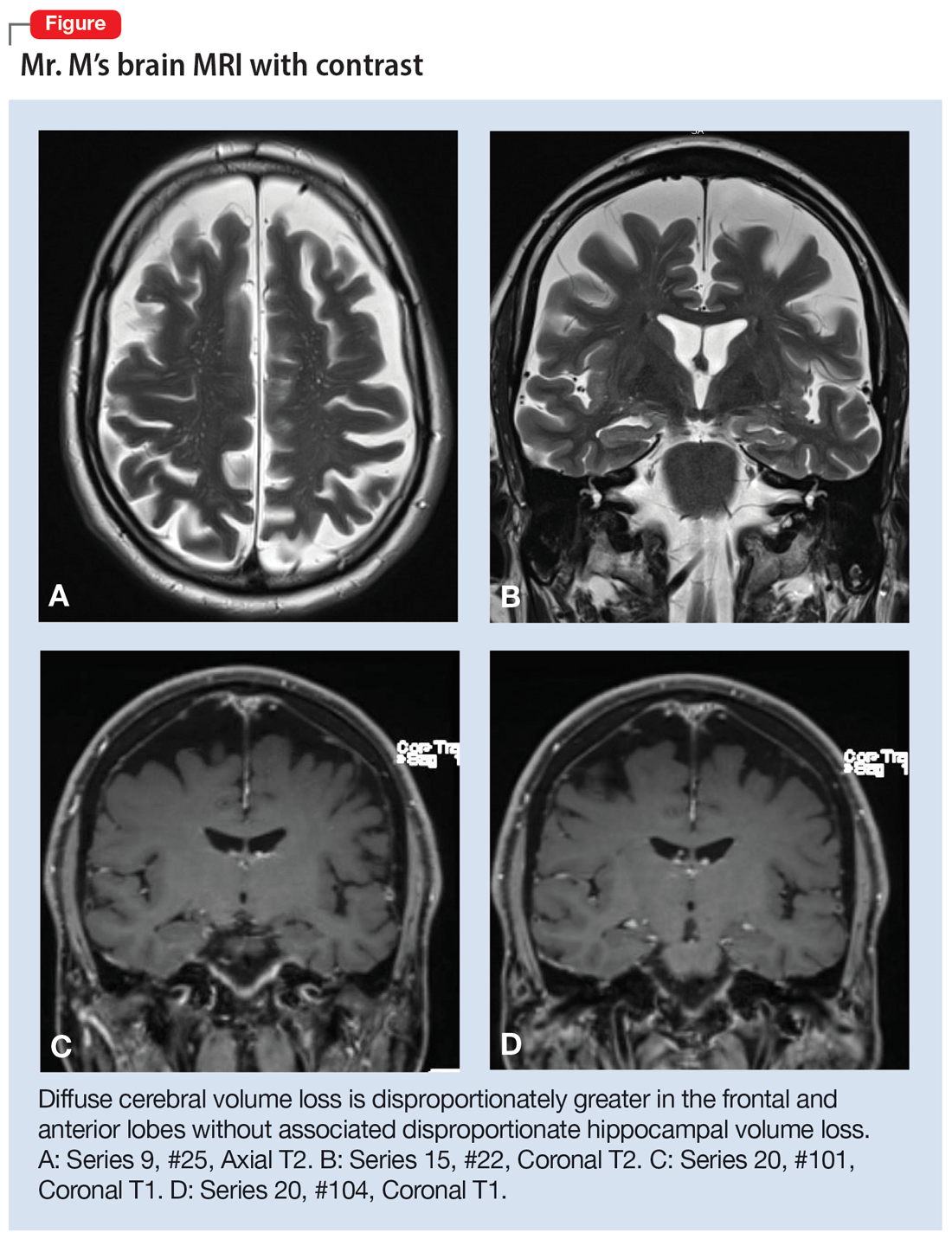
Mr. M’s neurodegenerative workup identified an intriguing diagnostic challenge. A repeat brain MRI (Figure) showed atrophy patterns suggestive of frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD). On the other hand, his CSF ATI (A-beta 42/T-tau index, a value used to aid in the diagnosis of AD) was <1, suggesting early-onset AD.5,6 Although significant advances have been made to distinguish AD and FTLD following an autopsy, there are still no reliable or definitive biomarkers to distinguish AD from FTLD (particularly in the early stages of FTLD). This can often leave the confirmatory diagnosis as a question.7
A PPA diagnosis (and other dementias) can have a significant impact on the patient and their family due to the uncertain nature of the progression of the disease and quality-of-life issues related to language and other cognitive deficits. Early identification and accurate diagnosis of PPA and its etiology (ie, AD vs FTLD) is important to avoid unnecessary exposure to medications or the use of polypharmacy to treat an inaccurate diagnosis of a primary psychiatric illness. For example, Mr. M was being treated with 3 psychiatric medications (aripiprazole, buspirone, and duloxetine) for depression and anxiety prior to the diagnosis of PPA.
Nonpharmacologic interventions can play an important role in the management of patients with PPA. These include educating the patient and their family about the diagnosis and discussions about future planning, including appropriate social support, employment, and finances.4 Pharmacologic interventions may be limited, as there are currently no disease-modifying treatments for PPA or FTLD. For patients with nonfluent PPA or AD, cholinesterase inhibitors such as donepezil or N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists such as memantine may be utilized, though benefits can be limited.4 Recent research has explored the role of transcranial magnetic stimulation and suggest short-term benefits, as have case reports of behavioral interventions targeting language.8
Psychiatrists should continue to treat patients with PPA for comorbid anxiety or depression, with appropriate medications and/or supportive therapy to guide the patient through the process of grief. Assessing for suicide risk is also important in patients diagnosed with dementia. A retrospective cohort study of patients age ≥60 with a diagnosis of dementia suggested that the majority of suicides occurred in those with a new dementia diagnosis.9 End-of-life decisions such as advanced directives should be made when the patient still has legal capacity, ideally as soon as possible after diagnosis.10
OUTCOME Remaining engaged in treatment
Mr. M continues to follow-up with the Neurology team. He has also been regularly seeing his psychiatric team for medication management and supportive therapy, and his psychiatric medications have been optimized to reduce polypharmacy. During his sessions, Mr. M discusses his grief and plans for the future. Despite his anxiety about the uncertainty of his prognosis, Mr. M continues to report that he is doing reasonably well and remains engaged in treatment.
Bottom Line
Patients with primary progressive aphasia and rare neurodegenerative disorders may present to an outpatient or emergency setting with symptoms of anxiety and confusion. They are frequently misdiagnosed with a primary psychiatric disorder due to the nature of cognitive and language deficits, particularly in the early stages of the disease. Paying close attention to language and conducting cognitive screening are critical in identifying the true cause of a patient’s symptoms.
Related Resources
- Primary progressive aphasia. National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center. https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/8541/primary-progressive-aphasia
- Moller MD, Parmenter BA, Lane DW. Neuropsychological testing: A useful but underutilized resource. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(11):40-46,51.
Drug Brand Names
Aripiprazole • Abilify
Donepezil • Aricept
Duloxetine • Cymbalta
Memantine • Namenda