User login
Decline in U.S. flu activity puts end of season within sight
Outpatient visits for influenza were down again in the United States during the week ending April 1, and the number of states at the highest level of flu activity dropped from seven to four, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 2.9% for the week ending April 1, compared with 3.2% the week before, the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network reported. The national baseline level is 2.2%.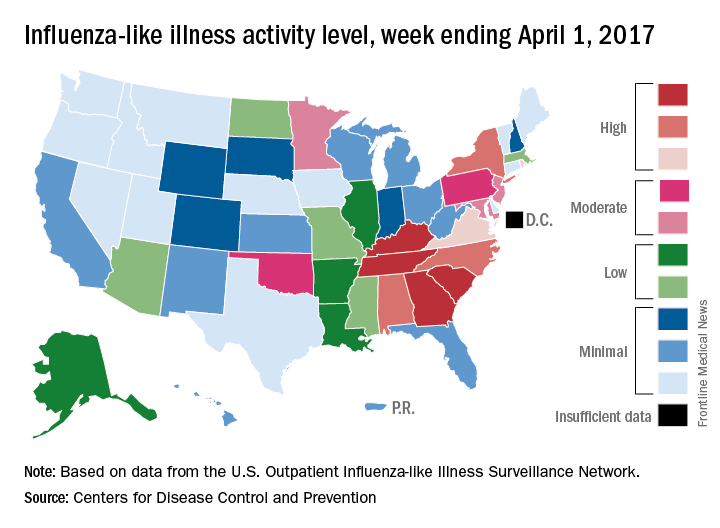
There were 7 flu-related pediatric deaths reported for the week ending April 1 – six of the deaths occurred in previous weeks – which brings the total for the 2016-2017 season to 68, the CDC said. The largest share of those deaths by age group has been among 5- to 11-year-olds (36.8%), followed by those aged 12-17 years (26.5%), 6-23 months (16.2%), 2-4 years (14.7%), and 0-5 months (5.9%).
Outpatient visits for influenza were down again in the United States during the week ending April 1, and the number of states at the highest level of flu activity dropped from seven to four, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 2.9% for the week ending April 1, compared with 3.2% the week before, the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network reported. The national baseline level is 2.2%.
There were 7 flu-related pediatric deaths reported for the week ending April 1 – six of the deaths occurred in previous weeks – which brings the total for the 2016-2017 season to 68, the CDC said. The largest share of those deaths by age group has been among 5- to 11-year-olds (36.8%), followed by those aged 12-17 years (26.5%), 6-23 months (16.2%), 2-4 years (14.7%), and 0-5 months (5.9%).
Outpatient visits for influenza were down again in the United States during the week ending April 1, and the number of states at the highest level of flu activity dropped from seven to four, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 2.9% for the week ending April 1, compared with 3.2% the week before, the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network reported. The national baseline level is 2.2%.
There were 7 flu-related pediatric deaths reported for the week ending April 1 – six of the deaths occurred in previous weeks – which brings the total for the 2016-2017 season to 68, the CDC said. The largest share of those deaths by age group has been among 5- to 11-year-olds (36.8%), followed by those aged 12-17 years (26.5%), 6-23 months (16.2%), 2-4 years (14.7%), and 0-5 months (5.9%).
Make assessment of immunization status of older adults routine
ATLANTA – In the opinion of John M. Kelso, MD, assessment of immunization status in older adults should be a routine part of all visits.
“Don’t assume that your patients are getting their vaccines someplace else,” he said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology. “We should be taking advantage of the fact that these patients are in our offices.”
Inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV3)
For adults aged 65 and older, the high-dose, trivalent version of the flu vaccine (60 micrograms of hemagglutinin per strain, or IIV3-HD) may be preferable to the standard dose of 15 micrograms of hemagglutinin per strain (IIV3-SD). A study of nearly 32,000 patients found that IIV3-HD induced significantly higher antibody responses and provided better protection against laboratory-confirmed influenza, compared with IIV3-SD (N Engl J Med. 2014;371:635-45). The relative efficacy of high dose vs. standard dose was 24.2%. “That means that one-quarter of all breakthrough influenza illnesses could be prevented if IIV3HD were used instead of IIV3-SD,” Dr. Kelso said.
Another approach is to use an adjuvanted influenza vaccine, which contains the standard 15 micrograms of influenza antigen but the adjuvant is MF59, a squalene-based oil-in-water emulsion. One small study of 282 patients aged 65 and older showed the adjuvanted vaccine to be more effective than the unadjuvanted vaccine (Vaccine. 2013;51:1622-8).
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention does not express a preference for the high-dose or adjuvanted vaccine, but rather stresses the importance of influenza vaccination with whatever age-appropriate IIV formulation is available at the time of the patient’s visit.
The 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23)
All adults who turn 65 years of age should receive the PCV13, followed 1 year later by the PPSV23. For those who already received the PPSV23 after age 65 years of age, they should receive the PCV13 at least 1 year later. “The real bulk of hospitalizations and fatalities from invasive pneumococcal disease are happening to people over 65 year of age,” said Dr. Kelso, who is also a clinical professor of pediatrics and internal medicine at the University of California, San Diego “So there’s a real need here for vaccination.”
Tdap
This should be administered to all adolescents and adults regardless of interval since their last tetanus-diphtheria vaccine. “This includes those age 65 years of age and older in whom the vaccine has been found to be equally safe and immunogenic,” Dr. Kelso said. “This is important not only to prevent pertussis in older adults, but also to prevent them from spreading the disease to infants where it can be fatal.”
Zoster vaccine
One in three adults will develop zoster during their lifetime, he said, and one million episodes occur in the United States each year. Common complications include postherpetic neuralgia and eye involvement that can result in loss of vision. The CDC recommends routine vaccination of all immunocompetent persons over age 60 with one dose of zoster vaccine. “Persons who report a previous episode of zoster can be vaccinated but it is not indicated to treat acute zoster, to prevent persons with acute zoster from developing postherpetic neuralgia, or to treat ongoing postherpetic neuralgia,” Dr. Kelso said.
He reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
ATLANTA – In the opinion of John M. Kelso, MD, assessment of immunization status in older adults should be a routine part of all visits.
“Don’t assume that your patients are getting their vaccines someplace else,” he said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology. “We should be taking advantage of the fact that these patients are in our offices.”
Inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV3)
For adults aged 65 and older, the high-dose, trivalent version of the flu vaccine (60 micrograms of hemagglutinin per strain, or IIV3-HD) may be preferable to the standard dose of 15 micrograms of hemagglutinin per strain (IIV3-SD). A study of nearly 32,000 patients found that IIV3-HD induced significantly higher antibody responses and provided better protection against laboratory-confirmed influenza, compared with IIV3-SD (N Engl J Med. 2014;371:635-45). The relative efficacy of high dose vs. standard dose was 24.2%. “That means that one-quarter of all breakthrough influenza illnesses could be prevented if IIV3HD were used instead of IIV3-SD,” Dr. Kelso said.
Another approach is to use an adjuvanted influenza vaccine, which contains the standard 15 micrograms of influenza antigen but the adjuvant is MF59, a squalene-based oil-in-water emulsion. One small study of 282 patients aged 65 and older showed the adjuvanted vaccine to be more effective than the unadjuvanted vaccine (Vaccine. 2013;51:1622-8).
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention does not express a preference for the high-dose or adjuvanted vaccine, but rather stresses the importance of influenza vaccination with whatever age-appropriate IIV formulation is available at the time of the patient’s visit.
The 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23)
All adults who turn 65 years of age should receive the PCV13, followed 1 year later by the PPSV23. For those who already received the PPSV23 after age 65 years of age, they should receive the PCV13 at least 1 year later. “The real bulk of hospitalizations and fatalities from invasive pneumococcal disease are happening to people over 65 year of age,” said Dr. Kelso, who is also a clinical professor of pediatrics and internal medicine at the University of California, San Diego “So there’s a real need here for vaccination.”
Tdap
This should be administered to all adolescents and adults regardless of interval since their last tetanus-diphtheria vaccine. “This includes those age 65 years of age and older in whom the vaccine has been found to be equally safe and immunogenic,” Dr. Kelso said. “This is important not only to prevent pertussis in older adults, but also to prevent them from spreading the disease to infants where it can be fatal.”
Zoster vaccine
One in three adults will develop zoster during their lifetime, he said, and one million episodes occur in the United States each year. Common complications include postherpetic neuralgia and eye involvement that can result in loss of vision. The CDC recommends routine vaccination of all immunocompetent persons over age 60 with one dose of zoster vaccine. “Persons who report a previous episode of zoster can be vaccinated but it is not indicated to treat acute zoster, to prevent persons with acute zoster from developing postherpetic neuralgia, or to treat ongoing postherpetic neuralgia,” Dr. Kelso said.
He reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
ATLANTA – In the opinion of John M. Kelso, MD, assessment of immunization status in older adults should be a routine part of all visits.
“Don’t assume that your patients are getting their vaccines someplace else,” he said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology. “We should be taking advantage of the fact that these patients are in our offices.”
Inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV3)
For adults aged 65 and older, the high-dose, trivalent version of the flu vaccine (60 micrograms of hemagglutinin per strain, or IIV3-HD) may be preferable to the standard dose of 15 micrograms of hemagglutinin per strain (IIV3-SD). A study of nearly 32,000 patients found that IIV3-HD induced significantly higher antibody responses and provided better protection against laboratory-confirmed influenza, compared with IIV3-SD (N Engl J Med. 2014;371:635-45). The relative efficacy of high dose vs. standard dose was 24.2%. “That means that one-quarter of all breakthrough influenza illnesses could be prevented if IIV3HD were used instead of IIV3-SD,” Dr. Kelso said.
Another approach is to use an adjuvanted influenza vaccine, which contains the standard 15 micrograms of influenza antigen but the adjuvant is MF59, a squalene-based oil-in-water emulsion. One small study of 282 patients aged 65 and older showed the adjuvanted vaccine to be more effective than the unadjuvanted vaccine (Vaccine. 2013;51:1622-8).
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention does not express a preference for the high-dose or adjuvanted vaccine, but rather stresses the importance of influenza vaccination with whatever age-appropriate IIV formulation is available at the time of the patient’s visit.
The 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23)
All adults who turn 65 years of age should receive the PCV13, followed 1 year later by the PPSV23. For those who already received the PPSV23 after age 65 years of age, they should receive the PCV13 at least 1 year later. “The real bulk of hospitalizations and fatalities from invasive pneumococcal disease are happening to people over 65 year of age,” said Dr. Kelso, who is also a clinical professor of pediatrics and internal medicine at the University of California, San Diego “So there’s a real need here for vaccination.”
Tdap
This should be administered to all adolescents and adults regardless of interval since their last tetanus-diphtheria vaccine. “This includes those age 65 years of age and older in whom the vaccine has been found to be equally safe and immunogenic,” Dr. Kelso said. “This is important not only to prevent pertussis in older adults, but also to prevent them from spreading the disease to infants where it can be fatal.”
Zoster vaccine
One in three adults will develop zoster during their lifetime, he said, and one million episodes occur in the United States each year. Common complications include postherpetic neuralgia and eye involvement that can result in loss of vision. The CDC recommends routine vaccination of all immunocompetent persons over age 60 with one dose of zoster vaccine. “Persons who report a previous episode of zoster can be vaccinated but it is not indicated to treat acute zoster, to prevent persons with acute zoster from developing postherpetic neuralgia, or to treat ongoing postherpetic neuralgia,” Dr. Kelso said.
He reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS AT THE 2017 AAAAI ANNUAL MEETING
Latest weekly flu data show no decline in visits
Outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) held steady for the week ending March 25, but the number of states at the “high” range of activity dropped from 12 from 10 the previous week, according to the Centers for Disease Prevention and Control.
The proportion of outpatient visits for ILI was 3.2% for the second consecutive week, which halted the slowdown in activity that began the week ending Feb. 18. That 3.2% represents just under 25,000 visits for ILI of the almost 747,000 total visits reported to the Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network (ILINet) for the week ending March 25. By age, the largest groups with ILI visits for the week were individuals aged 5-24 years (41%) and those aged 4 years and under (20%), the CDC reported.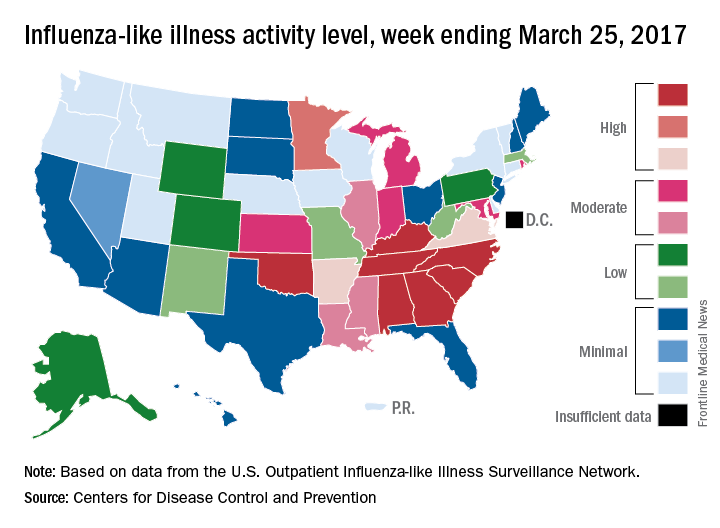
There were six flu-related pediatric deaths reported during the week ending March 25, but all occurred in earlier weeks. The total number of such deaths is now 61 for the 2016-2017 season, the CDC said.
Outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) held steady for the week ending March 25, but the number of states at the “high” range of activity dropped from 12 from 10 the previous week, according to the Centers for Disease Prevention and Control.
The proportion of outpatient visits for ILI was 3.2% for the second consecutive week, which halted the slowdown in activity that began the week ending Feb. 18. That 3.2% represents just under 25,000 visits for ILI of the almost 747,000 total visits reported to the Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network (ILINet) for the week ending March 25. By age, the largest groups with ILI visits for the week were individuals aged 5-24 years (41%) and those aged 4 years and under (20%), the CDC reported.
There were six flu-related pediatric deaths reported during the week ending March 25, but all occurred in earlier weeks. The total number of such deaths is now 61 for the 2016-2017 season, the CDC said.
Outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) held steady for the week ending March 25, but the number of states at the “high” range of activity dropped from 12 from 10 the previous week, according to the Centers for Disease Prevention and Control.
The proportion of outpatient visits for ILI was 3.2% for the second consecutive week, which halted the slowdown in activity that began the week ending Feb. 18. That 3.2% represents just under 25,000 visits for ILI of the almost 747,000 total visits reported to the Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network (ILINet) for the week ending March 25. By age, the largest groups with ILI visits for the week were individuals aged 5-24 years (41%) and those aged 4 years and under (20%), the CDC reported.
There were six flu-related pediatric deaths reported during the week ending March 25, but all occurred in earlier weeks. The total number of such deaths is now 61 for the 2016-2017 season, the CDC said.
2016-2017 flu season continues to wind down
Influenza activity took another healthy step down as outpatient visits continued to drop, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was down to 3.2% for the week ending March 18, 2017, the CDC reported, compared with 3.6% the week before. (The figure of 3.7% previously reported for last week has been adjusted this week, so the halt in the decline in outpatient visits was actually more of a slowdown.) The national baseline for outpatient ILI visits is 2.2%.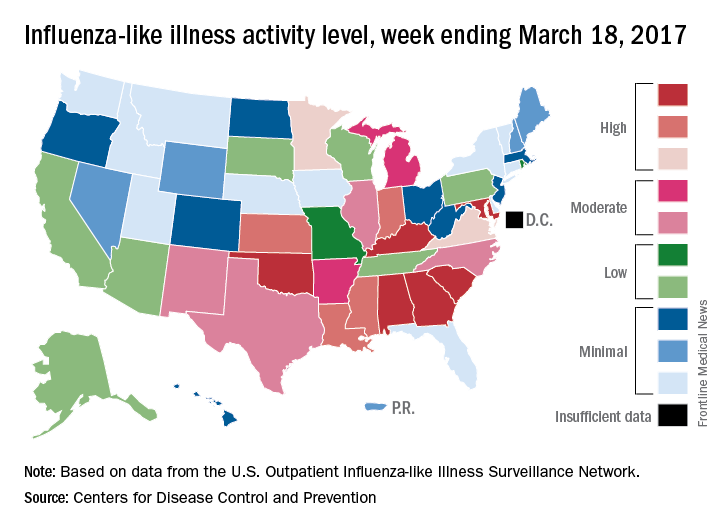
Two flu-related pediatric deaths were reported during the week of March 18, but both occurred earlier: one during the week ending Feb. 18 and the other in the week ending Feb. 25, the CDC reported. The total number of pediatric flu deaths reported is now 55 for the 2016-2017 season.
Influenza activity took another healthy step down as outpatient visits continued to drop, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was down to 3.2% for the week ending March 18, 2017, the CDC reported, compared with 3.6% the week before. (The figure of 3.7% previously reported for last week has been adjusted this week, so the halt in the decline in outpatient visits was actually more of a slowdown.) The national baseline for outpatient ILI visits is 2.2%.
Two flu-related pediatric deaths were reported during the week of March 18, but both occurred earlier: one during the week ending Feb. 18 and the other in the week ending Feb. 25, the CDC reported. The total number of pediatric flu deaths reported is now 55 for the 2016-2017 season.
Influenza activity took another healthy step down as outpatient visits continued to drop, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was down to 3.2% for the week ending March 18, 2017, the CDC reported, compared with 3.6% the week before. (The figure of 3.7% previously reported for last week has been adjusted this week, so the halt in the decline in outpatient visits was actually more of a slowdown.) The national baseline for outpatient ILI visits is 2.2%.
Two flu-related pediatric deaths were reported during the week of March 18, but both occurred earlier: one during the week ending Feb. 18 and the other in the week ending Feb. 25, the CDC reported. The total number of pediatric flu deaths reported is now 55 for the 2016-2017 season.
U.S. influenza activity remains steady
The decline in U.S. influenza activity that started in February paused during the week ending March 11, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) stayed at 3.7% for a second consecutive week after declining for 3 weeks in a row. The peak for the season, 5.2%, came during the week ending Feb. 11, CDC data show. The national baseline is 2.2%.
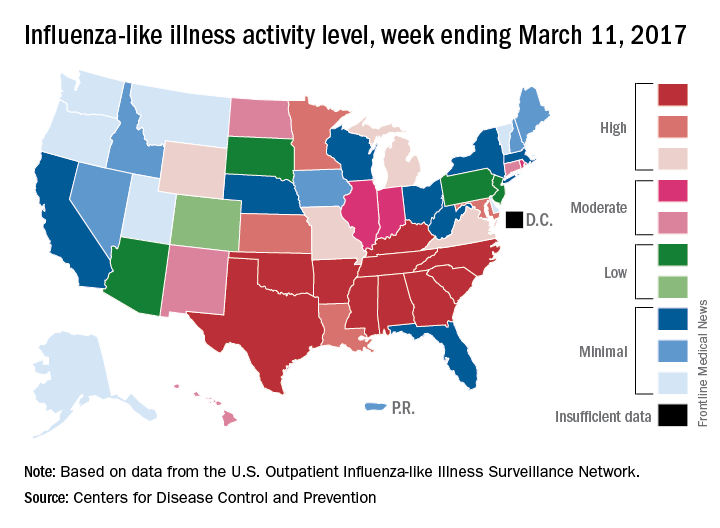
Five ILI-related pediatric deaths were reported to the CDC for the week – all of which occurred during previous weeks – bringing the total to 53 for the 2016-2017 season, the CDC said.
The decline in U.S. influenza activity that started in February paused during the week ending March 11, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) stayed at 3.7% for a second consecutive week after declining for 3 weeks in a row. The peak for the season, 5.2%, came during the week ending Feb. 11, CDC data show. The national baseline is 2.2%.

Five ILI-related pediatric deaths were reported to the CDC for the week – all of which occurred during previous weeks – bringing the total to 53 for the 2016-2017 season, the CDC said.
The decline in U.S. influenza activity that started in February paused during the week ending March 11, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) stayed at 3.7% for a second consecutive week after declining for 3 weeks in a row. The peak for the season, 5.2%, came during the week ending Feb. 11, CDC data show. The national baseline is 2.2%.

Five ILI-related pediatric deaths were reported to the CDC for the week – all of which occurred during previous weeks – bringing the total to 53 for the 2016-2017 season, the CDC said.
U.S. flu activity continues to decline
The 2016-2017 U.S. influenza season appears to have peaked, as activity measures dropped for the third consecutive week, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
For the week ending March 4, there were 11 states at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of influenza-like illness (ILI) activity, with another three in the “high” range at levels 8 and 9. The previous week (Feb. 25), there were 22 states at level 10, with a total of 27 in the high range of ILI activity. At the peak of activity during the week of Feb. 11, there were 25 states at level 10, data from the CDC’s Outpatient ILI Surveillance Network show.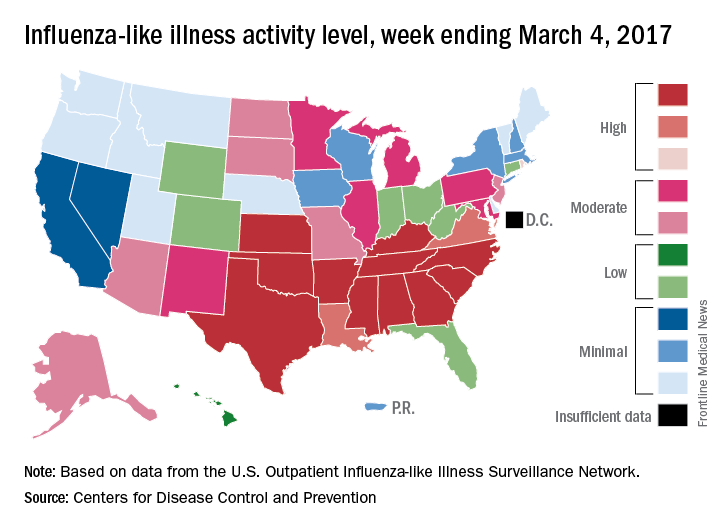
There were eight ILI-related pediatric deaths reported during the week ending March 4, although all occurred in earlier weeks. For the 2016-2017 season so far, 48 ILI-related pediatric deaths have been reported, the CDC said.
For the 70 counties in 13 states that report to the Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network, the flu-related hospitalization rate for the season is 43.5 per 100,000 population. The highest rate by age group is for those 65 years and over at 198.8 per 100,000, followed by 50- to 64-year-olds at 42.2 per 100,000 and children aged 0-4 years at 28.8 per 100,000, according to the CDC.
The 2016-2017 U.S. influenza season appears to have peaked, as activity measures dropped for the third consecutive week, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
For the week ending March 4, there were 11 states at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of influenza-like illness (ILI) activity, with another three in the “high” range at levels 8 and 9. The previous week (Feb. 25), there were 22 states at level 10, with a total of 27 in the high range of ILI activity. At the peak of activity during the week of Feb. 11, there were 25 states at level 10, data from the CDC’s Outpatient ILI Surveillance Network show.
There were eight ILI-related pediatric deaths reported during the week ending March 4, although all occurred in earlier weeks. For the 2016-2017 season so far, 48 ILI-related pediatric deaths have been reported, the CDC said.
For the 70 counties in 13 states that report to the Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network, the flu-related hospitalization rate for the season is 43.5 per 100,000 population. The highest rate by age group is for those 65 years and over at 198.8 per 100,000, followed by 50- to 64-year-olds at 42.2 per 100,000 and children aged 0-4 years at 28.8 per 100,000, according to the CDC.
The 2016-2017 U.S. influenza season appears to have peaked, as activity measures dropped for the third consecutive week, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
For the week ending March 4, there were 11 states at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of influenza-like illness (ILI) activity, with another three in the “high” range at levels 8 and 9. The previous week (Feb. 25), there were 22 states at level 10, with a total of 27 in the high range of ILI activity. At the peak of activity during the week of Feb. 11, there were 25 states at level 10, data from the CDC’s Outpatient ILI Surveillance Network show.
There were eight ILI-related pediatric deaths reported during the week ending March 4, although all occurred in earlier weeks. For the 2016-2017 season so far, 48 ILI-related pediatric deaths have been reported, the CDC said.
For the 70 counties in 13 states that report to the Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network, the flu-related hospitalization rate for the season is 43.5 per 100,000 population. The highest rate by age group is for those 65 years and over at 198.8 per 100,000, followed by 50- to 64-year-olds at 42.2 per 100,000 and children aged 0-4 years at 28.8 per 100,000, according to the CDC.
FDA committee approves strains for 2017-2018 flu shot
ROCKVILLE, MD. – A committee of Food and Drug Administration advisers backed the World Health Organization’s influenza vaccine recommendations for the 2017-2018 season at a meeting March 9.
In a unanimous vote, members of the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee recommended that trivalent vaccines for the 2017-2018 season should contain the following vaccine strains: A/Michigan/45/2015(H1N1)pdm09-like, A/Hong Kong/4801/2014(H3N2)-like, and B/Brisbane/60/2008-like.
These recommendations echo those from the 2016-2017 season, with the exception of a slight update to the H1N1 strain, which had previously been A/California/7/2009(H1N1)pdm09-like virus.
Regarding vaccine efficacy, the cell propagated A/Hong Kong strain was the strongest candidate, covering 93% of A(H3N2) viruses seen in the 2016-2017 season, according to Jacqueline Katz, PhD, director of the WHO Collaborating Center for Surveillance, Epidemiology and Control of Influenza at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. In comparison, the egg propagated version of the A/Hong Kong virus covered 59%.
For the influenza B virus, the Yamagata lineage and Victoria lineage strain cycled monthly as the predominant strain in the 2016-2017 season, with a split of “around 50/50,” leaning toward Yamagata in North America, Europe, and Oceana, Dr. Katz explained. The Victoria lineage, in some cases, accounted for nearly 75% of B viruses in Africa and South America.
Committee members expressed concern over the difference between strain prevalence in the United States and abroad and considered recommending a strain that did not coincide with the WHO recommendation, something that has not happened in the history of the advisory committee.
“I’m very aware of influenza vaccinations being a global enterprise, and companies manufacture vaccines for use in multiple countries,” said Committee Chair Kathryn Edwards, MD, professor of pediatrics at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn. “If we to select a B strain that differed from the WHO recommendation, would that adversely impact vaccine production for the U.S. market?”
Despite these questions, the committee continued to back the WHO recommendations.
Historically, the advisory committee has recommended flu vaccine strains earlier in the year, according to Beverly Taylor, PhD, head of influenza scientific affairs and pandemic readiness at Seqirus Vaccines. Dr. Taylor presented the vaccine manufacturers’ perspective. The delay has put added pressure on manufacturers.
“We haven’t seen impacts yet on start of vaccination dates,” said Dr. Taylor. “But the very clear message from manufacturers is if you keep squashing that manufacturing window, then there will reach a point where we are concerned we will see an impact on vaccine supply time.”
None of the committee members presented waivers of conflict of interest. While the FDA is not obligated to follow the recommendations of the advisory committee, it generally does.
ezimmerman@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @EAZTweets
ROCKVILLE, MD. – A committee of Food and Drug Administration advisers backed the World Health Organization’s influenza vaccine recommendations for the 2017-2018 season at a meeting March 9.
In a unanimous vote, members of the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee recommended that trivalent vaccines for the 2017-2018 season should contain the following vaccine strains: A/Michigan/45/2015(H1N1)pdm09-like, A/Hong Kong/4801/2014(H3N2)-like, and B/Brisbane/60/2008-like.
These recommendations echo those from the 2016-2017 season, with the exception of a slight update to the H1N1 strain, which had previously been A/California/7/2009(H1N1)pdm09-like virus.
Regarding vaccine efficacy, the cell propagated A/Hong Kong strain was the strongest candidate, covering 93% of A(H3N2) viruses seen in the 2016-2017 season, according to Jacqueline Katz, PhD, director of the WHO Collaborating Center for Surveillance, Epidemiology and Control of Influenza at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. In comparison, the egg propagated version of the A/Hong Kong virus covered 59%.
For the influenza B virus, the Yamagata lineage and Victoria lineage strain cycled monthly as the predominant strain in the 2016-2017 season, with a split of “around 50/50,” leaning toward Yamagata in North America, Europe, and Oceana, Dr. Katz explained. The Victoria lineage, in some cases, accounted for nearly 75% of B viruses in Africa and South America.
Committee members expressed concern over the difference between strain prevalence in the United States and abroad and considered recommending a strain that did not coincide with the WHO recommendation, something that has not happened in the history of the advisory committee.
“I’m very aware of influenza vaccinations being a global enterprise, and companies manufacture vaccines for use in multiple countries,” said Committee Chair Kathryn Edwards, MD, professor of pediatrics at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn. “If we to select a B strain that differed from the WHO recommendation, would that adversely impact vaccine production for the U.S. market?”
Despite these questions, the committee continued to back the WHO recommendations.
Historically, the advisory committee has recommended flu vaccine strains earlier in the year, according to Beverly Taylor, PhD, head of influenza scientific affairs and pandemic readiness at Seqirus Vaccines. Dr. Taylor presented the vaccine manufacturers’ perspective. The delay has put added pressure on manufacturers.
“We haven’t seen impacts yet on start of vaccination dates,” said Dr. Taylor. “But the very clear message from manufacturers is if you keep squashing that manufacturing window, then there will reach a point where we are concerned we will see an impact on vaccine supply time.”
None of the committee members presented waivers of conflict of interest. While the FDA is not obligated to follow the recommendations of the advisory committee, it generally does.
ezimmerman@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @EAZTweets
ROCKVILLE, MD. – A committee of Food and Drug Administration advisers backed the World Health Organization’s influenza vaccine recommendations for the 2017-2018 season at a meeting March 9.
In a unanimous vote, members of the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee recommended that trivalent vaccines for the 2017-2018 season should contain the following vaccine strains: A/Michigan/45/2015(H1N1)pdm09-like, A/Hong Kong/4801/2014(H3N2)-like, and B/Brisbane/60/2008-like.
These recommendations echo those from the 2016-2017 season, with the exception of a slight update to the H1N1 strain, which had previously been A/California/7/2009(H1N1)pdm09-like virus.
Regarding vaccine efficacy, the cell propagated A/Hong Kong strain was the strongest candidate, covering 93% of A(H3N2) viruses seen in the 2016-2017 season, according to Jacqueline Katz, PhD, director of the WHO Collaborating Center for Surveillance, Epidemiology and Control of Influenza at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. In comparison, the egg propagated version of the A/Hong Kong virus covered 59%.
For the influenza B virus, the Yamagata lineage and Victoria lineage strain cycled monthly as the predominant strain in the 2016-2017 season, with a split of “around 50/50,” leaning toward Yamagata in North America, Europe, and Oceana, Dr. Katz explained. The Victoria lineage, in some cases, accounted for nearly 75% of B viruses in Africa and South America.
Committee members expressed concern over the difference between strain prevalence in the United States and abroad and considered recommending a strain that did not coincide with the WHO recommendation, something that has not happened in the history of the advisory committee.
“I’m very aware of influenza vaccinations being a global enterprise, and companies manufacture vaccines for use in multiple countries,” said Committee Chair Kathryn Edwards, MD, professor of pediatrics at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn. “If we to select a B strain that differed from the WHO recommendation, would that adversely impact vaccine production for the U.S. market?”
Despite these questions, the committee continued to back the WHO recommendations.
Historically, the advisory committee has recommended flu vaccine strains earlier in the year, according to Beverly Taylor, PhD, head of influenza scientific affairs and pandemic readiness at Seqirus Vaccines. Dr. Taylor presented the vaccine manufacturers’ perspective. The delay has put added pressure on manufacturers.
“We haven’t seen impacts yet on start of vaccination dates,” said Dr. Taylor. “But the very clear message from manufacturers is if you keep squashing that manufacturing window, then there will reach a point where we are concerned we will see an impact on vaccine supply time.”
None of the committee members presented waivers of conflict of interest. While the FDA is not obligated to follow the recommendations of the advisory committee, it generally does.
ezimmerman@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @EAZTweets
AT AN FDA ADVISORY COMMITTEE MEETING
Outpatient flu visits down slightly
The overall national measure of outpatient flu activity was down for the week ending Feb. 18, and the number of states at the highest level of activity dropped from 25 to 24, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) decreased from 5.2% the previous week to 4.8% for the week ending Feb. 18, the CDC reported.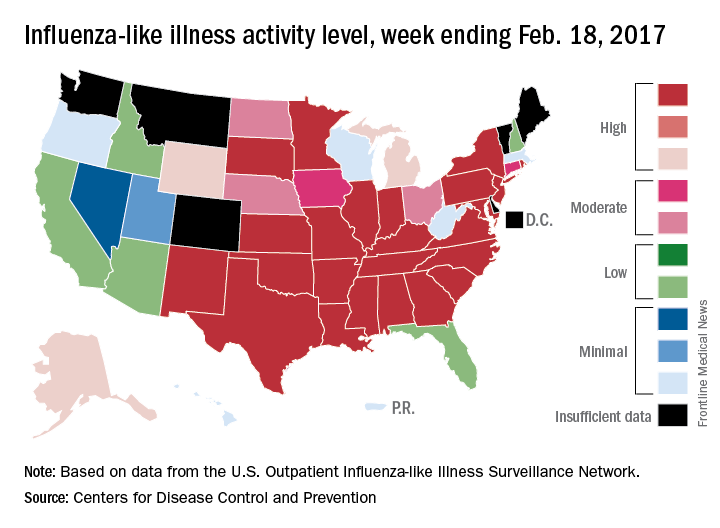
There were 5 ILI-related pediatric deaths reported during the week, bringing the total to 34 for the season so far, but none of the 5 occurred in the current week, the CDC said. There were 89 pediatric deaths reported during the 2015-2016 season, with the peak week occurring in late March/early April (11 deaths). During the 2014-2015 season, there were 148 deaths reported, and 111 were reported in 2013-2014.
The overall national measure of outpatient flu activity was down for the week ending Feb. 18, and the number of states at the highest level of activity dropped from 25 to 24, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) decreased from 5.2% the previous week to 4.8% for the week ending Feb. 18, the CDC reported.
There were 5 ILI-related pediatric deaths reported during the week, bringing the total to 34 for the season so far, but none of the 5 occurred in the current week, the CDC said. There were 89 pediatric deaths reported during the 2015-2016 season, with the peak week occurring in late March/early April (11 deaths). During the 2014-2015 season, there were 148 deaths reported, and 111 were reported in 2013-2014.
The overall national measure of outpatient flu activity was down for the week ending Feb. 18, and the number of states at the highest level of activity dropped from 25 to 24, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) decreased from 5.2% the previous week to 4.8% for the week ending Feb. 18, the CDC reported.
There were 5 ILI-related pediatric deaths reported during the week, bringing the total to 34 for the season so far, but none of the 5 occurred in the current week, the CDC said. There were 89 pediatric deaths reported during the 2015-2016 season, with the peak week occurring in late March/early April (11 deaths). During the 2014-2015 season, there were 148 deaths reported, and 111 were reported in 2013-2014.
Twenty-five states at highest flu activity level
Flu activity in the United States continued to increase as half of the states reached the highest level of influenza-like illness (ILI) activity in the week ending Feb. 11, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
For the week, the 25 states at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of ILI activity were joined in the high range by Illinois and Kentucky at level 9 and Iowa at level 8, the CDC reported. The previous week, there were 23 states in the high range.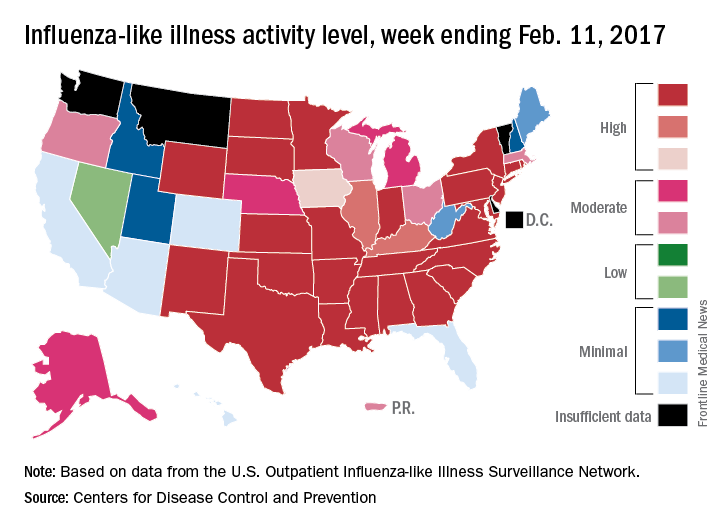
Of the nine flu-related pediatric deaths reported to the CDC during the latest week, eight occurred in earlier weeks. For the 2016-2017 season so far, 29 flu-related pediatric deaths have been reported, the CDC said.
Flu activity in the United States continued to increase as half of the states reached the highest level of influenza-like illness (ILI) activity in the week ending Feb. 11, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
For the week, the 25 states at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of ILI activity were joined in the high range by Illinois and Kentucky at level 9 and Iowa at level 8, the CDC reported. The previous week, there were 23 states in the high range.
Of the nine flu-related pediatric deaths reported to the CDC during the latest week, eight occurred in earlier weeks. For the 2016-2017 season so far, 29 flu-related pediatric deaths have been reported, the CDC said.
Flu activity in the United States continued to increase as half of the states reached the highest level of influenza-like illness (ILI) activity in the week ending Feb. 11, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
For the week, the 25 states at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of ILI activity were joined in the high range by Illinois and Kentucky at level 9 and Iowa at level 8, the CDC reported. The previous week, there were 23 states in the high range.
Of the nine flu-related pediatric deaths reported to the CDC during the latest week, eight occurred in earlier weeks. For the 2016-2017 season so far, 29 flu-related pediatric deaths have been reported, the CDC said.
Flu activity levels high in 23 states
The number of states at the highest level of flu activity jumped from 7 to 19 during the week ending Feb. 4, 2017, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The 19 states at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of influenza-like illness (ILI) activity were largely concentrated in the South and lower Midwest, with another grouping mainly in the Mid-Atlantic. They were joined in the “high” range of ILI activity by four other states: Indiana and Minnesota at level 9 and New Mexico and Virginia at level 8, the CDC reported.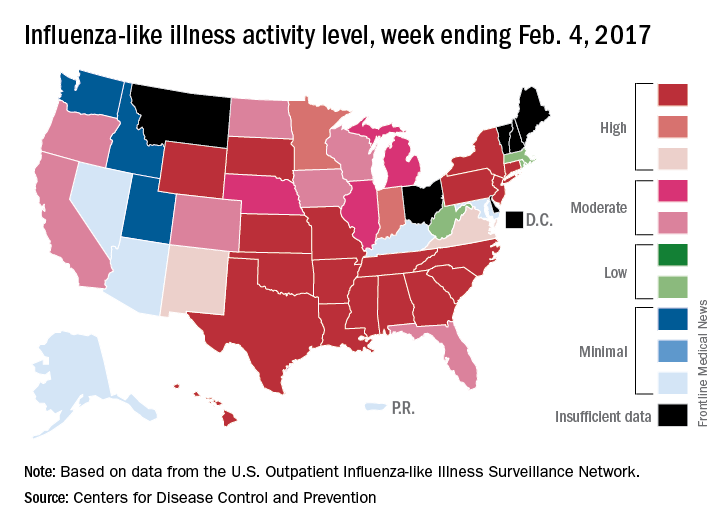
For the 2016-2017 season, 20 flu-related pediatric deaths have been reported: 5 were reported during the week ending Feb. 4, but 4 occurred during the week ending Jan. 28 and 1 occurred during the week ending Jan. 14, according to the CDC.
Since Oct. 1, 2016, there have been 6,804 laboratory-confirmed flu-related hospitalizations reported in the 13 states – including California, Georgia, New York, and Ohio – of the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network, for an overall hospitalization rate of 24.3 per 100,000 population. That rate, however, is “likely to be an underestimate as influenza-related hospitalizations can be missed, either because testing is not performed, or because cases may be attributed to other causes of pneumonia or other common influenza-related complications,” the CDC said.
The number of states at the highest level of flu activity jumped from 7 to 19 during the week ending Feb. 4, 2017, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The 19 states at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of influenza-like illness (ILI) activity were largely concentrated in the South and lower Midwest, with another grouping mainly in the Mid-Atlantic. They were joined in the “high” range of ILI activity by four other states: Indiana and Minnesota at level 9 and New Mexico and Virginia at level 8, the CDC reported.
For the 2016-2017 season, 20 flu-related pediatric deaths have been reported: 5 were reported during the week ending Feb. 4, but 4 occurred during the week ending Jan. 28 and 1 occurred during the week ending Jan. 14, according to the CDC.
Since Oct. 1, 2016, there have been 6,804 laboratory-confirmed flu-related hospitalizations reported in the 13 states – including California, Georgia, New York, and Ohio – of the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network, for an overall hospitalization rate of 24.3 per 100,000 population. That rate, however, is “likely to be an underestimate as influenza-related hospitalizations can be missed, either because testing is not performed, or because cases may be attributed to other causes of pneumonia or other common influenza-related complications,” the CDC said.
The number of states at the highest level of flu activity jumped from 7 to 19 during the week ending Feb. 4, 2017, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The 19 states at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of influenza-like illness (ILI) activity were largely concentrated in the South and lower Midwest, with another grouping mainly in the Mid-Atlantic. They were joined in the “high” range of ILI activity by four other states: Indiana and Minnesota at level 9 and New Mexico and Virginia at level 8, the CDC reported.
For the 2016-2017 season, 20 flu-related pediatric deaths have been reported: 5 were reported during the week ending Feb. 4, but 4 occurred during the week ending Jan. 28 and 1 occurred during the week ending Jan. 14, according to the CDC.
Since Oct. 1, 2016, there have been 6,804 laboratory-confirmed flu-related hospitalizations reported in the 13 states – including California, Georgia, New York, and Ohio – of the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network, for an overall hospitalization rate of 24.3 per 100,000 population. That rate, however, is “likely to be an underestimate as influenza-related hospitalizations can be missed, either because testing is not performed, or because cases may be attributed to other causes of pneumonia or other common influenza-related complications,” the CDC said.

