PD-MCI is present in approximately 25% of patients.35 PD-MCI does not always progress to dementia but increases the risk of dementia 6-fold. The prevalence of PDD increases with disease duration; it is present in approximately 50% of patients at 10 years and 80% of patients at 20 years of disease.35 Rivastigmine is the only FDA-approved medication to slow progression of PDD. There is insufficient evidence for other acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and memantine.15 Unfortunately, RCTs of pharmacotherapy for PD-MCI have failed to show efficacy. However, exercise, cognitive rehabilitation, and neuromodulation are being studied. In the meantime, addressing modifiable risk factors (such as vascular risk factors and alcohol consumption) and treating comorbid orthostatic hypotension, obstructive sleep apnea, and depression may improve cognition.35,39
Treatment-related disorders
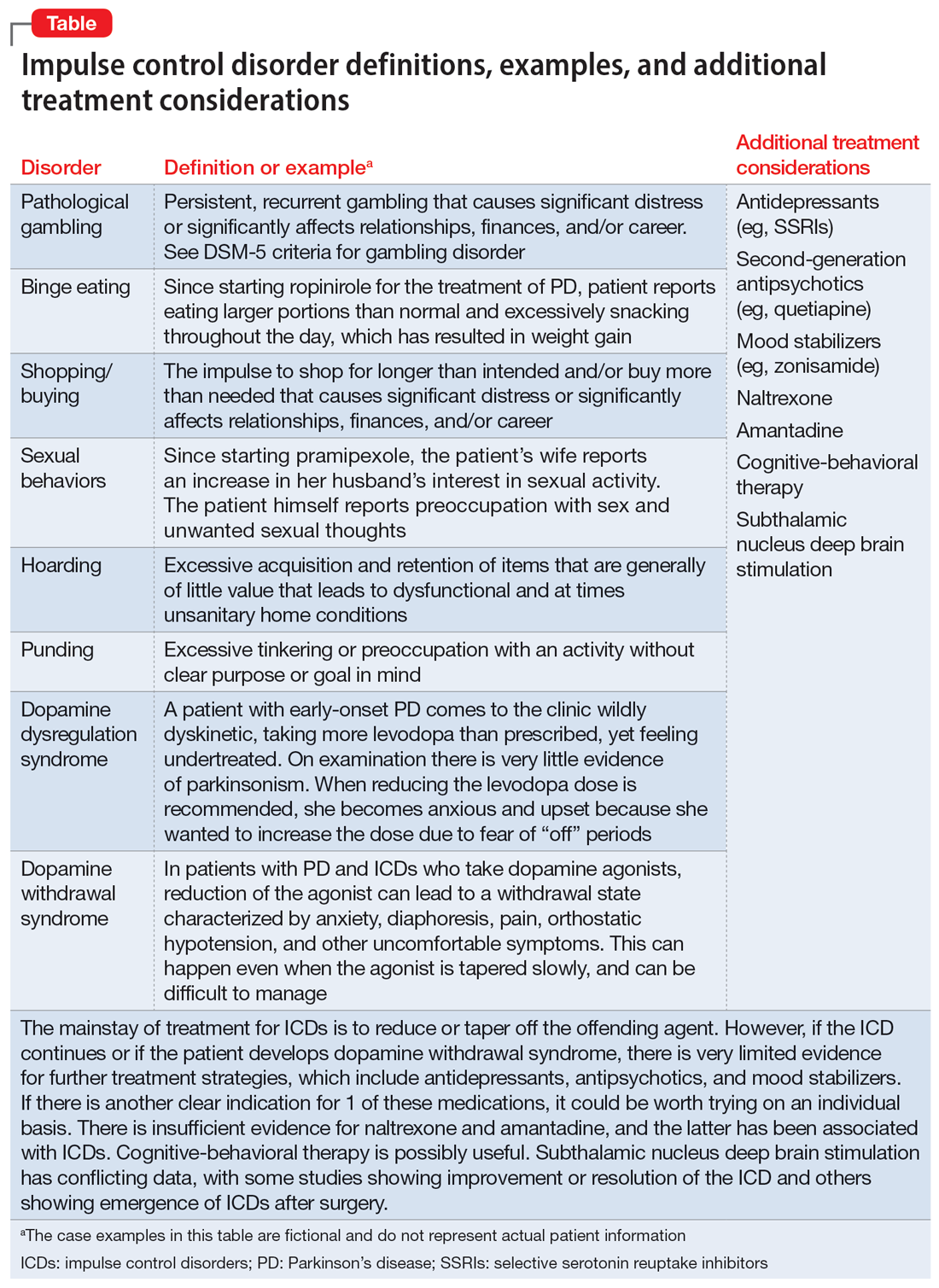
Impulse control disorders
Impulse control disorders (ICDs) are an important medication-related consideration in patients with PD. The ICDs seen in PD include pathological gambling, binge eating, excessive shopping, hypersexual behaviors, and dopamine dysregulation syndrome (Table). These disorders are more common in younger patients with a history of impulsive personality traits and addictive behaviors (eg, history of tobacco or alcohol abuse), and are most strongly associated with dopaminergic therapies, particularly the dopamine agonists.40,41 In the DOMINION study, the odds of ICDs were 2- to 3.5-fold higher in patients taking dopamine agonists.42 This is mainly thought to be due to stimulation of D2/D3 receptors in the mesolimbic system.40 High doses of levodopa, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and amantadine are also associated with ICDs.40-42
The first step in managing ICDs is diagnosing them, which can be difficult because patients often are not forthcoming about these problems due to embarrassment or failure to recognize that the ICD is related to PD medications. If a family member accompanies the patient at the visit, the patient may not want to disclose the amount of money they spend or the extent to which the behavior is a problem. Thus, a screening questionnaire, such as the Questionnaire for Impulsive-Compulsive Disorders in Parkinson’s Disease (QUIP) can be a helpful way for patients to alert the clinician to the issue.41 Education for the patient and family is crucial before the ICD causes significant financial, health, or relationship problems.
The mainstay of treatment is to reduce or taper off the dopamine agonist or other offending agent while monitoring for worsening motor symptoms and dopamine withdrawal syndrome. If this is unsuccessful, there is very limited evidence for further treatment strategies (Table), including antidepressants, antipsychotics, and mood stabilizers.40,43,44 There is insufficient evidence for naltrexone based on an RCT that failed to meet its primary endpoint, although naltrexone did significantly reduce QUIP scores.15,44 There is also insufficient evidence for amantadine, which showed benefit in some studies but was associated with ICDs in the DOMINION study.15,40,42 In terms of nonpharmacologic treatments, CBT is likely efficacious.15,40 There are mixed results for STN DBS. Some studies showed improvement in the ICD, due at least in part to dopaminergic medication reduction postoperatively, but this treatment has also been reported to increase impulsivity.40,45
Deep brain stimulation–related disorders
For patients with PD, the ideal lead location for STN DBS is the dorsolateral aspect of the STN, as this is the motor region of the nucleus. The STN functions in indirect and hyperdirect pathways to put the brake on certain motor programs so only the desired movement can be executed. Its function is clinically demonstrated by patients with STN stroke who develop excessive ballistic movements. Adjacent to the motor region of the STN is a centrally located associative region and a medially located limbic region. Thus, when stimulating the dorsolateral STN, current can spread to those regions as well, and the STN’s ability to put the brake on behavioral and emotional programs can be affected.46 Stimulation of the STN has been associated with mania, euphoria, new-onset ICDs, decreased verbal fluency, and executive dysfunction. Depression, apathy, and anxiety can also occur, but more commonly result from rapid withdrawal of antiparkinsonian medications after DBS surgery.46,47 Therefore, for PD patients with DBS with new or worsening psychiatric or cognitive symptoms, it is important to inquire about any recent programming sessions with neurology as well as recent self-increases in stimulation by the patient using their controller. Collaboration with neurology is important to troubleshoot whether stimulation could be contributing to the patient’s psychiatric or cognitive symptoms.
Continue to: Bottom Line