User login
How to have a safer and more joyful holiday season
This holiday season, I am looking forward to spending some time with family, as I have in the past. As I have chatted with others, many friends are looking forward to events that are potentially larger and potentially returning to prepandemic type gatherings.
Gathering is important and can bring joy, sense of community, and love to the lives of many. Unfortunately, the risks associated with gathering are not over. as our country faces many cases of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), COVID-19, and influenza at the same time.
During the first week of December, cases of influenza were rising across the country1 and were rising faster than in previous years. Although getting the vaccine is an important method of influenza prevention and is recommended for everyone over the age of 6 months with rare exception, many have not gotten their vaccine this year.
Influenza
Thus far, “nearly 50% of reported flu-associated hospitalizations in women of childbearing age have been in women who are pregnant.” We are seeing this at a time with lower-than-average uptake of influenza vaccine leaving both the pregnant persons and their babies unprotected. In addition to utilizing vaccines as prevention, isolating when ill, cleaning surfaces, and practicing good hand hygiene can all decrease transmission.
RSV
In addition to rises of influenza, there are currently high rates of RSV in various parts of the country. Prior to 2020, RSV typically started in the fall and peaked in the winter months. However, since the pandemic, the typical seasonal pattern has not returned, and it is unclear when it will. Although RSV hits the very young, the old, and the immunocompromised the most, RSV can infect anyone. Unfortunately, we do not currently have a vaccine for everyone against this virus. Prevention of transmission includes, as with flu, isolating when ill, cleaning surfaces, and washing hands.2
COVID-19
Of course, the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic are also still here as well. During the first week of December, the CDC reported rising cases of COVID across the country. Within the past few months, there have been several developments, though, for protection. There are now bivalent vaccines available as either third doses or booster doses approved for all persons over 6 months of age. As of the first week of December, only 13.5% of those aged 5 and over had received an updated booster.
There is currently wider access to rapid testing, including at-home testing, which can allow individuals to identify if COVID positive. Additionally, there is access to medication to decrease the likelihood of severe disease – though this does not take the place of vaccinations.
If anyone does test positive for COVID, they should follow the most recent quarantine guidelines including wearing a well-fitted mask when they do begin returning to activities.3
With rising cases of all three of these viruses, some may be asking how we can safely gather. There are several things to consider and do to enjoy our events. The first thing everyone can do is to receive updated vaccinations for both influenza and COVID-19 if eligible. Although it may take some time to be effective, vaccination is still one of our most effective methods of disease prevention and is important this winter season. Vaccinations can also help decrease the risk of severe disease.
Although many have stopped masking, as cases rise, it is time to consider masking particularly when community levels of any of these viruses are high. Masks help with preventing and spreading more than just COVID-19. Using them can be especially important for those going places such as stores and to large public gatherings and when riding on buses, planes, or trains.
In summary
Preventing exposure by masking can help keep individuals healthy prior to celebrating the holidays with others. With access to rapid testing, it makes sense to consider testing prior to gathering with friends and family. Most importantly, although we all are looking forward to spending time with our loved ones, it is important to stay home if not feeling well. Following these recommendations will allow us to have a safer and more joyful holiday season.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center and program director of Northwestern University’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, both in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at fpnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Influenza (flu). [Online] Dec. 1, 2022. [Cited: 2022 Dec 10.] https://www.cdc.gov/flu/index.htm.
2. Respiratory syncytial virus. Respiratory syncytial virus infection (RSV). [Online] Oct. 28, 2022. [Cited: 2022 Dec 10.] https://www.cdc.gov/rsv/index.html.
3. COVID-19. [Online] Dec. 7, 2022. [Cited: 2022 Dec 10.] https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/index.html.
This holiday season, I am looking forward to spending some time with family, as I have in the past. As I have chatted with others, many friends are looking forward to events that are potentially larger and potentially returning to prepandemic type gatherings.
Gathering is important and can bring joy, sense of community, and love to the lives of many. Unfortunately, the risks associated with gathering are not over. as our country faces many cases of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), COVID-19, and influenza at the same time.
During the first week of December, cases of influenza were rising across the country1 and were rising faster than in previous years. Although getting the vaccine is an important method of influenza prevention and is recommended for everyone over the age of 6 months with rare exception, many have not gotten their vaccine this year.
Influenza
Thus far, “nearly 50% of reported flu-associated hospitalizations in women of childbearing age have been in women who are pregnant.” We are seeing this at a time with lower-than-average uptake of influenza vaccine leaving both the pregnant persons and their babies unprotected. In addition to utilizing vaccines as prevention, isolating when ill, cleaning surfaces, and practicing good hand hygiene can all decrease transmission.
RSV
In addition to rises of influenza, there are currently high rates of RSV in various parts of the country. Prior to 2020, RSV typically started in the fall and peaked in the winter months. However, since the pandemic, the typical seasonal pattern has not returned, and it is unclear when it will. Although RSV hits the very young, the old, and the immunocompromised the most, RSV can infect anyone. Unfortunately, we do not currently have a vaccine for everyone against this virus. Prevention of transmission includes, as with flu, isolating when ill, cleaning surfaces, and washing hands.2
COVID-19
Of course, the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic are also still here as well. During the first week of December, the CDC reported rising cases of COVID across the country. Within the past few months, there have been several developments, though, for protection. There are now bivalent vaccines available as either third doses or booster doses approved for all persons over 6 months of age. As of the first week of December, only 13.5% of those aged 5 and over had received an updated booster.
There is currently wider access to rapid testing, including at-home testing, which can allow individuals to identify if COVID positive. Additionally, there is access to medication to decrease the likelihood of severe disease – though this does not take the place of vaccinations.
If anyone does test positive for COVID, they should follow the most recent quarantine guidelines including wearing a well-fitted mask when they do begin returning to activities.3
With rising cases of all three of these viruses, some may be asking how we can safely gather. There are several things to consider and do to enjoy our events. The first thing everyone can do is to receive updated vaccinations for both influenza and COVID-19 if eligible. Although it may take some time to be effective, vaccination is still one of our most effective methods of disease prevention and is important this winter season. Vaccinations can also help decrease the risk of severe disease.
Although many have stopped masking, as cases rise, it is time to consider masking particularly when community levels of any of these viruses are high. Masks help with preventing and spreading more than just COVID-19. Using them can be especially important for those going places such as stores and to large public gatherings and when riding on buses, planes, or trains.
In summary
Preventing exposure by masking can help keep individuals healthy prior to celebrating the holidays with others. With access to rapid testing, it makes sense to consider testing prior to gathering with friends and family. Most importantly, although we all are looking forward to spending time with our loved ones, it is important to stay home if not feeling well. Following these recommendations will allow us to have a safer and more joyful holiday season.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center and program director of Northwestern University’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, both in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at fpnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Influenza (flu). [Online] Dec. 1, 2022. [Cited: 2022 Dec 10.] https://www.cdc.gov/flu/index.htm.
2. Respiratory syncytial virus. Respiratory syncytial virus infection (RSV). [Online] Oct. 28, 2022. [Cited: 2022 Dec 10.] https://www.cdc.gov/rsv/index.html.
3. COVID-19. [Online] Dec. 7, 2022. [Cited: 2022 Dec 10.] https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/index.html.
This holiday season, I am looking forward to spending some time with family, as I have in the past. As I have chatted with others, many friends are looking forward to events that are potentially larger and potentially returning to prepandemic type gatherings.
Gathering is important and can bring joy, sense of community, and love to the lives of many. Unfortunately, the risks associated with gathering are not over. as our country faces many cases of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), COVID-19, and influenza at the same time.
During the first week of December, cases of influenza were rising across the country1 and were rising faster than in previous years. Although getting the vaccine is an important method of influenza prevention and is recommended for everyone over the age of 6 months with rare exception, many have not gotten their vaccine this year.
Influenza
Thus far, “nearly 50% of reported flu-associated hospitalizations in women of childbearing age have been in women who are pregnant.” We are seeing this at a time with lower-than-average uptake of influenza vaccine leaving both the pregnant persons and their babies unprotected. In addition to utilizing vaccines as prevention, isolating when ill, cleaning surfaces, and practicing good hand hygiene can all decrease transmission.
RSV
In addition to rises of influenza, there are currently high rates of RSV in various parts of the country. Prior to 2020, RSV typically started in the fall and peaked in the winter months. However, since the pandemic, the typical seasonal pattern has not returned, and it is unclear when it will. Although RSV hits the very young, the old, and the immunocompromised the most, RSV can infect anyone. Unfortunately, we do not currently have a vaccine for everyone against this virus. Prevention of transmission includes, as with flu, isolating when ill, cleaning surfaces, and washing hands.2
COVID-19
Of course, the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic are also still here as well. During the first week of December, the CDC reported rising cases of COVID across the country. Within the past few months, there have been several developments, though, for protection. There are now bivalent vaccines available as either third doses or booster doses approved for all persons over 6 months of age. As of the first week of December, only 13.5% of those aged 5 and over had received an updated booster.
There is currently wider access to rapid testing, including at-home testing, which can allow individuals to identify if COVID positive. Additionally, there is access to medication to decrease the likelihood of severe disease – though this does not take the place of vaccinations.
If anyone does test positive for COVID, they should follow the most recent quarantine guidelines including wearing a well-fitted mask when they do begin returning to activities.3
With rising cases of all three of these viruses, some may be asking how we can safely gather. There are several things to consider and do to enjoy our events. The first thing everyone can do is to receive updated vaccinations for both influenza and COVID-19 if eligible. Although it may take some time to be effective, vaccination is still one of our most effective methods of disease prevention and is important this winter season. Vaccinations can also help decrease the risk of severe disease.
Although many have stopped masking, as cases rise, it is time to consider masking particularly when community levels of any of these viruses are high. Masks help with preventing and spreading more than just COVID-19. Using them can be especially important for those going places such as stores and to large public gatherings and when riding on buses, planes, or trains.
In summary
Preventing exposure by masking can help keep individuals healthy prior to celebrating the holidays with others. With access to rapid testing, it makes sense to consider testing prior to gathering with friends and family. Most importantly, although we all are looking forward to spending time with our loved ones, it is important to stay home if not feeling well. Following these recommendations will allow us to have a safer and more joyful holiday season.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center and program director of Northwestern University’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, both in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at fpnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Influenza (flu). [Online] Dec. 1, 2022. [Cited: 2022 Dec 10.] https://www.cdc.gov/flu/index.htm.
2. Respiratory syncytial virus. Respiratory syncytial virus infection (RSV). [Online] Oct. 28, 2022. [Cited: 2022 Dec 10.] https://www.cdc.gov/rsv/index.html.
3. COVID-19. [Online] Dec. 7, 2022. [Cited: 2022 Dec 10.] https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/index.html.
Scientists use mRNA technology for universal flu vaccine
Two years ago, when the first COVID-19 vaccines were administered, marked a game-changing moment in the fight against the pandemic. But it also was a significant moment for messenger RNA (mRNA) technology, which up until then had shown promise but had never quite broken through.
It’s the latest advance in a new age of vaccinology, where vaccines are easier and faster to produce, as well as more flexible and customizable.
“It’s all about covering the different flavors of flu in a way the current vaccines cannot do,” says Ofer Levy, MD, PhD, director of the Precision Vaccines Program at Boston Children’s Hospital, who is not involved with the UPenn research. “The mRNA platform is attractive here given its scalability and modularity, where you can mix and match different mRNAs.”
A recent paper, published in Science, reports successful animal tests of the experimental vaccine, which, like the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna COVID vaccines, relies on mRNA. But the idea is not to replace the annual flu shot. It’s to develop a primer that could be administered in childhood, readying the body’s B cells and T cells to react quickly if faced with a flu virus.
It’s all part of a National Institutes of Health–funded effort to develop a universal flu vaccine, with hopes of heading off future flu pandemics. Annual shots protect against flu subtypes known to spread in humans. But many subtypes circulate in animals, like birds and pigs, and occasionally jump to humans, causing pandemics.
“The current vaccines provide very little protection against these other subtypes,” says lead study author Scott Hensley, PhD, a professor of microbiology at UPenn. “We set out to make a vaccine that would provide some level of immunity against essentially every influenza subtype we know about.”
That’s 20 subtypes altogether. The unique properties of mRNA vaccines make immune responses against all those antigens possible, Dr. Hensley says.
Old-school vaccines introduce a weakened or dead bacteria or virus into the body, but mRNA vaccines use mRNA encoded with a protein from the virus. That’s the “spike” protein for COVID, and for the experimental vaccine, it’s hemagglutinin, the major protein found on the surface of all flu viruses.
Mice and ferrets that had never been exposed to the flu were given the vaccine and produced high levels of antibodies against all 20 flu subtypes. Vaccinated mice exposed to the exact strains in the vaccine stayed pretty healthy, while those exposed to strains not found in the vaccine got sick but recovered quickly and survived. Unvaccinated mice exposed to the flu strain died.
The vaccine seems to be able to “induce broad immunity against all the different influenza subtypes,” Dr. Hensley says, preventing severe illness if not infection overall.
Still, whether it could truly stave off a pandemic that hasn’t happened yet is hard to say, Dr. Levy cautions.
“We are going to need to better learn the molecular rules by which these vaccines protect,” he says.
But the UPenn team is forging ahead, with plans to test their vaccine in human adults in 2023 to determine safety, dosing, and antibody response.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Two years ago, when the first COVID-19 vaccines were administered, marked a game-changing moment in the fight against the pandemic. But it also was a significant moment for messenger RNA (mRNA) technology, which up until then had shown promise but had never quite broken through.
It’s the latest advance in a new age of vaccinology, where vaccines are easier and faster to produce, as well as more flexible and customizable.
“It’s all about covering the different flavors of flu in a way the current vaccines cannot do,” says Ofer Levy, MD, PhD, director of the Precision Vaccines Program at Boston Children’s Hospital, who is not involved with the UPenn research. “The mRNA platform is attractive here given its scalability and modularity, where you can mix and match different mRNAs.”
A recent paper, published in Science, reports successful animal tests of the experimental vaccine, which, like the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna COVID vaccines, relies on mRNA. But the idea is not to replace the annual flu shot. It’s to develop a primer that could be administered in childhood, readying the body’s B cells and T cells to react quickly if faced with a flu virus.
It’s all part of a National Institutes of Health–funded effort to develop a universal flu vaccine, with hopes of heading off future flu pandemics. Annual shots protect against flu subtypes known to spread in humans. But many subtypes circulate in animals, like birds and pigs, and occasionally jump to humans, causing pandemics.
“The current vaccines provide very little protection against these other subtypes,” says lead study author Scott Hensley, PhD, a professor of microbiology at UPenn. “We set out to make a vaccine that would provide some level of immunity against essentially every influenza subtype we know about.”
That’s 20 subtypes altogether. The unique properties of mRNA vaccines make immune responses against all those antigens possible, Dr. Hensley says.
Old-school vaccines introduce a weakened or dead bacteria or virus into the body, but mRNA vaccines use mRNA encoded with a protein from the virus. That’s the “spike” protein for COVID, and for the experimental vaccine, it’s hemagglutinin, the major protein found on the surface of all flu viruses.
Mice and ferrets that had never been exposed to the flu were given the vaccine and produced high levels of antibodies against all 20 flu subtypes. Vaccinated mice exposed to the exact strains in the vaccine stayed pretty healthy, while those exposed to strains not found in the vaccine got sick but recovered quickly and survived. Unvaccinated mice exposed to the flu strain died.
The vaccine seems to be able to “induce broad immunity against all the different influenza subtypes,” Dr. Hensley says, preventing severe illness if not infection overall.
Still, whether it could truly stave off a pandemic that hasn’t happened yet is hard to say, Dr. Levy cautions.
“We are going to need to better learn the molecular rules by which these vaccines protect,” he says.
But the UPenn team is forging ahead, with plans to test their vaccine in human adults in 2023 to determine safety, dosing, and antibody response.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Two years ago, when the first COVID-19 vaccines were administered, marked a game-changing moment in the fight against the pandemic. But it also was a significant moment for messenger RNA (mRNA) technology, which up until then had shown promise but had never quite broken through.
It’s the latest advance in a new age of vaccinology, where vaccines are easier and faster to produce, as well as more flexible and customizable.
“It’s all about covering the different flavors of flu in a way the current vaccines cannot do,” says Ofer Levy, MD, PhD, director of the Precision Vaccines Program at Boston Children’s Hospital, who is not involved with the UPenn research. “The mRNA platform is attractive here given its scalability and modularity, where you can mix and match different mRNAs.”
A recent paper, published in Science, reports successful animal tests of the experimental vaccine, which, like the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna COVID vaccines, relies on mRNA. But the idea is not to replace the annual flu shot. It’s to develop a primer that could be administered in childhood, readying the body’s B cells and T cells to react quickly if faced with a flu virus.
It’s all part of a National Institutes of Health–funded effort to develop a universal flu vaccine, with hopes of heading off future flu pandemics. Annual shots protect against flu subtypes known to spread in humans. But many subtypes circulate in animals, like birds and pigs, and occasionally jump to humans, causing pandemics.
“The current vaccines provide very little protection against these other subtypes,” says lead study author Scott Hensley, PhD, a professor of microbiology at UPenn. “We set out to make a vaccine that would provide some level of immunity against essentially every influenza subtype we know about.”
That’s 20 subtypes altogether. The unique properties of mRNA vaccines make immune responses against all those antigens possible, Dr. Hensley says.
Old-school vaccines introduce a weakened or dead bacteria or virus into the body, but mRNA vaccines use mRNA encoded with a protein from the virus. That’s the “spike” protein for COVID, and for the experimental vaccine, it’s hemagglutinin, the major protein found on the surface of all flu viruses.
Mice and ferrets that had never been exposed to the flu were given the vaccine and produced high levels of antibodies against all 20 flu subtypes. Vaccinated mice exposed to the exact strains in the vaccine stayed pretty healthy, while those exposed to strains not found in the vaccine got sick but recovered quickly and survived. Unvaccinated mice exposed to the flu strain died.
The vaccine seems to be able to “induce broad immunity against all the different influenza subtypes,” Dr. Hensley says, preventing severe illness if not infection overall.
Still, whether it could truly stave off a pandemic that hasn’t happened yet is hard to say, Dr. Levy cautions.
“We are going to need to better learn the molecular rules by which these vaccines protect,” he says.
But the UPenn team is forging ahead, with plans to test their vaccine in human adults in 2023 to determine safety, dosing, and antibody response.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM SCIENCE
Flu hospitalizations drop amid signs of an early peak
It’s beginning to look less like an epidemic as seasonal flu activity “appears to be declining in some areas,” according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Declines in a few states and territories were enough to lower national activity, as measured by outpatient visits for influenza-like illness, for the second consecutive week. This reduced the weekly number of hospital admissions for the first time in the 2022-2023 season, according to the CDC influenza division’s weekly FluView report.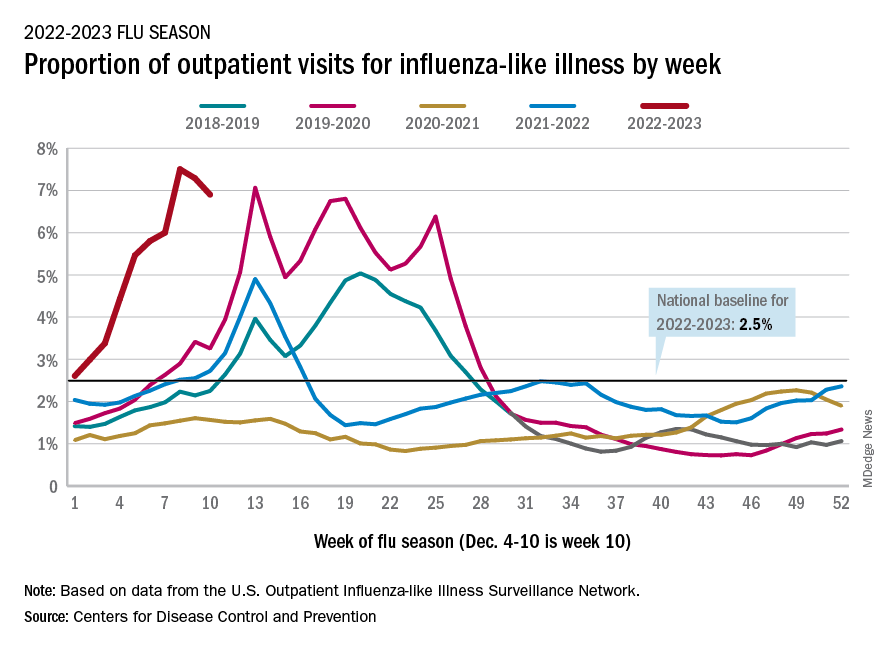
Flu-related hospital admissions slipped to about 23,500 during the week of Dec. 4-10, after topping 26,000 the week before, based on data reported by 5,000 hospitals from all states and territories.
which was still higher than any other December rate from all previous seasons going back to 2009-10, CDC data shows.
Visits for flu-like illness represented 6.9% of all outpatient visits reported to the CDC during the week of Dec. 4-10. The rate reached 7.5% during the last full week of November before dropping to 7.3%, the CDC said.
There were 28 states or territories with “very high” activity for the latest reporting week, compared with 32 the previous week. Eight states – Colorado, Idaho, Kentucky, Nebraska, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Tennessee, and Washington – and New York City were at the very highest level on the CDC’s 1-13 scale of activity, compared with 14 areas the week before, the agency reported.
So far for the 2022-2023 season, the CDC estimated there have been at least 15 million cases of the flu, 150,000 hospitalizations, and 9,300 deaths. Among those deaths have been 30 reported in children, compared with 44 for the entire 2021-22 season and just 1 for 2020-21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
It’s beginning to look less like an epidemic as seasonal flu activity “appears to be declining in some areas,” according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Declines in a few states and territories were enough to lower national activity, as measured by outpatient visits for influenza-like illness, for the second consecutive week. This reduced the weekly number of hospital admissions for the first time in the 2022-2023 season, according to the CDC influenza division’s weekly FluView report.
Flu-related hospital admissions slipped to about 23,500 during the week of Dec. 4-10, after topping 26,000 the week before, based on data reported by 5,000 hospitals from all states and territories.
which was still higher than any other December rate from all previous seasons going back to 2009-10, CDC data shows.
Visits for flu-like illness represented 6.9% of all outpatient visits reported to the CDC during the week of Dec. 4-10. The rate reached 7.5% during the last full week of November before dropping to 7.3%, the CDC said.
There were 28 states or territories with “very high” activity for the latest reporting week, compared with 32 the previous week. Eight states – Colorado, Idaho, Kentucky, Nebraska, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Tennessee, and Washington – and New York City were at the very highest level on the CDC’s 1-13 scale of activity, compared with 14 areas the week before, the agency reported.
So far for the 2022-2023 season, the CDC estimated there have been at least 15 million cases of the flu, 150,000 hospitalizations, and 9,300 deaths. Among those deaths have been 30 reported in children, compared with 44 for the entire 2021-22 season and just 1 for 2020-21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
It’s beginning to look less like an epidemic as seasonal flu activity “appears to be declining in some areas,” according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Declines in a few states and territories were enough to lower national activity, as measured by outpatient visits for influenza-like illness, for the second consecutive week. This reduced the weekly number of hospital admissions for the first time in the 2022-2023 season, according to the CDC influenza division’s weekly FluView report.
Flu-related hospital admissions slipped to about 23,500 during the week of Dec. 4-10, after topping 26,000 the week before, based on data reported by 5,000 hospitals from all states and territories.
which was still higher than any other December rate from all previous seasons going back to 2009-10, CDC data shows.
Visits for flu-like illness represented 6.9% of all outpatient visits reported to the CDC during the week of Dec. 4-10. The rate reached 7.5% during the last full week of November before dropping to 7.3%, the CDC said.
There were 28 states or territories with “very high” activity for the latest reporting week, compared with 32 the previous week. Eight states – Colorado, Idaho, Kentucky, Nebraska, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Tennessee, and Washington – and New York City were at the very highest level on the CDC’s 1-13 scale of activity, compared with 14 areas the week before, the agency reported.
So far for the 2022-2023 season, the CDC estimated there have been at least 15 million cases of the flu, 150,000 hospitalizations, and 9,300 deaths. Among those deaths have been 30 reported in children, compared with 44 for the entire 2021-22 season and just 1 for 2020-21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Hospital financial decisions play a role in the critical shortage of pediatric beds for RSV patients
The dire shortage of pediatric hospital beds plaguing the nation in the fall of 2022 is a byproduct of financial decisions made by hospitals over the past decade, as they shuttered children’s wards, which often operate in the red, and expanded the number of beds available for more profitable endeavors like joint replacements and cancer care.
To cope with the flood of young patients sickened by a sweeping convergence of nasty bugs – especially respiratory syncytial virus, influenza, and coronavirus – medical centers nationwide have deployed triage tents, delayed elective surgeries, and transferred critically ill children out of state.
A major factor in the bed shortage is a years-long trend among hospitals of eliminating pediatric units, which tend to be less profitable than adult units, said Mark Wietecha, MS, MBA, CEO of the Children’s Hospital Association. Hospitals optimize revenue by striving to keep their beds 100% full – and filled with patients whose conditions command generous insurance reimbursements.
“It really has to do with dollars,” said Scott Krugman, MD, MS, vice chair of pediatrics at the Herman and Walter Samuelson Children’s Hospital at Sinai in Baltimore. “Hospitals rely on high-volume, high-reimbursement procedures from good payers to make money. There’s no incentive for hospitals to provide money-losing services.”
The number of pediatric inpatient units in hospitals fell 19% from 2008 to 2018, according to a study published in 2021 in the journal Pediatrics. Just this year, hospitals have closed pediatric units in Boston and Springfield, Mass.; Richmond, Va.; and Tulsa, Okla.
The current surge in dangerous respiratory illnesses among children is yet another example of how COVID-19 has upended the health care system. The lockdowns and isolation that marked the first years of the pandemic left kids largely unexposed – and still vulnerable – to viruses other than COVID for two winters, and doctors are now essentially treating multiple years’ worth of respiratory ailments.
The pandemic also accelerated changes in the health care industry that have left many communities with fewer hospital beds available for children who are acutely ill, along with fewer doctors and nurses to care for them.
When intensive care units were flooded with older COVID patients in 2020, some hospitals began using children’s beds to treat adults. Many of those pediatric beds haven’t been restored, said Daniel Rauch, MD, chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics’ committee on hospital care.
In addition, the relentless pace of the pandemic has spurred more than 230,000 health care providers – including doctors, nurses, and physician assistants – to quit. Before the pandemic, about 10% of nurses left their jobs every year; the rate has risen to about 20%, Dr. Wietecha said. He estimates that pediatric hospitals are unable to maintain as many as 10% of their beds because of staffing shortages.
“There is just not enough space for all the kids who need beds,” said Megan Ranney, MD, MPH, who works in several emergency departments in Providence, R.I., including Hasbro Children’s Hospital. The number of children seeking emergency care in recent weeks was 25% higher than the hospital’s previous record.
“We have doctors who are cleaning beds so we can get children into them faster,” said Dr. Ranney, a deputy dean at Brown University’s School of Public Health.
There’s not great money in treating kids. About 40% of U.S. children are covered by Medicaid, a joint federal-state program for low-income patients and people with disabilities. Base Medicaid rates are typically more than 20% below those paid by Medicare, the government insurance program for older adults, and are even lower when compared with private insurance. While specialty care for a range of common adult procedures, from knee and hip replacements to heart surgeries and cancer treatments, generates major profits for medical centers, hospitals complain they typically lose money on inpatient pediatric care.
When Tufts Children’s Hospital closed 41 pediatric beds this summer, hospital officials assured residents that young patients could receive care at nearby Boston Children’s Hospital. Now, Boston Children’s is delaying some elective surgeries to make room for kids who are acutely ill.
Dr. Rauch noted that children’s hospitals, which specialize in treating rare and serious conditions such as pediatric cancer, cystic fibrosis, and heart defects, simply aren’t designed to handle this season’s crush of kids acutely ill with respiratory bugs.
Even before the autumn’s viral trifecta, pediatric units were straining to absorb rising numbers of young people in acute mental distress. Stories abound of children in mental crises being marooned for weeks in emergency departments while awaiting transfer to a pediatric psychiatric unit. On a good day, Dr. Ranney said, 20% of pediatric emergency room beds at Hasbro Children’s Hospital are occupied by children experiencing mental health issues.
In hopes of adding pediatric capacity, the American Academy of Pediatrics joined the Children’s Hospital Association last month in calling on the White House to declare a national emergency due to child respiratory infections and provide additional resources to help cover the costs of care. The Biden administration has said that the flexibility hospital systems and providers have been given during the pandemic to sidestep certain staffing requirements also applies to RSV and flu.
Doernbecher Children’s Hospital at Oregon Health & Science University has shifted to “crisis standards of care,” enabling intensive care nurses to treat more patients than they’re usually assigned. Hospitals in Atlanta, Pittsburgh, and Aurora, Colorado, meanwhile, have resorted to treating young patients in overflow tents in parking lots.
Alex Kon, MD, a pediatric critical care physician at Community Medical Center in Missoula, Mont., said providers there have made plans to care for older kids in the adult intensive care unit, and to divert ambulances to other facilities when necessary. With only three pediatric ICUs in the state, that means young patients may be flown as far as Seattle or Spokane, Wash., or Idaho.
Hollis Lillard took her 1-year-old son, Calder, to an Army hospital in Northern Virginia last month after he experienced several days of fever, coughing, and labored breathing. They spent 7 anguished hours in the emergency room before the hospital found an open bed and transferred them by ambulance to Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Maryland.
With proper therapy and instructions for home care, Calder’s virus was readily treatable: He recovered after he was given oxygen and treated with steroids, which fight inflammation, and albuterol, which counteracts bronchospasms. He was discharged the next day.
Although hospitalizations for RSV are falling, rates remain well above the norm for this time of year. And hospitals may not get much relief.
People can be infected with RSV more than once a year, and Dr. Krugman worries about a resurgence in the months to come. Because of the coronavirus, which competes with other viruses, “the usual seasonal pattern of viruses has gone out the window,” he said.
Like RSV, influenza arrived early this season. Both viruses usually peak around January. Three strains of flu are circulating and have caused an estimated 8.7 million illnesses, 78,000 hospitalizations, and 4,500 deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Dr. Krugman doubts the health care industry will learn any quick lessons from the current crisis. “Unless there is a radical change in how we pay for pediatric hospital care,” Dr. Krugman said, “the bed shortage is only going to get worse.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
The dire shortage of pediatric hospital beds plaguing the nation in the fall of 2022 is a byproduct of financial decisions made by hospitals over the past decade, as they shuttered children’s wards, which often operate in the red, and expanded the number of beds available for more profitable endeavors like joint replacements and cancer care.
To cope with the flood of young patients sickened by a sweeping convergence of nasty bugs – especially respiratory syncytial virus, influenza, and coronavirus – medical centers nationwide have deployed triage tents, delayed elective surgeries, and transferred critically ill children out of state.
A major factor in the bed shortage is a years-long trend among hospitals of eliminating pediatric units, which tend to be less profitable than adult units, said Mark Wietecha, MS, MBA, CEO of the Children’s Hospital Association. Hospitals optimize revenue by striving to keep their beds 100% full – and filled with patients whose conditions command generous insurance reimbursements.
“It really has to do with dollars,” said Scott Krugman, MD, MS, vice chair of pediatrics at the Herman and Walter Samuelson Children’s Hospital at Sinai in Baltimore. “Hospitals rely on high-volume, high-reimbursement procedures from good payers to make money. There’s no incentive for hospitals to provide money-losing services.”
The number of pediatric inpatient units in hospitals fell 19% from 2008 to 2018, according to a study published in 2021 in the journal Pediatrics. Just this year, hospitals have closed pediatric units in Boston and Springfield, Mass.; Richmond, Va.; and Tulsa, Okla.
The current surge in dangerous respiratory illnesses among children is yet another example of how COVID-19 has upended the health care system. The lockdowns and isolation that marked the first years of the pandemic left kids largely unexposed – and still vulnerable – to viruses other than COVID for two winters, and doctors are now essentially treating multiple years’ worth of respiratory ailments.
The pandemic also accelerated changes in the health care industry that have left many communities with fewer hospital beds available for children who are acutely ill, along with fewer doctors and nurses to care for them.
When intensive care units were flooded with older COVID patients in 2020, some hospitals began using children’s beds to treat adults. Many of those pediatric beds haven’t been restored, said Daniel Rauch, MD, chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics’ committee on hospital care.
In addition, the relentless pace of the pandemic has spurred more than 230,000 health care providers – including doctors, nurses, and physician assistants – to quit. Before the pandemic, about 10% of nurses left their jobs every year; the rate has risen to about 20%, Dr. Wietecha said. He estimates that pediatric hospitals are unable to maintain as many as 10% of their beds because of staffing shortages.
“There is just not enough space for all the kids who need beds,” said Megan Ranney, MD, MPH, who works in several emergency departments in Providence, R.I., including Hasbro Children’s Hospital. The number of children seeking emergency care in recent weeks was 25% higher than the hospital’s previous record.
“We have doctors who are cleaning beds so we can get children into them faster,” said Dr. Ranney, a deputy dean at Brown University’s School of Public Health.
There’s not great money in treating kids. About 40% of U.S. children are covered by Medicaid, a joint federal-state program for low-income patients and people with disabilities. Base Medicaid rates are typically more than 20% below those paid by Medicare, the government insurance program for older adults, and are even lower when compared with private insurance. While specialty care for a range of common adult procedures, from knee and hip replacements to heart surgeries and cancer treatments, generates major profits for medical centers, hospitals complain they typically lose money on inpatient pediatric care.
When Tufts Children’s Hospital closed 41 pediatric beds this summer, hospital officials assured residents that young patients could receive care at nearby Boston Children’s Hospital. Now, Boston Children’s is delaying some elective surgeries to make room for kids who are acutely ill.
Dr. Rauch noted that children’s hospitals, which specialize in treating rare and serious conditions such as pediatric cancer, cystic fibrosis, and heart defects, simply aren’t designed to handle this season’s crush of kids acutely ill with respiratory bugs.
Even before the autumn’s viral trifecta, pediatric units were straining to absorb rising numbers of young people in acute mental distress. Stories abound of children in mental crises being marooned for weeks in emergency departments while awaiting transfer to a pediatric psychiatric unit. On a good day, Dr. Ranney said, 20% of pediatric emergency room beds at Hasbro Children’s Hospital are occupied by children experiencing mental health issues.
In hopes of adding pediatric capacity, the American Academy of Pediatrics joined the Children’s Hospital Association last month in calling on the White House to declare a national emergency due to child respiratory infections and provide additional resources to help cover the costs of care. The Biden administration has said that the flexibility hospital systems and providers have been given during the pandemic to sidestep certain staffing requirements also applies to RSV and flu.
Doernbecher Children’s Hospital at Oregon Health & Science University has shifted to “crisis standards of care,” enabling intensive care nurses to treat more patients than they’re usually assigned. Hospitals in Atlanta, Pittsburgh, and Aurora, Colorado, meanwhile, have resorted to treating young patients in overflow tents in parking lots.
Alex Kon, MD, a pediatric critical care physician at Community Medical Center in Missoula, Mont., said providers there have made plans to care for older kids in the adult intensive care unit, and to divert ambulances to other facilities when necessary. With only three pediatric ICUs in the state, that means young patients may be flown as far as Seattle or Spokane, Wash., or Idaho.
Hollis Lillard took her 1-year-old son, Calder, to an Army hospital in Northern Virginia last month after he experienced several days of fever, coughing, and labored breathing. They spent 7 anguished hours in the emergency room before the hospital found an open bed and transferred them by ambulance to Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Maryland.
With proper therapy and instructions for home care, Calder’s virus was readily treatable: He recovered after he was given oxygen and treated with steroids, which fight inflammation, and albuterol, which counteracts bronchospasms. He was discharged the next day.
Although hospitalizations for RSV are falling, rates remain well above the norm for this time of year. And hospitals may not get much relief.
People can be infected with RSV more than once a year, and Dr. Krugman worries about a resurgence in the months to come. Because of the coronavirus, which competes with other viruses, “the usual seasonal pattern of viruses has gone out the window,” he said.
Like RSV, influenza arrived early this season. Both viruses usually peak around January. Three strains of flu are circulating and have caused an estimated 8.7 million illnesses, 78,000 hospitalizations, and 4,500 deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Dr. Krugman doubts the health care industry will learn any quick lessons from the current crisis. “Unless there is a radical change in how we pay for pediatric hospital care,” Dr. Krugman said, “the bed shortage is only going to get worse.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
The dire shortage of pediatric hospital beds plaguing the nation in the fall of 2022 is a byproduct of financial decisions made by hospitals over the past decade, as they shuttered children’s wards, which often operate in the red, and expanded the number of beds available for more profitable endeavors like joint replacements and cancer care.
To cope with the flood of young patients sickened by a sweeping convergence of nasty bugs – especially respiratory syncytial virus, influenza, and coronavirus – medical centers nationwide have deployed triage tents, delayed elective surgeries, and transferred critically ill children out of state.
A major factor in the bed shortage is a years-long trend among hospitals of eliminating pediatric units, which tend to be less profitable than adult units, said Mark Wietecha, MS, MBA, CEO of the Children’s Hospital Association. Hospitals optimize revenue by striving to keep their beds 100% full – and filled with patients whose conditions command generous insurance reimbursements.
“It really has to do with dollars,” said Scott Krugman, MD, MS, vice chair of pediatrics at the Herman and Walter Samuelson Children’s Hospital at Sinai in Baltimore. “Hospitals rely on high-volume, high-reimbursement procedures from good payers to make money. There’s no incentive for hospitals to provide money-losing services.”
The number of pediatric inpatient units in hospitals fell 19% from 2008 to 2018, according to a study published in 2021 in the journal Pediatrics. Just this year, hospitals have closed pediatric units in Boston and Springfield, Mass.; Richmond, Va.; and Tulsa, Okla.
The current surge in dangerous respiratory illnesses among children is yet another example of how COVID-19 has upended the health care system. The lockdowns and isolation that marked the first years of the pandemic left kids largely unexposed – and still vulnerable – to viruses other than COVID for two winters, and doctors are now essentially treating multiple years’ worth of respiratory ailments.
The pandemic also accelerated changes in the health care industry that have left many communities with fewer hospital beds available for children who are acutely ill, along with fewer doctors and nurses to care for them.
When intensive care units were flooded with older COVID patients in 2020, some hospitals began using children’s beds to treat adults. Many of those pediatric beds haven’t been restored, said Daniel Rauch, MD, chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics’ committee on hospital care.
In addition, the relentless pace of the pandemic has spurred more than 230,000 health care providers – including doctors, nurses, and physician assistants – to quit. Before the pandemic, about 10% of nurses left their jobs every year; the rate has risen to about 20%, Dr. Wietecha said. He estimates that pediatric hospitals are unable to maintain as many as 10% of their beds because of staffing shortages.
“There is just not enough space for all the kids who need beds,” said Megan Ranney, MD, MPH, who works in several emergency departments in Providence, R.I., including Hasbro Children’s Hospital. The number of children seeking emergency care in recent weeks was 25% higher than the hospital’s previous record.
“We have doctors who are cleaning beds so we can get children into them faster,” said Dr. Ranney, a deputy dean at Brown University’s School of Public Health.
There’s not great money in treating kids. About 40% of U.S. children are covered by Medicaid, a joint federal-state program for low-income patients and people with disabilities. Base Medicaid rates are typically more than 20% below those paid by Medicare, the government insurance program for older adults, and are even lower when compared with private insurance. While specialty care for a range of common adult procedures, from knee and hip replacements to heart surgeries and cancer treatments, generates major profits for medical centers, hospitals complain they typically lose money on inpatient pediatric care.
When Tufts Children’s Hospital closed 41 pediatric beds this summer, hospital officials assured residents that young patients could receive care at nearby Boston Children’s Hospital. Now, Boston Children’s is delaying some elective surgeries to make room for kids who are acutely ill.
Dr. Rauch noted that children’s hospitals, which specialize in treating rare and serious conditions such as pediatric cancer, cystic fibrosis, and heart defects, simply aren’t designed to handle this season’s crush of kids acutely ill with respiratory bugs.
Even before the autumn’s viral trifecta, pediatric units were straining to absorb rising numbers of young people in acute mental distress. Stories abound of children in mental crises being marooned for weeks in emergency departments while awaiting transfer to a pediatric psychiatric unit. On a good day, Dr. Ranney said, 20% of pediatric emergency room beds at Hasbro Children’s Hospital are occupied by children experiencing mental health issues.
In hopes of adding pediatric capacity, the American Academy of Pediatrics joined the Children’s Hospital Association last month in calling on the White House to declare a national emergency due to child respiratory infections and provide additional resources to help cover the costs of care. The Biden administration has said that the flexibility hospital systems and providers have been given during the pandemic to sidestep certain staffing requirements also applies to RSV and flu.
Doernbecher Children’s Hospital at Oregon Health & Science University has shifted to “crisis standards of care,” enabling intensive care nurses to treat more patients than they’re usually assigned. Hospitals in Atlanta, Pittsburgh, and Aurora, Colorado, meanwhile, have resorted to treating young patients in overflow tents in parking lots.
Alex Kon, MD, a pediatric critical care physician at Community Medical Center in Missoula, Mont., said providers there have made plans to care for older kids in the adult intensive care unit, and to divert ambulances to other facilities when necessary. With only three pediatric ICUs in the state, that means young patients may be flown as far as Seattle or Spokane, Wash., or Idaho.
Hollis Lillard took her 1-year-old son, Calder, to an Army hospital in Northern Virginia last month after he experienced several days of fever, coughing, and labored breathing. They spent 7 anguished hours in the emergency room before the hospital found an open bed and transferred them by ambulance to Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Maryland.
With proper therapy and instructions for home care, Calder’s virus was readily treatable: He recovered after he was given oxygen and treated with steroids, which fight inflammation, and albuterol, which counteracts bronchospasms. He was discharged the next day.
Although hospitalizations for RSV are falling, rates remain well above the norm for this time of year. And hospitals may not get much relief.
People can be infected with RSV more than once a year, and Dr. Krugman worries about a resurgence in the months to come. Because of the coronavirus, which competes with other viruses, “the usual seasonal pattern of viruses has gone out the window,” he said.
Like RSV, influenza arrived early this season. Both viruses usually peak around January. Three strains of flu are circulating and have caused an estimated 8.7 million illnesses, 78,000 hospitalizations, and 4,500 deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Dr. Krugman doubts the health care industry will learn any quick lessons from the current crisis. “Unless there is a radical change in how we pay for pediatric hospital care,” Dr. Krugman said, “the bed shortage is only going to get worse.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
RSV surge stuns parents and strains providers, but doctors offer help
RSV cases peaked in mid-November, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, with RSV-associated hospitalizations in the United States among patients 0-4 years having maxed out five times higher than they were at the same time in 2021. These surges strained providers and left parents scrambling for care. Fortunately, pediatric hospitalizations appear to be subsiding.
In interviews, the parents of the child who had a severe case of RSV reflected on their son’s bout with the illness, and doctors described challenges to dealing with the surge in RSV cases this season. The physicians also offered advice on how recognize and respond to future cases of the virus.
Sebastian Witt’s story
“I didn’t even know what RSV was,” said Malte Witt, whose son, Sebastian, 2, was recently hospitalized for RSV in Denver.
Mr. Witt and his wife, Emily Witt, both 32, thought they were dealing with a typical cold until Sebastian’s condition dramatically deteriorated about 36 hours after symptom onset.
“He basically just slumped over and collapsed, coughing uncontrollably,” Mr. Witt said in an interview. “He couldn’t catch his breath.”
The Witts rushed Sebastian to the ED at Children’s Hospital Colorado, expecting to see a doctor immediately. Instead, they spent the night in an overcrowded waiting room alongside many other families in the same situation.
“There was no room for anyone to sit anywhere,” Mr. Witt said. “There were people sitting on the floor. I counted maybe six children hooked up to oxygen when we walked in.”
After waiting approximately 45 minutes, a nurse checked Sebastian’s oxygen saturation. The readings were 79%-83%. This range is significantly below thresholds for supplemental oxygen described by most pediatric guidelines, which range from 90 to 94%.
The nurse connected Sebastian to bottled oxygen in the waiting room, and a recheck 4 hours later showed that his oxygen saturation had improved.
But the improvement didn’t last.
“At roughly hour 10 in the waiting room – it was 4 in the morning – you could tell that Seb was exhausted, really not acting like himself,” Mr. Witt said. “We thought maybe it’s just late at night, he hasn’t really slept. But then Emily noticed that his oxygen tank had run out.”
Mr. Witt told a nurse, and after another check revealed low oxygen saturation, Sebastian was finally admitted.
Early RSV surge strains pediatric providers
With RSV-associated hospitalizations peaking at 48 per 100,000 children, Colorado has been among the states hardest hit by the virus. New Mexico – where hospitalizations peaked at 56.4 per 100,000 children – comes in second. Even in states like California, where hospitalization rates have been almost 10-fold lower than New Mexico, pediatric providers have been stretched to their limits.
“Many hospitals are really being overwhelmed with admissions for RSV, both routine RSV – relatively mild hospitalizations with bronchiolitis – as well as kids in the ICU with more severe cases,” said Dean Blumberg, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at UC Davis Health, Sacramento, said in an interview.
Dr. Blumberg believes the severity of the 2022-2023 RSV season is likely COVID related.
“All community-associated respiratory viral infections are out of whack because of the pandemic, and all the masking and social distancing that was occurring,” he said.
This may also explain why older kids are coming down with more severe cases of RSV.
“Some children are getting RSV for the first time as older children,” Dr. Blumberg said, noting that, historically, most children were infected in the first 2 years of life. “There are reports of children 3 or 4 years of age being admitted with their first episode of RSV because of the [COVID] pandemic.”
This year’s RSV season is also notable for arriving early, potentially catching the community off guard, according to Jennifer D. Kusma, MD, a primary care pediatrician at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
“People who should have been protected often weren’t protected yet,” Dr. Kusma said in an interview.
Treatments new, old, and unproven
On Nov. 17, in the midst of the RSV surge, the American Academy of Pediatrics issued updated guidance for palivizumab, an RSV-targeting monoclonal antibody labeled for children at risk of severe RSV, including those with pre-existing lung or heart conditions, and infants with a history of premature birth (less than or equal to 35 weeks’ gestational age).
“If RSV disease activity persists at high levels in a given region through the fall and winter, the AAP supports providing more than five consecutive doses of palivizumab to eligible children,” the update stated.
Insurance companies appear to be responding in kind, covering additional doses for children in need.
“[Payers] have agreed that, if [palivizumab] needs to be given for an additional month or 2 or 3, then they’re making a commitment that they’ll reimburse hospitals for providing that,” Dr. Blumberg said.
For ineligible patients, such as Sebastian, who was born prematurely at 36 weeks – 1 week shy of the label requirement – treatment relies upon supportive care with oxygen and IV fluids.
At home, parents are left with simpler options.
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma recommended keeping children hydrated, maintaining humidified air, and using saline nose drops with bulb suction to clear mucus.
In the Witts’ experience, that last step may be easier said than done.
“Every time a nurse would walk into the room, Sebastian would yell: ‘Go away, doctor! I don’t want snot sucker!’” Mr. Witt said.
“If you over snot-suck, that’s really uncomfortable for the kid, and really hard for you,” Ms. Witt said. “And it doesn’t make much of a difference. It’s just very hard to find a middle ground, where you’re helping and keeping them comfortable.”
Some parents are turning to novel strategies, such as nebulized hypertonic saline, currently marketed on Amazon for children with RSV.
Although the AAP offers a weak recommendation for nebulized hypertonic saline in children hospitalized more than 72 hours, they advise against it in the emergency setting, citing inconsistent findings in clinical trials.
To any parents tempted by thousands of positive Amazon reviews, Dr. Blumberg said, “I wouldn’t waste my money on that.”
Dr. Kusma agreed.
“[Nebulized hypertonic saline] can be irritating,” she said. “It’s saltwater, essentially. If a parent is in the position where they’re worried about their child’s breathing to the point that they think they need to use it, I would err on the side of calling your pediatrician and being seen.”
Going in, coming home
Dr. Kusma said parents should seek medical attention if a child is breathing faster and working harder to get air. Increased work of breathing is characterized by pulling of the skin at the notch where the throat meets the chest bone (tracheal tugging), and flattening of the belly that makes the ribcage more prominent.
Mr. Witt saw these signs in Sebastian. He knew they were significant, because a friend who is a nurse had previously shown him some examples of children who exhibited these symptoms online.
“That’s how I knew that things were actually really dangerous,” Mr. Witt said. “Had she not shown me those videos a month and a half before this happened, I don’t know that we would have hit the alarm bell as quickly as we did.”
After spending their second night and the following day in a cramped preoperative room converted to manage overflow from the emergency department, Sebastian’s condition improved, and he was discharged. The Witts are relieved to be home, but frustrations from their ordeal remain, especially considering the estimated $5,000 in out-of-pocket costs they expect to pay.
“How is this our health care system?” Ms. Witt asked. “This is unbelievable.”
An optimistic outlook
RSV seasons typically demonstrate a clear peak, followed by a decline through the rest of the season, suggesting better times lie ahead; however, this season has been anything but typical.
“I’m hopeful that it will just go away and stay away,” Dr. Kusma said, citing this trend. “But I can’t know for sure.”
To anxious parents, Dr. Blumberg offered an optimistic view of RSV seasons to come.
“There’s hope,” he said. “There are vaccines that are being developed that are very close to FDA approval. So, it’s possible that this time next year, we might have widespread RSV vaccination available for children so that we don’t have to go through this nightmare again.”
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
RSV cases peaked in mid-November, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, with RSV-associated hospitalizations in the United States among patients 0-4 years having maxed out five times higher than they were at the same time in 2021. These surges strained providers and left parents scrambling for care. Fortunately, pediatric hospitalizations appear to be subsiding.
In interviews, the parents of the child who had a severe case of RSV reflected on their son’s bout with the illness, and doctors described challenges to dealing with the surge in RSV cases this season. The physicians also offered advice on how recognize and respond to future cases of the virus.
Sebastian Witt’s story
“I didn’t even know what RSV was,” said Malte Witt, whose son, Sebastian, 2, was recently hospitalized for RSV in Denver.
Mr. Witt and his wife, Emily Witt, both 32, thought they were dealing with a typical cold until Sebastian’s condition dramatically deteriorated about 36 hours after symptom onset.
“He basically just slumped over and collapsed, coughing uncontrollably,” Mr. Witt said in an interview. “He couldn’t catch his breath.”
The Witts rushed Sebastian to the ED at Children’s Hospital Colorado, expecting to see a doctor immediately. Instead, they spent the night in an overcrowded waiting room alongside many other families in the same situation.
“There was no room for anyone to sit anywhere,” Mr. Witt said. “There were people sitting on the floor. I counted maybe six children hooked up to oxygen when we walked in.”
After waiting approximately 45 minutes, a nurse checked Sebastian’s oxygen saturation. The readings were 79%-83%. This range is significantly below thresholds for supplemental oxygen described by most pediatric guidelines, which range from 90 to 94%.
The nurse connected Sebastian to bottled oxygen in the waiting room, and a recheck 4 hours later showed that his oxygen saturation had improved.
But the improvement didn’t last.
“At roughly hour 10 in the waiting room – it was 4 in the morning – you could tell that Seb was exhausted, really not acting like himself,” Mr. Witt said. “We thought maybe it’s just late at night, he hasn’t really slept. But then Emily noticed that his oxygen tank had run out.”
Mr. Witt told a nurse, and after another check revealed low oxygen saturation, Sebastian was finally admitted.
Early RSV surge strains pediatric providers
With RSV-associated hospitalizations peaking at 48 per 100,000 children, Colorado has been among the states hardest hit by the virus. New Mexico – where hospitalizations peaked at 56.4 per 100,000 children – comes in second. Even in states like California, where hospitalization rates have been almost 10-fold lower than New Mexico, pediatric providers have been stretched to their limits.
“Many hospitals are really being overwhelmed with admissions for RSV, both routine RSV – relatively mild hospitalizations with bronchiolitis – as well as kids in the ICU with more severe cases,” said Dean Blumberg, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at UC Davis Health, Sacramento, said in an interview.
Dr. Blumberg believes the severity of the 2022-2023 RSV season is likely COVID related.
“All community-associated respiratory viral infections are out of whack because of the pandemic, and all the masking and social distancing that was occurring,” he said.
This may also explain why older kids are coming down with more severe cases of RSV.
“Some children are getting RSV for the first time as older children,” Dr. Blumberg said, noting that, historically, most children were infected in the first 2 years of life. “There are reports of children 3 or 4 years of age being admitted with their first episode of RSV because of the [COVID] pandemic.”
This year’s RSV season is also notable for arriving early, potentially catching the community off guard, according to Jennifer D. Kusma, MD, a primary care pediatrician at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
“People who should have been protected often weren’t protected yet,” Dr. Kusma said in an interview.
Treatments new, old, and unproven
On Nov. 17, in the midst of the RSV surge, the American Academy of Pediatrics issued updated guidance for palivizumab, an RSV-targeting monoclonal antibody labeled for children at risk of severe RSV, including those with pre-existing lung or heart conditions, and infants with a history of premature birth (less than or equal to 35 weeks’ gestational age).
“If RSV disease activity persists at high levels in a given region through the fall and winter, the AAP supports providing more than five consecutive doses of palivizumab to eligible children,” the update stated.
Insurance companies appear to be responding in kind, covering additional doses for children in need.
“[Payers] have agreed that, if [palivizumab] needs to be given for an additional month or 2 or 3, then they’re making a commitment that they’ll reimburse hospitals for providing that,” Dr. Blumberg said.
For ineligible patients, such as Sebastian, who was born prematurely at 36 weeks – 1 week shy of the label requirement – treatment relies upon supportive care with oxygen and IV fluids.
At home, parents are left with simpler options.
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma recommended keeping children hydrated, maintaining humidified air, and using saline nose drops with bulb suction to clear mucus.
In the Witts’ experience, that last step may be easier said than done.
“Every time a nurse would walk into the room, Sebastian would yell: ‘Go away, doctor! I don’t want snot sucker!’” Mr. Witt said.
“If you over snot-suck, that’s really uncomfortable for the kid, and really hard for you,” Ms. Witt said. “And it doesn’t make much of a difference. It’s just very hard to find a middle ground, where you’re helping and keeping them comfortable.”
Some parents are turning to novel strategies, such as nebulized hypertonic saline, currently marketed on Amazon for children with RSV.
Although the AAP offers a weak recommendation for nebulized hypertonic saline in children hospitalized more than 72 hours, they advise against it in the emergency setting, citing inconsistent findings in clinical trials.
To any parents tempted by thousands of positive Amazon reviews, Dr. Blumberg said, “I wouldn’t waste my money on that.”
Dr. Kusma agreed.
“[Nebulized hypertonic saline] can be irritating,” she said. “It’s saltwater, essentially. If a parent is in the position where they’re worried about their child’s breathing to the point that they think they need to use it, I would err on the side of calling your pediatrician and being seen.”
Going in, coming home
Dr. Kusma said parents should seek medical attention if a child is breathing faster and working harder to get air. Increased work of breathing is characterized by pulling of the skin at the notch where the throat meets the chest bone (tracheal tugging), and flattening of the belly that makes the ribcage more prominent.
Mr. Witt saw these signs in Sebastian. He knew they were significant, because a friend who is a nurse had previously shown him some examples of children who exhibited these symptoms online.
“That’s how I knew that things were actually really dangerous,” Mr. Witt said. “Had she not shown me those videos a month and a half before this happened, I don’t know that we would have hit the alarm bell as quickly as we did.”
After spending their second night and the following day in a cramped preoperative room converted to manage overflow from the emergency department, Sebastian’s condition improved, and he was discharged. The Witts are relieved to be home, but frustrations from their ordeal remain, especially considering the estimated $5,000 in out-of-pocket costs they expect to pay.
“How is this our health care system?” Ms. Witt asked. “This is unbelievable.”
An optimistic outlook
RSV seasons typically demonstrate a clear peak, followed by a decline through the rest of the season, suggesting better times lie ahead; however, this season has been anything but typical.
“I’m hopeful that it will just go away and stay away,” Dr. Kusma said, citing this trend. “But I can’t know for sure.”
To anxious parents, Dr. Blumberg offered an optimistic view of RSV seasons to come.
“There’s hope,” he said. “There are vaccines that are being developed that are very close to FDA approval. So, it’s possible that this time next year, we might have widespread RSV vaccination available for children so that we don’t have to go through this nightmare again.”
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
RSV cases peaked in mid-November, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, with RSV-associated hospitalizations in the United States among patients 0-4 years having maxed out five times higher than they were at the same time in 2021. These surges strained providers and left parents scrambling for care. Fortunately, pediatric hospitalizations appear to be subsiding.
In interviews, the parents of the child who had a severe case of RSV reflected on their son’s bout with the illness, and doctors described challenges to dealing with the surge in RSV cases this season. The physicians also offered advice on how recognize and respond to future cases of the virus.
Sebastian Witt’s story
“I didn’t even know what RSV was,” said Malte Witt, whose son, Sebastian, 2, was recently hospitalized for RSV in Denver.
Mr. Witt and his wife, Emily Witt, both 32, thought they were dealing with a typical cold until Sebastian’s condition dramatically deteriorated about 36 hours after symptom onset.
“He basically just slumped over and collapsed, coughing uncontrollably,” Mr. Witt said in an interview. “He couldn’t catch his breath.”
The Witts rushed Sebastian to the ED at Children’s Hospital Colorado, expecting to see a doctor immediately. Instead, they spent the night in an overcrowded waiting room alongside many other families in the same situation.
“There was no room for anyone to sit anywhere,” Mr. Witt said. “There were people sitting on the floor. I counted maybe six children hooked up to oxygen when we walked in.”
After waiting approximately 45 minutes, a nurse checked Sebastian’s oxygen saturation. The readings were 79%-83%. This range is significantly below thresholds for supplemental oxygen described by most pediatric guidelines, which range from 90 to 94%.
The nurse connected Sebastian to bottled oxygen in the waiting room, and a recheck 4 hours later showed that his oxygen saturation had improved.
But the improvement didn’t last.
“At roughly hour 10 in the waiting room – it was 4 in the morning – you could tell that Seb was exhausted, really not acting like himself,” Mr. Witt said. “We thought maybe it’s just late at night, he hasn’t really slept. But then Emily noticed that his oxygen tank had run out.”
Mr. Witt told a nurse, and after another check revealed low oxygen saturation, Sebastian was finally admitted.
Early RSV surge strains pediatric providers
With RSV-associated hospitalizations peaking at 48 per 100,000 children, Colorado has been among the states hardest hit by the virus. New Mexico – where hospitalizations peaked at 56.4 per 100,000 children – comes in second. Even in states like California, where hospitalization rates have been almost 10-fold lower than New Mexico, pediatric providers have been stretched to their limits.
“Many hospitals are really being overwhelmed with admissions for RSV, both routine RSV – relatively mild hospitalizations with bronchiolitis – as well as kids in the ICU with more severe cases,” said Dean Blumberg, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at UC Davis Health, Sacramento, said in an interview.
Dr. Blumberg believes the severity of the 2022-2023 RSV season is likely COVID related.
“All community-associated respiratory viral infections are out of whack because of the pandemic, and all the masking and social distancing that was occurring,” he said.
This may also explain why older kids are coming down with more severe cases of RSV.
“Some children are getting RSV for the first time as older children,” Dr. Blumberg said, noting that, historically, most children were infected in the first 2 years of life. “There are reports of children 3 or 4 years of age being admitted with their first episode of RSV because of the [COVID] pandemic.”
This year’s RSV season is also notable for arriving early, potentially catching the community off guard, according to Jennifer D. Kusma, MD, a primary care pediatrician at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
“People who should have been protected often weren’t protected yet,” Dr. Kusma said in an interview.
Treatments new, old, and unproven
On Nov. 17, in the midst of the RSV surge, the American Academy of Pediatrics issued updated guidance for palivizumab, an RSV-targeting monoclonal antibody labeled for children at risk of severe RSV, including those with pre-existing lung or heart conditions, and infants with a history of premature birth (less than or equal to 35 weeks’ gestational age).
“If RSV disease activity persists at high levels in a given region through the fall and winter, the AAP supports providing more than five consecutive doses of palivizumab to eligible children,” the update stated.
Insurance companies appear to be responding in kind, covering additional doses for children in need.
“[Payers] have agreed that, if [palivizumab] needs to be given for an additional month or 2 or 3, then they’re making a commitment that they’ll reimburse hospitals for providing that,” Dr. Blumberg said.
For ineligible patients, such as Sebastian, who was born prematurely at 36 weeks – 1 week shy of the label requirement – treatment relies upon supportive care with oxygen and IV fluids.
At home, parents are left with simpler options.
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma recommended keeping children hydrated, maintaining humidified air, and using saline nose drops with bulb suction to clear mucus.
In the Witts’ experience, that last step may be easier said than done.
“Every time a nurse would walk into the room, Sebastian would yell: ‘Go away, doctor! I don’t want snot sucker!’” Mr. Witt said.
“If you over snot-suck, that’s really uncomfortable for the kid, and really hard for you,” Ms. Witt said. “And it doesn’t make much of a difference. It’s just very hard to find a middle ground, where you’re helping and keeping them comfortable.”
Some parents are turning to novel strategies, such as nebulized hypertonic saline, currently marketed on Amazon for children with RSV.
Although the AAP offers a weak recommendation for nebulized hypertonic saline in children hospitalized more than 72 hours, they advise against it in the emergency setting, citing inconsistent findings in clinical trials.
To any parents tempted by thousands of positive Amazon reviews, Dr. Blumberg said, “I wouldn’t waste my money on that.”
Dr. Kusma agreed.
“[Nebulized hypertonic saline] can be irritating,” she said. “It’s saltwater, essentially. If a parent is in the position where they’re worried about their child’s breathing to the point that they think they need to use it, I would err on the side of calling your pediatrician and being seen.”
Going in, coming home
Dr. Kusma said parents should seek medical attention if a child is breathing faster and working harder to get air. Increased work of breathing is characterized by pulling of the skin at the notch where the throat meets the chest bone (tracheal tugging), and flattening of the belly that makes the ribcage more prominent.
Mr. Witt saw these signs in Sebastian. He knew they were significant, because a friend who is a nurse had previously shown him some examples of children who exhibited these symptoms online.
“That’s how I knew that things were actually really dangerous,” Mr. Witt said. “Had she not shown me those videos a month and a half before this happened, I don’t know that we would have hit the alarm bell as quickly as we did.”
After spending their second night and the following day in a cramped preoperative room converted to manage overflow from the emergency department, Sebastian’s condition improved, and he was discharged. The Witts are relieved to be home, but frustrations from their ordeal remain, especially considering the estimated $5,000 in out-of-pocket costs they expect to pay.
“How is this our health care system?” Ms. Witt asked. “This is unbelievable.”
An optimistic outlook
RSV seasons typically demonstrate a clear peak, followed by a decline through the rest of the season, suggesting better times lie ahead; however, this season has been anything but typical.
“I’m hopeful that it will just go away and stay away,” Dr. Kusma said, citing this trend. “But I can’t know for sure.”
To anxious parents, Dr. Blumberg offered an optimistic view of RSV seasons to come.
“There’s hope,” he said. “There are vaccines that are being developed that are very close to FDA approval. So, it’s possible that this time next year, we might have widespread RSV vaccination available for children so that we don’t have to go through this nightmare again.”
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Experts explain the ‘perfect storm’ of rampant RSV and flu
Headlines over the past few weeks are ringing the alarm about earlier and more serious influenza (flu) and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) outbreaks compared with previous years. Add COVID-19 to the mix and you have a dangerous mash of viruses that have many experts calling for caution and searching for explanations.
RSV and the flu “are certainly getting more attention, and they’re getting more attention for two reasons,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
“The first is that they’re both extraordinarily early. The second is that they’re both out there spreading very, very rapidly,” he told this news organization.
RSV usually follows a seasonal pattern with cases peaking in January and February. Both viruses tend to hit different regions of the country at different times, and that’s not the case in 2022.
“This is particularly striking for RSV, which usually doesn’t affect the entire country simultaneously,” Dr. Schaffner said.
“Yes, RSV is causing many more hospitalizations and earlier than any previously recorded season in the U.S.,” according to figures from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on RSV hospitalizations, said Kevin Messacar, MD, PhD, associate professor at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora.
Although there could be some increase in diagnoses because of increased awareness, the jump in RSV and flu cases “is a real phenomenon for multiple reasons,” said Peter Chin-Hong, MD, professor in the division of infectious diseases at the University of California, San Francisco.
With fewer COVID-related restrictions, people are moving around more. Also, during fall and winter, people tend to gather indoors. Colder temperatures and lower humidity contribute as well, Dr. Chin-Hong said, because “the droplets are just simply lighter.
“I think those are all factors,” he told this news organization.
Paul Auwaerter, MD, agreed that there are likely multiple causes for the unusual timing and severity of RSV and flu this year.
“Change in behaviors is a leading cause,” said the clinical director for the division of infectious diseases at the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. More people returning to the workplace and children going to school without masks are examples, he added.
Less exposure to these three viruses also means there was less immune boosting among existing populations, he said. This can lead to “larger susceptible populations, especially infants and younger children, due to the relative absence of circulating virus in past years.”
A leading theory
Are we paying a price now for people following the edicts from officials to mask up, stand apart, and take other personal and public health precautions during the COVID-19 pandemic?
It’s possible, but that may not be the whole story.
“When it comes to RSV, I think that theory of isolation, social distancing, mask wearing, and not attending schools is a very valid one,” Dr. Schaffner said. “That’s everybody’s favorite [reason].”
He said he is confident that the jump in RSV cases is being driven by previous COVID public health protections. However, he’s “a little more cautious about influenza, in part because influenza is so variable.
“Like people in influenza say, if you’ve seen one influenza season, you’ve seen one influenza season,” Dr. Schaffner said.
“There’s a lot of debate,” he added. “Nobody can say definitively whether the immune deficit or debt is a consequence of not being stimulated and restimulated by the influenza virus over the past two seasons.”
‘A perfect storm’
“Now you kind of have the perfect storm,” Dr. Chin-Hong said. “It’s not a good situation for COVID with the variants that are emerging. For influenza, not having seen a lot of influenza the last 2 years, we’re probably more susceptible to getting infected.”
RSV cases rose during summer 2021, but now the weather is colder, and people are interacting more closely. “And it’s very, very transmissible,” he said.
Dr. Chin-Hong also predicted that “even though we don’t have a lot of COVID now, COVID will probably pick up.”
The rise in RSV was unexpected by some experts. “This early influenza is also a bit of a surprise and may be influenced by the fact that lots of us are going back and seeing each other again close-to-close, face-to-face in many enclosed environments,” Dr. Schaffner said.
He estimated the 2022-2023 flu season started 4-6 weeks early “and it’s taken off like a rocket. It started in the Southeast, quickly went to the Southwest and up the East Coast. Now it’s moving dramatically through the Midwest and will continue. It’s quite sure to hit the West Coast if it isn’t there already.”
A phenomenon by any other name
Some are calling the situation an “immunity debt,” while others dub it an “immunity pause” or an “immunity deficit.” Many physicians and immunologists have taken to social media to push back on the term “immunity debt,” saying it’s a mischaracterization that is being used to vilify COVID precautions, such as masking, social distancing, and other protective measures taken during the pandemic.
“I prefer the term ‘immunity gap’ ... which is more established in the epidemiology literature, especially given the politicization of the term ‘immunity debt’ by folks recently,” Dr. Messacar said.
“To me, the immunity gap is a scientific observation, not a political argument,” he added.
In a July 2022 publication in The Lancet, Dr. Messacar and his colleagues stated that “decreased exposure to endemic viruses created an immunity gap – a group of susceptible individuals who avoided infection and therefore lack pathogen-specific immunity to protect against future infection. Decreases in childhood vaccinations with pandemic disruptions to health care delivery contribute to this immunity gap for vaccine-preventable diseases, such as influenza,measles, and polio.”
The researchers noted that because of isolation during the pandemic, older children and newborns are being exposed to RSV for the first time. Returning to birthday parties, playing with friends, and going to school without masks means “children are being exposed to RSV, and that’s likely the reason that RSV is moving early and very, very substantially through this now expanded pool of susceptible children,” Dr. Schaffner said.
How likely are coinfections?
With peaks in RSV, flu, and COVID-19 cases each predicted in the coming months, how likely is it that someone could get sick with more than one infection at the same time?
Early in the pandemic, coinfection with COVID and the flu was reported in people at some centers on the West Coast, Dr. Auwaerter said. Now, however, “the unpredictable nature of the Omicron subvariants and the potential for further change, along with the never-before-seen significant lessening of influenza over 2 years, leave little for predictability.
“I do think it is less likely, given the extent of immunity now to SARS-CoV-2 in the population,” Dr. Auwaerter said.
“I most worry about viral coinfections ... in people with suppressed immune systems if we have high community rates of the SARS-CoV-2 and influenza circulating this fall and winter,” he added.
Studies during the pandemic suggest that coinfection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus and another respiratory virus were either rare or nonexistent.
Dr. Schaffner said these findings align with his experience at Vanderbilt University, which is part of a CDC-sponsored network that tracks laboratory-confirmed RSV, flu, and COVID cases among people in the hospital. “Coinfections are, at least to date, very unusual.”
There needs to be an asterisk next to that, Dr. Schaffner added. “Looking back over the last 2 years, we’ve had very little influenza, and we’ve had curtailed RSV seasons. So there hasn’t been a whole lot of opportunity for dual infections to occur.
“So this year may be more revelatory as we go forward,” he said.
Future concerns
The future is uncertain, Dr. Messacar and colleagues wrote in The Lancet: “Crucially, the patterns of these returning viral outbreaks have been heterogeneous across locations, populations, and pathogens, making predictions and preparations challenging.”
Dr. Chin-Hong used a horse race analogy to illustrate the situation now and going forward. RSV is the front-running horse, and influenza is running behind but trying to catch up. “And then COVID is the dark horse. It’s trailing the race right now – but all these variants are giving the horse extra supplements.
“And the COVID horse is probably going to be very competitive with the front-runner,” he said.
“We’re just at the beginning of the race right now,” Dr. Chin-Hong said, “so that’s why we’re worried that these three [viruses] will be even more pronounced come later in the year.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Headlines over the past few weeks are ringing the alarm about earlier and more serious influenza (flu) and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) outbreaks compared with previous years. Add COVID-19 to the mix and you have a dangerous mash of viruses that have many experts calling for caution and searching for explanations.
RSV and the flu “are certainly getting more attention, and they’re getting more attention for two reasons,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
“The first is that they’re both extraordinarily early. The second is that they’re both out there spreading very, very rapidly,” he told this news organization.
RSV usually follows a seasonal pattern with cases peaking in January and February. Both viruses tend to hit different regions of the country at different times, and that’s not the case in 2022.
“This is particularly striking for RSV, which usually doesn’t affect the entire country simultaneously,” Dr. Schaffner said.
“Yes, RSV is causing many more hospitalizations and earlier than any previously recorded season in the U.S.,” according to figures from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on RSV hospitalizations, said Kevin Messacar, MD, PhD, associate professor at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora.
Although there could be some increase in diagnoses because of increased awareness, the jump in RSV and flu cases “is a real phenomenon for multiple reasons,” said Peter Chin-Hong, MD, professor in the division of infectious diseases at the University of California, San Francisco.
With fewer COVID-related restrictions, people are moving around more. Also, during fall and winter, people tend to gather indoors. Colder temperatures and lower humidity contribute as well, Dr. Chin-Hong said, because “the droplets are just simply lighter.
“I think those are all factors,” he told this news organization.
Paul Auwaerter, MD, agreed that there are likely multiple causes for the unusual timing and severity of RSV and flu this year.
“Change in behaviors is a leading cause,” said the clinical director for the division of infectious diseases at the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. More people returning to the workplace and children going to school without masks are examples, he added.
Less exposure to these three viruses also means there was less immune boosting among existing populations, he said. This can lead to “larger susceptible populations, especially infants and younger children, due to the relative absence of circulating virus in past years.”
A leading theory
Are we paying a price now for people following the edicts from officials to mask up, stand apart, and take other personal and public health precautions during the COVID-19 pandemic?
It’s possible, but that may not be the whole story.
“When it comes to RSV, I think that theory of isolation, social distancing, mask wearing, and not attending schools is a very valid one,” Dr. Schaffner said. “That’s everybody’s favorite [reason].”
He said he is confident that the jump in RSV cases is being driven by previous COVID public health protections. However, he’s “a little more cautious about influenza, in part because influenza is so variable.
“Like people in influenza say, if you’ve seen one influenza season, you’ve seen one influenza season,” Dr. Schaffner said.
“There’s a lot of debate,” he added. “Nobody can say definitively whether the immune deficit or debt is a consequence of not being stimulated and restimulated by the influenza virus over the past two seasons.”
‘A perfect storm’
“Now you kind of have the perfect storm,” Dr. Chin-Hong said. “It’s not a good situation for COVID with the variants that are emerging. For influenza, not having seen a lot of influenza the last 2 years, we’re probably more susceptible to getting infected.”
RSV cases rose during summer 2021, but now the weather is colder, and people are interacting more closely. “And it’s very, very transmissible,” he said.
Dr. Chin-Hong also predicted that “even though we don’t have a lot of COVID now, COVID will probably pick up.”
The rise in RSV was unexpected by some experts. “This early influenza is also a bit of a surprise and may be influenced by the fact that lots of us are going back and seeing each other again close-to-close, face-to-face in many enclosed environments,” Dr. Schaffner said.
He estimated the 2022-2023 flu season started 4-6 weeks early “and it’s taken off like a rocket. It started in the Southeast, quickly went to the Southwest and up the East Coast. Now it’s moving dramatically through the Midwest and will continue. It’s quite sure to hit the West Coast if it isn’t there already.”
A phenomenon by any other name
Some are calling the situation an “immunity debt,” while others dub it an “immunity pause” or an “immunity deficit.” Many physicians and immunologists have taken to social media to push back on the term “immunity debt,” saying it’s a mischaracterization that is being used to vilify COVID precautions, such as masking, social distancing, and other protective measures taken during the pandemic.
“I prefer the term ‘immunity gap’ ... which is more established in the epidemiology literature, especially given the politicization of the term ‘immunity debt’ by folks recently,” Dr. Messacar said.
“To me, the immunity gap is a scientific observation, not a political argument,” he added.
In a July 2022 publication in The Lancet, Dr. Messacar and his colleagues stated that “decreased exposure to endemic viruses created an immunity gap – a group of susceptible individuals who avoided infection and therefore lack pathogen-specific immunity to protect against future infection. Decreases in childhood vaccinations with pandemic disruptions to health care delivery contribute to this immunity gap for vaccine-preventable diseases, such as influenza,measles, and polio.”
The researchers noted that because of isolation during the pandemic, older children and newborns are being exposed to RSV for the first time. Returning to birthday parties, playing with friends, and going to school without masks means “children are being exposed to RSV, and that’s likely the reason that RSV is moving early and very, very substantially through this now expanded pool of susceptible children,” Dr. Schaffner said.
How likely are coinfections?
With peaks in RSV, flu, and COVID-19 cases each predicted in the coming months, how likely is it that someone could get sick with more than one infection at the same time?
Early in the pandemic, coinfection with COVID and the flu was reported in people at some centers on the West Coast, Dr. Auwaerter said. Now, however, “the unpredictable nature of the Omicron subvariants and the potential for further change, along with the never-before-seen significant lessening of influenza over 2 years, leave little for predictability.
“I do think it is less likely, given the extent of immunity now to SARS-CoV-2 in the population,” Dr. Auwaerter said.
“I most worry about viral coinfections ... in people with suppressed immune systems if we have high community rates of the SARS-CoV-2 and influenza circulating this fall and winter,” he added.
Studies during the pandemic suggest that coinfection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus and another respiratory virus were either rare or nonexistent.
Dr. Schaffner said these findings align with his experience at Vanderbilt University, which is part of a CDC-sponsored network that tracks laboratory-confirmed RSV, flu, and COVID cases among people in the hospital. “Coinfections are, at least to date, very unusual.”
There needs to be an asterisk next to that, Dr. Schaffner added. “Looking back over the last 2 years, we’ve had very little influenza, and we’ve had curtailed RSV seasons. So there hasn’t been a whole lot of opportunity for dual infections to occur.
“So this year may be more revelatory as we go forward,” he said.
Future concerns
The future is uncertain, Dr. Messacar and colleagues wrote in The Lancet: “Crucially, the patterns of these returning viral outbreaks have been heterogeneous across locations, populations, and pathogens, making predictions and preparations challenging.”
Dr. Chin-Hong used a horse race analogy to illustrate the situation now and going forward. RSV is the front-running horse, and influenza is running behind but trying to catch up. “And then COVID is the dark horse. It’s trailing the race right now – but all these variants are giving the horse extra supplements.
“And the COVID horse is probably going to be very competitive with the front-runner,” he said.
“We’re just at the beginning of the race right now,” Dr. Chin-Hong said, “so that’s why we’re worried that these three [viruses] will be even more pronounced come later in the year.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Headlines over the past few weeks are ringing the alarm about earlier and more serious influenza (flu) and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) outbreaks compared with previous years. Add COVID-19 to the mix and you have a dangerous mash of viruses that have many experts calling for caution and searching for explanations.
RSV and the flu “are certainly getting more attention, and they’re getting more attention for two reasons,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
“The first is that they’re both extraordinarily early. The second is that they’re both out there spreading very, very rapidly,” he told this news organization.
RSV usually follows a seasonal pattern with cases peaking in January and February. Both viruses tend to hit different regions of the country at different times, and that’s not the case in 2022.
“This is particularly striking for RSV, which usually doesn’t affect the entire country simultaneously,” Dr. Schaffner said.
“Yes, RSV is causing many more hospitalizations and earlier than any previously recorded season in the U.S.,” according to figures from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on RSV hospitalizations, said Kevin Messacar, MD, PhD, associate professor at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora.
Although there could be some increase in diagnoses because of increased awareness, the jump in RSV and flu cases “is a real phenomenon for multiple reasons,” said Peter Chin-Hong, MD, professor in the division of infectious diseases at the University of California, San Francisco.
With fewer COVID-related restrictions, people are moving around more. Also, during fall and winter, people tend to gather indoors. Colder temperatures and lower humidity contribute as well, Dr. Chin-Hong said, because “the droplets are just simply lighter.
“I think those are all factors,” he told this news organization.
Paul Auwaerter, MD, agreed that there are likely multiple causes for the unusual timing and severity of RSV and flu this year.
“Change in behaviors is a leading cause,” said the clinical director for the division of infectious diseases at the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. More people returning to the workplace and children going to school without masks are examples, he added.
Less exposure to these three viruses also means there was less immune boosting among existing populations, he said. This can lead to “larger susceptible populations, especially infants and younger children, due to the relative absence of circulating virus in past years.”
A leading theory
Are we paying a price now for people following the edicts from officials to mask up, stand apart, and take other personal and public health precautions during the COVID-19 pandemic?
It’s possible, but that may not be the whole story.
“When it comes to RSV, I think that theory of isolation, social distancing, mask wearing, and not attending schools is a very valid one,” Dr. Schaffner said. “That’s everybody’s favorite [reason].”
He said he is confident that the jump in RSV cases is being driven by previous COVID public health protections. However, he’s “a little more cautious about influenza, in part because influenza is so variable.
“Like people in influenza say, if you’ve seen one influenza season, you’ve seen one influenza season,” Dr. Schaffner said.
“There’s a lot of debate,” he added. “Nobody can say definitively whether the immune deficit or debt is a consequence of not being stimulated and restimulated by the influenza virus over the past two seasons.”
‘A perfect storm’
“Now you kind of have the perfect storm,” Dr. Chin-Hong said. “It’s not a good situation for COVID with the variants that are emerging. For influenza, not having seen a lot of influenza the last 2 years, we’re probably more susceptible to getting infected.”
RSV cases rose during summer 2021, but now the weather is colder, and people are interacting more closely. “And it’s very, very transmissible,” he said.
Dr. Chin-Hong also predicted that “even though we don’t have a lot of COVID now, COVID will probably pick up.”
The rise in RSV was unexpected by some experts. “This early influenza is also a bit of a surprise and may be influenced by the fact that lots of us are going back and seeing each other again close-to-close, face-to-face in many enclosed environments,” Dr. Schaffner said.
He estimated the 2022-2023 flu season started 4-6 weeks early “and it’s taken off like a rocket. It started in the Southeast, quickly went to the Southwest and up the East Coast. Now it’s moving dramatically through the Midwest and will continue. It’s quite sure to hit the West Coast if it isn’t there already.”
A phenomenon by any other name
Some are calling the situation an “immunity debt,” while others dub it an “immunity pause” or an “immunity deficit.” Many physicians and immunologists have taken to social media to push back on the term “immunity debt,” saying it’s a mischaracterization that is being used to vilify COVID precautions, such as masking, social distancing, and other protective measures taken during the pandemic.
“I prefer the term ‘immunity gap’ ... which is more established in the epidemiology literature, especially given the politicization of the term ‘immunity debt’ by folks recently,” Dr. Messacar said.
“To me, the immunity gap is a scientific observation, not a political argument,” he added.
In a July 2022 publication in The Lancet, Dr. Messacar and his colleagues stated that “decreased exposure to endemic viruses created an immunity gap – a group of susceptible individuals who avoided infection and therefore lack pathogen-specific immunity to protect against future infection. Decreases in childhood vaccinations with pandemic disruptions to health care delivery contribute to this immunity gap for vaccine-preventable diseases, such as influenza,measles, and polio.”
The researchers noted that because of isolation during the pandemic, older children and newborns are being exposed to RSV for the first time. Returning to birthday parties, playing with friends, and going to school without masks means “children are being exposed to RSV, and that’s likely the reason that RSV is moving early and very, very substantially through this now expanded pool of susceptible children,” Dr. Schaffner said.
How likely are coinfections?
With peaks in RSV, flu, and COVID-19 cases each predicted in the coming months, how likely is it that someone could get sick with more than one infection at the same time?
Early in the pandemic, coinfection with COVID and the flu was reported in people at some centers on the West Coast, Dr. Auwaerter said. Now, however, “the unpredictable nature of the Omicron subvariants and the potential for further change, along with the never-before-seen significant lessening of influenza over 2 years, leave little for predictability.
“I do think it is less likely, given the extent of immunity now to SARS-CoV-2 in the population,” Dr. Auwaerter said.
“I most worry about viral coinfections ... in people with suppressed immune systems if we have high community rates of the SARS-CoV-2 and influenza circulating this fall and winter,” he added.
Studies during the pandemic suggest that coinfection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus and another respiratory virus were either rare or nonexistent.
Dr. Schaffner said these findings align with his experience at Vanderbilt University, which is part of a CDC-sponsored network that tracks laboratory-confirmed RSV, flu, and COVID cases among people in the hospital. “Coinfections are, at least to date, very unusual.”
There needs to be an asterisk next to that, Dr. Schaffner added. “Looking back over the last 2 years, we’ve had very little influenza, and we’ve had curtailed RSV seasons. So there hasn’t been a whole lot of opportunity for dual infections to occur.
“So this year may be more revelatory as we go forward,” he said.
Future concerns
The future is uncertain, Dr. Messacar and colleagues wrote in The Lancet: “Crucially, the patterns of these returning viral outbreaks have been heterogeneous across locations, populations, and pathogens, making predictions and preparations challenging.”
Dr. Chin-Hong used a horse race analogy to illustrate the situation now and going forward. RSV is the front-running horse, and influenza is running behind but trying to catch up. “And then COVID is the dark horse. It’s trailing the race right now – but all these variants are giving the horse extra supplements.
“And the COVID horse is probably going to be very competitive with the front-runner,” he said.
“We’re just at the beginning of the race right now,” Dr. Chin-Hong said, “so that’s why we’re worried that these three [viruses] will be even more pronounced come later in the year.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More children should be getting flu vaccines
Cold and flu season came early in 2022.
On Nov. 4, 2022, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued a Health Alert Network Health Advisory about early, elevated respiratory disease incidence caused by multiple viruses other than SARS-CoV-2.
Interseasonal spread of respiratory syncytial virus has continued in 2022, with RSV-associated hospitalizations increasing in the late spring and continuing throughout the summer and into the fall. In October, some regions of the country were seeing RSV activity near the peak seasonal levels typically observed in December and January.
Cases of severe respiratory infection in children who tested positive for rhinovirus or enterovirus spiked in August; further testing confirmed the presence of EV-D68 in some children. Rhinovirus and enterovirus continue to circulate and are isolated in hospitalized children with respiratory illness.
In some parts of the country, influenza cases have rapidly increased ahead of what we normally anticipate. According to preliminary estimates from the CDC, between Oct. 1 and Oct. 22, 880,000 people were sickened with flu, 420,000 people visited a health care provider for flu illness, and 6,900 people were hospitalized for flu. The cumulative hospitalization rate is higher than observed at this time of year in every previous flu season since 2010-2011. Hospitalization rates are highest in children aged 0-4 years and adults 65 years and older.
Of course, this report came as no surprise to pediatric health care providers. Many children’s hospitals had been operating at or over capacity for weeks. While a systematic assessment of the surge on children’s hospitals has not been published, anecdotally, hospitals from around the country have described record emergency department visits and inpatient census numbers. Some have set up tents or other temporary facilities to see ambulatory patients and have canceled elective surgeries because of a lack of beds.
There is no quick or easy solution to stem the tide of RSV-related or enterovirus/rhinovirus admissions, but many flu-related hospitalizations are vaccine preventable. Unfortunately, too few children are receiving influenza vaccine. As of the week ending Oct. 15, only about 22.1% of eligible children had been immunized. The American Academy of Pediatrics and the CDC recommend that all children are vaccinated, preferably by the end of October so they have time to develop immunity before influenza starts circulating. As it stands now, the majority of the nation’s children are facing a flu season without the benefits of vaccine.
There is still time to take steps to prevent this flu season from becoming one of the worst in recent memory. A strong provider recommendation for influenza vaccine is consistently associated with higher rates of vaccine acceptance. We need to recommend influenza vaccine to all eligible patients at every visit and in every setting. It will help if we can say it like we mean it. Some of us are tired of debating the merits of COVID-19 vaccine with families and may be leery of additional debates about flu. Some of us may just be tired, as many practices have already expanded office hours to care for the influx of kids with respiratory illness. On the heels of two atypical flu seasons, a few of us may be quietly complacent about the importance of flu vaccines for children.
Anyone in need of a little motivation should check out a paper recently published in Clinical Infectious Diseases that reinforces the value of flu vaccine, even in a year when there is a poor match between the vaccine and circulating viruses.
The 2019-2020 flu season was a bad flu season for children. Two antigenically drifted influenza viruses predominated and cases of influenza soared, resulting in the largest influenza epidemic in children in the United States since 1992. Pediatric Intensive Care Influenza Study investigators used a test-negative design to estimate the effectiveness of influenza vaccine in preventing critical and life-threatening influenza in children during that season. The good news: vaccination reduced the risk of critical influenza by 78% against H1N1pdm09 viruses that were well-matched to vaccine and by 47% against mismatched viruses. Vaccination was estimated to be 75% protective against antigenically drifted B-Victoria viruses. Overall vaccine effectiveness against critical illness from any influenza virus was 63% (95% confidence interval, 38%-78%).
While it might be tempting to attribute suboptimal immunization rates to vaccine hesitancy, ready availability remains an issue for some families. We need to eliminate barriers to access. While the AAP continues to emphasize immunization in the medical home, especially for the youngest infants, the 2022 policy statement suggests that vaccinating children in schools, pharmacies, and other nontraditional settings could improve immunization rates. To the extent feasible, we need to work with partners to support community-based initiatives and promote these to families who struggle to make it into the office.
Improving access is just one potential way to reduce health disparities related to influenza and influenza vaccination. Over 10 influenza seasons, higher rates of influenza-associated hospitalizations and intensive care unit admissions were observed in Black, Hispanic, and American Indian/Alaska Native people. These disparities were highest in children aged younger than 4 years and influenza-associated in-hospital deaths were three- to fourfold higher in Black, Hispanic, and Asian/Pacific Islander children, compared with White children. The reason for the disparities isn’t completely clear but increasing immunization rates may be part of the solution. During the 2020-2021 influenza season, flu immunization rates in Black children (51.6%) were lower than those seen in White (57.4%) and Hispanic children (58.9%).
The AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022–2023, highlight a variety of evidence-based strategies to increase influenza immunization rates. These may provide a little inspiration for clinicians looking to try a new approach. If you wish to share your experience with increasing influenza immunization rates in your practice setting, please email me at Kristina.bryant@louisville.edu.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases and one of the lead authors of the AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022–2023. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta, and Gilead.
Cold and flu season came early in 2022.
On Nov. 4, 2022, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued a Health Alert Network Health Advisory about early, elevated respiratory disease incidence caused by multiple viruses other than SARS-CoV-2.
Interseasonal spread of respiratory syncytial virus has continued in 2022, with RSV-associated hospitalizations increasing in the late spring and continuing throughout the summer and into the fall. In October, some regions of the country were seeing RSV activity near the peak seasonal levels typically observed in December and January.
Cases of severe respiratory infection in children who tested positive for rhinovirus or enterovirus spiked in August; further testing confirmed the presence of EV-D68 in some children. Rhinovirus and enterovirus continue to circulate and are isolated in hospitalized children with respiratory illness.
In some parts of the country, influenza cases have rapidly increased ahead of what we normally anticipate. According to preliminary estimates from the CDC, between Oct. 1 and Oct. 22, 880,000 people were sickened with flu, 420,000 people visited a health care provider for flu illness, and 6,900 people were hospitalized for flu. The cumulative hospitalization rate is higher than observed at this time of year in every previous flu season since 2010-2011. Hospitalization rates are highest in children aged 0-4 years and adults 65 years and older.
Of course, this report came as no surprise to pediatric health care providers. Many children’s hospitals had been operating at or over capacity for weeks. While a systematic assessment of the surge on children’s hospitals has not been published, anecdotally, hospitals from around the country have described record emergency department visits and inpatient census numbers. Some have set up tents or other temporary facilities to see ambulatory patients and have canceled elective surgeries because of a lack of beds.
There is no quick or easy solution to stem the tide of RSV-related or enterovirus/rhinovirus admissions, but many flu-related hospitalizations are vaccine preventable. Unfortunately, too few children are receiving influenza vaccine. As of the week ending Oct. 15, only about 22.1% of eligible children had been immunized. The American Academy of Pediatrics and the CDC recommend that all children are vaccinated, preferably by the end of October so they have time to develop immunity before influenza starts circulating. As it stands now, the majority of the nation’s children are facing a flu season without the benefits of vaccine.
There is still time to take steps to prevent this flu season from becoming one of the worst in recent memory. A strong provider recommendation for influenza vaccine is consistently associated with higher rates of vaccine acceptance. We need to recommend influenza vaccine to all eligible patients at every visit and in every setting. It will help if we can say it like we mean it. Some of us are tired of debating the merits of COVID-19 vaccine with families and may be leery of additional debates about flu. Some of us may just be tired, as many practices have already expanded office hours to care for the influx of kids with respiratory illness. On the heels of two atypical flu seasons, a few of us may be quietly complacent about the importance of flu vaccines for children.
Anyone in need of a little motivation should check out a paper recently published in Clinical Infectious Diseases that reinforces the value of flu vaccine, even in a year when there is a poor match between the vaccine and circulating viruses.
The 2019-2020 flu season was a bad flu season for children. Two antigenically drifted influenza viruses predominated and cases of influenza soared, resulting in the largest influenza epidemic in children in the United States since 1992. Pediatric Intensive Care Influenza Study investigators used a test-negative design to estimate the effectiveness of influenza vaccine in preventing critical and life-threatening influenza in children during that season. The good news: vaccination reduced the risk of critical influenza by 78% against H1N1pdm09 viruses that were well-matched to vaccine and by 47% against mismatched viruses. Vaccination was estimated to be 75% protective against antigenically drifted B-Victoria viruses. Overall vaccine effectiveness against critical illness from any influenza virus was 63% (95% confidence interval, 38%-78%).
While it might be tempting to attribute suboptimal immunization rates to vaccine hesitancy, ready availability remains an issue for some families. We need to eliminate barriers to access. While the AAP continues to emphasize immunization in the medical home, especially for the youngest infants, the 2022 policy statement suggests that vaccinating children in schools, pharmacies, and other nontraditional settings could improve immunization rates. To the extent feasible, we need to work with partners to support community-based initiatives and promote these to families who struggle to make it into the office.
Improving access is just one potential way to reduce health disparities related to influenza and influenza vaccination. Over 10 influenza seasons, higher rates of influenza-associated hospitalizations and intensive care unit admissions were observed in Black, Hispanic, and American Indian/Alaska Native people. These disparities were highest in children aged younger than 4 years and influenza-associated in-hospital deaths were three- to fourfold higher in Black, Hispanic, and Asian/Pacific Islander children, compared with White children. The reason for the disparities isn’t completely clear but increasing immunization rates may be part of the solution. During the 2020-2021 influenza season, flu immunization rates in Black children (51.6%) were lower than those seen in White (57.4%) and Hispanic children (58.9%).
The AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022–2023, highlight a variety of evidence-based strategies to increase influenza immunization rates. These may provide a little inspiration for clinicians looking to try a new approach. If you wish to share your experience with increasing influenza immunization rates in your practice setting, please email me at Kristina.bryant@louisville.edu.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases and one of the lead authors of the AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022–2023. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta, and Gilead.
Cold and flu season came early in 2022.
On Nov. 4, 2022, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued a Health Alert Network Health Advisory about early, elevated respiratory disease incidence caused by multiple viruses other than SARS-CoV-2.
Interseasonal spread of respiratory syncytial virus has continued in 2022, with RSV-associated hospitalizations increasing in the late spring and continuing throughout the summer and into the fall. In October, some regions of the country were seeing RSV activity near the peak seasonal levels typically observed in December and January.
Cases of severe respiratory infection in children who tested positive for rhinovirus or enterovirus spiked in August; further testing confirmed the presence of EV-D68 in some children. Rhinovirus and enterovirus continue to circulate and are isolated in hospitalized children with respiratory illness.
In some parts of the country, influenza cases have rapidly increased ahead of what we normally anticipate. According to preliminary estimates from the CDC, between Oct. 1 and Oct. 22, 880,000 people were sickened with flu, 420,000 people visited a health care provider for flu illness, and 6,900 people were hospitalized for flu. The cumulative hospitalization rate is higher than observed at this time of year in every previous flu season since 2010-2011. Hospitalization rates are highest in children aged 0-4 years and adults 65 years and older.
Of course, this report came as no surprise to pediatric health care providers. Many children’s hospitals had been operating at or over capacity for weeks. While a systematic assessment of the surge on children’s hospitals has not been published, anecdotally, hospitals from around the country have described record emergency department visits and inpatient census numbers. Some have set up tents or other temporary facilities to see ambulatory patients and have canceled elective surgeries because of a lack of beds.
There is no quick or easy solution to stem the tide of RSV-related or enterovirus/rhinovirus admissions, but many flu-related hospitalizations are vaccine preventable. Unfortunately, too few children are receiving influenza vaccine. As of the week ending Oct. 15, only about 22.1% of eligible children had been immunized. The American Academy of Pediatrics and the CDC recommend that all children are vaccinated, preferably by the end of October so they have time to develop immunity before influenza starts circulating. As it stands now, the majority of the nation’s children are facing a flu season without the benefits of vaccine.
There is still time to take steps to prevent this flu season from becoming one of the worst in recent memory. A strong provider recommendation for influenza vaccine is consistently associated with higher rates of vaccine acceptance. We need to recommend influenza vaccine to all eligible patients at every visit and in every setting. It will help if we can say it like we mean it. Some of us are tired of debating the merits of COVID-19 vaccine with families and may be leery of additional debates about flu. Some of us may just be tired, as many practices have already expanded office hours to care for the influx of kids with respiratory illness. On the heels of two atypical flu seasons, a few of us may be quietly complacent about the importance of flu vaccines for children.
Anyone in need of a little motivation should check out a paper recently published in Clinical Infectious Diseases that reinforces the value of flu vaccine, even in a year when there is a poor match between the vaccine and circulating viruses.
The 2019-2020 flu season was a bad flu season for children. Two antigenically drifted influenza viruses predominated and cases of influenza soared, resulting in the largest influenza epidemic in children in the United States since 1992. Pediatric Intensive Care Influenza Study investigators used a test-negative design to estimate the effectiveness of influenza vaccine in preventing critical and life-threatening influenza in children during that season. The good news: vaccination reduced the risk of critical influenza by 78% against H1N1pdm09 viruses that were well-matched to vaccine and by 47% against mismatched viruses. Vaccination was estimated to be 75% protective against antigenically drifted B-Victoria viruses. Overall vaccine effectiveness against critical illness from any influenza virus was 63% (95% confidence interval, 38%-78%).
While it might be tempting to attribute suboptimal immunization rates to vaccine hesitancy, ready availability remains an issue for some families. We need to eliminate barriers to access. While the AAP continues to emphasize immunization in the medical home, especially for the youngest infants, the 2022 policy statement suggests that vaccinating children in schools, pharmacies, and other nontraditional settings could improve immunization rates. To the extent feasible, we need to work with partners to support community-based initiatives and promote these to families who struggle to make it into the office.
Improving access is just one potential way to reduce health disparities related to influenza and influenza vaccination. Over 10 influenza seasons, higher rates of influenza-associated hospitalizations and intensive care unit admissions were observed in Black, Hispanic, and American Indian/Alaska Native people. These disparities were highest in children aged younger than 4 years and influenza-associated in-hospital deaths were three- to fourfold higher in Black, Hispanic, and Asian/Pacific Islander children, compared with White children. The reason for the disparities isn’t completely clear but increasing immunization rates may be part of the solution. During the 2020-2021 influenza season, flu immunization rates in Black children (51.6%) were lower than those seen in White (57.4%) and Hispanic children (58.9%).
The AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022–2023, highlight a variety of evidence-based strategies to increase influenza immunization rates. These may provide a little inspiration for clinicians looking to try a new approach. If you wish to share your experience with increasing influenza immunization rates in your practice setting, please email me at Kristina.bryant@louisville.edu.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases and one of the lead authors of the AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022–2023. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta, and Gilead.
CDC warns of early uptick in respiratory disease
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is warning of an early surge in respiratory disease caused by multiple viruses. As influenza viruses, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), SARS-CoV-2, and rhinovirus/enterovirus simultaneously circulate, the agency cautioned that this confluence of viral activity could strain the health care system, according to a CDC Health Network Alert advisory issued Nov. 4.
“This early increase in disease incidence highlights the importance of optimizing respiratory virus prevention and treatment measures, including prompt vaccination and antiviral treatment,” the alert stated.
The CDC reports that RSV activity is increasing nationally, but in some areas – such as the South and Mountain West – cases appear to be trending downward.
Influenza cases continue to climb, with the virus activity being the highest in the South, Mid-Atlantic, and the south-central West Coast, according to CDC data. “In fact, we’re seeing the highest influenza hospitalization rates going back a decade,” said José Romero, MD, director of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, during a press briefing. The agency estimates that there have been 1.6 million illnesses, 13,000 hospitalizations, and 730 deaths from the flu so far this season. As of Nov. 4, there have been two pediatric deaths.
COVID-19 cases appear to have plateaued in the past three weeks, Dr. Romero said; however, the CDC expects that there will be “high-level circulation of SARS-CoV-2 this fall and winter,” the health alert stated.
The CDC advised that all eligible individuals aged 6-months or older should be vaccinated against COVID-19 and influenza. To protect against RSV-hospitalization, high-risk children should receive the monoclonal antibody drug palivizumab (Synagis). High-risk children include infants born before 29 weeks, children younger than age 2 with chronic lung disease or hemodynamically significant congenital heart disease, and children with suppressed immune systems or neuromuscular disorders.
Any patient with confirmed or suspected flu who is hospitalized, at higher risk for influenza complications, or who has a severe or progressive illness should be treated as early as possible with antivirals, such as oral oseltamivir (Tamiflu).
Patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection with increased risk of complications should also be treated with antivirals, such as nirmatrelvir and ritonavir (Paxlovid) or remdesivir (Veklury).
Patients should also be reminded to wash their hands frequently, cover coughs and sneezes, stay home when sick, and avoid close contact with people who are sick, the CDC advised.
“There’s no doubt that we will face some challenges this winter,” said Dawn O’Connell, HHS Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response, “but it’s important to remember that RSV and flu are not new, and we have safe and effective vaccines for COVID-19 and the flu.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is warning of an early surge in respiratory disease caused by multiple viruses. As influenza viruses, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), SARS-CoV-2, and rhinovirus/enterovirus simultaneously circulate, the agency cautioned that this confluence of viral activity could strain the health care system, according to a CDC Health Network Alert advisory issued Nov. 4.
“This early increase in disease incidence highlights the importance of optimizing respiratory virus prevention and treatment measures, including prompt vaccination and antiviral treatment,” the alert stated.
The CDC reports that RSV activity is increasing nationally, but in some areas – such as the South and Mountain West – cases appear to be trending downward.
Influenza cases continue to climb, with the virus activity being the highest in the South, Mid-Atlantic, and the south-central West Coast, according to CDC data. “In fact, we’re seeing the highest influenza hospitalization rates going back a decade,” said José Romero, MD, director of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, during a press briefing. The agency estimates that there have been 1.6 million illnesses, 13,000 hospitalizations, and 730 deaths from the flu so far this season. As of Nov. 4, there have been two pediatric deaths.
COVID-19 cases appear to have plateaued in the past three weeks, Dr. Romero said; however, the CDC expects that there will be “high-level circulation of SARS-CoV-2 this fall and winter,” the health alert stated.
The CDC advised that all eligible individuals aged 6-months or older should be vaccinated against COVID-19 and influenza. To protect against RSV-hospitalization, high-risk children should receive the monoclonal antibody drug palivizumab (Synagis). High-risk children include infants born before 29 weeks, children younger than age 2 with chronic lung disease or hemodynamically significant congenital heart disease, and children with suppressed immune systems or neuromuscular disorders.
Any patient with confirmed or suspected flu who is hospitalized, at higher risk for influenza complications, or who has a severe or progressive illness should be treated as early as possible with antivirals, such as oral oseltamivir (Tamiflu).
Patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection with increased risk of complications should also be treated with antivirals, such as nirmatrelvir and ritonavir (Paxlovid) or remdesivir (Veklury).
Patients should also be reminded to wash their hands frequently, cover coughs and sneezes, stay home when sick, and avoid close contact with people who are sick, the CDC advised.
“There’s no doubt that we will face some challenges this winter,” said Dawn O’Connell, HHS Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response, “but it’s important to remember that RSV and flu are not new, and we have safe and effective vaccines for COVID-19 and the flu.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is warning of an early surge in respiratory disease caused by multiple viruses. As influenza viruses, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), SARS-CoV-2, and rhinovirus/enterovirus simultaneously circulate, the agency cautioned that this confluence of viral activity could strain the health care system, according to a CDC Health Network Alert advisory issued Nov. 4.
“This early increase in disease incidence highlights the importance of optimizing respiratory virus prevention and treatment measures, including prompt vaccination and antiviral treatment,” the alert stated.
The CDC reports that RSV activity is increasing nationally, but in some areas – such as the South and Mountain West – cases appear to be trending downward.
Influenza cases continue to climb, with the virus activity being the highest in the South, Mid-Atlantic, and the south-central West Coast, according to CDC data. “In fact, we’re seeing the highest influenza hospitalization rates going back a decade,” said José Romero, MD, director of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, during a press briefing. The agency estimates that there have been 1.6 million illnesses, 13,000 hospitalizations, and 730 deaths from the flu so far this season. As of Nov. 4, there have been two pediatric deaths.
COVID-19 cases appear to have plateaued in the past three weeks, Dr. Romero said; however, the CDC expects that there will be “high-level circulation of SARS-CoV-2 this fall and winter,” the health alert stated.
The CDC advised that all eligible individuals aged 6-months or older should be vaccinated against COVID-19 and influenza. To protect against RSV-hospitalization, high-risk children should receive the monoclonal antibody drug palivizumab (Synagis). High-risk children include infants born before 29 weeks, children younger than age 2 with chronic lung disease or hemodynamically significant congenital heart disease, and children with suppressed immune systems or neuromuscular disorders.
Any patient with confirmed or suspected flu who is hospitalized, at higher risk for influenza complications, or who has a severe or progressive illness should be treated as early as possible with antivirals, such as oral oseltamivir (Tamiflu).
Patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection with increased risk of complications should also be treated with antivirals, such as nirmatrelvir and ritonavir (Paxlovid) or remdesivir (Veklury).
Patients should also be reminded to wash their hands frequently, cover coughs and sneezes, stay home when sick, and avoid close contact with people who are sick, the CDC advised.
“There’s no doubt that we will face some challenges this winter,” said Dawn O’Connell, HHS Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response, “but it’s important to remember that RSV and flu are not new, and we have safe and effective vaccines for COVID-19 and the flu.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mid-October flulike illness cases higher than past 5 years
Outpatient visits for influenzalike illness (ILI), which includes influenza, SARS-CoV-2, and RSV, were higher after 3 weeks than for any of the previous five flu seasons: 3.3% of visits reported through the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network involved ILI as of Oct. 22. The highest comparable rate in the previous 5 years was the 1.9% recorded in late October of 2021, shortly after the definition of ILI was changed to also include illnesses other than influenza.
This season’s higher flu activity is in contrast to the previous two, which were unusually mild. The change, however, is not unexpected, as William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert and professor of preventive medicine at Vanderbilt University, recently told CNN.
“Here we are in the middle of October – not the middle of November – we’re already seeing scattered influenza cases, even hospitalized influenza cases, around the country,” he said. “So we know that this virus is now spreading out in the community already. It’s gathering speed already. It looks to me to be about a month early.”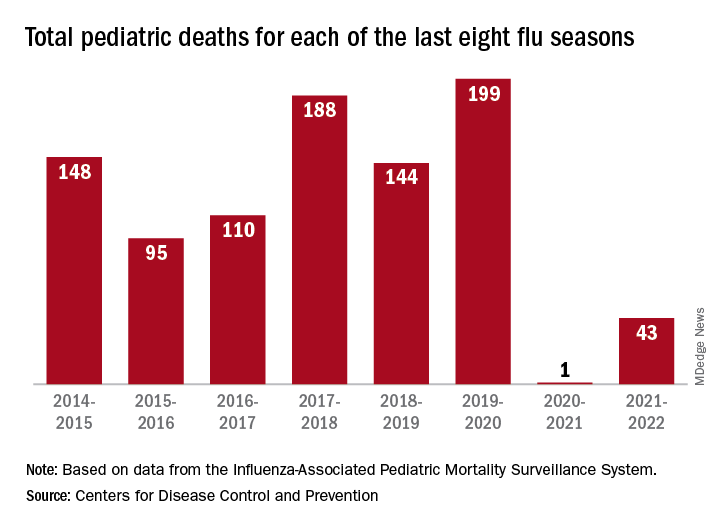
One indication of the mildness of the previous two flu seasons was the number of deaths, both pediatric and overall. Influenza-associated pediatric deaths had averaged about 110 per season over the previous eight seasons, compared with just 1 for 2020-2021 and 43 in 2021-2022. Overall flu deaths never reached 1% of all weekly deaths for either season, well below baseline levels for the flu, which range from 5.5% to 6.8%, CDC data show.
Other indicators of early severity
This season’s early rise in viral activity also can be seen in hospitalizations. The cumulative rate of flu-related admissions was 1.5 per 100,000 population as of Oct. 22, higher than the rate observed in the comparable week of previous seasons going back to 2010-2011, according to the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network.
A look at state reports of ILI outpatient visit rates shows that the District of Columbia and South Carolina are already in the very high range of the CDC’s severity scale, while 11 states are in the high range. Again going back to 2010-2011, no jurisdiction has ever been in the very high range this early in the season, based on data from the Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network.
Outpatient visits for influenzalike illness (ILI), which includes influenza, SARS-CoV-2, and RSV, were higher after 3 weeks than for any of the previous five flu seasons: 3.3% of visits reported through the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network involved ILI as of Oct. 22. The highest comparable rate in the previous 5 years was the 1.9% recorded in late October of 2021, shortly after the definition of ILI was changed to also include illnesses other than influenza.
This season’s higher flu activity is in contrast to the previous two, which were unusually mild. The change, however, is not unexpected, as William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert and professor of preventive medicine at Vanderbilt University, recently told CNN.
“Here we are in the middle of October – not the middle of November – we’re already seeing scattered influenza cases, even hospitalized influenza cases, around the country,” he said. “So we know that this virus is now spreading out in the community already. It’s gathering speed already. It looks to me to be about a month early.”
One indication of the mildness of the previous two flu seasons was the number of deaths, both pediatric and overall. Influenza-associated pediatric deaths had averaged about 110 per season over the previous eight seasons, compared with just 1 for 2020-2021 and 43 in 2021-2022. Overall flu deaths never reached 1% of all weekly deaths for either season, well below baseline levels for the flu, which range from 5.5% to 6.8%, CDC data show.
Other indicators of early severity
This season’s early rise in viral activity also can be seen in hospitalizations. The cumulative rate of flu-related admissions was 1.5 per 100,000 population as of Oct. 22, higher than the rate observed in the comparable week of previous seasons going back to 2010-2011, according to the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network.
A look at state reports of ILI outpatient visit rates shows that the District of Columbia and South Carolina are already in the very high range of the CDC’s severity scale, while 11 states are in the high range. Again going back to 2010-2011, no jurisdiction has ever been in the very high range this early in the season, based on data from the Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network.
Outpatient visits for influenzalike illness (ILI), which includes influenza, SARS-CoV-2, and RSV, were higher after 3 weeks than for any of the previous five flu seasons: 3.3% of visits reported through the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network involved ILI as of Oct. 22. The highest comparable rate in the previous 5 years was the 1.9% recorded in late October of 2021, shortly after the definition of ILI was changed to also include illnesses other than influenza.
This season’s higher flu activity is in contrast to the previous two, which were unusually mild. The change, however, is not unexpected, as William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert and professor of preventive medicine at Vanderbilt University, recently told CNN.
“Here we are in the middle of October – not the middle of November – we’re already seeing scattered influenza cases, even hospitalized influenza cases, around the country,” he said. “So we know that this virus is now spreading out in the community already. It’s gathering speed already. It looks to me to be about a month early.”
One indication of the mildness of the previous two flu seasons was the number of deaths, both pediatric and overall. Influenza-associated pediatric deaths had averaged about 110 per season over the previous eight seasons, compared with just 1 for 2020-2021 and 43 in 2021-2022. Overall flu deaths never reached 1% of all weekly deaths for either season, well below baseline levels for the flu, which range from 5.5% to 6.8%, CDC data show.
Other indicators of early severity
This season’s early rise in viral activity also can be seen in hospitalizations. The cumulative rate of flu-related admissions was 1.5 per 100,000 population as of Oct. 22, higher than the rate observed in the comparable week of previous seasons going back to 2010-2011, according to the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network.
A look at state reports of ILI outpatient visit rates shows that the District of Columbia and South Carolina are already in the very high range of the CDC’s severity scale, while 11 states are in the high range. Again going back to 2010-2011, no jurisdiction has ever been in the very high range this early in the season, based on data from the Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network.
People of color more likely to be hospitalized for influenza, CDC report finds
Black Americans are 80% more likely to be hospitalized for the flu, compared with White Americans, according to new federal data.
Black, Hispanic, and American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) adults in the United States also have had lower influenza vaccination rates, compared with their White counterparts, since 2010, researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) revealed in a report.
The inequalities are the result of barriers to care, distrust of the medical system, and misinformation, the report said.
“We have many of the tools we need to address inequities and flu vaccination coverage and outcomes,” said CDC Acting Principal Deputy Director Debra Houry, MD, MPH, in a press call; “however, we must acknowledge that inequities in access to care continue to exist. To improve vaccine uptake, we must address the root causes of these ongoing disparities.”
The CDC has already reported early increases in flu activity in the United States, with the highest activity in the southeastern and south-central parts of the country. Experts also warn of a potentially more severe influenza season than in the previous 2 years. CDC officials emphasized that vaccination is the best protection against severe illness, hospitalization, and death from the flu. “Everyone should get vaccinated against flu today and encourage others and their community to get a flu vaccine for the best protection against flu this fall and winter,” Dr. Houry said.
In the recent report on disparities by community published October 18 in CDC Vital Signs, researchers looked at hospitalization rates from 2009 to 2022 and vaccination rates from 2010 to 2022 based on race and ethnicity using two national databases, the Influenza-Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network and the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. All individuals included in the analysis were aged 18 years or older, and the 2020-2021 flu season was excluded from the analysis because of insufficient data.
Compared with those for White adults, hospitalization rates were 80% higher for Black adults, 30% higher for Hispanic adults, and 20% higher for AI/AN adults. While flu vaccination rates were similar in White and Asian adults (about 54%), coverage was lower in Black (42%), Hispanic (38%), AI/AN (41%), and other/multiracial (43%) adults. This disparity persisted even among individuals who had medical insurance, a personal health care provider, and a routine checkup within the last year.
Carla Black, PhD, MPH, an epidemiologist at the CDC’s Immunization Services Division, said during the press call. While flu vaccines may not always prevent infection, people who do get sick after being vaccinated tend to have better outcomes, she added. The report noted that building trust, increasing access to vaccination services, and combating misinformation are important steps to increasing vaccine coverage in minority groups.
While social distancing measures such as masking have made it difficult for the flu to spread, the relaxation of these safety measures could also lead to higher case counts. “We’ve had two mild flu seasons, and this means we might be ripe for a severe season,” Dr. Black said. “People haven’t had natural disease in 2 years, so there’s less natural immunity out there. People are going back to work. People are traveling again. All of these factors could contribute to us having a more severe flu season.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Black Americans are 80% more likely to be hospitalized for the flu, compared with White Americans, according to new federal data.
Black, Hispanic, and American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) adults in the United States also have had lower influenza vaccination rates, compared with their White counterparts, since 2010, researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) revealed in a report.
The inequalities are the result of barriers to care, distrust of the medical system, and misinformation, the report said.
“We have many of the tools we need to address inequities and flu vaccination coverage and outcomes,” said CDC Acting Principal Deputy Director Debra Houry, MD, MPH, in a press call; “however, we must acknowledge that inequities in access to care continue to exist. To improve vaccine uptake, we must address the root causes of these ongoing disparities.”
The CDC has already reported early increases in flu activity in the United States, with the highest activity in the southeastern and south-central parts of the country. Experts also warn of a potentially more severe influenza season than in the previous 2 years. CDC officials emphasized that vaccination is the best protection against severe illness, hospitalization, and death from the flu. “Everyone should get vaccinated against flu today and encourage others and their community to get a flu vaccine for the best protection against flu this fall and winter,” Dr. Houry said.
In the recent report on disparities by community published October 18 in CDC Vital Signs, researchers looked at hospitalization rates from 2009 to 2022 and vaccination rates from 2010 to 2022 based on race and ethnicity using two national databases, the Influenza-Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network and the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. All individuals included in the analysis were aged 18 years or older, and the 2020-2021 flu season was excluded from the analysis because of insufficient data.
Compared with those for White adults, hospitalization rates were 80% higher for Black adults, 30% higher for Hispanic adults, and 20% higher for AI/AN adults. While flu vaccination rates were similar in White and Asian adults (about 54%), coverage was lower in Black (42%), Hispanic (38%), AI/AN (41%), and other/multiracial (43%) adults. This disparity persisted even among individuals who had medical insurance, a personal health care provider, and a routine checkup within the last year.
Carla Black, PhD, MPH, an epidemiologist at the CDC’s Immunization Services Division, said during the press call. While flu vaccines may not always prevent infection, people who do get sick after being vaccinated tend to have better outcomes, she added. The report noted that building trust, increasing access to vaccination services, and combating misinformation are important steps to increasing vaccine coverage in minority groups.
While social distancing measures such as masking have made it difficult for the flu to spread, the relaxation of these safety measures could also lead to higher case counts. “We’ve had two mild flu seasons, and this means we might be ripe for a severe season,” Dr. Black said. “People haven’t had natural disease in 2 years, so there’s less natural immunity out there. People are going back to work. People are traveling again. All of these factors could contribute to us having a more severe flu season.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Black Americans are 80% more likely to be hospitalized for the flu, compared with White Americans, according to new federal data.
Black, Hispanic, and American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) adults in the United States also have had lower influenza vaccination rates, compared with their White counterparts, since 2010, researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) revealed in a report.
The inequalities are the result of barriers to care, distrust of the medical system, and misinformation, the report said.
“We have many of the tools we need to address inequities and flu vaccination coverage and outcomes,” said CDC Acting Principal Deputy Director Debra Houry, MD, MPH, in a press call; “however, we must acknowledge that inequities in access to care continue to exist. To improve vaccine uptake, we must address the root causes of these ongoing disparities.”
The CDC has already reported early increases in flu activity in the United States, with the highest activity in the southeastern and south-central parts of the country. Experts also warn of a potentially more severe influenza season than in the previous 2 years. CDC officials emphasized that vaccination is the best protection against severe illness, hospitalization, and death from the flu. “Everyone should get vaccinated against flu today and encourage others and their community to get a flu vaccine for the best protection against flu this fall and winter,” Dr. Houry said.
In the recent report on disparities by community published October 18 in CDC Vital Signs, researchers looked at hospitalization rates from 2009 to 2022 and vaccination rates from 2010 to 2022 based on race and ethnicity using two national databases, the Influenza-Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network and the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. All individuals included in the analysis were aged 18 years or older, and the 2020-2021 flu season was excluded from the analysis because of insufficient data.
Compared with those for White adults, hospitalization rates were 80% higher for Black adults, 30% higher for Hispanic adults, and 20% higher for AI/AN adults. While flu vaccination rates were similar in White and Asian adults (about 54%), coverage was lower in Black (42%), Hispanic (38%), AI/AN (41%), and other/multiracial (43%) adults. This disparity persisted even among individuals who had medical insurance, a personal health care provider, and a routine checkup within the last year.
Carla Black, PhD, MPH, an epidemiologist at the CDC’s Immunization Services Division, said during the press call. While flu vaccines may not always prevent infection, people who do get sick after being vaccinated tend to have better outcomes, she added. The report noted that building trust, increasing access to vaccination services, and combating misinformation are important steps to increasing vaccine coverage in minority groups.
While social distancing measures such as masking have made it difficult for the flu to spread, the relaxation of these safety measures could also lead to higher case counts. “We’ve had two mild flu seasons, and this means we might be ripe for a severe season,” Dr. Black said. “People haven’t had natural disease in 2 years, so there’s less natural immunity out there. People are going back to work. People are traveling again. All of these factors could contribute to us having a more severe flu season.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.





