Psychosis
Psychosis can occur in prodromal and early PD but is most common in advanced PD.28 One study reported that 60% of patients developed hallucinations or delusions after 12 years of follow-up.29 Disease duration, disease severity, dementia, and rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder are significant risk factors for psychosis in PD.30 Well-formed visual hallucinations are the most common manifestation of psychosis in patients with PD. Auditory hallucinations and delusions are less common. Delusions are usually seen in patients with dementia and are often paranoid delusions, such as of spousal infidelity.30 Sensory hallucinations can occur, but should not be mistaken with formication, a central pain syndrome in PD that can represent a nonmotor “off” symptom that may respond to dopaminergic medication.31 Other more mild psychotic symptoms include illusions or misinterpretation of stimuli, false sense of presence, and passage hallucinations of fleeting figures in the peripheral vision.30
The pathophysiology of PD psychosis is not entirely understood but differs from psychosis in other disorders. It can occur in the absence of antiparkinsonian medication exposure and is thought to be a consequence of the underlying disease process of PD involving neurodegeneration in certain brain regions and aberrant neurotransmission of not only dopamine but also serotonin, acetylcholine, and glutamate.30
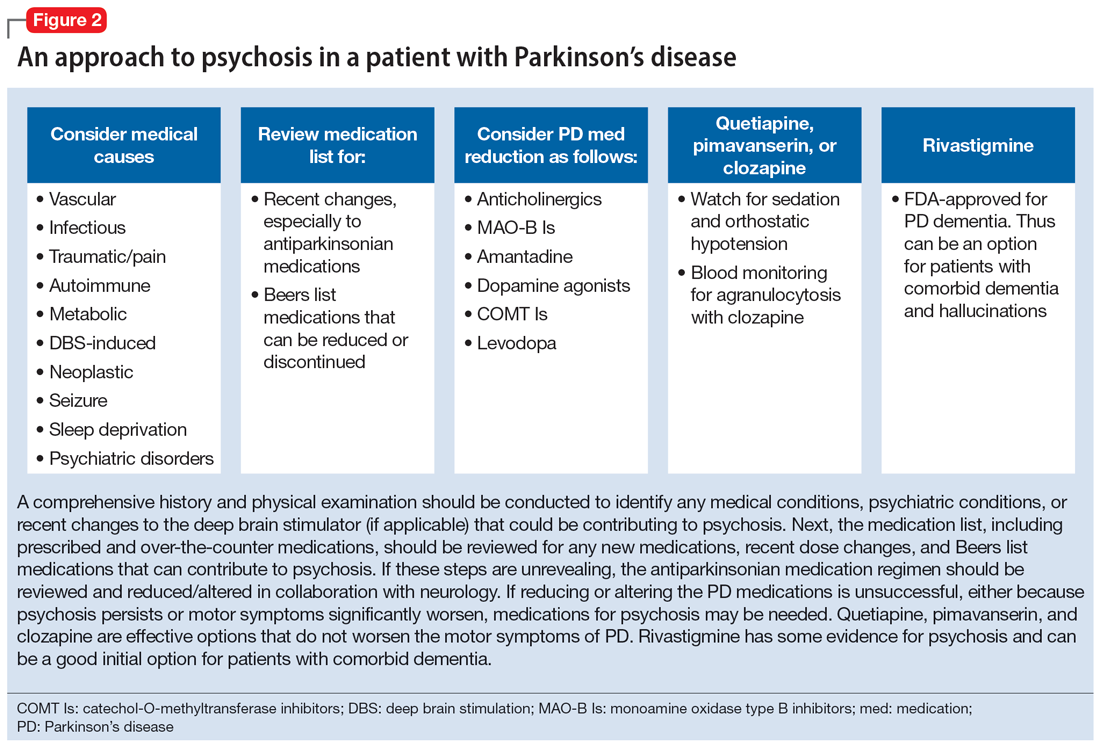
Figure 2 outlines the management of psychosis in PD. After addressing medical and medication-related causes, it is important to determine if the psychotic symptom is sufficiently bothersome to and/or potentially dangerous for the patient to warrant treatment. If treatment is indicated, pimavanserin and clozapine are efficacious for psychosis in PD without worsening motor symptoms, and quetiapine is possibly efficacious with a low risk of worsening motor symptoms.15 Other antipsychotics, such as olanzapine, risperidone, and haloperidol, can substantially worsen motor symptoms.15 Both second-generation antipsychotics and pimavanserin have an FDA black-box warning for a higher risk of all-cause mortality in older patients with dementia; however, because psychosis is associated with early mortality in PD, the risk/benefit ratio should be discussed with the patient and family for shared decision-making.30 If the patient also has dementia, rivastigmine—which is FDA-approved for PD dementia (PDD)—may also improve hallucinations.32
Cognitive disorders
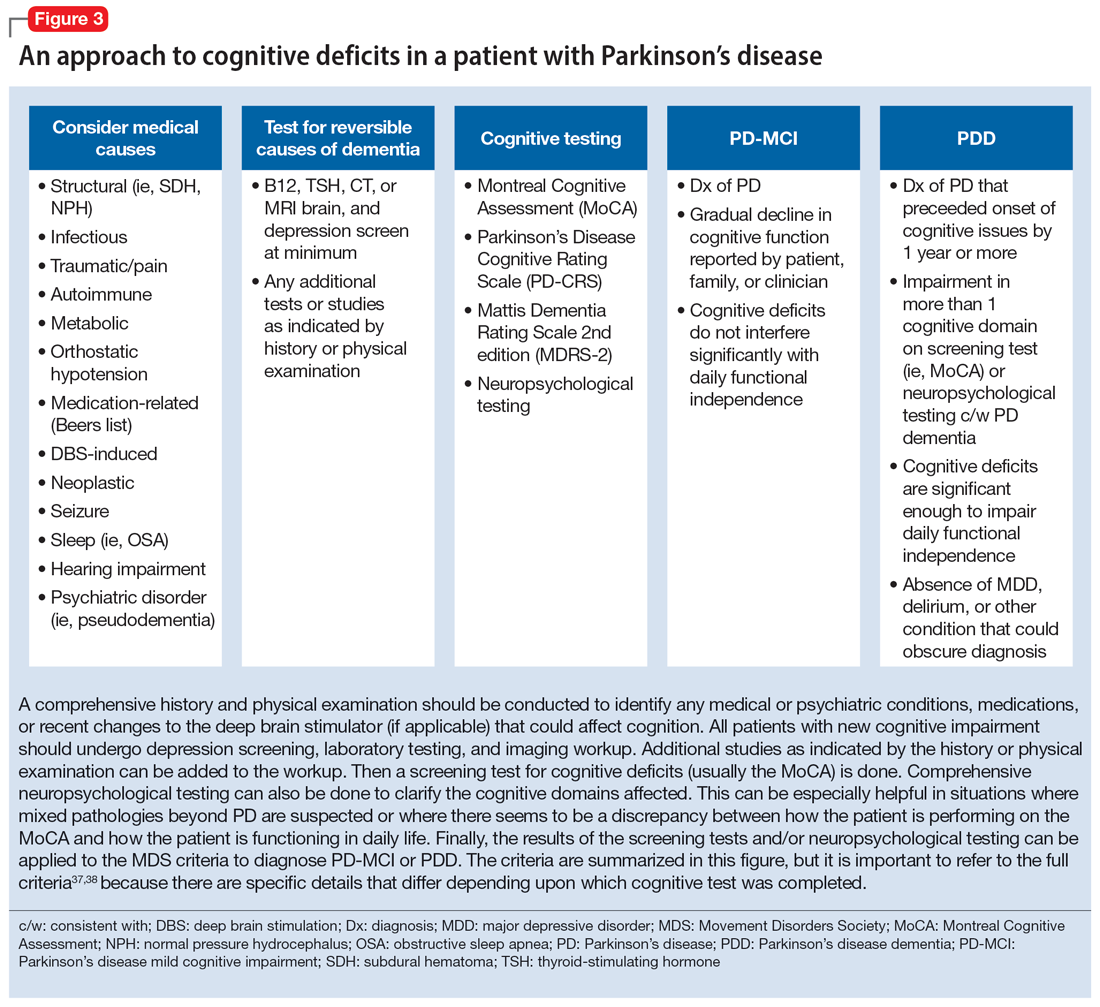
This section focuses on PD mild cognitive impairment (PD-MCI) and PDD. When a patient with PD reports cognitive concerns, the approach outlined in Figure 3 can be used to diagnose the cognitive disorder. A detailed history, medication review, and physical examination can identify any medical or psychiatric conditions that could affect cognition. The American Academy of Neurology recommends screening for depression, obtaining blood levels of vitamin B12 and thyroid-stimulating hormone, and obtaining a CT or MRI of the brain to rule out reversible causes of dementia.33 A validated screening test such as the Montreal Cognitive Assessment, which has higher sensitivity for PD-MCI than the Mini-Mental State Examination, is used to identify and quantify cognitive impairment.34 Neuropsychological testing is the gold standard and can be used to confirm and/or better quantify the degree and domains of cognitive impairment.35 Typically, cognitive deficits in PD affect executive function, attention, and/or visuospatial domains more than memory and language early on, and deficits in visuospatial and language domains have the highest sensitivity for predicting progression to PDD.36
Once reversible causes of dementia are addressed or ruled out and cognitive testing is completed, the Movement Disorder Society (MDS) criteria for PD-MCI and PDD summarized in Figure 3 can be used to diagnose the cognitive disorder.37,38 The MDS criteria for PDD require a diagnosis of PD for ≥1 year prior to the onset of dementia to differentiate PDD from dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB). If the dementia starts within 1 year of the onset of parkinsonism, the diagnosis would be DLB. PDD and DLB are on the spectrum of Lewy body dementia, with the same Lewy body pathology in different temporal and spatial distributions in the brain.38
Continue to: PD-MCI is present in...