User login
High salt intake linked to atherosclerosis even with normal BP
A high salt intake is an important risk factor for atherosclerosis, even in the absence of hypertension, a large study from Sweden concludes.
The study, including more than 10,000 individuals between the ages of 50 and 64 years from the Swedish Cardiopulmonary bioImage Study, showed a significant link between dietary salt intake and the risk for atherosclerotic lesions in the coronary and carotid arteries, even in participants with normal blood pressure and without known cardiovascular disease.
The finding suggests that salt could be a damaging factor in its own right before the development of hypertension, the authors write. The results were published online in European Heart Journal Open.
It has been known for a long time that salt is linked to hypertension, but the role that salt plays in atherosclerosis has not been examined, first author Jonas Wuopio, MD, Karolinska Institutet, Huddinge, and Clinical Research Center, Falun, Uppsala University, both in Sweden, told this news organization.
“Hardly anyone looks at changes in the arteries’ calcification, the atherosclerotic plaques and the association with salt intake,” Dr. Wuopio said. “We had this exclusive data from our cohort, so we wanted to use it to close this knowledge gap.”
The analysis included 10,788 adults aged 50-64 years, (average age, 58 years; 52% women) who underwent a coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) scan. The estimated 24-hour sodium excretion was used to measure sodium intake.
CCTA was used to obtain 3-D images of the coronary arteries to measure the degree of coronary artery calcium as well as detect stenosis in the coronary arteries. Participants also had an ultrasound of the carotid arteries.
After adjusting for age, sex, and study site (the study was done at Uppsala and Malmö, Sweden), the researchers found that rising salt consumption was linked with increasing atherosclerosis in a linear fashion in both the coronary and carotid arteries.
Each 1,000 mg rise in sodium excretion was associated with a 9% increased occurrence of carotid plaque (odds ratio, 1.09; P < .001; confidence interval, 1.06-1.12), a higher coronary artery calcium score (OR, 1.16; P < .001; CI, 1.12-1.19), and a 17% increased occurrence of coronary artery stenosis (OR, 1.17; P < .001; CI, 1.13-1.20).
The association was abolished, though, after adjusting for blood pressure, they note. Their “interpretation is that the increase in blood pressure from sodium intake, even below the level that currently defines arterial hypertension, is an important factor that mediates the interplay between salt intake and the atherosclerotic process,” they write. “As we observed an association in individuals with normal blood pressure, one possible explanation for these findings is that the detrimental pathological processes begin already prior to the development of hypertension,” they note, although they caution that no causal relationships can be gleaned from this cross-sectional study.
They also reported no sign of a “J-curve”; participants with the lowest levels of sodium excretion had the lowest occurrence of both coronary and carotid atherosclerosis, which contradicts findings in some studies that found very low sodium linked to increased cardiovascular disease–related events.
“There have been some controversies among researchers regarding very low intake, where some say very low salt intake can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, but we could not find this in this study,” Dr. Wuopio said.
“Our study is confirming that excess salt is not a good thing, but the fact that it is linked to atherosclerosis, even in the absence of hypertension, was a bit of a surprise,” he said.
“I will be telling my patients to follow the advice given by the World Health Organization and other medical societies, to limit your intake of salt to approximately 1 teaspoon, even if your blood pressure is normal.”
Time to scrutinize salt’s role in atherosclerosis
In an accompanying editorial, Maciej Banach, MD, Medical University of Lodz, and Stanislaw Surma, MD, Faculty of Medical Sciences in Katowice, both in Poland, write that excessive dietary salt intake is a well-documented cardiovascular risk factor, and that the association is explained in most studies by increased blood pressure.
“We should look more extensively on the role of dietary salt, as it affects many pathological mechanisms, by which, especially with the coexistence of other risk factors, atherosclerosis may progress very fast,” they write.
“The results of the study shed new light on the direct relationship between excessive dietary salt intake and the risk of ASCVD [atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease], indicating that salt intake might be a risk factor for atherosclerosis even prior to the development of hypertension,” they conclude.
Confirmatory and novel
“Nobody questions the fact that high blood pressure is a powerful risk factor for atherosclerotic disease, but not all studies have suggested that, at least at significantly higher levels of sodium intake, that high salt intake tracks with risk for atherosclerotic disease,” Alon Gitig, MD, assistant professor and director of cardiology, Mount Sinai Doctors-Westchester, Yonkers, New York, told this news organization.
Most of the studies of salt intake in the diet are based on patient self-reports via food frequency questionnaires, which can give a general idea of salt intake, but are often not totally accurate, Dr. Gitig said.
“Here, they measured sodium in the urine and estimated the 24-hour salt intake from that, which is slightly novel,” he said.
Everybody knows that high blood pressure is associated with future cardiovascular disease risk, but what many don’t realize is that that risk starts to increase slightly but significantly above a blood pressure that is already in the range of 115 mm Hg/75 mm Hg, he said.
“The lower you can get your blood pressure down, to around 115-120, the lower your risk for cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Gitig said.
It is possible for most people to lower blood pressure through attention to diet, restricting sodium, performing cardio and weight training exercises, and maintaining a healthy weight, he said.
An example of a cardiovascular health diet is the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet.
“The DASH diet, consisting of 9 servings of fruits and vegetables a day with few refined carbs, flour and sugar, has been shown in a randomized trial to dramatically reduce blood pressure. There are two reasons for that. One is that the fruits and vegetables have many phytonutrients that are good for arteries. The other is that a large proportion of U.S. adults have insulin resistance, which leads to high blood pressure.
“The more fruits and vegetables and healthy animal products, and less sugar and flour, the more you are going to improve your insulin resistance, so you can bring your blood pressure down that way,” Dr. Gitig said.
The study was funded by the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, the Swedish Research Council and Vinnova (Sweden’s Innovation agency), the University of Gothenburg and Sahlgrenska University Hospital, the Karolinska Institutet and Stockholm County Council, the Linköping University and University Hospital, the Lund University and Skane University Hospital, the Umea University and University Hospital, and the Uppsala University and University Hospital. Dr. Wuopio and Dr. Gitig report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Banach reports financial relationships with Adamed, Amgen, Daichii Sankyo, Esperion, KrKa, NewAmsterdam, Polpharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Teva, Viatris, and CMDO at Longevity Group (LU). Dr. Surma reports a financial relationship with Sanofi and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A high salt intake is an important risk factor for atherosclerosis, even in the absence of hypertension, a large study from Sweden concludes.
The study, including more than 10,000 individuals between the ages of 50 and 64 years from the Swedish Cardiopulmonary bioImage Study, showed a significant link between dietary salt intake and the risk for atherosclerotic lesions in the coronary and carotid arteries, even in participants with normal blood pressure and without known cardiovascular disease.
The finding suggests that salt could be a damaging factor in its own right before the development of hypertension, the authors write. The results were published online in European Heart Journal Open.
It has been known for a long time that salt is linked to hypertension, but the role that salt plays in atherosclerosis has not been examined, first author Jonas Wuopio, MD, Karolinska Institutet, Huddinge, and Clinical Research Center, Falun, Uppsala University, both in Sweden, told this news organization.
“Hardly anyone looks at changes in the arteries’ calcification, the atherosclerotic plaques and the association with salt intake,” Dr. Wuopio said. “We had this exclusive data from our cohort, so we wanted to use it to close this knowledge gap.”
The analysis included 10,788 adults aged 50-64 years, (average age, 58 years; 52% women) who underwent a coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) scan. The estimated 24-hour sodium excretion was used to measure sodium intake.
CCTA was used to obtain 3-D images of the coronary arteries to measure the degree of coronary artery calcium as well as detect stenosis in the coronary arteries. Participants also had an ultrasound of the carotid arteries.
After adjusting for age, sex, and study site (the study was done at Uppsala and Malmö, Sweden), the researchers found that rising salt consumption was linked with increasing atherosclerosis in a linear fashion in both the coronary and carotid arteries.
Each 1,000 mg rise in sodium excretion was associated with a 9% increased occurrence of carotid plaque (odds ratio, 1.09; P < .001; confidence interval, 1.06-1.12), a higher coronary artery calcium score (OR, 1.16; P < .001; CI, 1.12-1.19), and a 17% increased occurrence of coronary artery stenosis (OR, 1.17; P < .001; CI, 1.13-1.20).
The association was abolished, though, after adjusting for blood pressure, they note. Their “interpretation is that the increase in blood pressure from sodium intake, even below the level that currently defines arterial hypertension, is an important factor that mediates the interplay between salt intake and the atherosclerotic process,” they write. “As we observed an association in individuals with normal blood pressure, one possible explanation for these findings is that the detrimental pathological processes begin already prior to the development of hypertension,” they note, although they caution that no causal relationships can be gleaned from this cross-sectional study.
They also reported no sign of a “J-curve”; participants with the lowest levels of sodium excretion had the lowest occurrence of both coronary and carotid atherosclerosis, which contradicts findings in some studies that found very low sodium linked to increased cardiovascular disease–related events.
“There have been some controversies among researchers regarding very low intake, where some say very low salt intake can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, but we could not find this in this study,” Dr. Wuopio said.
“Our study is confirming that excess salt is not a good thing, but the fact that it is linked to atherosclerosis, even in the absence of hypertension, was a bit of a surprise,” he said.
“I will be telling my patients to follow the advice given by the World Health Organization and other medical societies, to limit your intake of salt to approximately 1 teaspoon, even if your blood pressure is normal.”
Time to scrutinize salt’s role in atherosclerosis
In an accompanying editorial, Maciej Banach, MD, Medical University of Lodz, and Stanislaw Surma, MD, Faculty of Medical Sciences in Katowice, both in Poland, write that excessive dietary salt intake is a well-documented cardiovascular risk factor, and that the association is explained in most studies by increased blood pressure.
“We should look more extensively on the role of dietary salt, as it affects many pathological mechanisms, by which, especially with the coexistence of other risk factors, atherosclerosis may progress very fast,” they write.
“The results of the study shed new light on the direct relationship between excessive dietary salt intake and the risk of ASCVD [atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease], indicating that salt intake might be a risk factor for atherosclerosis even prior to the development of hypertension,” they conclude.
Confirmatory and novel
“Nobody questions the fact that high blood pressure is a powerful risk factor for atherosclerotic disease, but not all studies have suggested that, at least at significantly higher levels of sodium intake, that high salt intake tracks with risk for atherosclerotic disease,” Alon Gitig, MD, assistant professor and director of cardiology, Mount Sinai Doctors-Westchester, Yonkers, New York, told this news organization.
Most of the studies of salt intake in the diet are based on patient self-reports via food frequency questionnaires, which can give a general idea of salt intake, but are often not totally accurate, Dr. Gitig said.
“Here, they measured sodium in the urine and estimated the 24-hour salt intake from that, which is slightly novel,” he said.
Everybody knows that high blood pressure is associated with future cardiovascular disease risk, but what many don’t realize is that that risk starts to increase slightly but significantly above a blood pressure that is already in the range of 115 mm Hg/75 mm Hg, he said.
“The lower you can get your blood pressure down, to around 115-120, the lower your risk for cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Gitig said.
It is possible for most people to lower blood pressure through attention to diet, restricting sodium, performing cardio and weight training exercises, and maintaining a healthy weight, he said.
An example of a cardiovascular health diet is the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet.
“The DASH diet, consisting of 9 servings of fruits and vegetables a day with few refined carbs, flour and sugar, has been shown in a randomized trial to dramatically reduce blood pressure. There are two reasons for that. One is that the fruits and vegetables have many phytonutrients that are good for arteries. The other is that a large proportion of U.S. adults have insulin resistance, which leads to high blood pressure.
“The more fruits and vegetables and healthy animal products, and less sugar and flour, the more you are going to improve your insulin resistance, so you can bring your blood pressure down that way,” Dr. Gitig said.
The study was funded by the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, the Swedish Research Council and Vinnova (Sweden’s Innovation agency), the University of Gothenburg and Sahlgrenska University Hospital, the Karolinska Institutet and Stockholm County Council, the Linköping University and University Hospital, the Lund University and Skane University Hospital, the Umea University and University Hospital, and the Uppsala University and University Hospital. Dr. Wuopio and Dr. Gitig report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Banach reports financial relationships with Adamed, Amgen, Daichii Sankyo, Esperion, KrKa, NewAmsterdam, Polpharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Teva, Viatris, and CMDO at Longevity Group (LU). Dr. Surma reports a financial relationship with Sanofi and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A high salt intake is an important risk factor for atherosclerosis, even in the absence of hypertension, a large study from Sweden concludes.
The study, including more than 10,000 individuals between the ages of 50 and 64 years from the Swedish Cardiopulmonary bioImage Study, showed a significant link between dietary salt intake and the risk for atherosclerotic lesions in the coronary and carotid arteries, even in participants with normal blood pressure and without known cardiovascular disease.
The finding suggests that salt could be a damaging factor in its own right before the development of hypertension, the authors write. The results were published online in European Heart Journal Open.
It has been known for a long time that salt is linked to hypertension, but the role that salt plays in atherosclerosis has not been examined, first author Jonas Wuopio, MD, Karolinska Institutet, Huddinge, and Clinical Research Center, Falun, Uppsala University, both in Sweden, told this news organization.
“Hardly anyone looks at changes in the arteries’ calcification, the atherosclerotic plaques and the association with salt intake,” Dr. Wuopio said. “We had this exclusive data from our cohort, so we wanted to use it to close this knowledge gap.”
The analysis included 10,788 adults aged 50-64 years, (average age, 58 years; 52% women) who underwent a coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) scan. The estimated 24-hour sodium excretion was used to measure sodium intake.
CCTA was used to obtain 3-D images of the coronary arteries to measure the degree of coronary artery calcium as well as detect stenosis in the coronary arteries. Participants also had an ultrasound of the carotid arteries.
After adjusting for age, sex, and study site (the study was done at Uppsala and Malmö, Sweden), the researchers found that rising salt consumption was linked with increasing atherosclerosis in a linear fashion in both the coronary and carotid arteries.
Each 1,000 mg rise in sodium excretion was associated with a 9% increased occurrence of carotid plaque (odds ratio, 1.09; P < .001; confidence interval, 1.06-1.12), a higher coronary artery calcium score (OR, 1.16; P < .001; CI, 1.12-1.19), and a 17% increased occurrence of coronary artery stenosis (OR, 1.17; P < .001; CI, 1.13-1.20).
The association was abolished, though, after adjusting for blood pressure, they note. Their “interpretation is that the increase in blood pressure from sodium intake, even below the level that currently defines arterial hypertension, is an important factor that mediates the interplay between salt intake and the atherosclerotic process,” they write. “As we observed an association in individuals with normal blood pressure, one possible explanation for these findings is that the detrimental pathological processes begin already prior to the development of hypertension,” they note, although they caution that no causal relationships can be gleaned from this cross-sectional study.
They also reported no sign of a “J-curve”; participants with the lowest levels of sodium excretion had the lowest occurrence of both coronary and carotid atherosclerosis, which contradicts findings in some studies that found very low sodium linked to increased cardiovascular disease–related events.
“There have been some controversies among researchers regarding very low intake, where some say very low salt intake can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, but we could not find this in this study,” Dr. Wuopio said.
“Our study is confirming that excess salt is not a good thing, but the fact that it is linked to atherosclerosis, even in the absence of hypertension, was a bit of a surprise,” he said.
“I will be telling my patients to follow the advice given by the World Health Organization and other medical societies, to limit your intake of salt to approximately 1 teaspoon, even if your blood pressure is normal.”
Time to scrutinize salt’s role in atherosclerosis
In an accompanying editorial, Maciej Banach, MD, Medical University of Lodz, and Stanislaw Surma, MD, Faculty of Medical Sciences in Katowice, both in Poland, write that excessive dietary salt intake is a well-documented cardiovascular risk factor, and that the association is explained in most studies by increased blood pressure.
“We should look more extensively on the role of dietary salt, as it affects many pathological mechanisms, by which, especially with the coexistence of other risk factors, atherosclerosis may progress very fast,” they write.
“The results of the study shed new light on the direct relationship between excessive dietary salt intake and the risk of ASCVD [atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease], indicating that salt intake might be a risk factor for atherosclerosis even prior to the development of hypertension,” they conclude.
Confirmatory and novel
“Nobody questions the fact that high blood pressure is a powerful risk factor for atherosclerotic disease, but not all studies have suggested that, at least at significantly higher levels of sodium intake, that high salt intake tracks with risk for atherosclerotic disease,” Alon Gitig, MD, assistant professor and director of cardiology, Mount Sinai Doctors-Westchester, Yonkers, New York, told this news organization.
Most of the studies of salt intake in the diet are based on patient self-reports via food frequency questionnaires, which can give a general idea of salt intake, but are often not totally accurate, Dr. Gitig said.
“Here, they measured sodium in the urine and estimated the 24-hour salt intake from that, which is slightly novel,” he said.
Everybody knows that high blood pressure is associated with future cardiovascular disease risk, but what many don’t realize is that that risk starts to increase slightly but significantly above a blood pressure that is already in the range of 115 mm Hg/75 mm Hg, he said.
“The lower you can get your blood pressure down, to around 115-120, the lower your risk for cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Gitig said.
It is possible for most people to lower blood pressure through attention to diet, restricting sodium, performing cardio and weight training exercises, and maintaining a healthy weight, he said.
An example of a cardiovascular health diet is the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet.
“The DASH diet, consisting of 9 servings of fruits and vegetables a day with few refined carbs, flour and sugar, has been shown in a randomized trial to dramatically reduce blood pressure. There are two reasons for that. One is that the fruits and vegetables have many phytonutrients that are good for arteries. The other is that a large proportion of U.S. adults have insulin resistance, which leads to high blood pressure.
“The more fruits and vegetables and healthy animal products, and less sugar and flour, the more you are going to improve your insulin resistance, so you can bring your blood pressure down that way,” Dr. Gitig said.
The study was funded by the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, the Swedish Research Council and Vinnova (Sweden’s Innovation agency), the University of Gothenburg and Sahlgrenska University Hospital, the Karolinska Institutet and Stockholm County Council, the Linköping University and University Hospital, the Lund University and Skane University Hospital, the Umea University and University Hospital, and the Uppsala University and University Hospital. Dr. Wuopio and Dr. Gitig report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Banach reports financial relationships with Adamed, Amgen, Daichii Sankyo, Esperion, KrKa, NewAmsterdam, Polpharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Teva, Viatris, and CMDO at Longevity Group (LU). Dr. Surma reports a financial relationship with Sanofi and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New update on left atrial appendage closure recommendations
An updated consensus statement on transcatheter left atrial appendage closure (LAAC) has put a newfound focus on patient selection for the procedure, specifically recommending that the procedure is appropriate for patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation who have risk for thromboembolism, aren’t well suited for direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) and have a good chance of living for at least another year.
The statement, published online in the Journal of the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions, also makes recommendations for how much experience operators should have, how many procedures they should perform to keep their skills up, and when and how to use imaging and prescribe DOACs, among other suggestions.
The statement represents the first updated guidance for LAAC since 2015. “Since then this field has really expanded and evolved,” writing group chair Jacqueline Saw, MD, said in an interview. “For instance, the indications are more matured and specific, and the procedural technical steps have matured. Imaging has also advanced, there’s more understanding about postprocedural care and there are also new devices that have been approved.”
Dr. Saw, an interventional cardiologist at Vancouver General Hospital and St. Paul’s Hospital, and a professor at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, called the statement “a piece that puts everything together.”
“This document really summarizes the whole practice for doing transcatheter procedures,” she added, “so it’s all-in-one document in terms of recommendation of who we do the procedure for, how we should do it, how we should image and guide the procedure, and what complications to look out for and how to manage patients post procedure, be it with antithrombotic therapy and/or device surveillance.”
13 recommendations
In all, the statement carries 13 recommendations for LAAC. The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions and the Heart Rhythm Society commissioned the writing group. The American College of Cardiology and Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography have endorsed the statement. The following are among the recommendations:
- Transcatheter LAAC is appropriate for patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation with high thromboembolic risk but for whom long-term oral anticoagulation may be contraindicated and who have at least 1 year’s life expectancy.
- Operators should have performed at least 50 prior left-sided ablations or structural procedures and at least 25 transseptal punctures (TSPs). Interventional-imaging physicians should have experience in guiding 25 or more TSPs before supporting LAAC procedures independently.
- To maintain skills, operators should do 25 or more TSPs and at least 12 LAACs over each 2-year period.
- On-site cardiovascular surgery backup should be available for new programs and for operators early in their learning curve.
- Baseline imaging with transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) or cardiac computed tomography should be performed before LAAC.
- Intraprocedural imaging guidance with TEE or intracardiac echocardiography.
- Follow labeling of each specific LAAC device for technical aspects of the procedure.
- Familiarity with avoiding, recognizing, and managing LAAC complications.
- Predischarge 2-dimensional TEE to rule out pericardial effusion and device embolization.
- Anticoagulation for device-related thrombus.
- Make all efforts to minimize peridevice leaks during implantation because their clinical impact and management isn’t well understood.
- Antithrombotic therapy with warfarin, DOAC, or dual-antiplatelet therapy after LAAC based on the studied regimen and instructions for each specific device, tailored to the bleeding risks for each patient.
- TEE or cardiac computed tomography at 45-90 days after LAAC for device surveillance to assess for peridevice leak and device-related thrombus.
The statement also includes precautionary recommendations. It advises against using routine closure of LAAC-associated iatrogenic atrial septal defects and states that combined procedures with LAAC, such as structural interventions and pulmonary vein isolation, should be avoided because randomized controlled trial data are pending.
“These recommendations are based upon data from updated publications and randomized trial data as well as large registries, including the National Cardiovascular Data Registry, so I think this is a very practical statement that puts all these pieces together for any budding interventionalist doing this procedure and even experienced operations,” Dr. Saw said.
Authors of an accompanying editorial agreed that the “rigorous standards” set out in the statement will help maintain “a high level of procedural safety in the setting of rapid expansion.”
The editorialists, Faisal M. Merchant, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, and Mohamad Alkhouli, MD, professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic School of Medicine, Rochester, Minn., point out that the incidence of pericardial effusion has decreased from more than 5% in the pivotal Watchman trials to less than 1.5% in the most recent report from the National Cardiovascular Data Registry, which shows that more than 100,000 procedures have been performed in the United States.
But most important as the field moves forward, they stress, is patient selection. The recommendation of limiting patients to those with a life expectancy of 1 year “is a tacit recognition of the fact that the benefits of LAAC take time to accrue, and many older and frail patients are unlikely to derive meaningful benefit.”
Dr. Merchant and Dr. Alkhouli also note that there remains a conundrum in patient selection that remains from the original LAAC trials, which enrolled patients who were eligible for anticoagulation. “Somewhat paradoxically, after its approval, LAAC is mostly prescribed to patients who are not felt to be good anticoagulation candidates.” This leaves physicians “in the precarious position of extrapolating data to patients who were excluded from the original clinical trials.”
Therefore, the consensus statement “is right to put patient selection front and center in its recommendations, but as the field of LAAC comes of age, better evidence to support patient selection will be the real sign of maturity.”
Dr. Saw said she envisions another update over the next 2 years or so as ongoing clinical trials comparing DOAC and LAAC, namely the CHAMPION-AF and OPTION trials, report results.
Dr. Saw and Dr. Merchant, reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Alkhouli has financial ties to Boston Scientific, Abbott, and Philips.
An updated consensus statement on transcatheter left atrial appendage closure (LAAC) has put a newfound focus on patient selection for the procedure, specifically recommending that the procedure is appropriate for patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation who have risk for thromboembolism, aren’t well suited for direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) and have a good chance of living for at least another year.
The statement, published online in the Journal of the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions, also makes recommendations for how much experience operators should have, how many procedures they should perform to keep their skills up, and when and how to use imaging and prescribe DOACs, among other suggestions.
The statement represents the first updated guidance for LAAC since 2015. “Since then this field has really expanded and evolved,” writing group chair Jacqueline Saw, MD, said in an interview. “For instance, the indications are more matured and specific, and the procedural technical steps have matured. Imaging has also advanced, there’s more understanding about postprocedural care and there are also new devices that have been approved.”
Dr. Saw, an interventional cardiologist at Vancouver General Hospital and St. Paul’s Hospital, and a professor at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, called the statement “a piece that puts everything together.”
“This document really summarizes the whole practice for doing transcatheter procedures,” she added, “so it’s all-in-one document in terms of recommendation of who we do the procedure for, how we should do it, how we should image and guide the procedure, and what complications to look out for and how to manage patients post procedure, be it with antithrombotic therapy and/or device surveillance.”
13 recommendations
In all, the statement carries 13 recommendations for LAAC. The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions and the Heart Rhythm Society commissioned the writing group. The American College of Cardiology and Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography have endorsed the statement. The following are among the recommendations:
- Transcatheter LAAC is appropriate for patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation with high thromboembolic risk but for whom long-term oral anticoagulation may be contraindicated and who have at least 1 year’s life expectancy.
- Operators should have performed at least 50 prior left-sided ablations or structural procedures and at least 25 transseptal punctures (TSPs). Interventional-imaging physicians should have experience in guiding 25 or more TSPs before supporting LAAC procedures independently.
- To maintain skills, operators should do 25 or more TSPs and at least 12 LAACs over each 2-year period.
- On-site cardiovascular surgery backup should be available for new programs and for operators early in their learning curve.
- Baseline imaging with transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) or cardiac computed tomography should be performed before LAAC.
- Intraprocedural imaging guidance with TEE or intracardiac echocardiography.
- Follow labeling of each specific LAAC device for technical aspects of the procedure.
- Familiarity with avoiding, recognizing, and managing LAAC complications.
- Predischarge 2-dimensional TEE to rule out pericardial effusion and device embolization.
- Anticoagulation for device-related thrombus.
- Make all efforts to minimize peridevice leaks during implantation because their clinical impact and management isn’t well understood.
- Antithrombotic therapy with warfarin, DOAC, or dual-antiplatelet therapy after LAAC based on the studied regimen and instructions for each specific device, tailored to the bleeding risks for each patient.
- TEE or cardiac computed tomography at 45-90 days after LAAC for device surveillance to assess for peridevice leak and device-related thrombus.
The statement also includes precautionary recommendations. It advises against using routine closure of LAAC-associated iatrogenic atrial septal defects and states that combined procedures with LAAC, such as structural interventions and pulmonary vein isolation, should be avoided because randomized controlled trial data are pending.
“These recommendations are based upon data from updated publications and randomized trial data as well as large registries, including the National Cardiovascular Data Registry, so I think this is a very practical statement that puts all these pieces together for any budding interventionalist doing this procedure and even experienced operations,” Dr. Saw said.
Authors of an accompanying editorial agreed that the “rigorous standards” set out in the statement will help maintain “a high level of procedural safety in the setting of rapid expansion.”
The editorialists, Faisal M. Merchant, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, and Mohamad Alkhouli, MD, professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic School of Medicine, Rochester, Minn., point out that the incidence of pericardial effusion has decreased from more than 5% in the pivotal Watchman trials to less than 1.5% in the most recent report from the National Cardiovascular Data Registry, which shows that more than 100,000 procedures have been performed in the United States.
But most important as the field moves forward, they stress, is patient selection. The recommendation of limiting patients to those with a life expectancy of 1 year “is a tacit recognition of the fact that the benefits of LAAC take time to accrue, and many older and frail patients are unlikely to derive meaningful benefit.”
Dr. Merchant and Dr. Alkhouli also note that there remains a conundrum in patient selection that remains from the original LAAC trials, which enrolled patients who were eligible for anticoagulation. “Somewhat paradoxically, after its approval, LAAC is mostly prescribed to patients who are not felt to be good anticoagulation candidates.” This leaves physicians “in the precarious position of extrapolating data to patients who were excluded from the original clinical trials.”
Therefore, the consensus statement “is right to put patient selection front and center in its recommendations, but as the field of LAAC comes of age, better evidence to support patient selection will be the real sign of maturity.”
Dr. Saw said she envisions another update over the next 2 years or so as ongoing clinical trials comparing DOAC and LAAC, namely the CHAMPION-AF and OPTION trials, report results.
Dr. Saw and Dr. Merchant, reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Alkhouli has financial ties to Boston Scientific, Abbott, and Philips.
An updated consensus statement on transcatheter left atrial appendage closure (LAAC) has put a newfound focus on patient selection for the procedure, specifically recommending that the procedure is appropriate for patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation who have risk for thromboembolism, aren’t well suited for direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) and have a good chance of living for at least another year.
The statement, published online in the Journal of the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions, also makes recommendations for how much experience operators should have, how many procedures they should perform to keep their skills up, and when and how to use imaging and prescribe DOACs, among other suggestions.
The statement represents the first updated guidance for LAAC since 2015. “Since then this field has really expanded and evolved,” writing group chair Jacqueline Saw, MD, said in an interview. “For instance, the indications are more matured and specific, and the procedural technical steps have matured. Imaging has also advanced, there’s more understanding about postprocedural care and there are also new devices that have been approved.”
Dr. Saw, an interventional cardiologist at Vancouver General Hospital and St. Paul’s Hospital, and a professor at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, called the statement “a piece that puts everything together.”
“This document really summarizes the whole practice for doing transcatheter procedures,” she added, “so it’s all-in-one document in terms of recommendation of who we do the procedure for, how we should do it, how we should image and guide the procedure, and what complications to look out for and how to manage patients post procedure, be it with antithrombotic therapy and/or device surveillance.”
13 recommendations
In all, the statement carries 13 recommendations for LAAC. The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions and the Heart Rhythm Society commissioned the writing group. The American College of Cardiology and Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography have endorsed the statement. The following are among the recommendations:
- Transcatheter LAAC is appropriate for patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation with high thromboembolic risk but for whom long-term oral anticoagulation may be contraindicated and who have at least 1 year’s life expectancy.
- Operators should have performed at least 50 prior left-sided ablations or structural procedures and at least 25 transseptal punctures (TSPs). Interventional-imaging physicians should have experience in guiding 25 or more TSPs before supporting LAAC procedures independently.
- To maintain skills, operators should do 25 or more TSPs and at least 12 LAACs over each 2-year period.
- On-site cardiovascular surgery backup should be available for new programs and for operators early in their learning curve.
- Baseline imaging with transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) or cardiac computed tomography should be performed before LAAC.
- Intraprocedural imaging guidance with TEE or intracardiac echocardiography.
- Follow labeling of each specific LAAC device for technical aspects of the procedure.
- Familiarity with avoiding, recognizing, and managing LAAC complications.
- Predischarge 2-dimensional TEE to rule out pericardial effusion and device embolization.
- Anticoagulation for device-related thrombus.
- Make all efforts to minimize peridevice leaks during implantation because their clinical impact and management isn’t well understood.
- Antithrombotic therapy with warfarin, DOAC, or dual-antiplatelet therapy after LAAC based on the studied regimen and instructions for each specific device, tailored to the bleeding risks for each patient.
- TEE or cardiac computed tomography at 45-90 days after LAAC for device surveillance to assess for peridevice leak and device-related thrombus.
The statement also includes precautionary recommendations. It advises against using routine closure of LAAC-associated iatrogenic atrial septal defects and states that combined procedures with LAAC, such as structural interventions and pulmonary vein isolation, should be avoided because randomized controlled trial data are pending.
“These recommendations are based upon data from updated publications and randomized trial data as well as large registries, including the National Cardiovascular Data Registry, so I think this is a very practical statement that puts all these pieces together for any budding interventionalist doing this procedure and even experienced operations,” Dr. Saw said.
Authors of an accompanying editorial agreed that the “rigorous standards” set out in the statement will help maintain “a high level of procedural safety in the setting of rapid expansion.”
The editorialists, Faisal M. Merchant, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, and Mohamad Alkhouli, MD, professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic School of Medicine, Rochester, Minn., point out that the incidence of pericardial effusion has decreased from more than 5% in the pivotal Watchman trials to less than 1.5% in the most recent report from the National Cardiovascular Data Registry, which shows that more than 100,000 procedures have been performed in the United States.
But most important as the field moves forward, they stress, is patient selection. The recommendation of limiting patients to those with a life expectancy of 1 year “is a tacit recognition of the fact that the benefits of LAAC take time to accrue, and many older and frail patients are unlikely to derive meaningful benefit.”
Dr. Merchant and Dr. Alkhouli also note that there remains a conundrum in patient selection that remains from the original LAAC trials, which enrolled patients who were eligible for anticoagulation. “Somewhat paradoxically, after its approval, LAAC is mostly prescribed to patients who are not felt to be good anticoagulation candidates.” This leaves physicians “in the precarious position of extrapolating data to patients who were excluded from the original clinical trials.”
Therefore, the consensus statement “is right to put patient selection front and center in its recommendations, but as the field of LAAC comes of age, better evidence to support patient selection will be the real sign of maturity.”
Dr. Saw said she envisions another update over the next 2 years or so as ongoing clinical trials comparing DOAC and LAAC, namely the CHAMPION-AF and OPTION trials, report results.
Dr. Saw and Dr. Merchant, reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Alkhouli has financial ties to Boston Scientific, Abbott, and Philips.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY FOR CARDIOVASCULAR ANGIOGRAPHY & INTERVENTIONS
COAPT 5-year results ‘remarkable,’ but patient selection issues remain
It remained an open question in 2018, on the unveiling of the COAPT trial’s 2-year primary results, whether the striking reductions in mortality and heart-failure (HF) hospitalization observed for transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (TEER) with the MitraClip (Abbott) would be durable with longer follow-up.
The trial had enrolled an especially sick population of symptomatic patients with mitral regurgitation (MR) secondary to HF.
As it turns out, the therapy’s benefits at 2 years were indeed durable, at least out to 5 years, investigators reported March 5 at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The results were simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Patients who received the MitraClip on top of intensive medical therapy, compared with a group assigned to medical management alone, benefited significantly at 5 years with risk reductions of 51% for HF hospitalization, 28% for death from any cause, and 47% for the composite of the two events.
Still, mortality at 5 years among the 614 randomized patients was steep at 57.3% in the MitraClip group and 67.2% for those assigned to meds only, underscoring the need for early identification of patients appropriate for the device therapy, Gregg W. Stone, MD, said during his presentation.
Dr. Stone, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, is a COAPT co-principal investigator and lead author of the 5-year outcomes publication.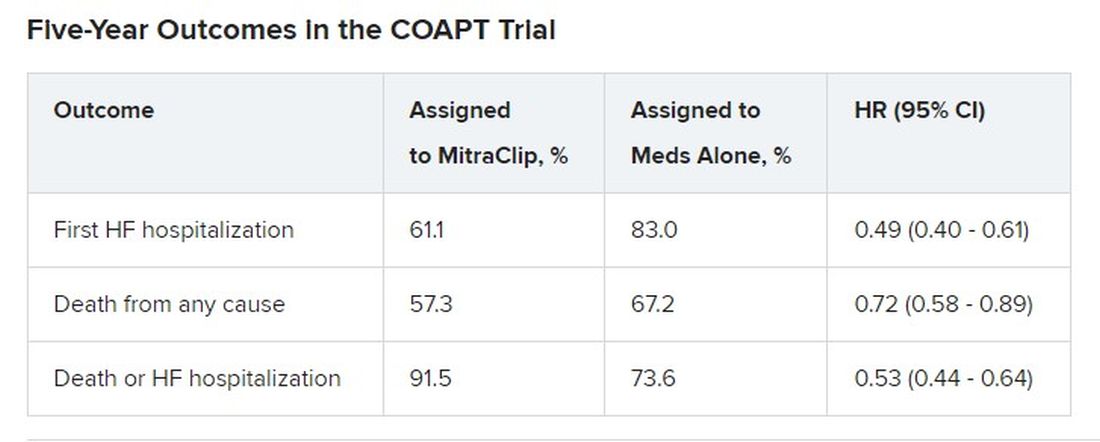
Outcomes were consistent across all prespecified patient subgroups, including by age, sex, MR, left ventricular (LV) function and volume, cardiomyopathy etiology, and degree of surgical risk, the researchers reported.
Symptom status, as measured by New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class, improved throughout the 5-year follow-up for patients assigned to the MitraClip group, compared with the control group, and the intervention group was significantly more likely to be in NYHA class 1 or 2, the authors noted.
The relative benefits in terms of clinical outcomes of MitraClip therapy narrowed after 2-3 years, Dr. Stone said, primarily because at 2 years, patients who had been assigned to meds only were eligible to undergo TEER. Indeed, he noted, 45% of the 138 patients in the control group who were eligible for TEER at 2 years “crossed over” to receive a MitraClip. Those patients benefited despite their delay in undergoing the procedure, he observed.
However, nearly half of the control patients died before becoming eligible for crossover at 2 years. “We have to identify the appropriate patients for treatment and treat them early because the mortality is very high in this population,” Dr. Stone said.
“We need to do more because the MitraClip doesn’t do anything directly to the underlying left ventricular dysfunction, which is the cause of the patient’s disease,” he said. “We need advanced therapies to address the underlying left ventricular dysfunction” in this high-risk population.
Exclusions based on LV dimension
The COAPT trial included 614 patients with HF and symptomatic MR despite guideline-directed medical therapy. They were required to have moderate to severe (3+) or severe (4+) MR confirmed by an echocardiographic core laboratory and a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 20%-50%.
Among the exclusion criteria were an LV end-systolic diameter greater than 70 mm, severe pulmonary hypertension, and moderate to severe symptomatic right ventricular failure.
The systolic LV dimension exclusion helped address the persistent question of whether “severe mitral regurgitation is a marker of a bad left ventricle or ... contributes to the pathophysiology” of MR and its poor outcomes, Dr. Stone said.
The 51% reduction in risk for time-to-first HF hospitalization among patients assigned to TEER “accrued very early,” Dr. Stone pointed out. “You can see the curves start to separate almost immediately after you reduce left atrial pressure and volume overload with the MitraClip.”
The curves stopped diverging after about 3 years because of crossover from the control group, he said. Still, “we had shown a substantial absolute 17% reduction in mortality at 2 years” with MitraClip. “That has continued out to 5 years, with a statistically significant 28% relative reduction,” he continued, and the absolute risk reduction reaching 10%.
Patients in the control group who crossed over “basically assumed the death and heart failure hospitalization rate of the MitraClip group,” Dr. Stone said. That wasn’t surprising “because most of the patients enrolled in the trial originally had chronic heart failure.” It’s “confirmation of the principal results of the trial.”
Comparison With MITRA-FR
“We know that MITRA-FR was a negative trial,” observed Wayne B. Batchelor, MD, an invited discussant following Dr. Stone’s presentation, referring to an earlier similar trial that showed no advantage for MitraClip. Compared with MITRA-FR, COAPT “has created an entirely different story.”
The marked reductions in mortality and risk for adverse events and low number-needed-to-treat with MitraClip are “really remarkable,” said Dr. Batchelor, who is with the Inova Heart and Vascular Institute, Falls Church, Va.
But the high absolute mortality for patients in the COAPT control group “speaks volumes to me and tells us that we’ve got to identify our patients well early,” he agreed, and to “implement transcatheter edge-to-edge therapy in properly selected patients on guideline-directed medical therapy in order to avoid that.”
The trial findings “suggest that we’re reducing HF hospitalization,” he said, “so this is an extremely potent therapy, potentially.
“The dramatic difference between the treated arm and the medical therapy arm in this trial makes me feel that this therapy is here to stay,” Dr. Batchelor concluded. “We just have to figure out how to deploy it properly in the right patients.”
The COAPT trial presents “a practice-changing paradigm,” said Suzanne J. Baron, MD, of Lahey Hospital & Medical Center, Burlington, Mass., another invited discussant.
The crossover data “really jumped out,” she added. “Waiting to treat patients with TEER may be harmful, so if we’re going to consider treating earlier, how do we identify the right patient?” Dr. Baron asked, especially given the negative MITRA-FR results.
MITRA-FR didn’t follow patients beyond 2 years, Dr. Stone noted. Still, “we do think that the main difference was that COAPT enrolled a patient population with more severe MR and slightly less LV dysfunction, at least in terms of the LV not being as dilated, so they didn’t have end-stage LV disease. Whereas in MITRA-FR, more of the patients had only moderate mitral regurgitation.” And big dilated left ventricles “are less likely to benefit.”
There were also differences between the studies in technique and background medical therapies, he added.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved – and payers are paying – for the treatment of patients who meet the COAPT criteria, “in whom we can be very confident they have a benefit,” Dr. Stone said.
“The real question is: Where are the edges where we should consider this? LVEF slightly less than 20% or slightly greater than 50%? Or primary atrial functional mitral regurgitation? There are registry data to suggest that they would benefit,” he said, but “we need more data.”
COAPT was supported by Abbott. Dr. Stone disclosed receiving speaker honoraria from Abbott and consulting fees or equity from Neovasc, Ancora, Valfix, and Cardiac Success; and that Mount Sinai receives research funding from Abbott. Disclosures for the other authors are available at nejm.org. Dr. Batchelor has disclosed receiving consultant fees or honoraria from Abbott, Boston Scientific, Idorsia, and V-Wave Medical, and having other ties with Medtronic. Dr. Baron has disclosed receiving consultant fees or honoraria from Abiomed, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, Shockwave, and Zoll Medical, and conducting research or receiving research grants from Abiomed and Boston Scientific.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
It remained an open question in 2018, on the unveiling of the COAPT trial’s 2-year primary results, whether the striking reductions in mortality and heart-failure (HF) hospitalization observed for transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (TEER) with the MitraClip (Abbott) would be durable with longer follow-up.
The trial had enrolled an especially sick population of symptomatic patients with mitral regurgitation (MR) secondary to HF.
As it turns out, the therapy’s benefits at 2 years were indeed durable, at least out to 5 years, investigators reported March 5 at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The results were simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Patients who received the MitraClip on top of intensive medical therapy, compared with a group assigned to medical management alone, benefited significantly at 5 years with risk reductions of 51% for HF hospitalization, 28% for death from any cause, and 47% for the composite of the two events.
Still, mortality at 5 years among the 614 randomized patients was steep at 57.3% in the MitraClip group and 67.2% for those assigned to meds only, underscoring the need for early identification of patients appropriate for the device therapy, Gregg W. Stone, MD, said during his presentation.
Dr. Stone, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, is a COAPT co-principal investigator and lead author of the 5-year outcomes publication.
Outcomes were consistent across all prespecified patient subgroups, including by age, sex, MR, left ventricular (LV) function and volume, cardiomyopathy etiology, and degree of surgical risk, the researchers reported.
Symptom status, as measured by New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class, improved throughout the 5-year follow-up for patients assigned to the MitraClip group, compared with the control group, and the intervention group was significantly more likely to be in NYHA class 1 or 2, the authors noted.
The relative benefits in terms of clinical outcomes of MitraClip therapy narrowed after 2-3 years, Dr. Stone said, primarily because at 2 years, patients who had been assigned to meds only were eligible to undergo TEER. Indeed, he noted, 45% of the 138 patients in the control group who were eligible for TEER at 2 years “crossed over” to receive a MitraClip. Those patients benefited despite their delay in undergoing the procedure, he observed.
However, nearly half of the control patients died before becoming eligible for crossover at 2 years. “We have to identify the appropriate patients for treatment and treat them early because the mortality is very high in this population,” Dr. Stone said.
“We need to do more because the MitraClip doesn’t do anything directly to the underlying left ventricular dysfunction, which is the cause of the patient’s disease,” he said. “We need advanced therapies to address the underlying left ventricular dysfunction” in this high-risk population.
Exclusions based on LV dimension
The COAPT trial included 614 patients with HF and symptomatic MR despite guideline-directed medical therapy. They were required to have moderate to severe (3+) or severe (4+) MR confirmed by an echocardiographic core laboratory and a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 20%-50%.
Among the exclusion criteria were an LV end-systolic diameter greater than 70 mm, severe pulmonary hypertension, and moderate to severe symptomatic right ventricular failure.
The systolic LV dimension exclusion helped address the persistent question of whether “severe mitral regurgitation is a marker of a bad left ventricle or ... contributes to the pathophysiology” of MR and its poor outcomes, Dr. Stone said.
The 51% reduction in risk for time-to-first HF hospitalization among patients assigned to TEER “accrued very early,” Dr. Stone pointed out. “You can see the curves start to separate almost immediately after you reduce left atrial pressure and volume overload with the MitraClip.”
The curves stopped diverging after about 3 years because of crossover from the control group, he said. Still, “we had shown a substantial absolute 17% reduction in mortality at 2 years” with MitraClip. “That has continued out to 5 years, with a statistically significant 28% relative reduction,” he continued, and the absolute risk reduction reaching 10%.
Patients in the control group who crossed over “basically assumed the death and heart failure hospitalization rate of the MitraClip group,” Dr. Stone said. That wasn’t surprising “because most of the patients enrolled in the trial originally had chronic heart failure.” It’s “confirmation of the principal results of the trial.”
Comparison With MITRA-FR
“We know that MITRA-FR was a negative trial,” observed Wayne B. Batchelor, MD, an invited discussant following Dr. Stone’s presentation, referring to an earlier similar trial that showed no advantage for MitraClip. Compared with MITRA-FR, COAPT “has created an entirely different story.”
The marked reductions in mortality and risk for adverse events and low number-needed-to-treat with MitraClip are “really remarkable,” said Dr. Batchelor, who is with the Inova Heart and Vascular Institute, Falls Church, Va.
But the high absolute mortality for patients in the COAPT control group “speaks volumes to me and tells us that we’ve got to identify our patients well early,” he agreed, and to “implement transcatheter edge-to-edge therapy in properly selected patients on guideline-directed medical therapy in order to avoid that.”
The trial findings “suggest that we’re reducing HF hospitalization,” he said, “so this is an extremely potent therapy, potentially.
“The dramatic difference between the treated arm and the medical therapy arm in this trial makes me feel that this therapy is here to stay,” Dr. Batchelor concluded. “We just have to figure out how to deploy it properly in the right patients.”
The COAPT trial presents “a practice-changing paradigm,” said Suzanne J. Baron, MD, of Lahey Hospital & Medical Center, Burlington, Mass., another invited discussant.
The crossover data “really jumped out,” she added. “Waiting to treat patients with TEER may be harmful, so if we’re going to consider treating earlier, how do we identify the right patient?” Dr. Baron asked, especially given the negative MITRA-FR results.
MITRA-FR didn’t follow patients beyond 2 years, Dr. Stone noted. Still, “we do think that the main difference was that COAPT enrolled a patient population with more severe MR and slightly less LV dysfunction, at least in terms of the LV not being as dilated, so they didn’t have end-stage LV disease. Whereas in MITRA-FR, more of the patients had only moderate mitral regurgitation.” And big dilated left ventricles “are less likely to benefit.”
There were also differences between the studies in technique and background medical therapies, he added.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved – and payers are paying – for the treatment of patients who meet the COAPT criteria, “in whom we can be very confident they have a benefit,” Dr. Stone said.
“The real question is: Where are the edges where we should consider this? LVEF slightly less than 20% or slightly greater than 50%? Or primary atrial functional mitral regurgitation? There are registry data to suggest that they would benefit,” he said, but “we need more data.”
COAPT was supported by Abbott. Dr. Stone disclosed receiving speaker honoraria from Abbott and consulting fees or equity from Neovasc, Ancora, Valfix, and Cardiac Success; and that Mount Sinai receives research funding from Abbott. Disclosures for the other authors are available at nejm.org. Dr. Batchelor has disclosed receiving consultant fees or honoraria from Abbott, Boston Scientific, Idorsia, and V-Wave Medical, and having other ties with Medtronic. Dr. Baron has disclosed receiving consultant fees or honoraria from Abiomed, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, Shockwave, and Zoll Medical, and conducting research or receiving research grants from Abiomed and Boston Scientific.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
It remained an open question in 2018, on the unveiling of the COAPT trial’s 2-year primary results, whether the striking reductions in mortality and heart-failure (HF) hospitalization observed for transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (TEER) with the MitraClip (Abbott) would be durable with longer follow-up.
The trial had enrolled an especially sick population of symptomatic patients with mitral regurgitation (MR) secondary to HF.
As it turns out, the therapy’s benefits at 2 years were indeed durable, at least out to 5 years, investigators reported March 5 at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The results were simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Patients who received the MitraClip on top of intensive medical therapy, compared with a group assigned to medical management alone, benefited significantly at 5 years with risk reductions of 51% for HF hospitalization, 28% for death from any cause, and 47% for the composite of the two events.
Still, mortality at 5 years among the 614 randomized patients was steep at 57.3% in the MitraClip group and 67.2% for those assigned to meds only, underscoring the need for early identification of patients appropriate for the device therapy, Gregg W. Stone, MD, said during his presentation.
Dr. Stone, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, is a COAPT co-principal investigator and lead author of the 5-year outcomes publication.
Outcomes were consistent across all prespecified patient subgroups, including by age, sex, MR, left ventricular (LV) function and volume, cardiomyopathy etiology, and degree of surgical risk, the researchers reported.
Symptom status, as measured by New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class, improved throughout the 5-year follow-up for patients assigned to the MitraClip group, compared with the control group, and the intervention group was significantly more likely to be in NYHA class 1 or 2, the authors noted.
The relative benefits in terms of clinical outcomes of MitraClip therapy narrowed after 2-3 years, Dr. Stone said, primarily because at 2 years, patients who had been assigned to meds only were eligible to undergo TEER. Indeed, he noted, 45% of the 138 patients in the control group who were eligible for TEER at 2 years “crossed over” to receive a MitraClip. Those patients benefited despite their delay in undergoing the procedure, he observed.
However, nearly half of the control patients died before becoming eligible for crossover at 2 years. “We have to identify the appropriate patients for treatment and treat them early because the mortality is very high in this population,” Dr. Stone said.
“We need to do more because the MitraClip doesn’t do anything directly to the underlying left ventricular dysfunction, which is the cause of the patient’s disease,” he said. “We need advanced therapies to address the underlying left ventricular dysfunction” in this high-risk population.
Exclusions based on LV dimension
The COAPT trial included 614 patients with HF and symptomatic MR despite guideline-directed medical therapy. They were required to have moderate to severe (3+) or severe (4+) MR confirmed by an echocardiographic core laboratory and a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 20%-50%.
Among the exclusion criteria were an LV end-systolic diameter greater than 70 mm, severe pulmonary hypertension, and moderate to severe symptomatic right ventricular failure.
The systolic LV dimension exclusion helped address the persistent question of whether “severe mitral regurgitation is a marker of a bad left ventricle or ... contributes to the pathophysiology” of MR and its poor outcomes, Dr. Stone said.
The 51% reduction in risk for time-to-first HF hospitalization among patients assigned to TEER “accrued very early,” Dr. Stone pointed out. “You can see the curves start to separate almost immediately after you reduce left atrial pressure and volume overload with the MitraClip.”
The curves stopped diverging after about 3 years because of crossover from the control group, he said. Still, “we had shown a substantial absolute 17% reduction in mortality at 2 years” with MitraClip. “That has continued out to 5 years, with a statistically significant 28% relative reduction,” he continued, and the absolute risk reduction reaching 10%.
Patients in the control group who crossed over “basically assumed the death and heart failure hospitalization rate of the MitraClip group,” Dr. Stone said. That wasn’t surprising “because most of the patients enrolled in the trial originally had chronic heart failure.” It’s “confirmation of the principal results of the trial.”
Comparison With MITRA-FR
“We know that MITRA-FR was a negative trial,” observed Wayne B. Batchelor, MD, an invited discussant following Dr. Stone’s presentation, referring to an earlier similar trial that showed no advantage for MitraClip. Compared with MITRA-FR, COAPT “has created an entirely different story.”
The marked reductions in mortality and risk for adverse events and low number-needed-to-treat with MitraClip are “really remarkable,” said Dr. Batchelor, who is with the Inova Heart and Vascular Institute, Falls Church, Va.
But the high absolute mortality for patients in the COAPT control group “speaks volumes to me and tells us that we’ve got to identify our patients well early,” he agreed, and to “implement transcatheter edge-to-edge therapy in properly selected patients on guideline-directed medical therapy in order to avoid that.”
The trial findings “suggest that we’re reducing HF hospitalization,” he said, “so this is an extremely potent therapy, potentially.
“The dramatic difference between the treated arm and the medical therapy arm in this trial makes me feel that this therapy is here to stay,” Dr. Batchelor concluded. “We just have to figure out how to deploy it properly in the right patients.”
The COAPT trial presents “a practice-changing paradigm,” said Suzanne J. Baron, MD, of Lahey Hospital & Medical Center, Burlington, Mass., another invited discussant.
The crossover data “really jumped out,” she added. “Waiting to treat patients with TEER may be harmful, so if we’re going to consider treating earlier, how do we identify the right patient?” Dr. Baron asked, especially given the negative MITRA-FR results.
MITRA-FR didn’t follow patients beyond 2 years, Dr. Stone noted. Still, “we do think that the main difference was that COAPT enrolled a patient population with more severe MR and slightly less LV dysfunction, at least in terms of the LV not being as dilated, so they didn’t have end-stage LV disease. Whereas in MITRA-FR, more of the patients had only moderate mitral regurgitation.” And big dilated left ventricles “are less likely to benefit.”
There were also differences between the studies in technique and background medical therapies, he added.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved – and payers are paying – for the treatment of patients who meet the COAPT criteria, “in whom we can be very confident they have a benefit,” Dr. Stone said.
“The real question is: Where are the edges where we should consider this? LVEF slightly less than 20% or slightly greater than 50%? Or primary atrial functional mitral regurgitation? There are registry data to suggest that they would benefit,” he said, but “we need more data.”
COAPT was supported by Abbott. Dr. Stone disclosed receiving speaker honoraria from Abbott and consulting fees or equity from Neovasc, Ancora, Valfix, and Cardiac Success; and that Mount Sinai receives research funding from Abbott. Disclosures for the other authors are available at nejm.org. Dr. Batchelor has disclosed receiving consultant fees or honoraria from Abbott, Boston Scientific, Idorsia, and V-Wave Medical, and having other ties with Medtronic. Dr. Baron has disclosed receiving consultant fees or honoraria from Abiomed, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, Shockwave, and Zoll Medical, and conducting research or receiving research grants from Abiomed and Boston Scientific.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACC 2023
Does new heart transplant method challenge definition of death?
The relatively recent innovation of heart transplantation after circulatory death of the donor is increasing the number of donor hearts available and leading to many more lives on the heart transplant waiting list being saved. Experts agree it’s a major and very welcome advance in medicine.
However, some of the processes involved in one approach to donation after circulatory death has raised ethical concerns and questions about whether they violate the “dead donor rule” – a principle that requires patients be declared dead before removal of life-sustaining organs for transplant.
Experts in the fields of transplantation and medical ethics have yet to reach consensus, causing problems for the transplant community, who worry that this could cause a loss of confidence in the entire transplant process.
A new pathway for heart transplantation
The traditional approach to transplantation is to retrieve organs from a donor who has been declared brain dead, known as “donation after brain death (DBD).” These patients have usually suffered a catastrophic brain injury but survived to get to intensive care.
As the brain swells because of injury, it becomes evident that all brain function is lost, and the patient is declared brain dead. However, breathing is maintained by the ventilator and the heart is still beating. Because the organs are being oxygenated, there is no immediate rush to retrieve the organs and the heart can be evaluated for its suitability for transplant in a calm and methodical way before it is removed.
However, there is a massive shortage of organs, especially hearts, partially because of the limited number of donors who are declared brain dead in that setting.
In recent years, another pathway for organ transplantation has become available: “donation after circulatory death (DCD).” These patients also have suffered a catastrophic brain injury considered to be nonsurvivable, but unlike the DBD situation, the brain still has some function, so the patient does not meet the criteria for brain death.
Still, because the patient is considered to have no chance of a meaningful recovery, the family often recognizes the futility of treatment and agrees to the withdrawal of life support. When this happens, the heart normally stops beating after a period of time. There is then a “stand-off time” – normally 5 minutes – after which death is declared and the organs can be removed.
The difficulty with this approach, however, is that because the heart has been stopped, it has been deprived of oxygen, potentially causing injury. While DCD has been practiced for several years to retrieve organs such as the kidney, liver, lungs, and pancreas, the heart is more difficult as it is more susceptible to oxygen deprivation. And for the heart to be assessed for transplant suitability, it should ideally be beating, so it has to be reperfused and restarted quickly after death has been declared.
For many years it was thought the oxygen deprivation that occurs after circulatory death would be too much to provide a functional organ. But researchers in the United Kingdom and Australia developed techniques to overcome this problem, and early DCD heart transplants took place in 2014 in Australia, and in 2015 in the United Kingdom.
Heart transplantation after circulatory death has now become a routine part of the transplant program in many countries, including the United States, Spain, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Austria.
In the United States, 348 DCD heart transplants were performed in 2022, with numbers expected to reach 700 to 800 this year as more centers come online.
It is expected that most countries with heart transplant programs will follow suit and the number of donor hearts will increase by up to 30% worldwide because of DCD.
Currently, there are about 8,000 heart transplants worldwide each year and with DCD this could rise to about 10,000, potentially an extra 2,000 lives saved each year, experts estimate.
Two different approaches to DCD heart transplantation have been developed.
The direct procurement approach
The Australian group, based at St. Vincent’s Hospital in Sydney, developed a technique referred to as “direct procurement”: after the standoff period and declaration of circulatory death, the chest is opened, and the heart is removed. New technology, the Organ Care System (OCS) heart box (Transmedics), is then used to reperfuse and restart the heart outside the body so its suitability for transplant can be assessed.
The heart is kept perfused and beating in the OCS box while it is being transported to the recipient. This has enabled longer transit times than the traditional way of transporting the nonbeating heart on ice.
Peter MacDonald, MD, PhD, from the St Vincent’s group that developed this approach, said, “Most people thought a heart from a DCD donor would not survive transport – that the injury to the heart from the combination of life support withdrawal, stand-off time, and cold storage would be too much. But we modeled the process in the lab and were able to show that we were able to get the heart beating again after withdrawal of life support.”
Dr. McDonald noted that “the recipient of their first human DCD heart transplant using this machine in 2014 is still alive and well.” The Australian group has now done 85 of these DCD heart transplants, and they have increased the number of heart transplant procedures at St. Vincent’s Hospital by 25%.
Normothermic regional perfusion (NRP)
The U.K. group, based at the Royal Papworth Hospital in Cambridge, England, developed a different approach to DCD: After the standoff period and the declaration of circulatory death, the donor is connected to a heart/lung machine using extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) so that the heart is perfused and starts beating again inside the body. This approach is known as normothermic regional perfusion (NRP).
Marius Berman, MD, surgical lead for Transplantation and Mechanical Circulatory Support at Papworth, explained that the NRP approach allows the heart to be perfused and restarted faster than direct procurement, resulting in a shorter ischemic time. The heart can be evaluated thoroughly for suitability for transplantation in situ before committing to transplantation, and because the heart is less damaged, it can be transported on ice without use of the OCS box.
“DCD is more complicated than DBD, because the heart has stopped and has to be restarted. Retrieval teams have to be very experienced,” Dr. Berman noted. “This is more of an issue for the direct procurement approach, where the chest has to be opened and the heart retrieved as fast as possible. It is a rush. The longer time without the heart being perfused correlates to an increased incidence of primary graft dysfunction. With NRP, we can get the heart started again more quickly, which is crucial.”
Stephen Large, MBBS, another cardiothoracic surgeon with the Papworth team, added that they have reduced ischemic time to about 15 minutes. “That’s considerably shorter than reperfusing the heart outside the body,” he said. “This results in a healthier organ for the recipient.”
The NRP approach is also less expensive than direct procurement as one OCS box costs about $75,000.
He pointed out that the NRP approach can also be used for heart transplants in children and even small babies, while currently the direct procurement technique is not typically suitable for children because the OCS box was not designed for small hearts.
DCD, using either technique, has increased the heart transplant rate by 40% at Papworth, and is being used at all seven transplant centers in the United Kingdom, “a world first,” noted Dr. Large.
The Papworth team recently published its 5-year experience with 25 NRP transplants and 85 direct procurement transplants. Survival in recipients was no different, although there was some suggestion that the NRP hearts may have been in slightly better condition, possibly being more resistant to immunological rejection.
Ethical concerns about NRP
Restarting the circulation during the NRP process has raised ethical concerns.
When the NRP technique was first used in the United States, these ethical questions were raised by several groups, including the American College of Physicians (ACP).
Harry Peled, MD, Providence St. Jude Medical Center, Fullerton, Calif., coauthor of a recent Viewpoint on the issue, is board-certified in both cardiology and critical care, and said he is a supporter of DCD using direct procurement, but he does not believe that NRP is ethical at present. He is not part of the ACP, but said his views align with those of the organization.
There are two ethical problems with NRP, he said. The first is whether by restarting the circulation, the NRP process violates the U.S. definition of death, and retrieval of organs would therefore violate the dead donor rule.
“American law states that death is the irreversible cessation of brain function or of circulatory function. But with NRP, the circulation is artificially restored, so the cessation of circulatory function is not irreversible,” Dr. Peled pointed out.
“I have no problem with DCD using direct procurement as we are not restarting the circulation. But NRP is restarting the circulation and that is a problem for me,” Dr. Peled said. “I would argue that by performing NRP, we are resuscitating the patient.”
The second ethical problem with NRP is concern about whether, during the process, there would be any circulation to the brain, and if so, would this be enough to restore some brain function? Before NRP is started, the main arch vessel arteries to the head are clamped to prevent flow to the brain, but there are worries that some blood flow may still be possible through small collateral vessels.
“We have established that these patients do not have enough brain function for a meaningful life, which is why a decision has been made to remove life support, but they have not been declared brain dead,” Dr. Peled said.
With direct procurement, the circulation is not restarted so there is no chance that any brain function will be restored, he said. “But with NRP, because the arch vessels have to be clamped to prevent brain circulation, that is admitting there is concern that brain function may be restored if circulation to the brain is reestablished, and brain function is compatible with life. As we do not know whether there is any meaningful circulation to the brain via the small collaterals, there is, in effect, a risk of bringing the patient back to life.”
The other major concern for some is whether even a very small amount of circulation to the brain would be enough to support consciousness, and “we don’t know that for certain,” Dr. Peled said.
The argument for NRP
Nader Moazami, MD, professor of cardiovascular surgery, NYU Langone Health, New York, is one of the more vocal proponents of NRP for DCD heart transplantation in the United States, and has coauthored responses to these ethical concerns.
“People are confusing many issues to produce an argument against NRP,” he said.
“Our position is that death has already been declared based on the lack of circulatory function for over 5 minutes and this has been with the full agreement of the family, knowing that the patient has no chance of a meaningful life. No one is thinking of trying to resuscitate the patient. It has already been established that any future efforts to resuscitate are futile. In this case, we are not resuscitating the patient by restarting the circulation. It is just regional perfusion of the organs.”
Dr. Moazami pointed out this concept was accepted for the practice of abdominal DCD when it first started in the United States in the 1990s where cold perfusion was used to preserve the abdominal organs before they were retrieved from the body.
“The new approach of using NRP is similar except that it involves circulating warm blood, which will preserve organs better and result in higher quality organs for the recipient.”
On the issue of concern about possible circulation to the brain, Dr. Moazami said: “The ethical critics of NRP are questioning whether the brain may not be dead. We are arguing that the patient has already been declared dead as they have had a circulatory death. You cannot die twice.”
He maintained that the clamping of the arch vessels to the head will ensure that when the circulation is restarted “the natural process of circulatory death leading to brain death will continue to progress.”
On the concerns about possible collateral flow to the brain, Dr. Moazami said there is no evidence that this occurs. “Prominent neurologists have said it is impossible for collaterals to provide any meaningful blood flow to the brain in this situation. And even if there is small amount of blood flow to the brain, this would be insufficient to maintain any meaningful brain function.”
But Dr. Peled argues that this has not been proved. “Even though we don’t think there is enough circulation to the brain for any function with NRP, we don’t know that with 100% certainty,” he said. “In my view, if there is a possibility of even the smallest amount of brain flow, we are going against the dead donor rule. We are rewriting the rules of death.”
Dr. Moazami countered: “Nothing in life is 100%, particularly in medicine. With that argument can you also prove with 100% certainty to me that there is absolutely no brain function with regular direct procurement DCD? We know that brain death has started, but the question is: Has it been completed? We don’t know the answer to this question with 100% certainty, but that is the case for regular direct procurement DCD as well, and that has been accepted by almost everyone.
“The whole issue revolves around when are we comfortable that death has occurred,” he said. “Those against NRP are concerned that organs are being taken before the patient is dead. But the key point is that the patient has already been declared dead.”
Since there is some concern over the ethics of NRP, why not just stick to DCD with direct procurement?
Dr. Moazami argued that NRP results in healthier organs. “NRP allows more successful heart transplants, liver transplants, lung transplants. It preserves all the organs better,” he said. “This will have a big impact on recipients – they would obviously much prefer a healthier organ. In addition, the process is easier and cheaper, so more centers will be able to do it, therefore more transplants will get done and more lives will be saved if NRP is used.”
He added: “I am a physician taking care of sick patients. I believe I have to respect the wishes of the donor and the donor family; make sure I’m not doing any harm to the donor; and ensure the best quality possible of the organ I am retrieving to best serve the recipient. I am happy I am doing this by using NRP for DCD heart transplantation.”
But Dr. Peled argued that while NRP may have some possible advantages over direct procurement, that does not justify allowing a process to go ahead that is unethical.
“The fact that NRP may result in some benefits doesn’t justify violating the dead donor rule or the possibility, however small, of causing pain to the donor. If it’s unethical, it’s unethical. Full stop,” he said.
“I feel that NRP is not respecting the rights of our patients and that the process does not have adequate transparency. We took it to our local ethics committee, and they decided not to approve NRP in our health care system. I agree with this decision,” Dr. Peled said.
“The trouble is different experts and different countries are not in agreement about this,” he added. “Reasonable, well-informed people are in disagreement. I do not believe we can have a standard of care where there is not consensus.”
Cautious nod
In a 2022 consensus statement, the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) gave a cautious nod toward DCD and NRP, dependent on local recommendations.
The ISHLT conclusion reads: “With appropriate consideration of the ethical principles involved in organ donation, DCD can be undertaken in a morally permissible manner. In all cases, the introduction of DCD programs should be in accordance with local legal regulations. Countries lacking a DCD pathway should be encouraged to develop national ethical, professional, and legal frameworks to address both public and professional concerns.”
The author of a recent editorial on the subject, Ulrich P. Jorde, MD, head of the heart transplant program at Montefiore Medical Center, New York, said, “DCD is a great step forward. People regularly die on the heart transplant waiting list. DCD will increase the supply of donor hearts by 20% to 30%.”
However, he noted that while most societies have agreed on a protocol for organ donation based on brain death, the situation is more complicated with circulatory death.
“Different countries have different definitions of circulatory death. How long do we have to wait after the heart has stopped beating before the patient is declared dead? Most countries have agreed on 5 minutes, but other countries have imposed different periods and as such, different definitions of death.
“The ISHLT statement says that restarting the circulation is acceptable if death has been certified according to prevailing law and surgical interventions are undertaken to preclude any restoration of cerebral circulation. But our problem is that different regional societies have different definitions of circulatory, death which makes the situation confusing.”
Dr. Jorde added: “We also have to weigh the wishes of the donor and their family. If family, advocating what are presumed to be the donor’s wishes, have decided that DCD would be acceptable and they understand the concept and wish to donate the organs after circulatory death, this should be strongly considered under the concept of self-determination, a basic human right.”
Variations in practice around the world
This ethical debate has led to large variations in practice around the world, with some countries, such as Spain, allowing both methods of DCD, while Australia allows direct procurement but not NRP, and Germany currently does not allow DCD at all.
In the United States, things are even more complicated, with some states allowing NRP while others don’t. Even within states, some hospitals and transplant organizations allow NRP, and others don’t.
David A. D’Alessandro, MD, cardiac surgeon at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, uses only the direct procurement approach as his region does not allow NRP.
“The direct procurement approach is not controversial and to me that’s a big advantage. I believe we need to agree on the ethics first, and then get into a debate about which technique is better,” he told this news organization.
Dr. D’Alessandro and his group recently published the results of their study, with direct procurement DCD heart transplantation showing similar short-term clinical outcomes to DBD.
“We are only doing direct procurement and we are seeing good results that appear to be comparable to DBD. That is good enough for me,” he said.
Dr. D’Alessandro estimates that in the United States both types of DCD procedures are currently being done about equally.
“Anything we can do to increase the amount of hearts available for transplantation is a big deal,” he said. “At the moment, only the very sickest patients get a heart transplant, and many patients die on the transplant waiting list. Very sadly, many young people die every year from a circulatory death after having life support withdrawn. Before DCD, these beautiful functional organs were not able to be used. Now we have a way of saving lives with these organs.”
Dr. D’Alessandro noted that more and more centers in the United States are starting to perform DCD heart transplants.
“Not every transplant center may join in as the DCD procedures are very resource-intensive and time-consuming. For low-volume transplant centers, it may not be worth the expense and anguish to do DCD heart transplants. But bigger centers will need to engage in DCD to remain competitive. My guess is that 50%-70% of U.S. transplant centers will do DCD in future.”
He said he thinks it is a “medical shortcoming” that agreement cannot be reached on the ethics of NRP. “In an ideal world everyone would be on the same page. It makes me a bit uncomfortable that some people think it’s okay and some people don’t.”
Adam DeVore, MD, a cardiologist at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., the first U.S. center to perform an adult DCD heart transplant, reported that his institution uses both methods, with the choice sometimes depending on how far the heart must travel.
“If the recipient is near, NRP may be chosen as the heart is transported on ice, but if it needs to go further away we are more likely to choose direct procurement and use of the OCS box,” he said.
“I am really proud of what we’ve been able to do, helping to introduce DCD in the U.S.,” Dr. DeVore said. “This is having a massive benefit in increasing the number of hearts for donation with great outcomes.”
But he acknowledged that the whole concept of DCD is somewhat controversial.
“The idea of brain death really came about for the purpose of heart donation. The two things are very intricately tied. Trying to do heart donation without brain death having been declared is foreign to people. Also, in DCD there is the issue of [this]: When life support is removed, how long do we wait before death can be declared? That could be in conflict with how long the organ needs to remain viable. We are going through the process now of looking at these questions. There is a lot of variation in the U.S. about the withdrawal of care and the declaration of death, which is not completely standardized.
“But the concept of circulatory death itself is accepted after the withdrawal of life support. I think it’s the rush to take the organs out that makes it more difficult.”
Dr. DeVore said the field is moving forward now. “As the process has become more common, people have become more comfortable, probably because of the big difference it will make to saving lives. But we do need to try and standardize best practices.”
A recent Canadian review of the ethics of DCD concluded that the direct procurement approach would be in alignment with current medical guidelines, but that further work is required to evaluate the consistency of NRP with current Canadian death determination policy and to ensure the absence of brain perfusion during this process.
In the United Kingdom, the definition of death is brain-based, and brain death is defined on a neurological basis.
Dr. Stephen Large from Papworth explained that this recognizes the presence of brain-stem death through brain stem reflex testing after the withdrawal of life support, cardiorespiratory arrest and 5 further minutes of ischemia. As long as NRP does not restore intracranial (brainstem) perfusion after death has been confirmed, then it is consistent with laws for death determination and therefore both direct procurement and NRP are permissible.
However, the question over possible collateral flow to the brain has led the United Kingdom to pause the NRP technique as routine practice while this is investigated further. So, at the present time, the vast majority of DCD heart transplants are being conducted using the direct procurement approach.
But the United Kingdom is facing the bigger challenge: national funding that will soon end. “The DCD program in the U.K. has been extremely successful, increasing heart transplant rates by up to 28%,” Dr. Berman said. “Everybody wants it to continue. But at present the DCD program only has national funding in the U.K. until March 2023. We don’t know what will happen after that.”
The current model in the United Kingdom consists of three specialized DCD heart retrieval teams, a national protocol of direct organ procurement and delivery of DCD hearts to all seven transplant programs, both adult and pediatric.
If the national funding is not extended, “we will go back to individual hospitals trying to fund their own programs. That will be a serious threat to the program and could result in a large reduction in heart transplants,” said Dr. Berman.
Definition of death
The crux of the issue with regard to NRP seems to be variations in how death is defined and the interpretation of those definitions.
DCD donors will have had many tests indicating severe brain damage, a neurologist will have declared the prognosis is futile, and relatives will have agreed to withdraw life support, Dr. Jorde said. “The heart stops beating, and the stand-off time means that blood flow to the brain ceases completely for at least 5 minutes before circulatory death is declared. This is enough on its own to stop brain function.”
Dr. Large made the point that by the time the circulation is reestablished with NRP, more time has elapsed, and the brain will have been without perfusion for much longer than 5 minutes, so it would be “physiologically almost impossible” for there to be any blood flow to the brain.
“Because these brains are already very damaged before life support was removed, the intracranial pressure is high, which will further discourage blood flow to the brain,” he said. Then the donor goes through a period of anoxic heart arrest, up to 16 minutes at a minimum of no blood supply, enough on its own to stop meaningful brain function.
“It’s asking an awful lot to believe that there might be any brain function left,” he said. “And if, on reestablishing the circulation with NRP, there is any blood in the collaterals, the pressure of such flow is so low it won’t enter the brain.”
Dr. Large also pointed out that the fact that the United Kingdom requires a neurologic definition for brain-stem death makes the process easier.
In Australia, St. Vincent’s cardiologist Dr. MacDonald noted that death is defined as the irreversible cessation of circulation, so the NRP procedure is not allowed.
“With NRP, there is an ethical dilemma over whether the patient has legally died or not. Different countries have different ways of defining death. Perhaps society will have to review of the definition of death,” he suggested. Death is a process, “but for organ donation, we have to choose a moment in time of that process that satisfies everyone – when there is no prospect of recovery of the donor but the organs can still be utilized without harming the donor.”
Dr. MacDonald said the field is in transition. “I don’t want to argue that one technique is better than the other; I think it’s good to have access to both techniques. Anything that will increase the number of transplants we can do is a good thing.”
Collaborative decision
Everyone seems to agree that there should be an effort to try to define death in a uniform way worldwide, and that international, national and local regulations are aligned with each other.
Dr. Jorde said: “It is of critical importance that local guidelines are streamlined, firstly in any one given country and then globally, and these things must be discussed transparently within society with all stakeholders – doctors, patients, citizens.”
Dr. Peled, from Providence St. Jude in California, concurred: “There is the possibility that we could change the definition of death, but that cannot be a decision based solely on transplant organizations. It has to be a collaborative decision with a large input from groups who do not have an interest in the procurement of organs.”
He added: “The dialogue so far has been civil, and everybody is trying to do the right thing. My hope is that as a civilized society we will figure out a way forward. At present, there is significant controversy about NRP, and families need to know that. My main concern is that if there is any lack of transparency in getting informed consent, then this risks people losing trust in the donation system.”
Dr. Moazami, from NYU Langone, said the controversy has cast a cloud over the practice of NRP throughout the world. “We need to get it sorted out.”
He said he believes the way forward is to settle the question of whether there is any meaningful blood flow to the brain with the NRP technique.
“This is where the research has to focus. I believe this concern is hypothetical, but I am happy to do the studies to confirm that. Then, the issue should come to a rest. I think that is the right way forward – to do the studies rather than enforcing a moratorium on the practice because of a hypothetical concern.”
These studies on blood flow to the brain are now getting started in both the United Kingdom and the United States.
The U.K. study is being run by Antonio Rubino, MD, consultant in cardiothoracic anesthesia and intensive care at Papworth Hospital NHS Foundation and clinical lead, organ donation. Dr. Rubino explained that the study will assess cerebral blood flow using CT angiography of the brain. “We hypothesize that this will provide evidence to indicate that brain blood flow is not present during NRP and promote trust in the use of NRP in routine practice,” he said.
Dr. Large said: “Rather than having these tortured arguments, we will do the measurements. For the sake of society in this situation, I think it’s good to stop and take a breath. We must measure this, and we are doing just that.”
If there is any blood flow at all, Dr. Large said they will then have to seek expert guidance. “Say we find there is 50 mL of blood flow and normal blood flow is 1,500 mL/min. We will need expert guidance on whether it is remotely possible to be sentient on that. I would say it would be extraordinarily unlikely.”
Dr. Berman summarized the situation: “DCD is increasing the availability of hearts for transplant. This is saving lives, reducing the number of patients on the waiting list, and reducing hospital stays for patients unable to leave the hospital without a transplant. It is definitely here to stay. It is crucial that it gets funded properly, and it is also crucial that we resolve the NRP ethical issues as soon as possible.”
He is hopeful that some of these issues will be resolved this year.
Dr. MacDonald reported he has received “in-kind” support from Transmedics through provision of research modules for preclinical research studies. Dr. D’Alessandro reported he is on the speakers bureau for Abiomed, not relevant to this article. No other relevant disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The relatively recent innovation of heart transplantation after circulatory death of the donor is increasing the number of donor hearts available and leading to many more lives on the heart transplant waiting list being saved. Experts agree it’s a major and very welcome advance in medicine.
However, some of the processes involved in one approach to donation after circulatory death has raised ethical concerns and questions about whether they violate the “dead donor rule” – a principle that requires patients be declared dead before removal of life-sustaining organs for transplant.
Experts in the fields of transplantation and medical ethics have yet to reach consensus, causing problems for the transplant community, who worry that this could cause a loss of confidence in the entire transplant process.
A new pathway for heart transplantation
The traditional approach to transplantation is to retrieve organs from a donor who has been declared brain dead, known as “donation after brain death (DBD).” These patients have usually suffered a catastrophic brain injury but survived to get to intensive care.
As the brain swells because of injury, it becomes evident that all brain function is lost, and the patient is declared brain dead. However, breathing is maintained by the ventilator and the heart is still beating. Because the organs are being oxygenated, there is no immediate rush to retrieve the organs and the heart can be evaluated for its suitability for transplant in a calm and methodical way before it is removed.
However, there is a massive shortage of organs, especially hearts, partially because of the limited number of donors who are declared brain dead in that setting.
In recent years, another pathway for organ transplantation has become available: “donation after circulatory death (DCD).” These patients also have suffered a catastrophic brain injury considered to be nonsurvivable, but unlike the DBD situation, the brain still has some function, so the patient does not meet the criteria for brain death.
Still, because the patient is considered to have no chance of a meaningful recovery, the family often recognizes the futility of treatment and agrees to the withdrawal of life support. When this happens, the heart normally stops beating after a period of time. There is then a “stand-off time” – normally 5 minutes – after which death is declared and the organs can be removed.
The difficulty with this approach, however, is that because the heart has been stopped, it has been deprived of oxygen, potentially causing injury. While DCD has been practiced for several years to retrieve organs such as the kidney, liver, lungs, and pancreas, the heart is more difficult as it is more susceptible to oxygen deprivation. And for the heart to be assessed for transplant suitability, it should ideally be beating, so it has to be reperfused and restarted quickly after death has been declared.
For many years it was thought the oxygen deprivation that occurs after circulatory death would be too much to provide a functional organ. But researchers in the United Kingdom and Australia developed techniques to overcome this problem, and early DCD heart transplants took place in 2014 in Australia, and in 2015 in the United Kingdom.
Heart transplantation after circulatory death has now become a routine part of the transplant program in many countries, including the United States, Spain, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Austria.
In the United States, 348 DCD heart transplants were performed in 2022, with numbers expected to reach 700 to 800 this year as more centers come online.
It is expected that most countries with heart transplant programs will follow suit and the number of donor hearts will increase by up to 30% worldwide because of DCD.
Currently, there are about 8,000 heart transplants worldwide each year and with DCD this could rise to about 10,000, potentially an extra 2,000 lives saved each year, experts estimate.
Two different approaches to DCD heart transplantation have been developed.
The direct procurement approach
The Australian group, based at St. Vincent’s Hospital in Sydney, developed a technique referred to as “direct procurement”: after the standoff period and declaration of circulatory death, the chest is opened, and the heart is removed. New technology, the Organ Care System (OCS) heart box (Transmedics), is then used to reperfuse and restart the heart outside the body so its suitability for transplant can be assessed.
The heart is kept perfused and beating in the OCS box while it is being transported to the recipient. This has enabled longer transit times than the traditional way of transporting the nonbeating heart on ice.
Peter MacDonald, MD, PhD, from the St Vincent’s group that developed this approach, said, “Most people thought a heart from a DCD donor would not survive transport – that the injury to the heart from the combination of life support withdrawal, stand-off time, and cold storage would be too much. But we modeled the process in the lab and were able to show that we were able to get the heart beating again after withdrawal of life support.”
Dr. McDonald noted that “the recipient of their first human DCD heart transplant using this machine in 2014 is still alive and well.” The Australian group has now done 85 of these DCD heart transplants, and they have increased the number of heart transplant procedures at St. Vincent’s Hospital by 25%.
Normothermic regional perfusion (NRP)
The U.K. group, based at the Royal Papworth Hospital in Cambridge, England, developed a different approach to DCD: After the standoff period and the declaration of circulatory death, the donor is connected to a heart/lung machine using extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) so that the heart is perfused and starts beating again inside the body. This approach is known as normothermic regional perfusion (NRP).
Marius Berman, MD, surgical lead for Transplantation and Mechanical Circulatory Support at Papworth, explained that the NRP approach allows the heart to be perfused and restarted faster than direct procurement, resulting in a shorter ischemic time. The heart can be evaluated thoroughly for suitability for transplantation in situ before committing to transplantation, and because the heart is less damaged, it can be transported on ice without use of the OCS box.
“DCD is more complicated than DBD, because the heart has stopped and has to be restarted. Retrieval teams have to be very experienced,” Dr. Berman noted. “This is more of an issue for the direct procurement approach, where the chest has to be opened and the heart retrieved as fast as possible. It is a rush. The longer time without the heart being perfused correlates to an increased incidence of primary graft dysfunction. With NRP, we can get the heart started again more quickly, which is crucial.”
Stephen Large, MBBS, another cardiothoracic surgeon with the Papworth team, added that they have reduced ischemic time to about 15 minutes. “That’s considerably shorter than reperfusing the heart outside the body,” he said. “This results in a healthier organ for the recipient.”
The NRP approach is also less expensive than direct procurement as one OCS box costs about $75,000.
He pointed out that the NRP approach can also be used for heart transplants in children and even small babies, while currently the direct procurement technique is not typically suitable for children because the OCS box was not designed for small hearts.
DCD, using either technique, has increased the heart transplant rate by 40% at Papworth, and is being used at all seven transplant centers in the United Kingdom, “a world first,” noted Dr. Large.
The Papworth team recently published its 5-year experience with 25 NRP transplants and 85 direct procurement transplants. Survival in recipients was no different, although there was some suggestion that the NRP hearts may have been in slightly better condition, possibly being more resistant to immunological rejection.
Ethical concerns about NRP
Restarting the circulation during the NRP process has raised ethical concerns.
When the NRP technique was first used in the United States, these ethical questions were raised by several groups, including the American College of Physicians (ACP).
Harry Peled, MD, Providence St. Jude Medical Center, Fullerton, Calif., coauthor of a recent Viewpoint on the issue, is board-certified in both cardiology and critical care, and said he is a supporter of DCD using direct procurement, but he does not believe that NRP is ethical at present. He is not part of the ACP, but said his views align with those of the organization.
There are two ethical problems with NRP, he said. The first is whether by restarting the circulation, the NRP process violates the U.S. definition of death, and retrieval of organs would therefore violate the dead donor rule.
“American law states that death is the irreversible cessation of brain function or of circulatory function. But with NRP, the circulation is artificially restored, so the cessation of circulatory function is not irreversible,” Dr. Peled pointed out.
“I have no problem with DCD using direct procurement as we are not restarting the circulation. But NRP is restarting the circulation and that is a problem for me,” Dr. Peled said. “I would argue that by performing NRP, we are resuscitating the patient.”
The second ethical problem with NRP is concern about whether, during the process, there would be any circulation to the brain, and if so, would this be enough to restore some brain function? Before NRP is started, the main arch vessel arteries to the head are clamped to prevent flow to the brain, but there are worries that some blood flow may still be possible through small collateral vessels.
“We have established that these patients do not have enough brain function for a meaningful life, which is why a decision has been made to remove life support, but they have not been declared brain dead,” Dr. Peled said.
With direct procurement, the circulation is not restarted so there is no chance that any brain function will be restored, he said. “But with NRP, because the arch vessels have to be clamped to prevent brain circulation, that is admitting there is concern that brain function may be restored if circulation to the brain is reestablished, and brain function is compatible with life. As we do not know whether there is any meaningful circulation to the brain via the small collaterals, there is, in effect, a risk of bringing the patient back to life.”
The other major concern for some is whether even a very small amount of circulation to the brain would be enough to support consciousness, and “we don’t know that for certain,” Dr. Peled said.
The argument for NRP
Nader Moazami, MD, professor of cardiovascular surgery, NYU Langone Health, New York, is one of the more vocal proponents of NRP for DCD heart transplantation in the United States, and has coauthored responses to these ethical concerns.
“People are confusing many issues to produce an argument against NRP,” he said.
“Our position is that death has already been declared based on the lack of circulatory function for over 5 minutes and this has been with the full agreement of the family, knowing that the patient has no chance of a meaningful life. No one is thinking of trying to resuscitate the patient. It has already been established that any future efforts to resuscitate are futile. In this case, we are not resuscitating the patient by restarting the circulation. It is just regional perfusion of the organs.”
Dr. Moazami pointed out this concept was accepted for the practice of abdominal DCD when it first started in the United States in the 1990s where cold perfusion was used to preserve the abdominal organs before they were retrieved from the body.
“The new approach of using NRP is similar except that it involves circulating warm blood, which will preserve organs better and result in higher quality organs for the recipient.”
On the issue of concern about possible circulation to the brain, Dr. Moazami said: “The ethical critics of NRP are questioning whether the brain may not be dead. We are arguing that the patient has already been declared dead as they have had a circulatory death. You cannot die twice.”
He maintained that the clamping of the arch vessels to the head will ensure that when the circulation is restarted “the natural process of circulatory death leading to brain death will continue to progress.”
On the concerns about possible collateral flow to the brain, Dr. Moazami said there is no evidence that this occurs. “Prominent neurologists have said it is impossible for collaterals to provide any meaningful blood flow to the brain in this situation. And even if there is small amount of blood flow to the brain, this would be insufficient to maintain any meaningful brain function.”
But Dr. Peled argues that this has not been proved. “Even though we don’t think there is enough circulation to the brain for any function with NRP, we don’t know that with 100% certainty,” he said. “In my view, if there is a possibility of even the smallest amount of brain flow, we are going against the dead donor rule. We are rewriting the rules of death.”
Dr. Moazami countered: “Nothing in life is 100%, particularly in medicine. With that argument can you also prove with 100% certainty to me that there is absolutely no brain function with regular direct procurement DCD? We know that brain death has started, but the question is: Has it been completed? We don’t know the answer to this question with 100% certainty, but that is the case for regular direct procurement DCD as well, and that has been accepted by almost everyone.
“The whole issue revolves around when are we comfortable that death has occurred,” he said. “Those against NRP are concerned that organs are being taken before the patient is dead. But the key point is that the patient has already been declared dead.”
Since there is some concern over the ethics of NRP, why not just stick to DCD with direct procurement?
Dr. Moazami argued that NRP results in healthier organs. “NRP allows more successful heart transplants, liver transplants, lung transplants. It preserves all the organs better,” he said. “This will have a big impact on recipients – they would obviously much prefer a healthier organ. In addition, the process is easier and cheaper, so more centers will be able to do it, therefore more transplants will get done and more lives will be saved if NRP is used.”
He added: “I am a physician taking care of sick patients. I believe I have to respect the wishes of the donor and the donor family; make sure I’m not doing any harm to the donor; and ensure the best quality possible of the organ I am retrieving to best serve the recipient. I am happy I am doing this by using NRP for DCD heart transplantation.”
But Dr. Peled argued that while NRP may have some possible advantages over direct procurement, that does not justify allowing a process to go ahead that is unethical.
“The fact that NRP may result in some benefits doesn’t justify violating the dead donor rule or the possibility, however small, of causing pain to the donor. If it’s unethical, it’s unethical. Full stop,” he said.
“I feel that NRP is not respecting the rights of our patients and that the process does not have adequate transparency. We took it to our local ethics committee, and they decided not to approve NRP in our health care system. I agree with this decision,” Dr. Peled said.
“The trouble is different experts and different countries are not in agreement about this,” he added. “Reasonable, well-informed people are in disagreement. I do not believe we can have a standard of care where there is not consensus.”
Cautious nod
In a 2022 consensus statement, the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) gave a cautious nod toward DCD and NRP, dependent on local recommendations.
The ISHLT conclusion reads: “With appropriate consideration of the ethical principles involved in organ donation, DCD can be undertaken in a morally permissible manner. In all cases, the introduction of DCD programs should be in accordance with local legal regulations. Countries lacking a DCD pathway should be encouraged to develop national ethical, professional, and legal frameworks to address both public and professional concerns.”
The author of a recent editorial on the subject, Ulrich P. Jorde, MD, head of the heart transplant program at Montefiore Medical Center, New York, said, “DCD is a great step forward. People regularly die on the heart transplant waiting list. DCD will increase the supply of donor hearts by 20% to 30%.”
However, he noted that while most societies have agreed on a protocol for organ donation based on brain death, the situation is more complicated with circulatory death.
“Different countries have different definitions of circulatory death. How long do we have to wait after the heart has stopped beating before the patient is declared dead? Most countries have agreed on 5 minutes, but other countries have imposed different periods and as such, different definitions of death.
“The ISHLT statement says that restarting the circulation is acceptable if death has been certified according to prevailing law and surgical interventions are undertaken to preclude any restoration of cerebral circulation. But our problem is that different regional societies have different definitions of circulatory, death which makes the situation confusing.”
Dr. Jorde added: “We also have to weigh the wishes of the donor and their family. If family, advocating what are presumed to be the donor’s wishes, have decided that DCD would be acceptable and they understand the concept and wish to donate the organs after circulatory death, this should be strongly considered under the concept of self-determination, a basic human right.”
Variations in practice around the world
This ethical debate has led to large variations in practice around the world, with some countries, such as Spain, allowing both methods of DCD, while Australia allows direct procurement but not NRP, and Germany currently does not allow DCD at all.
In the United States, things are even more complicated, with some states allowing NRP while others don’t. Even within states, some hospitals and transplant organizations allow NRP, and others don’t.
David A. D’Alessandro, MD, cardiac surgeon at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, uses only the direct procurement approach as his region does not allow NRP.
“The direct procurement approach is not controversial and to me that’s a big advantage. I believe we need to agree on the ethics first, and then get into a debate about which technique is better,” he told this news organization.
Dr. D’Alessandro and his group recently published the results of their study, with direct procurement DCD heart transplantation showing similar short-term clinical outcomes to DBD.
“We are only doing direct procurement and we are seeing good results that appear to be comparable to DBD. That is good enough for me,” he said.
Dr. D’Alessandro estimates that in the United States both types of DCD procedures are currently being done about equally.
“Anything we can do to increase the amount of hearts available for transplantation is a big deal,” he said. “At the moment, only the very sickest patients get a heart transplant, and many patients die on the transplant waiting list. Very sadly, many young people die every year from a circulatory death after having life support withdrawn. Before DCD, these beautiful functional organs were not able to be used. Now we have a way of saving lives with these organs.”
Dr. D’Alessandro noted that more and more centers in the United States are starting to perform DCD heart transplants.
“Not every transplant center may join in as the DCD procedures are very resource-intensive and time-consuming. For low-volume transplant centers, it may not be worth the expense and anguish to do DCD heart transplants. But bigger centers will need to engage in DCD to remain competitive. My guess is that 50%-70% of U.S. transplant centers will do DCD in future.”
He said he thinks it is a “medical shortcoming” that agreement cannot be reached on the ethics of NRP. “In an ideal world everyone would be on the same page. It makes me a bit uncomfortable that some people think it’s okay and some people don’t.”
Adam DeVore, MD, a cardiologist at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., the first U.S. center to perform an adult DCD heart transplant, reported that his institution uses both methods, with the choice sometimes depending on how far the heart must travel.
“If the recipient is near, NRP may be chosen as the heart is transported on ice, but if it needs to go further away we are more likely to choose direct procurement and use of the OCS box,” he said.
“I am really proud of what we’ve been able to do, helping to introduce DCD in the U.S.,” Dr. DeVore said. “This is having a massive benefit in increasing the number of hearts for donation with great outcomes.”
But he acknowledged that the whole concept of DCD is somewhat controversial.
“The idea of brain death really came about for the purpose of heart donation. The two things are very intricately tied. Trying to do heart donation without brain death having been declared is foreign to people. Also, in DCD there is the issue of [this]: When life support is removed, how long do we wait before death can be declared? That could be in conflict with how long the organ needs to remain viable. We are going through the process now of looking at these questions. There is a lot of variation in the U.S. about the withdrawal of care and the declaration of death, which is not completely standardized.
“But the concept of circulatory death itself is accepted after the withdrawal of life support. I think it’s the rush to take the organs out that makes it more difficult.”
Dr. DeVore said the field is moving forward now. “As the process has become more common, people have become more comfortable, probably because of the big difference it will make to saving lives. But we do need to try and standardize best practices.”
A recent Canadian review of the ethics of DCD concluded that the direct procurement approach would be in alignment with current medical guidelines, but that further work is required to evaluate the consistency of NRP with current Canadian death determination policy and to ensure the absence of brain perfusion during this process.
In the United Kingdom, the definition of death is brain-based, and brain death is defined on a neurological basis.
Dr. Stephen Large from Papworth explained that this recognizes the presence of brain-stem death through brain stem reflex testing after the withdrawal of life support, cardiorespiratory arrest and 5 further minutes of ischemia. As long as NRP does not restore intracranial (brainstem) perfusion after death has been confirmed, then it is consistent with laws for death determination and therefore both direct procurement and NRP are permissible.
However, the question over possible collateral flow to the brain has led the United Kingdom to pause the NRP technique as routine practice while this is investigated further. So, at the present time, the vast majority of DCD heart transplants are being conducted using the direct procurement approach.
But the United Kingdom is facing the bigger challenge: national funding that will soon end. “The DCD program in the U.K. has been extremely successful, increasing heart transplant rates by up to 28%,” Dr. Berman said. “Everybody wants it to continue. But at present the DCD program only has national funding in the U.K. until March 2023. We don’t know what will happen after that.”
The current model in the United Kingdom consists of three specialized DCD heart retrieval teams, a national protocol of direct organ procurement and delivery of DCD hearts to all seven transplant programs, both adult and pediatric.
If the national funding is not extended, “we will go back to individual hospitals trying to fund their own programs. That will be a serious threat to the program and could result in a large reduction in heart transplants,” said Dr. Berman.
Definition of death
The crux of the issue with regard to NRP seems to be variations in how death is defined and the interpretation of those definitions.
DCD donors will have had many tests indicating severe brain damage, a neurologist will have declared the prognosis is futile, and relatives will have agreed to withdraw life support, Dr. Jorde said. “The heart stops beating, and the stand-off time means that blood flow to the brain ceases completely for at least 5 minutes before circulatory death is declared. This is enough on its own to stop brain function.”
Dr. Large made the point that by the time the circulation is reestablished with NRP, more time has elapsed, and the brain will have been without perfusion for much longer than 5 minutes, so it would be “physiologically almost impossible” for there to be any blood flow to the brain.
“Because these brains are already very damaged before life support was removed, the intracranial pressure is high, which will further discourage blood flow to the brain,” he said. Then the donor goes through a period of anoxic heart arrest, up to 16 minutes at a minimum of no blood supply, enough on its own to stop meaningful brain function.
“It’s asking an awful lot to believe that there might be any brain function left,” he said. “And if, on reestablishing the circulation with NRP, there is any blood in the collaterals, the pressure of such flow is so low it won’t enter the brain.”
Dr. Large also pointed out that the fact that the United Kingdom requires a neurologic definition for brain-stem death makes the process easier.
In Australia, St. Vincent’s cardiologist Dr. MacDonald noted that death is defined as the irreversible cessation of circulation, so the NRP procedure is not allowed.
“With NRP, there is an ethical dilemma over whether the patient has legally died or not. Different countries have different ways of defining death. Perhaps society will have to review of the definition of death,” he suggested. Death is a process, “but for organ donation, we have to choose a moment in time of that process that satisfies everyone – when there is no prospect of recovery of the donor but the organs can still be utilized without harming the donor.”
Dr. MacDonald said the field is in transition. “I don’t want to argue that one technique is better than the other; I think it’s good to have access to both techniques. Anything that will increase the number of transplants we can do is a good thing.”
Collaborative decision
Everyone seems to agree that there should be an effort to try to define death in a uniform way worldwide, and that international, national and local regulations are aligned with each other.
Dr. Jorde said: “It is of critical importance that local guidelines are streamlined, firstly in any one given country and then globally, and these things must be discussed transparently within society with all stakeholders – doctors, patients, citizens.”
Dr. Peled, from Providence St. Jude in California, concurred: “There is the possibility that we could change the definition of death, but that cannot be a decision based solely on transplant organizations. It has to be a collaborative decision with a large input from groups who do not have an interest in the procurement of organs.”
He added: “The dialogue so far has been civil, and everybody is trying to do the right thing. My hope is that as a civilized society we will figure out a way forward. At present, there is significant controversy about NRP, and families need to know that. My main concern is that if there is any lack of transparency in getting informed consent, then this risks people losing trust in the donation system.”
Dr. Moazami, from NYU Langone, said the controversy has cast a cloud over the practice of NRP throughout the world. “We need to get it sorted out.”
He said he believes the way forward is to settle the question of whether there is any meaningful blood flow to the brain with the NRP technique.
“This is where the research has to focus. I believe this concern is hypothetical, but I am happy to do the studies to confirm that. Then, the issue should come to a rest. I think that is the right way forward – to do the studies rather than enforcing a moratorium on the practice because of a hypothetical concern.”
These studies on blood flow to the brain are now getting started in both the United Kingdom and the United States.
The U.K. study is being run by Antonio Rubino, MD, consultant in cardiothoracic anesthesia and intensive care at Papworth Hospital NHS Foundation and clinical lead, organ donation. Dr. Rubino explained that the study will assess cerebral blood flow using CT angiography of the brain. “We hypothesize that this will provide evidence to indicate that brain blood flow is not present during NRP and promote trust in the use of NRP in routine practice,” he said.
Dr. Large said: “Rather than having these tortured arguments, we will do the measurements. For the sake of society in this situation, I think it’s good to stop and take a breath. We must measure this, and we are doing just that.”
If there is any blood flow at all, Dr. Large said they will then have to seek expert guidance. “Say we find there is 50 mL of blood flow and normal blood flow is 1,500 mL/min. We will need expert guidance on whether it is remotely possible to be sentient on that. I would say it would be extraordinarily unlikely.”
Dr. Berman summarized the situation: “DCD is increasing the availability of hearts for transplant. This is saving lives, reducing the number of patients on the waiting list, and reducing hospital stays for patients unable to leave the hospital without a transplant. It is definitely here to stay. It is crucial that it gets funded properly, and it is also crucial that we resolve the NRP ethical issues as soon as possible.”
He is hopeful that some of these issues will be resolved this year.
Dr. MacDonald reported he has received “in-kind” support from Transmedics through provision of research modules for preclinical research studies. Dr. D’Alessandro reported he is on the speakers bureau for Abiomed, not relevant to this article. No other relevant disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The relatively recent innovation of heart transplantation after circulatory death of the donor is increasing the number of donor hearts available and leading to many more lives on the heart transplant waiting list being saved. Experts agree it’s a major and very welcome advance in medicine.
However, some of the processes involved in one approach to donation after circulatory death has raised ethical concerns and questions about whether they violate the “dead donor rule” – a principle that requires patients be declared dead before removal of life-sustaining organs for transplant.
Experts in the fields of transplantation and medical ethics have yet to reach consensus, causing problems for the transplant community, who worry that this could cause a loss of confidence in the entire transplant process.
A new pathway for heart transplantation
The traditional approach to transplantation is to retrieve organs from a donor who has been declared brain dead, known as “donation after brain death (DBD).” These patients have usually suffered a catastrophic brain injury but survived to get to intensive care.
As the brain swells because of injury, it becomes evident that all brain function is lost, and the patient is declared brain dead. However, breathing is maintained by the ventilator and the heart is still beating. Because the organs are being oxygenated, there is no immediate rush to retrieve the organs and the heart can be evaluated for its suitability for transplant in a calm and methodical way before it is removed.
However, there is a massive shortage of organs, especially hearts, partially because of the limited number of donors who are declared brain dead in that setting.
In recent years, another pathway for organ transplantation has become available: “donation after circulatory death (DCD).” These patients also have suffered a catastrophic brain injury considered to be nonsurvivable, but unlike the DBD situation, the brain still has some function, so the patient does not meet the criteria for brain death.
Still, because the patient is considered to have no chance of a meaningful recovery, the family often recognizes the futility of treatment and agrees to the withdrawal of life support. When this happens, the heart normally stops beating after a period of time. There is then a “stand-off time” – normally 5 minutes – after which death is declared and the organs can be removed.
The difficulty with this approach, however, is that because the heart has been stopped, it has been deprived of oxygen, potentially causing injury. While DCD has been practiced for several years to retrieve organs such as the kidney, liver, lungs, and pancreas, the heart is more difficult as it is more susceptible to oxygen deprivation. And for the heart to be assessed for transplant suitability, it should ideally be beating, so it has to be reperfused and restarted quickly after death has been declared.
For many years it was thought the oxygen deprivation that occurs after circulatory death would be too much to provide a functional organ. But researchers in the United Kingdom and Australia developed techniques to overcome this problem, and early DCD heart transplants took place in 2014 in Australia, and in 2015 in the United Kingdom.
Heart transplantation after circulatory death has now become a routine part of the transplant program in many countries, including the United States, Spain, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Austria.
In the United States, 348 DCD heart transplants were performed in 2022, with numbers expected to reach 700 to 800 this year as more centers come online.
It is expected that most countries with heart transplant programs will follow suit and the number of donor hearts will increase by up to 30% worldwide because of DCD.
Currently, there are about 8,000 heart transplants worldwide each year and with DCD this could rise to about 10,000, potentially an extra 2,000 lives saved each year, experts estimate.
Two different approaches to DCD heart transplantation have been developed.
The direct procurement approach
The Australian group, based at St. Vincent’s Hospital in Sydney, developed a technique referred to as “direct procurement”: after the standoff period and declaration of circulatory death, the chest is opened, and the heart is removed. New technology, the Organ Care System (OCS) heart box (Transmedics), is then used to reperfuse and restart the heart outside the body so its suitability for transplant can be assessed.
The heart is kept perfused and beating in the OCS box while it is being transported to the recipient. This has enabled longer transit times than the traditional way of transporting the nonbeating heart on ice.
Peter MacDonald, MD, PhD, from the St Vincent’s group that developed this approach, said, “Most people thought a heart from a DCD donor would not survive transport – that the injury to the heart from the combination of life support withdrawal, stand-off time, and cold storage would be too much. But we modeled the process in the lab and were able to show that we were able to get the heart beating again after withdrawal of life support.”
Dr. McDonald noted that “the recipient of their first human DCD heart transplant using this machine in 2014 is still alive and well.” The Australian group has now done 85 of these DCD heart transplants, and they have increased the number of heart transplant procedures at St. Vincent’s Hospital by 25%.
Normothermic regional perfusion (NRP)
The U.K. group, based at the Royal Papworth Hospital in Cambridge, England, developed a different approach to DCD: After the standoff period and the declaration of circulatory death, the donor is connected to a heart/lung machine using extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) so that the heart is perfused and starts beating again inside the body. This approach is known as normothermic regional perfusion (NRP).
Marius Berman, MD, surgical lead for Transplantation and Mechanical Circulatory Support at Papworth, explained that the NRP approach allows the heart to be perfused and restarted faster than direct procurement, resulting in a shorter ischemic time. The heart can be evaluated thoroughly for suitability for transplantation in situ before committing to transplantation, and because the heart is less damaged, it can be transported on ice without use of the OCS box.
“DCD is more complicated than DBD, because the heart has stopped and has to be restarted. Retrieval teams have to be very experienced,” Dr. Berman noted. “This is more of an issue for the direct procurement approach, where the chest has to be opened and the heart retrieved as fast as possible. It is a rush. The longer time without the heart being perfused correlates to an increased incidence of primary graft dysfunction. With NRP, we can get the heart started again more quickly, which is crucial.”
Stephen Large, MBBS, another cardiothoracic surgeon with the Papworth team, added that they have reduced ischemic time to about 15 minutes. “That’s considerably shorter than reperfusing the heart outside the body,” he said. “This results in a healthier organ for the recipient.”
The NRP approach is also less expensive than direct procurement as one OCS box costs about $75,000.
He pointed out that the NRP approach can also be used for heart transplants in children and even small babies, while currently the direct procurement technique is not typically suitable for children because the OCS box was not designed for small hearts.
DCD, using either technique, has increased the heart transplant rate by 40% at Papworth, and is being used at all seven transplant centers in the United Kingdom, “a world first,” noted Dr. Large.
The Papworth team recently published its 5-year experience with 25 NRP transplants and 85 direct procurement transplants. Survival in recipients was no different, although there was some suggestion that the NRP hearts may have been in slightly better condition, possibly being more resistant to immunological rejection.
Ethical concerns about NRP
Restarting the circulation during the NRP process has raised ethical concerns.
When the NRP technique was first used in the United States, these ethical questions were raised by several groups, including the American College of Physicians (ACP).
Harry Peled, MD, Providence St. Jude Medical Center, Fullerton, Calif., coauthor of a recent Viewpoint on the issue, is board-certified in both cardiology and critical care, and said he is a supporter of DCD using direct procurement, but he does not believe that NRP is ethical at present. He is not part of the ACP, but said his views align with those of the organization.
There are two ethical problems with NRP, he said. The first is whether by restarting the circulation, the NRP process violates the U.S. definition of death, and retrieval of organs would therefore violate the dead donor rule.
“American law states that death is the irreversible cessation of brain function or of circulatory function. But with NRP, the circulation is artificially restored, so the cessation of circulatory function is not irreversible,” Dr. Peled pointed out.
“I have no problem with DCD using direct procurement as we are not restarting the circulation. But NRP is restarting the circulation and that is a problem for me,” Dr. Peled said. “I would argue that by performing NRP, we are resuscitating the patient.”
The second ethical problem with NRP is concern about whether, during the process, there would be any circulation to the brain, and if so, would this be enough to restore some brain function? Before NRP is started, the main arch vessel arteries to the head are clamped to prevent flow to the brain, but there are worries that some blood flow may still be possible through small collateral vessels.
“We have established that these patients do not have enough brain function for a meaningful life, which is why a decision has been made to remove life support, but they have not been declared brain dead,” Dr. Peled said.
With direct procurement, the circulation is not restarted so there is no chance that any brain function will be restored, he said. “But with NRP, because the arch vessels have to be clamped to prevent brain circulation, that is admitting there is concern that brain function may be restored if circulation to the brain is reestablished, and brain function is compatible with life. As we do not know whether there is any meaningful circulation to the brain via the small collaterals, there is, in effect, a risk of bringing the patient back to life.”
The other major concern for some is whether even a very small amount of circulation to the brain would be enough to support consciousness, and “we don’t know that for certain,” Dr. Peled said.
The argument for NRP
Nader Moazami, MD, professor of cardiovascular surgery, NYU Langone Health, New York, is one of the more vocal proponents of NRP for DCD heart transplantation in the United States, and has coauthored responses to these ethical concerns.
“People are confusing many issues to produce an argument against NRP,” he said.
“Our position is that death has already been declared based on the lack of circulatory function for over 5 minutes and this has been with the full agreement of the family, knowing that the patient has no chance of a meaningful life. No one is thinking of trying to resuscitate the patient. It has already been established that any future efforts to resuscitate are futile. In this case, we are not resuscitating the patient by restarting the circulation. It is just regional perfusion of the organs.”
Dr. Moazami pointed out this concept was accepted for the practice of abdominal DCD when it first started in the United States in the 1990s where cold perfusion was used to preserve the abdominal organs before they were retrieved from the body.
“The new approach of using NRP is similar except that it involves circulating warm blood, which will preserve organs better and result in higher quality organs for the recipient.”
On the issue of concern about possible circulation to the brain, Dr. Moazami said: “The ethical critics of NRP are questioning whether the brain may not be dead. We are arguing that the patient has already been declared dead as they have had a circulatory death. You cannot die twice.”
He maintained that the clamping of the arch vessels to the head will ensure that when the circulation is restarted “the natural process of circulatory death leading to brain death will continue to progress.”
On the concerns about possible collateral flow to the brain, Dr. Moazami said there is no evidence that this occurs. “Prominent neurologists have said it is impossible for collaterals to provide any meaningful blood flow to the brain in this situation. And even if there is small amount of blood flow to the brain, this would be insufficient to maintain any meaningful brain function.”
But Dr. Peled argues that this has not been proved. “Even though we don’t think there is enough circulation to the brain for any function with NRP, we don’t know that with 100% certainty,” he said. “In my view, if there is a possibility of even the smallest amount of brain flow, we are going against the dead donor rule. We are rewriting the rules of death.”
Dr. Moazami countered: “Nothing in life is 100%, particularly in medicine. With that argument can you also prove with 100% certainty to me that there is absolutely no brain function with regular direct procurement DCD? We know that brain death has started, but the question is: Has it been completed? We don’t know the answer to this question with 100% certainty, but that is the case for regular direct procurement DCD as well, and that has been accepted by almost everyone.
“The whole issue revolves around when are we comfortable that death has occurred,” he said. “Those against NRP are concerned that organs are being taken before the patient is dead. But the key point is that the patient has already been declared dead.”
Since there is some concern over the ethics of NRP, why not just stick to DCD with direct procurement?
Dr. Moazami argued that NRP results in healthier organs. “NRP allows more successful heart transplants, liver transplants, lung transplants. It preserves all the organs better,” he said. “This will have a big impact on recipients – they would obviously much prefer a healthier organ. In addition, the process is easier and cheaper, so more centers will be able to do it, therefore more transplants will get done and more lives will be saved if NRP is used.”
He added: “I am a physician taking care of sick patients. I believe I have to respect the wishes of the donor and the donor family; make sure I’m not doing any harm to the donor; and ensure the best quality possible of the organ I am retrieving to best serve the recipient. I am happy I am doing this by using NRP for DCD heart transplantation.”
But Dr. Peled argued that while NRP may have some possible advantages over direct procurement, that does not justify allowing a process to go ahead that is unethical.
“The fact that NRP may result in some benefits doesn’t justify violating the dead donor rule or the possibility, however small, of causing pain to the donor. If it’s unethical, it’s unethical. Full stop,” he said.
“I feel that NRP is not respecting the rights of our patients and that the process does not have adequate transparency. We took it to our local ethics committee, and they decided not to approve NRP in our health care system. I agree with this decision,” Dr. Peled said.
“The trouble is different experts and different countries are not in agreement about this,” he added. “Reasonable, well-informed people are in disagreement. I do not believe we can have a standard of care where there is not consensus.”
Cautious nod
In a 2022 consensus statement, the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) gave a cautious nod toward DCD and NRP, dependent on local recommendations.
The ISHLT conclusion reads: “With appropriate consideration of the ethical principles involved in organ donation, DCD can be undertaken in a morally permissible manner. In all cases, the introduction of DCD programs should be in accordance with local legal regulations. Countries lacking a DCD pathway should be encouraged to develop national ethical, professional, and legal frameworks to address both public and professional concerns.”
The author of a recent editorial on the subject, Ulrich P. Jorde, MD, head of the heart transplant program at Montefiore Medical Center, New York, said, “DCD is a great step forward. People regularly die on the heart transplant waiting list. DCD will increase the supply of donor hearts by 20% to 30%.”
However, he noted that while most societies have agreed on a protocol for organ donation based on brain death, the situation is more complicated with circulatory death.
“Different countries have different definitions of circulatory death. How long do we have to wait after the heart has stopped beating before the patient is declared dead? Most countries have agreed on 5 minutes, but other countries have imposed different periods and as such, different definitions of death.
“The ISHLT statement says that restarting the circulation is acceptable if death has been certified according to prevailing law and surgical interventions are undertaken to preclude any restoration of cerebral circulation. But our problem is that different regional societies have different definitions of circulatory, death which makes the situation confusing.”
Dr. Jorde added: “We also have to weigh the wishes of the donor and their family. If family, advocating what are presumed to be the donor’s wishes, have decided that DCD would be acceptable and they understand the concept and wish to donate the organs after circulatory death, this should be strongly considered under the concept of self-determination, a basic human right.”
Variations in practice around the world
This ethical debate has led to large variations in practice around the world, with some countries, such as Spain, allowing both methods of DCD, while Australia allows direct procurement but not NRP, and Germany currently does not allow DCD at all.
In the United States, things are even more complicated, with some states allowing NRP while others don’t. Even within states, some hospitals and transplant organizations allow NRP, and others don’t.
David A. D’Alessandro, MD, cardiac surgeon at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, uses only the direct procurement approach as his region does not allow NRP.
“The direct procurement approach is not controversial and to me that’s a big advantage. I believe we need to agree on the ethics first, and then get into a debate about which technique is better,” he told this news organization.
Dr. D’Alessandro and his group recently published the results of their study, with direct procurement DCD heart transplantation showing similar short-term clinical outcomes to DBD.
“We are only doing direct procurement and we are seeing good results that appear to be comparable to DBD. That is good enough for me,” he said.
Dr. D’Alessandro estimates that in the United States both types of DCD procedures are currently being done about equally.
“Anything we can do to increase the amount of hearts available for transplantation is a big deal,” he said. “At the moment, only the very sickest patients get a heart transplant, and many patients die on the transplant waiting list. Very sadly, many young people die every year from a circulatory death after having life support withdrawn. Before DCD, these beautiful functional organs were not able to be used. Now we have a way of saving lives with these organs.”
Dr. D’Alessandro noted that more and more centers in the United States are starting to perform DCD heart transplants.
“Not every transplant center may join in as the DCD procedures are very resource-intensive and time-consuming. For low-volume transplant centers, it may not be worth the expense and anguish to do DCD heart transplants. But bigger centers will need to engage in DCD to remain competitive. My guess is that 50%-70% of U.S. transplant centers will do DCD in future.”
He said he thinks it is a “medical shortcoming” that agreement cannot be reached on the ethics of NRP. “In an ideal world everyone would be on the same page. It makes me a bit uncomfortable that some people think it’s okay and some people don’t.”
Adam DeVore, MD, a cardiologist at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., the first U.S. center to perform an adult DCD heart transplant, reported that his institution uses both methods, with the choice sometimes depending on how far the heart must travel.
“If the recipient is near, NRP may be chosen as the heart is transported on ice, but if it needs to go further away we are more likely to choose direct procurement and use of the OCS box,” he said.
“I am really proud of what we’ve been able to do, helping to introduce DCD in the U.S.,” Dr. DeVore said. “This is having a massive benefit in increasing the number of hearts for donation with great outcomes.”
But he acknowledged that the whole concept of DCD is somewhat controversial.
“The idea of brain death really came about for the purpose of heart donation. The two things are very intricately tied. Trying to do heart donation without brain death having been declared is foreign to people. Also, in DCD there is the issue of [this]: When life support is removed, how long do we wait before death can be declared? That could be in conflict with how long the organ needs to remain viable. We are going through the process now of looking at these questions. There is a lot of variation in the U.S. about the withdrawal of care and the declaration of death, which is not completely standardized.
“But the concept of circulatory death itself is accepted after the withdrawal of life support. I think it’s the rush to take the organs out that makes it more difficult.”
Dr. DeVore said the field is moving forward now. “As the process has become more common, people have become more comfortable, probably because of the big difference it will make to saving lives. But we do need to try and standardize best practices.”
A recent Canadian review of the ethics of DCD concluded that the direct procurement approach would be in alignment with current medical guidelines, but that further work is required to evaluate the consistency of NRP with current Canadian death determination policy and to ensure the absence of brain perfusion during this process.
In the United Kingdom, the definition of death is brain-based, and brain death is defined on a neurological basis.
Dr. Stephen Large from Papworth explained that this recognizes the presence of brain-stem death through brain stem reflex testing after the withdrawal of life support, cardiorespiratory arrest and 5 further minutes of ischemia. As long as NRP does not restore intracranial (brainstem) perfusion after death has been confirmed, then it is consistent with laws for death determination and therefore both direct procurement and NRP are permissible.
However, the question over possible collateral flow to the brain has led the United Kingdom to pause the NRP technique as routine practice while this is investigated further. So, at the present time, the vast majority of DCD heart transplants are being conducted using the direct procurement approach.
But the United Kingdom is facing the bigger challenge: national funding that will soon end. “The DCD program in the U.K. has been extremely successful, increasing heart transplant rates by up to 28%,” Dr. Berman said. “Everybody wants it to continue. But at present the DCD program only has national funding in the U.K. until March 2023. We don’t know what will happen after that.”
The current model in the United Kingdom consists of three specialized DCD heart retrieval teams, a national protocol of direct organ procurement and delivery of DCD hearts to all seven transplant programs, both adult and pediatric.
If the national funding is not extended, “we will go back to individual hospitals trying to fund their own programs. That will be a serious threat to the program and could result in a large reduction in heart transplants,” said Dr. Berman.
Definition of death
The crux of the issue with regard to NRP seems to be variations in how death is defined and the interpretation of those definitions.
DCD donors will have had many tests indicating severe brain damage, a neurologist will have declared the prognosis is futile, and relatives will have agreed to withdraw life support, Dr. Jorde said. “The heart stops beating, and the stand-off time means that blood flow to the brain ceases completely for at least 5 minutes before circulatory death is declared. This is enough on its own to stop brain function.”
Dr. Large made the point that by the time the circulation is reestablished with NRP, more time has elapsed, and the brain will have been without perfusion for much longer than 5 minutes, so it would be “physiologically almost impossible” for there to be any blood flow to the brain.
“Because these brains are already very damaged before life support was removed, the intracranial pressure is high, which will further discourage blood flow to the brain,” he said. Then the donor goes through a period of anoxic heart arrest, up to 16 minutes at a minimum of no blood supply, enough on its own to stop meaningful brain function.
“It’s asking an awful lot to believe that there might be any brain function left,” he said. “And if, on reestablishing the circulation with NRP, there is any blood in the collaterals, the pressure of such flow is so low it won’t enter the brain.”
Dr. Large also pointed out that the fact that the United Kingdom requires a neurologic definition for brain-stem death makes the process easier.
In Australia, St. Vincent’s cardiologist Dr. MacDonald noted that death is defined as the irreversible cessation of circulation, so the NRP procedure is not allowed.
“With NRP, there is an ethical dilemma over whether the patient has legally died or not. Different countries have different ways of defining death. Perhaps society will have to review of the definition of death,” he suggested. Death is a process, “but for organ donation, we have to choose a moment in time of that process that satisfies everyone – when there is no prospect of recovery of the donor but the organs can still be utilized without harming the donor.”
Dr. MacDonald said the field is in transition. “I don’t want to argue that one technique is better than the other; I think it’s good to have access to both techniques. Anything that will increase the number of transplants we can do is a good thing.”
Collaborative decision
Everyone seems to agree that there should be an effort to try to define death in a uniform way worldwide, and that international, national and local regulations are aligned with each other.
Dr. Jorde said: “It is of critical importance that local guidelines are streamlined, firstly in any one given country and then globally, and these things must be discussed transparently within society with all stakeholders – doctors, patients, citizens.”
Dr. Peled, from Providence St. Jude in California, concurred: “There is the possibility that we could change the definition of death, but that cannot be a decision based solely on transplant organizations. It has to be a collaborative decision with a large input from groups who do not have an interest in the procurement of organs.”
He added: “The dialogue so far has been civil, and everybody is trying to do the right thing. My hope is that as a civilized society we will figure out a way forward. At present, there is significant controversy about NRP, and families need to know that. My main concern is that if there is any lack of transparency in getting informed consent, then this risks people losing trust in the donation system.”
Dr. Moazami, from NYU Langone, said the controversy has cast a cloud over the practice of NRP throughout the world. “We need to get it sorted out.”
He said he believes the way forward is to settle the question of whether there is any meaningful blood flow to the brain with the NRP technique.
“This is where the research has to focus. I believe this concern is hypothetical, but I am happy to do the studies to confirm that. Then, the issue should come to a rest. I think that is the right way forward – to do the studies rather than enforcing a moratorium on the practice because of a hypothetical concern.”
These studies on blood flow to the brain are now getting started in both the United Kingdom and the United States.
The U.K. study is being run by Antonio Rubino, MD, consultant in cardiothoracic anesthesia and intensive care at Papworth Hospital NHS Foundation and clinical lead, organ donation. Dr. Rubino explained that the study will assess cerebral blood flow using CT angiography of the brain. “We hypothesize that this will provide evidence to indicate that brain blood flow is not present during NRP and promote trust in the use of NRP in routine practice,” he said.
Dr. Large said: “Rather than having these tortured arguments, we will do the measurements. For the sake of society in this situation, I think it’s good to stop and take a breath. We must measure this, and we are doing just that.”
If there is any blood flow at all, Dr. Large said they will then have to seek expert guidance. “Say we find there is 50 mL of blood flow and normal blood flow is 1,500 mL/min. We will need expert guidance on whether it is remotely possible to be sentient on that. I would say it would be extraordinarily unlikely.”
Dr. Berman summarized the situation: “DCD is increasing the availability of hearts for transplant. This is saving lives, reducing the number of patients on the waiting list, and reducing hospital stays for patients unable to leave the hospital without a transplant. It is definitely here to stay. It is crucial that it gets funded properly, and it is also crucial that we resolve the NRP ethical issues as soon as possible.”
He is hopeful that some of these issues will be resolved this year.
Dr. MacDonald reported he has received “in-kind” support from Transmedics through provision of research modules for preclinical research studies. Dr. D’Alessandro reported he is on the speakers bureau for Abiomed, not relevant to this article. No other relevant disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LAA closure device shown safe in groups omitted in trials
WASHINGTON – Left atrial appendage closure can be performed safely and effectively in older patients, those with end-stage renal disease, and likely others not included in the pivotal clinical trials, according to a series of new studies, including a late-breaker, presented on the both older and newer Watchman devices at the Cardiovascular Research Technologies conference.
In the case of the late-breaking clinical trial report, which included more than 60,000 patients, the goal was to look at the safety of the Watchman FLX, which is the newest of the devices in real-world practice, according to Samir R. Kapadia, MD, chairman of the department of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic.
In the SURPASS registry, the number of patients discharged on the Watchman FLX climbed from zero in August 2020, when data accrual began, to 66,894 by March 2022. For the current analysis, 45-day follow-up was available for 61,963 patients and 1-year follow-up was available for 18,233.
Based on this number of patients treated by more than 2,300 clinicians at more than 740 sites, the SURPASS registry establishes that Watchman FLX “can be accomplished safely with clinical outcomes similar to pivotal trials at 45 days and 1 year,” Dr. Kapadia reported.
No surprises found in real-world outcome
At 7 days or hospital discharge (whichever came last), the rate of all-cause death was 0.18%, the rate of ischemic stroke was 0.13%, and there were no systemic emboli. By 45 days, the rate of all-cause death (0.84%) and stroke of any kind (0.32%) remained less than 1% and there were still no systemic emboli. Major bleeding events, of which about one-third occurred during hospitalization, had reached 3.34% by day 45.
By 1 year, all-cause mortality had risen to 8.3%, the stroke rate was 1.6%, and major bleeding reached 6.7%. The rate of systemic emboli remained very low (0.1%). The rates of death and stroke rose at a slow but steady rate throughout the 1-year follow-up. In contrast, major bleeding events rose steeply in the first 90 days and were followed by a much slower accrual subsequently.
At 1 year, 84.4% of patients had a complete seal. Leaks ≤ 3 mm were observed in 12.1%. The remaining leaks were larger, but just 0.7% had a leak > 5 mm.
Relative to the first-generation Watchman, the Watchman FLX has numerous design changes, including a shorter profile, more struts, and a reduced metal exposure. Most of these changes were performed to make the device easier to deploy.
When the SURPASS data are compared to the pivotal trials with Watchman FLX or to the Ewolution and National Cardiovascular Data (NCD) registries, which were created to monitor efficacy and safety with the earlier generation Watchman, the outcomes are similar or, in many cases, numerically favorable for such outcomes as bleeding and rates of stroke.
In addition to providing reassurance for the real-world safety of Watchman FLX, Dr. Kapadia said that these data establish reasonable benchmarks for centers tracking in-hospital and 1-year outcomes.
Dr. Kapadia also reported that outcomes overall in SURPASS were similar in women and men with the exception of major bleeding, a finding common to other interventional studies.
The late-breaker panelists generally agreed that SURPASS provides a robust set of data by which to be reassured, but David J. Cohen, MD, director of Clinical and Outcomes Research at the Cardiovascular Research Foundation in New York, said that he thinks the rate of bleeding is unnecessarily high.
“You really need to figure out a way to get the rate of bleeding at 45 days down,” Dr. Cohen said. He called for studies of anticoagulation in the post-procedural period that offer a better benefit-to-risk ratio.
Elderly patients benefit equally from Watchman
Yet, Watchman devices are generally regarded as a success story, and this has led investigators to evaluate safety in patients not well represented or explicitly excluded from clinical trials, such as the elderly and those with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). New data derived from experience in both of these groups were presented at the conference, which was sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
To tease out the relative safety of Watchman in octogenarians, Samian Sulaiman, MD, a cardiology fellow at West Virginia University Heart and Vascular Institute, Morgantown, performed a competing risk analysis to study the relative benefit of Watchman devices after controlling for the greater overall risk of complications in the elderly.
In raw data comparisons of those 80 years of age or older to those younger in published trials, the not-surprising result is that overall rates of death and ischemic events are far higher in the elderly, according to Dr. Sulaiman, but it’s an “unfair comparison,” he said.
“It is easy to mistakenly conclude that left atrial appendage closure is associated with worse outcomes, but older patients have far higher rates of these events independent of other factors,” Dr. Sulaiman noted.
In fact, in his comparison of 472 older patients to 1,404 younger patients, the seal rates at 45 days, 6 months, and 12 months are almost identical. Moreover, after the extensive adjustments performed for competing risk analysis, the rates of death, stroke, and bleeding were also almost identical for those 80 years or older whether or not they received a Watchman.
Although he acknowledged the risk for residual confounding, Dr. Sulaiman concluded that elderly patients derive about the same benefits as younger patients from the Watchman. He concluded age alone should not be a factor in selecting candidates for this device.
ESRD is not Watchman contraindication
A similar point was made about ESRD based on analysis of 237 patients who received either an earlier generation Watchman or the Watchman FLX. Initiated in Spain, the study was amended to collect data from centers elsewhere in Europe, the United States, and Australia.
Successful implantation was achieved in 99.2% of the patients, reported Armando Perez de Prado, MD, PhD, head of interventional cardiology at the University of Leon, Spain.
After a median follow-up of 480 days, stroke or transient ischemic attacks were observed in 3.1%, leaks > 5 mm were observed in 1.4%, and systemic emboli were observed in 0.9%. Major bleeding (BARC > 2) occurred in 13.3%.
Although the all-cause mortality over the period of follow-up was high (37.4%), most of the deaths (61.2%) were of noncardiovascular origin, according to Dr. Sulaiman. He said mortality and adverse events linked to the Watchman appeared to be roughly comparable to those seen in patients with ESRD.
“The Watchman device for patients on hemodialysis with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation is an effective and safe intervention to prevent embolic events,” he said. However, he also cautioned these the ESRD and the accompanying comorbidities place these patients at high risk of a limited life expectancy.
“Given the high mortality rate of this population, proper selection of candidates is paramount to ensure the optimal clinical benefit,” he cautioned.
Dr. Samir reported no potential conflicts of interest but stated that this study was funded by Boston Scientific. Dr. Cohen reported financial ties with Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, Corvia Medical, Edwards Lifesciences, Impulse Dynamics, MyoKardia, Phillips, Svelte, V-Wave, and Zoll. Dr. Sulaiman reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Perez de Prado reported no potential conflicts of interest but stated that this study was funded by Boston Scientific.
WASHINGTON – Left atrial appendage closure can be performed safely and effectively in older patients, those with end-stage renal disease, and likely others not included in the pivotal clinical trials, according to a series of new studies, including a late-breaker, presented on the both older and newer Watchman devices at the Cardiovascular Research Technologies conference.
In the case of the late-breaking clinical trial report, which included more than 60,000 patients, the goal was to look at the safety of the Watchman FLX, which is the newest of the devices in real-world practice, according to Samir R. Kapadia, MD, chairman of the department of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic.
In the SURPASS registry, the number of patients discharged on the Watchman FLX climbed from zero in August 2020, when data accrual began, to 66,894 by March 2022. For the current analysis, 45-day follow-up was available for 61,963 patients and 1-year follow-up was available for 18,233.
Based on this number of patients treated by more than 2,300 clinicians at more than 740 sites, the SURPASS registry establishes that Watchman FLX “can be accomplished safely with clinical outcomes similar to pivotal trials at 45 days and 1 year,” Dr. Kapadia reported.
No surprises found in real-world outcome
At 7 days or hospital discharge (whichever came last), the rate of all-cause death was 0.18%, the rate of ischemic stroke was 0.13%, and there were no systemic emboli. By 45 days, the rate of all-cause death (0.84%) and stroke of any kind (0.32%) remained less than 1% and there were still no systemic emboli. Major bleeding events, of which about one-third occurred during hospitalization, had reached 3.34% by day 45.
By 1 year, all-cause mortality had risen to 8.3%, the stroke rate was 1.6%, and major bleeding reached 6.7%. The rate of systemic emboli remained very low (0.1%). The rates of death and stroke rose at a slow but steady rate throughout the 1-year follow-up. In contrast, major bleeding events rose steeply in the first 90 days and were followed by a much slower accrual subsequently.
At 1 year, 84.4% of patients had a complete seal. Leaks ≤ 3 mm were observed in 12.1%. The remaining leaks were larger, but just 0.7% had a leak > 5 mm.
Relative to the first-generation Watchman, the Watchman FLX has numerous design changes, including a shorter profile, more struts, and a reduced metal exposure. Most of these changes were performed to make the device easier to deploy.
When the SURPASS data are compared to the pivotal trials with Watchman FLX or to the Ewolution and National Cardiovascular Data (NCD) registries, which were created to monitor efficacy and safety with the earlier generation Watchman, the outcomes are similar or, in many cases, numerically favorable for such outcomes as bleeding and rates of stroke.
In addition to providing reassurance for the real-world safety of Watchman FLX, Dr. Kapadia said that these data establish reasonable benchmarks for centers tracking in-hospital and 1-year outcomes.
Dr. Kapadia also reported that outcomes overall in SURPASS were similar in women and men with the exception of major bleeding, a finding common to other interventional studies.
The late-breaker panelists generally agreed that SURPASS provides a robust set of data by which to be reassured, but David J. Cohen, MD, director of Clinical and Outcomes Research at the Cardiovascular Research Foundation in New York, said that he thinks the rate of bleeding is unnecessarily high.
“You really need to figure out a way to get the rate of bleeding at 45 days down,” Dr. Cohen said. He called for studies of anticoagulation in the post-procedural period that offer a better benefit-to-risk ratio.
Elderly patients benefit equally from Watchman
Yet, Watchman devices are generally regarded as a success story, and this has led investigators to evaluate safety in patients not well represented or explicitly excluded from clinical trials, such as the elderly and those with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). New data derived from experience in both of these groups were presented at the conference, which was sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
To tease out the relative safety of Watchman in octogenarians, Samian Sulaiman, MD, a cardiology fellow at West Virginia University Heart and Vascular Institute, Morgantown, performed a competing risk analysis to study the relative benefit of Watchman devices after controlling for the greater overall risk of complications in the elderly.
In raw data comparisons of those 80 years of age or older to those younger in published trials, the not-surprising result is that overall rates of death and ischemic events are far higher in the elderly, according to Dr. Sulaiman, but it’s an “unfair comparison,” he said.
“It is easy to mistakenly conclude that left atrial appendage closure is associated with worse outcomes, but older patients have far higher rates of these events independent of other factors,” Dr. Sulaiman noted.
In fact, in his comparison of 472 older patients to 1,404 younger patients, the seal rates at 45 days, 6 months, and 12 months are almost identical. Moreover, after the extensive adjustments performed for competing risk analysis, the rates of death, stroke, and bleeding were also almost identical for those 80 years or older whether or not they received a Watchman.
Although he acknowledged the risk for residual confounding, Dr. Sulaiman concluded that elderly patients derive about the same benefits as younger patients from the Watchman. He concluded age alone should not be a factor in selecting candidates for this device.
ESRD is not Watchman contraindication
A similar point was made about ESRD based on analysis of 237 patients who received either an earlier generation Watchman or the Watchman FLX. Initiated in Spain, the study was amended to collect data from centers elsewhere in Europe, the United States, and Australia.
Successful implantation was achieved in 99.2% of the patients, reported Armando Perez de Prado, MD, PhD, head of interventional cardiology at the University of Leon, Spain.
After a median follow-up of 480 days, stroke or transient ischemic attacks were observed in 3.1%, leaks > 5 mm were observed in 1.4%, and systemic emboli were observed in 0.9%. Major bleeding (BARC > 2) occurred in 13.3%.
Although the all-cause mortality over the period of follow-up was high (37.4%), most of the deaths (61.2%) were of noncardiovascular origin, according to Dr. Sulaiman. He said mortality and adverse events linked to the Watchman appeared to be roughly comparable to those seen in patients with ESRD.
“The Watchman device for patients on hemodialysis with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation is an effective and safe intervention to prevent embolic events,” he said. However, he also cautioned these the ESRD and the accompanying comorbidities place these patients at high risk of a limited life expectancy.
“Given the high mortality rate of this population, proper selection of candidates is paramount to ensure the optimal clinical benefit,” he cautioned.
Dr. Samir reported no potential conflicts of interest but stated that this study was funded by Boston Scientific. Dr. Cohen reported financial ties with Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, Corvia Medical, Edwards Lifesciences, Impulse Dynamics, MyoKardia, Phillips, Svelte, V-Wave, and Zoll. Dr. Sulaiman reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Perez de Prado reported no potential conflicts of interest but stated that this study was funded by Boston Scientific.
WASHINGTON – Left atrial appendage closure can be performed safely and effectively in older patients, those with end-stage renal disease, and likely others not included in the pivotal clinical trials, according to a series of new studies, including a late-breaker, presented on the both older and newer Watchman devices at the Cardiovascular Research Technologies conference.
In the case of the late-breaking clinical trial report, which included more than 60,000 patients, the goal was to look at the safety of the Watchman FLX, which is the newest of the devices in real-world practice, according to Samir R. Kapadia, MD, chairman of the department of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic.
In the SURPASS registry, the number of patients discharged on the Watchman FLX climbed from zero in August 2020, when data accrual began, to 66,894 by March 2022. For the current analysis, 45-day follow-up was available for 61,963 patients and 1-year follow-up was available for 18,233.
Based on this number of patients treated by more than 2,300 clinicians at more than 740 sites, the SURPASS registry establishes that Watchman FLX “can be accomplished safely with clinical outcomes similar to pivotal trials at 45 days and 1 year,” Dr. Kapadia reported.
No surprises found in real-world outcome
At 7 days or hospital discharge (whichever came last), the rate of all-cause death was 0.18%, the rate of ischemic stroke was 0.13%, and there were no systemic emboli. By 45 days, the rate of all-cause death (0.84%) and stroke of any kind (0.32%) remained less than 1% and there were still no systemic emboli. Major bleeding events, of which about one-third occurred during hospitalization, had reached 3.34% by day 45.
By 1 year, all-cause mortality had risen to 8.3%, the stroke rate was 1.6%, and major bleeding reached 6.7%. The rate of systemic emboli remained very low (0.1%). The rates of death and stroke rose at a slow but steady rate throughout the 1-year follow-up. In contrast, major bleeding events rose steeply in the first 90 days and were followed by a much slower accrual subsequently.
At 1 year, 84.4% of patients had a complete seal. Leaks ≤ 3 mm were observed in 12.1%. The remaining leaks were larger, but just 0.7% had a leak > 5 mm.
Relative to the first-generation Watchman, the Watchman FLX has numerous design changes, including a shorter profile, more struts, and a reduced metal exposure. Most of these changes were performed to make the device easier to deploy.
When the SURPASS data are compared to the pivotal trials with Watchman FLX or to the Ewolution and National Cardiovascular Data (NCD) registries, which were created to monitor efficacy and safety with the earlier generation Watchman, the outcomes are similar or, in many cases, numerically favorable for such outcomes as bleeding and rates of stroke.
In addition to providing reassurance for the real-world safety of Watchman FLX, Dr. Kapadia said that these data establish reasonable benchmarks for centers tracking in-hospital and 1-year outcomes.
Dr. Kapadia also reported that outcomes overall in SURPASS were similar in women and men with the exception of major bleeding, a finding common to other interventional studies.
The late-breaker panelists generally agreed that SURPASS provides a robust set of data by which to be reassured, but David J. Cohen, MD, director of Clinical and Outcomes Research at the Cardiovascular Research Foundation in New York, said that he thinks the rate of bleeding is unnecessarily high.
“You really need to figure out a way to get the rate of bleeding at 45 days down,” Dr. Cohen said. He called for studies of anticoagulation in the post-procedural period that offer a better benefit-to-risk ratio.
Elderly patients benefit equally from Watchman
Yet, Watchman devices are generally regarded as a success story, and this has led investigators to evaluate safety in patients not well represented or explicitly excluded from clinical trials, such as the elderly and those with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). New data derived from experience in both of these groups were presented at the conference, which was sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
To tease out the relative safety of Watchman in octogenarians, Samian Sulaiman, MD, a cardiology fellow at West Virginia University Heart and Vascular Institute, Morgantown, performed a competing risk analysis to study the relative benefit of Watchman devices after controlling for the greater overall risk of complications in the elderly.
In raw data comparisons of those 80 years of age or older to those younger in published trials, the not-surprising result is that overall rates of death and ischemic events are far higher in the elderly, according to Dr. Sulaiman, but it’s an “unfair comparison,” he said.
“It is easy to mistakenly conclude that left atrial appendage closure is associated with worse outcomes, but older patients have far higher rates of these events independent of other factors,” Dr. Sulaiman noted.
In fact, in his comparison of 472 older patients to 1,404 younger patients, the seal rates at 45 days, 6 months, and 12 months are almost identical. Moreover, after the extensive adjustments performed for competing risk analysis, the rates of death, stroke, and bleeding were also almost identical for those 80 years or older whether or not they received a Watchman.
Although he acknowledged the risk for residual confounding, Dr. Sulaiman concluded that elderly patients derive about the same benefits as younger patients from the Watchman. He concluded age alone should not be a factor in selecting candidates for this device.
ESRD is not Watchman contraindication
A similar point was made about ESRD based on analysis of 237 patients who received either an earlier generation Watchman or the Watchman FLX. Initiated in Spain, the study was amended to collect data from centers elsewhere in Europe, the United States, and Australia.
Successful implantation was achieved in 99.2% of the patients, reported Armando Perez de Prado, MD, PhD, head of interventional cardiology at the University of Leon, Spain.
After a median follow-up of 480 days, stroke or transient ischemic attacks were observed in 3.1%, leaks > 5 mm were observed in 1.4%, and systemic emboli were observed in 0.9%. Major bleeding (BARC > 2) occurred in 13.3%.
Although the all-cause mortality over the period of follow-up was high (37.4%), most of the deaths (61.2%) were of noncardiovascular origin, according to Dr. Sulaiman. He said mortality and adverse events linked to the Watchman appeared to be roughly comparable to those seen in patients with ESRD.
“The Watchman device for patients on hemodialysis with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation is an effective and safe intervention to prevent embolic events,” he said. However, he also cautioned these the ESRD and the accompanying comorbidities place these patients at high risk of a limited life expectancy.
“Given the high mortality rate of this population, proper selection of candidates is paramount to ensure the optimal clinical benefit,” he cautioned.
Dr. Samir reported no potential conflicts of interest but stated that this study was funded by Boston Scientific. Dr. Cohen reported financial ties with Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, Corvia Medical, Edwards Lifesciences, Impulse Dynamics, MyoKardia, Phillips, Svelte, V-Wave, and Zoll. Dr. Sulaiman reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Perez de Prado reported no potential conflicts of interest but stated that this study was funded by Boston Scientific.
AT CRT 2023
Another FDA class I recall of Cardiosave Hybrid/Rescue IABPs
Datascope/Getinge is recalling certain Cardiosave Hybrid and Cardiosave Rescue Intra-Aortic Balloon Pumps (IABPs) because the coiled cable connecting the display and base on some units may fail, causing an unexpected shutdown without warnings or alarms to alert the user.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has identified this as a class I recall, the most serious type of recall, because of the risk for serious injury or death.
The FDA warns that an unexpected pump shutdown and any interruption to therapy that occurs can lead to hemodynamic instability, organ damage, and/or death, especially in patients who are critically ill and most likely to receive therapy using these devices.
The devices are indicated for acute coronary syndrome, cardiac and noncardiac surgery, and complications of heart failure in adults.
From June 2019 to August 2022, Datascope/Getinge reported 44 complaints about damaged coiled cords resulting in unexpected shutdowns. There have been no reports of injuries or deaths related to this issue, according to the recall notice posted on the FDA’s website.
The recall includes a total of 2,300 CardioSave Hybrid or Rescue IABP units distributed prior to July 24, 2017, and/or coiled cord part number 0012-00-1801. Product model numbers for the recalled Cardiosave Hybrid and Cardiosave Rescue are available online.
The Cardiosave IABPs have previously been flagged by the FDA for subpar battery performance and fluid leaks.
To address the cable issue, Datascope/Getinge sent an urgent medical device correction letter to customers recommending that the coiled cable cord of the Cardiosave IABP be inspected for visible damage prior to use.
If an unexpected shutdown occurs, an attempt should be made to restart the Cardiosave IABP until an alternative pump is available. If the restart attempt is unsuccessful, an alternative IABP should be used. Any device that remains inoperable after a shutdown should be removed from patient care.
Customers should inspect their inventory to identify any Cardiosave Hybrid and/or Rescue IABPs that have the recalled coiled cord.
The company also asks customers to complete and sign the Medical Device Correction-Response form included with the letter and return it to Datascope/Getinge by emailing a scanned copy to cardiosave-sdhl23.act@getinge.com or by faxing the form to 1-877-660-5841.
Customers with questions about this recall should contact their Datascope/Getinge representative or call Datascope/Getinge technical support at 1-888-943-8872, Monday through Friday, between 8:00 AM and 6:00 PM ET.
The company has developed a hardware correction to address this issue and says a service representative will contact customers to schedule installation of the correction when the correction kit is available.
Any adverse events or suspected adverse events related to the recalled CardioSave Hybrid/Rescue IABPs should be reported to the FDA through MedWatch, its adverse event reporting program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Datascope/Getinge is recalling certain Cardiosave Hybrid and Cardiosave Rescue Intra-Aortic Balloon Pumps (IABPs) because the coiled cable connecting the display and base on some units may fail, causing an unexpected shutdown without warnings or alarms to alert the user.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has identified this as a class I recall, the most serious type of recall, because of the risk for serious injury or death.
The FDA warns that an unexpected pump shutdown and any interruption to therapy that occurs can lead to hemodynamic instability, organ damage, and/or death, especially in patients who are critically ill and most likely to receive therapy using these devices.
The devices are indicated for acute coronary syndrome, cardiac and noncardiac surgery, and complications of heart failure in adults.
From June 2019 to August 2022, Datascope/Getinge reported 44 complaints about damaged coiled cords resulting in unexpected shutdowns. There have been no reports of injuries or deaths related to this issue, according to the recall notice posted on the FDA’s website.
The recall includes a total of 2,300 CardioSave Hybrid or Rescue IABP units distributed prior to July 24, 2017, and/or coiled cord part number 0012-00-1801. Product model numbers for the recalled Cardiosave Hybrid and Cardiosave Rescue are available online.
The Cardiosave IABPs have previously been flagged by the FDA for subpar battery performance and fluid leaks.
To address the cable issue, Datascope/Getinge sent an urgent medical device correction letter to customers recommending that the coiled cable cord of the Cardiosave IABP be inspected for visible damage prior to use.
If an unexpected shutdown occurs, an attempt should be made to restart the Cardiosave IABP until an alternative pump is available. If the restart attempt is unsuccessful, an alternative IABP should be used. Any device that remains inoperable after a shutdown should be removed from patient care.
Customers should inspect their inventory to identify any Cardiosave Hybrid and/or Rescue IABPs that have the recalled coiled cord.
The company also asks customers to complete and sign the Medical Device Correction-Response form included with the letter and return it to Datascope/Getinge by emailing a scanned copy to cardiosave-sdhl23.act@getinge.com or by faxing the form to 1-877-660-5841.
Customers with questions about this recall should contact their Datascope/Getinge representative or call Datascope/Getinge technical support at 1-888-943-8872, Monday through Friday, between 8:00 AM and 6:00 PM ET.
The company has developed a hardware correction to address this issue and says a service representative will contact customers to schedule installation of the correction when the correction kit is available.
Any adverse events or suspected adverse events related to the recalled CardioSave Hybrid/Rescue IABPs should be reported to the FDA through MedWatch, its adverse event reporting program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Datascope/Getinge is recalling certain Cardiosave Hybrid and Cardiosave Rescue Intra-Aortic Balloon Pumps (IABPs) because the coiled cable connecting the display and base on some units may fail, causing an unexpected shutdown without warnings or alarms to alert the user.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has identified this as a class I recall, the most serious type of recall, because of the risk for serious injury or death.
The FDA warns that an unexpected pump shutdown and any interruption to therapy that occurs can lead to hemodynamic instability, organ damage, and/or death, especially in patients who are critically ill and most likely to receive therapy using these devices.
The devices are indicated for acute coronary syndrome, cardiac and noncardiac surgery, and complications of heart failure in adults.
From June 2019 to August 2022, Datascope/Getinge reported 44 complaints about damaged coiled cords resulting in unexpected shutdowns. There have been no reports of injuries or deaths related to this issue, according to the recall notice posted on the FDA’s website.
The recall includes a total of 2,300 CardioSave Hybrid or Rescue IABP units distributed prior to July 24, 2017, and/or coiled cord part number 0012-00-1801. Product model numbers for the recalled Cardiosave Hybrid and Cardiosave Rescue are available online.
The Cardiosave IABPs have previously been flagged by the FDA for subpar battery performance and fluid leaks.
To address the cable issue, Datascope/Getinge sent an urgent medical device correction letter to customers recommending that the coiled cable cord of the Cardiosave IABP be inspected for visible damage prior to use.
If an unexpected shutdown occurs, an attempt should be made to restart the Cardiosave IABP until an alternative pump is available. If the restart attempt is unsuccessful, an alternative IABP should be used. Any device that remains inoperable after a shutdown should be removed from patient care.
Customers should inspect their inventory to identify any Cardiosave Hybrid and/or Rescue IABPs that have the recalled coiled cord.
The company also asks customers to complete and sign the Medical Device Correction-Response form included with the letter and return it to Datascope/Getinge by emailing a scanned copy to cardiosave-sdhl23.act@getinge.com or by faxing the form to 1-877-660-5841.
Customers with questions about this recall should contact their Datascope/Getinge representative or call Datascope/Getinge technical support at 1-888-943-8872, Monday through Friday, between 8:00 AM and 6:00 PM ET.
The company has developed a hardware correction to address this issue and says a service representative will contact customers to schedule installation of the correction when the correction kit is available.
Any adverse events or suspected adverse events related to the recalled CardioSave Hybrid/Rescue IABPs should be reported to the FDA through MedWatch, its adverse event reporting program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Encouraging 3-year data for TAVR in low-risk patients: EVOLUT
Three-year results from the Evolut trial seem to provide more reassurance on the use of transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) in low-surgical-risk patients.
The 3-year results show that low-surgical-risk patients undergoing aortic valve replacement continue to show lower rates of all-cause mortality and disabling stroke with TAVR, compared with surgery.
The rates of all-cause mortality or disabling stroke (the primary endpoint) at 3 years were 7.4% with TAVR and 10.4% with surgery.
Rates of new pacemaker implantation continued to be higher after TAVR and the frequency of new onset atrial fibrillation was more common after surgery.
“At 3 years, the rate of all-cause mortality or disabling stroke after TAVR with the Evolut valve compared very favorably to surgery. The absolute difference between treatment arms remained consistent with a 30% relative reduction in the hazard of death or disabling stroke, with a P value that just missed statistical significance,” said Evolut investigator John Forrest, MD, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Conn.
“The Kaplan-Meier curves show what we’ve come to expect – an early separation of the curves – but what’s unique here, and seen for the first time, is that the early separation is maintained at year 1 and year 2, and between years 2 and 3 the curve didn’t start to come together, but, if anything, separated a little,” Dr. Forrest commented.
“Both components of the primary endpoint – all cause mortality and disabling stroke – numerically favor TAVR. The separation of the curves for stroke are maintained, and if anything, we see a further slight separation of the curves as we go forward out to 3 years in terms of all-cause mortality,” he added.
Dr. Forrest presented the 3-year results from the Evolut trial at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. They were simultaneously published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Dr. Forrest also reported that TAVR patients continued to have better valve hemodynamics at 3 years and very low rates of valve thrombosis; moreover, rates of moderate or greater paravalvular regurgitation and paravalvular leak (factors that can affect valve durability) were also low, although mild paravalvular regurgitation was higher with TAVR.
“In these low-risk patients, the durability of the valve is going to be critically important,” Dr. Forrest commented. “The excellent valve performance and durable outcomes out to 3 years in low-risk patients affirms the role of TAVR in this population,” he concluded.
On how these results may affect clinical practice, Dr. Forrest said: “I think in the U.S. these results reaffirm what we are doing. It gives us confidence to continue treating low-risk patients and being comfortable with that.”
He added: “Outside the U.S., the guidelines are a little different. Maybe we should reconsider some of these guidelines based on these data.”
David Moliterno, MD, Gill Heart and Vascular Institute, Lexington, Ky., who is not involved in the TAVR studies, said: “The results provide a little more reassurance ... that will go a little way further.”
“Uncertainty remains regarding long-term durability of the transcatheter valve in low-risk patients who are generally younger and likely more active than higher-risk cohorts,” he added. “The current 3-year results provide more confidence as the outcome curves for death and disabling stroke are trending in the right direction for TAVR versus surgery.”
Dr. Moliterno pointed out that while rates of paravalvular regurgitation and permanent pacemaker placement are decreasing with newer generation Evolut devices and implantation techniques, he noted that according to the U.S. Social Security Administration, patients aged 74 years as enrolled in this low-risk cohort have an additional life expectancy of approximately 12 years. “So, we have more device durability (and coronary access feasibility) to prove.”
In his presentation, Dr. Forrest explained that TAVR is now approved in the United States for all patients with aortic stenosis regardless of surgical risk and has become the dominant form of aortic valve replacement. Current ACC/AHA guidelines recommend that heart teams utilize a shared decision-making process when discussing aortic valve replacement with patients aged 65-80 years. In younger, lower-risk patients, the faster recovery and short-term benefits after TAVR must be balanced with long-term durability; however, only limited intermediate and long-term data exist to guide such discussions in this patient population.
The Evolut Low Risk trial randomly assigned 1,414 patients in need of aortic valve replacement to TAVR with a self-expanding, supra-annular valve or surgery. Results at 1 and 2 years have shown a similar benefit in the primary endpoint of all-cause mortality/disabling stroke for the less invasive TAVR procedure.
The current 3-year results suggest the benefit appears to be maintained out for another year.
The main results show that the rate of death or disabling stroke was 7.4% in the TAVR group versus 10.4% in the surgery group, giving a hazard ratio of 0.70 (P = .051).
In the JACC paper, the authors report that the absolute difference between treatment arms for all-cause mortality or disabling stroke remained broadly consistent over time: –1.8% at year 1; –2.0% at year 2; and –2.9% at year 3.
Other key results on valve durability show that mild paravalvular regurgitation was increased in the TAVR group (20.3%) versus 2.5% with surgery. However, rates of moderate or greater paravalvular regurgitation for both groups were below 1% and not significantly different between groups.
Patients who underwent TAVR had significantly improved valve hemodynamics (mean gradient 9.1 mm Hg TAVR vs. 12.1 mm Hg surgery; P < .001) at 3 years.
However, pacemaker placement was much higher in the TAVR group (23.2%), compared with 9.1% in the surgery group.
On the other hand, the surgery group had a greater incidence of atrial fibrillation (40%) versus 13% with TAVR.
Quality-of-life results looked good in both groups.
“As we’ve come to expect, patients recover more quickly after TAVR, so at 30 days their quality of life is better than those who have undergone surgery,” Dr. Forrest commented. “But by 1 year, both groups are doing exceptionally well and, remarkably, here by 3 years both groups have greater than a 20-point increase in their KCCQ score, showing a very large improvement in quality of life.”
Discussant of these latest results at the ACC late-breaking trials session, James Hermiller, MD, St. Vincent Ascension Heart Center, Indianapolis, said: “This 3-year data continues to demonstrate that the gift of TAVR keeps giving.”
Noting that the divergence in the effect curves was primarily driven by mortality rather than stroke, he asked whether this was cardiac or noncardiac mortality that was reduced.
Dr. Forrest responded: “It was a fairly equal contribution – a little bit more cardiac death. We have to remember that although the average age in this study was 74, there were some patients over 80 who were still low-surgical-risk included so we are going to see noncardiac death as well.”
Dr. Hermiller drew attention to the high pacemaker rate in the TAVR group and asked how these patients fared in comparison to those who didn’t need a pacemaker.
Dr. Forrest replied: “I think it’s fair to say that putting in a pacemaker is not a benign procedure. Patients who got a pacemaker did slightly worse than those who didn’t get a pacemaker, so we need to try to drive that rate down.”
He added that the number of patients needing a pacemaker after TAVR has come down with new implantation techniques and new generation valves.
“We realize that using a cusp overlap technique can significantly reduce the need for a pacemaker, and we see from registry data that with the use of this new technique the need for a pacemaker has dropped down to 8%-9%, significantly less than seen in this study,” Dr. Forrest commented.
Dr. Hermiller also asked about how TAVR affects future access for catheterization or percutaneous coronary intervention.
Dr. Forrest noted that 24 patients in the TAVR group required PCI in first 3 years, and all the PCI procedures had been successful. He noted that operators reported the procedure to be easy or moderately easy in about 75%-80% of cases and difficult in about 20% of patients. “So, it is slightly more challenging to engage the coronaries and have to go through the frame, but it is very feasible.”
Dr. Forrest concluded that: “These results provide patients and heart teams important data to aid in the shared decision-making process.”
But he acknowledged that longer term data are still needed. “And the potential impact that hemodynamics, valve design, new pacemakers, and other secondary endpoints have on long-term outcomes will be important to follow in this group of low-risk patients.”
The Evolut Low Risk trial was funded by Medtronic. Dr. Forrest has received grant support/research contracts and consultant fees/honoraria/speakers bureau fees from Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Three-year results from the Evolut trial seem to provide more reassurance on the use of transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) in low-surgical-risk patients.
The 3-year results show that low-surgical-risk patients undergoing aortic valve replacement continue to show lower rates of all-cause mortality and disabling stroke with TAVR, compared with surgery.
The rates of all-cause mortality or disabling stroke (the primary endpoint) at 3 years were 7.4% with TAVR and 10.4% with surgery.
Rates of new pacemaker implantation continued to be higher after TAVR and the frequency of new onset atrial fibrillation was more common after surgery.
“At 3 years, the rate of all-cause mortality or disabling stroke after TAVR with the Evolut valve compared very favorably to surgery. The absolute difference between treatment arms remained consistent with a 30% relative reduction in the hazard of death or disabling stroke, with a P value that just missed statistical significance,” said Evolut investigator John Forrest, MD, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Conn.
“The Kaplan-Meier curves show what we’ve come to expect – an early separation of the curves – but what’s unique here, and seen for the first time, is that the early separation is maintained at year 1 and year 2, and between years 2 and 3 the curve didn’t start to come together, but, if anything, separated a little,” Dr. Forrest commented.
“Both components of the primary endpoint – all cause mortality and disabling stroke – numerically favor TAVR. The separation of the curves for stroke are maintained, and if anything, we see a further slight separation of the curves as we go forward out to 3 years in terms of all-cause mortality,” he added.
Dr. Forrest presented the 3-year results from the Evolut trial at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. They were simultaneously published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Dr. Forrest also reported that TAVR patients continued to have better valve hemodynamics at 3 years and very low rates of valve thrombosis; moreover, rates of moderate or greater paravalvular regurgitation and paravalvular leak (factors that can affect valve durability) were also low, although mild paravalvular regurgitation was higher with TAVR.
“In these low-risk patients, the durability of the valve is going to be critically important,” Dr. Forrest commented. “The excellent valve performance and durable outcomes out to 3 years in low-risk patients affirms the role of TAVR in this population,” he concluded.
On how these results may affect clinical practice, Dr. Forrest said: “I think in the U.S. these results reaffirm what we are doing. It gives us confidence to continue treating low-risk patients and being comfortable with that.”
He added: “Outside the U.S., the guidelines are a little different. Maybe we should reconsider some of these guidelines based on these data.”
David Moliterno, MD, Gill Heart and Vascular Institute, Lexington, Ky., who is not involved in the TAVR studies, said: “The results provide a little more reassurance ... that will go a little way further.”
“Uncertainty remains regarding long-term durability of the transcatheter valve in low-risk patients who are generally younger and likely more active than higher-risk cohorts,” he added. “The current 3-year results provide more confidence as the outcome curves for death and disabling stroke are trending in the right direction for TAVR versus surgery.”
Dr. Moliterno pointed out that while rates of paravalvular regurgitation and permanent pacemaker placement are decreasing with newer generation Evolut devices and implantation techniques, he noted that according to the U.S. Social Security Administration, patients aged 74 years as enrolled in this low-risk cohort have an additional life expectancy of approximately 12 years. “So, we have more device durability (and coronary access feasibility) to prove.”
In his presentation, Dr. Forrest explained that TAVR is now approved in the United States for all patients with aortic stenosis regardless of surgical risk and has become the dominant form of aortic valve replacement. Current ACC/AHA guidelines recommend that heart teams utilize a shared decision-making process when discussing aortic valve replacement with patients aged 65-80 years. In younger, lower-risk patients, the faster recovery and short-term benefits after TAVR must be balanced with long-term durability; however, only limited intermediate and long-term data exist to guide such discussions in this patient population.
The Evolut Low Risk trial randomly assigned 1,414 patients in need of aortic valve replacement to TAVR with a self-expanding, supra-annular valve or surgery. Results at 1 and 2 years have shown a similar benefit in the primary endpoint of all-cause mortality/disabling stroke for the less invasive TAVR procedure.
The current 3-year results suggest the benefit appears to be maintained out for another year.
The main results show that the rate of death or disabling stroke was 7.4% in the TAVR group versus 10.4% in the surgery group, giving a hazard ratio of 0.70 (P = .051).
In the JACC paper, the authors report that the absolute difference between treatment arms for all-cause mortality or disabling stroke remained broadly consistent over time: –1.8% at year 1; –2.0% at year 2; and –2.9% at year 3.
Other key results on valve durability show that mild paravalvular regurgitation was increased in the TAVR group (20.3%) versus 2.5% with surgery. However, rates of moderate or greater paravalvular regurgitation for both groups were below 1% and not significantly different between groups.
Patients who underwent TAVR had significantly improved valve hemodynamics (mean gradient 9.1 mm Hg TAVR vs. 12.1 mm Hg surgery; P < .001) at 3 years.
However, pacemaker placement was much higher in the TAVR group (23.2%), compared with 9.1% in the surgery group.
On the other hand, the surgery group had a greater incidence of atrial fibrillation (40%) versus 13% with TAVR.
Quality-of-life results looked good in both groups.
“As we’ve come to expect, patients recover more quickly after TAVR, so at 30 days their quality of life is better than those who have undergone surgery,” Dr. Forrest commented. “But by 1 year, both groups are doing exceptionally well and, remarkably, here by 3 years both groups have greater than a 20-point increase in their KCCQ score, showing a very large improvement in quality of life.”
Discussant of these latest results at the ACC late-breaking trials session, James Hermiller, MD, St. Vincent Ascension Heart Center, Indianapolis, said: “This 3-year data continues to demonstrate that the gift of TAVR keeps giving.”
Noting that the divergence in the effect curves was primarily driven by mortality rather than stroke, he asked whether this was cardiac or noncardiac mortality that was reduced.
Dr. Forrest responded: “It was a fairly equal contribution – a little bit more cardiac death. We have to remember that although the average age in this study was 74, there were some patients over 80 who were still low-surgical-risk included so we are going to see noncardiac death as well.”
Dr. Hermiller drew attention to the high pacemaker rate in the TAVR group and asked how these patients fared in comparison to those who didn’t need a pacemaker.
Dr. Forrest replied: “I think it’s fair to say that putting in a pacemaker is not a benign procedure. Patients who got a pacemaker did slightly worse than those who didn’t get a pacemaker, so we need to try to drive that rate down.”
He added that the number of patients needing a pacemaker after TAVR has come down with new implantation techniques and new generation valves.
“We realize that using a cusp overlap technique can significantly reduce the need for a pacemaker, and we see from registry data that with the use of this new technique the need for a pacemaker has dropped down to 8%-9%, significantly less than seen in this study,” Dr. Forrest commented.
Dr. Hermiller also asked about how TAVR affects future access for catheterization or percutaneous coronary intervention.
Dr. Forrest noted that 24 patients in the TAVR group required PCI in first 3 years, and all the PCI procedures had been successful. He noted that operators reported the procedure to be easy or moderately easy in about 75%-80% of cases and difficult in about 20% of patients. “So, it is slightly more challenging to engage the coronaries and have to go through the frame, but it is very feasible.”
Dr. Forrest concluded that: “These results provide patients and heart teams important data to aid in the shared decision-making process.”
But he acknowledged that longer term data are still needed. “And the potential impact that hemodynamics, valve design, new pacemakers, and other secondary endpoints have on long-term outcomes will be important to follow in this group of low-risk patients.”
The Evolut Low Risk trial was funded by Medtronic. Dr. Forrest has received grant support/research contracts and consultant fees/honoraria/speakers bureau fees from Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Three-year results from the Evolut trial seem to provide more reassurance on the use of transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) in low-surgical-risk patients.
The 3-year results show that low-surgical-risk patients undergoing aortic valve replacement continue to show lower rates of all-cause mortality and disabling stroke with TAVR, compared with surgery.
The rates of all-cause mortality or disabling stroke (the primary endpoint) at 3 years were 7.4% with TAVR and 10.4% with surgery.
Rates of new pacemaker implantation continued to be higher after TAVR and the frequency of new onset atrial fibrillation was more common after surgery.
“At 3 years, the rate of all-cause mortality or disabling stroke after TAVR with the Evolut valve compared very favorably to surgery. The absolute difference between treatment arms remained consistent with a 30% relative reduction in the hazard of death or disabling stroke, with a P value that just missed statistical significance,” said Evolut investigator John Forrest, MD, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Conn.
“The Kaplan-Meier curves show what we’ve come to expect – an early separation of the curves – but what’s unique here, and seen for the first time, is that the early separation is maintained at year 1 and year 2, and between years 2 and 3 the curve didn’t start to come together, but, if anything, separated a little,” Dr. Forrest commented.
“Both components of the primary endpoint – all cause mortality and disabling stroke – numerically favor TAVR. The separation of the curves for stroke are maintained, and if anything, we see a further slight separation of the curves as we go forward out to 3 years in terms of all-cause mortality,” he added.
Dr. Forrest presented the 3-year results from the Evolut trial at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. They were simultaneously published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Dr. Forrest also reported that TAVR patients continued to have better valve hemodynamics at 3 years and very low rates of valve thrombosis; moreover, rates of moderate or greater paravalvular regurgitation and paravalvular leak (factors that can affect valve durability) were also low, although mild paravalvular regurgitation was higher with TAVR.
“In these low-risk patients, the durability of the valve is going to be critically important,” Dr. Forrest commented. “The excellent valve performance and durable outcomes out to 3 years in low-risk patients affirms the role of TAVR in this population,” he concluded.
On how these results may affect clinical practice, Dr. Forrest said: “I think in the U.S. these results reaffirm what we are doing. It gives us confidence to continue treating low-risk patients and being comfortable with that.”
He added: “Outside the U.S., the guidelines are a little different. Maybe we should reconsider some of these guidelines based on these data.”
David Moliterno, MD, Gill Heart and Vascular Institute, Lexington, Ky., who is not involved in the TAVR studies, said: “The results provide a little more reassurance ... that will go a little way further.”
“Uncertainty remains regarding long-term durability of the transcatheter valve in low-risk patients who are generally younger and likely more active than higher-risk cohorts,” he added. “The current 3-year results provide more confidence as the outcome curves for death and disabling stroke are trending in the right direction for TAVR versus surgery.”
Dr. Moliterno pointed out that while rates of paravalvular regurgitation and permanent pacemaker placement are decreasing with newer generation Evolut devices and implantation techniques, he noted that according to the U.S. Social Security Administration, patients aged 74 years as enrolled in this low-risk cohort have an additional life expectancy of approximately 12 years. “So, we have more device durability (and coronary access feasibility) to prove.”
In his presentation, Dr. Forrest explained that TAVR is now approved in the United States for all patients with aortic stenosis regardless of surgical risk and has become the dominant form of aortic valve replacement. Current ACC/AHA guidelines recommend that heart teams utilize a shared decision-making process when discussing aortic valve replacement with patients aged 65-80 years. In younger, lower-risk patients, the faster recovery and short-term benefits after TAVR must be balanced with long-term durability; however, only limited intermediate and long-term data exist to guide such discussions in this patient population.
The Evolut Low Risk trial randomly assigned 1,414 patients in need of aortic valve replacement to TAVR with a self-expanding, supra-annular valve or surgery. Results at 1 and 2 years have shown a similar benefit in the primary endpoint of all-cause mortality/disabling stroke for the less invasive TAVR procedure.
The current 3-year results suggest the benefit appears to be maintained out for another year.
The main results show that the rate of death or disabling stroke was 7.4% in the TAVR group versus 10.4% in the surgery group, giving a hazard ratio of 0.70 (P = .051).
In the JACC paper, the authors report that the absolute difference between treatment arms for all-cause mortality or disabling stroke remained broadly consistent over time: –1.8% at year 1; –2.0% at year 2; and –2.9% at year 3.
Other key results on valve durability show that mild paravalvular regurgitation was increased in the TAVR group (20.3%) versus 2.5% with surgery. However, rates of moderate or greater paravalvular regurgitation for both groups were below 1% and not significantly different between groups.
Patients who underwent TAVR had significantly improved valve hemodynamics (mean gradient 9.1 mm Hg TAVR vs. 12.1 mm Hg surgery; P < .001) at 3 years.
However, pacemaker placement was much higher in the TAVR group (23.2%), compared with 9.1% in the surgery group.
On the other hand, the surgery group had a greater incidence of atrial fibrillation (40%) versus 13% with TAVR.
Quality-of-life results looked good in both groups.
“As we’ve come to expect, patients recover more quickly after TAVR, so at 30 days their quality of life is better than those who have undergone surgery,” Dr. Forrest commented. “But by 1 year, both groups are doing exceptionally well and, remarkably, here by 3 years both groups have greater than a 20-point increase in their KCCQ score, showing a very large improvement in quality of life.”
Discussant of these latest results at the ACC late-breaking trials session, James Hermiller, MD, St. Vincent Ascension Heart Center, Indianapolis, said: “This 3-year data continues to demonstrate that the gift of TAVR keeps giving.”
Noting that the divergence in the effect curves was primarily driven by mortality rather than stroke, he asked whether this was cardiac or noncardiac mortality that was reduced.
Dr. Forrest responded: “It was a fairly equal contribution – a little bit more cardiac death. We have to remember that although the average age in this study was 74, there were some patients over 80 who were still low-surgical-risk included so we are going to see noncardiac death as well.”
Dr. Hermiller drew attention to the high pacemaker rate in the TAVR group and asked how these patients fared in comparison to those who didn’t need a pacemaker.
Dr. Forrest replied: “I think it’s fair to say that putting in a pacemaker is not a benign procedure. Patients who got a pacemaker did slightly worse than those who didn’t get a pacemaker, so we need to try to drive that rate down.”
He added that the number of patients needing a pacemaker after TAVR has come down with new implantation techniques and new generation valves.
“We realize that using a cusp overlap technique can significantly reduce the need for a pacemaker, and we see from registry data that with the use of this new technique the need for a pacemaker has dropped down to 8%-9%, significantly less than seen in this study,” Dr. Forrest commented.
Dr. Hermiller also asked about how TAVR affects future access for catheterization or percutaneous coronary intervention.
Dr. Forrest noted that 24 patients in the TAVR group required PCI in first 3 years, and all the PCI procedures had been successful. He noted that operators reported the procedure to be easy or moderately easy in about 75%-80% of cases and difficult in about 20% of patients. “So, it is slightly more challenging to engage the coronaries and have to go through the frame, but it is very feasible.”
Dr. Forrest concluded that: “These results provide patients and heart teams important data to aid in the shared decision-making process.”
But he acknowledged that longer term data are still needed. “And the potential impact that hemodynamics, valve design, new pacemakers, and other secondary endpoints have on long-term outcomes will be important to follow in this group of low-risk patients.”
The Evolut Low Risk trial was funded by Medtronic. Dr. Forrest has received grant support/research contracts and consultant fees/honoraria/speakers bureau fees from Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACC 2023
‘Keto-like’ diet linked to doubling of heart disease risk
Consumption of a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet, dubbed a “keto-like” diet, was associated with an increase in LDL levels and a twofold increase in the risk for future cardiovascular events, in a new observational study.
“To our knowledge this is the first study to demonstrate an association between a carbohydrate-restricted dietary platform and greater risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” said study investigator Iulia Iatan, MD, PhD, University of British Columbia, Vancouver.
“Hypercholesterolemia occurring during a low-carb, high-fat diet should not be assumed to be benign,” she concluded.
Dr. Iatan presented the study March 5 at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
The presentation received much media attention, with headlines implying a causal relationship with cardiac events based on these observational results. But lipid expert Steven Nissen, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic, warned against paying much attention to the headlines or to the study’s conclusions.
In an interview, Dr. Nissen pointed out that the LDL increase in the “keto-like” diet group was relatively small and “certainly not enough to produce a doubling in cardiovascular risk.
“The people who were on the ‘keto-like’ diet in this study were different than those who were on the standard diet,” he said. “Those on the ‘keto-like’ diet were on it for a reason – they were more overweight, they had a higher incidence of diabetes, so their risk profile was completely different. Even though the researchers tried to adjust for other cardiovascular risk factors, there will be unmeasured confounding in a study like this.”
He said he doesn’t think this study “answers any significant questions in a way that we want to have them answered. I’m not a big fan of this type of diet, but I don’t think it doubles the risk of adverse cardiovascular events, and I don’t think this study tells us one way or another.”
For the study, Dr. Iatan and colleagues defined a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet as consisting of no more than 25% of total daily energy from carbohydrates and more than 45% of total daily calories from fat. This is somewhat higher in carbohydrates and lower in fat than a strict ketogenic diet but could be thought of as a ‘keto-like’ diet.
They analyzed data from the UK Biobank, a large-scale prospective database with health information from over half a million people living in the United Kingdom who were followed for at least 10 years.
On enrollment in the Biobank, participants completed a one-time, self-reported 24-hour diet questionnaire and, at the same time, had blood drawn to check their levels of cholesterol. The researchers identified 305 participants whose questionnaire responses indicated that they followed a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet. These participants were matched by age and sex with 1,220 individuals who reported being on a standard diet.
Of the study population, 73% were women and the average age was 54 years. Those on a low carbohydrate/high fat diet had a higher average body mass index (27.7 vs. 26.7) and a higher incidence of diabetes (4.9% vs. 1.7%).
Results showed that compared with participants on a standard diet, those on the “keto-like” diet had significantly higher levels of both LDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein B (ApoB).
Levels of LDL were 3.80 mmol/L (147 mg/dL) in the keto-like group vs. 3.64 mmol/L (141 mg/dL) in the standard group (P = .004). Levels of ApoB were 1.09 g/L (109 mg/dL) in the keto-like group and 1.04 g/L (104 mg/dL) in the standard group (P < .001).
After an average of 11.8 years of follow-up, 9.8% of participants on the low-carbohydrate/high-fat diet vs. 4.3% in the standard diet group experienced one of the events included in the composite event endpoint: Angina, myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, ischemic stroke, peripheral arterial disease, or coronary/carotid revascularization.
After adjustment for other risk factors for heart disease – diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and smoking – individuals on a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet were found to have a twofold risk of having a cardiovascular event (HR, 2.18; P < .001).
‘Closer monitoring needed’
“Our results have shown, I think for the first time, that there is an association between this increasingly popular dietary pattern and high LDL cholesterol and an increased future risk of cardiovascular events,” senior author Liam Brunham, MD, of the University of British Columbia, said in an interview. “This is concerning as there are many people out there following this type of diet, and I think it suggests there is a need for closer monitoring of these people.”
He explained that while it would be expected for cholesterol levels to rise on a high-fat diet, “there has been a perception by some that this is not worrisome as it is reflecting certain metabolic changes. What we’ve shown in this study is that if your cholesterol does increase significantly on this diet then you should not assume that this is not a problem.
“For some people with diabetes this diet can help lower blood sugar and some people can lose weight on it,” he noted, “but what our data show is that there is a subgroup of people who experience high levels of LDL and ApoB and that seems to be driving the risk.”
He pointed out that overall the mean level of LDL was only slightly increased in the individuals on the low-carb/high-fat diet but severe high cholesterol (more than 5 mmol/L or 190 mg/dL) was about doubled in that group (10% vs. 5%). And these patients had a sixfold increase in risk of cardiovascular disease (P < .001).
“This suggests that there is a subgroup of people who are susceptible to this exacerbation of hypercholesterolemia in response to a low-carb/high-fat diet.”
Dr. Brunham said his advice would be that if people choose to follow this diet, they should have their cholesterol monitored, and manage their cardiovascular risk factors.
“I wouldn’t say it is not appropriate to follow this diet based on this study,” he added. “This is just an observational study. It is not definitive. But if people do want to follow this dietary pattern because they feel there would be some benefits, then they should be aware of the potential risks and take steps to mitigate those risks.”
Jury still out
Dr. Nissen said in his view “the jury was still out” on this type of diet. “I’m open to the possibility that, particularly in the short run, a ‘keto-like’ diet may help some people lose weight and that’s a good thing. But I do not generally recommend this type of diet.”
Rather, he advises patients to follow a Mediterranean diet, which has been proven to reduce cardiovascular events in a randomized study, the PREDIMED trial.
“We can’t make decisions on what type of diet to recommend to patients based on observational studies like this where there is a lot of subtlety missing. But when studies like this are reported, the mass media seize on it. That’s not the way the public needs to be educated,” Dr. Nissen said.
“We refer to this type of study as hypothesis-generating. It raises a hypothesis. It doesn’t answer the question. It is worth looking at the question of whether a ketogenic-like diet is harmful. We don’t know at present, and I don’t think we know any more after this study,” he added.
The authors of the study reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Consumption of a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet, dubbed a “keto-like” diet, was associated with an increase in LDL levels and a twofold increase in the risk for future cardiovascular events, in a new observational study.
“To our knowledge this is the first study to demonstrate an association between a carbohydrate-restricted dietary platform and greater risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” said study investigator Iulia Iatan, MD, PhD, University of British Columbia, Vancouver.
“Hypercholesterolemia occurring during a low-carb, high-fat diet should not be assumed to be benign,” she concluded.
Dr. Iatan presented the study March 5 at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
The presentation received much media attention, with headlines implying a causal relationship with cardiac events based on these observational results. But lipid expert Steven Nissen, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic, warned against paying much attention to the headlines or to the study’s conclusions.
In an interview, Dr. Nissen pointed out that the LDL increase in the “keto-like” diet group was relatively small and “certainly not enough to produce a doubling in cardiovascular risk.
“The people who were on the ‘keto-like’ diet in this study were different than those who were on the standard diet,” he said. “Those on the ‘keto-like’ diet were on it for a reason – they were more overweight, they had a higher incidence of diabetes, so their risk profile was completely different. Even though the researchers tried to adjust for other cardiovascular risk factors, there will be unmeasured confounding in a study like this.”
He said he doesn’t think this study “answers any significant questions in a way that we want to have them answered. I’m not a big fan of this type of diet, but I don’t think it doubles the risk of adverse cardiovascular events, and I don’t think this study tells us one way or another.”
For the study, Dr. Iatan and colleagues defined a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet as consisting of no more than 25% of total daily energy from carbohydrates and more than 45% of total daily calories from fat. This is somewhat higher in carbohydrates and lower in fat than a strict ketogenic diet but could be thought of as a ‘keto-like’ diet.
They analyzed data from the UK Biobank, a large-scale prospective database with health information from over half a million people living in the United Kingdom who were followed for at least 10 years.
On enrollment in the Biobank, participants completed a one-time, self-reported 24-hour diet questionnaire and, at the same time, had blood drawn to check their levels of cholesterol. The researchers identified 305 participants whose questionnaire responses indicated that they followed a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet. These participants were matched by age and sex with 1,220 individuals who reported being on a standard diet.
Of the study population, 73% were women and the average age was 54 years. Those on a low carbohydrate/high fat diet had a higher average body mass index (27.7 vs. 26.7) and a higher incidence of diabetes (4.9% vs. 1.7%).
Results showed that compared with participants on a standard diet, those on the “keto-like” diet had significantly higher levels of both LDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein B (ApoB).
Levels of LDL were 3.80 mmol/L (147 mg/dL) in the keto-like group vs. 3.64 mmol/L (141 mg/dL) in the standard group (P = .004). Levels of ApoB were 1.09 g/L (109 mg/dL) in the keto-like group and 1.04 g/L (104 mg/dL) in the standard group (P < .001).
After an average of 11.8 years of follow-up, 9.8% of participants on the low-carbohydrate/high-fat diet vs. 4.3% in the standard diet group experienced one of the events included in the composite event endpoint: Angina, myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, ischemic stroke, peripheral arterial disease, or coronary/carotid revascularization.
After adjustment for other risk factors for heart disease – diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and smoking – individuals on a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet were found to have a twofold risk of having a cardiovascular event (HR, 2.18; P < .001).
‘Closer monitoring needed’
“Our results have shown, I think for the first time, that there is an association between this increasingly popular dietary pattern and high LDL cholesterol and an increased future risk of cardiovascular events,” senior author Liam Brunham, MD, of the University of British Columbia, said in an interview. “This is concerning as there are many people out there following this type of diet, and I think it suggests there is a need for closer monitoring of these people.”
He explained that while it would be expected for cholesterol levels to rise on a high-fat diet, “there has been a perception by some that this is not worrisome as it is reflecting certain metabolic changes. What we’ve shown in this study is that if your cholesterol does increase significantly on this diet then you should not assume that this is not a problem.
“For some people with diabetes this diet can help lower blood sugar and some people can lose weight on it,” he noted, “but what our data show is that there is a subgroup of people who experience high levels of LDL and ApoB and that seems to be driving the risk.”
He pointed out that overall the mean level of LDL was only slightly increased in the individuals on the low-carb/high-fat diet but severe high cholesterol (more than 5 mmol/L or 190 mg/dL) was about doubled in that group (10% vs. 5%). And these patients had a sixfold increase in risk of cardiovascular disease (P < .001).
“This suggests that there is a subgroup of people who are susceptible to this exacerbation of hypercholesterolemia in response to a low-carb/high-fat diet.”
Dr. Brunham said his advice would be that if people choose to follow this diet, they should have their cholesterol monitored, and manage their cardiovascular risk factors.
“I wouldn’t say it is not appropriate to follow this diet based on this study,” he added. “This is just an observational study. It is not definitive. But if people do want to follow this dietary pattern because they feel there would be some benefits, then they should be aware of the potential risks and take steps to mitigate those risks.”
Jury still out
Dr. Nissen said in his view “the jury was still out” on this type of diet. “I’m open to the possibility that, particularly in the short run, a ‘keto-like’ diet may help some people lose weight and that’s a good thing. But I do not generally recommend this type of diet.”
Rather, he advises patients to follow a Mediterranean diet, which has been proven to reduce cardiovascular events in a randomized study, the PREDIMED trial.
“We can’t make decisions on what type of diet to recommend to patients based on observational studies like this where there is a lot of subtlety missing. But when studies like this are reported, the mass media seize on it. That’s not the way the public needs to be educated,” Dr. Nissen said.
“We refer to this type of study as hypothesis-generating. It raises a hypothesis. It doesn’t answer the question. It is worth looking at the question of whether a ketogenic-like diet is harmful. We don’t know at present, and I don’t think we know any more after this study,” he added.
The authors of the study reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Consumption of a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet, dubbed a “keto-like” diet, was associated with an increase in LDL levels and a twofold increase in the risk for future cardiovascular events, in a new observational study.
“To our knowledge this is the first study to demonstrate an association between a carbohydrate-restricted dietary platform and greater risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” said study investigator Iulia Iatan, MD, PhD, University of British Columbia, Vancouver.
“Hypercholesterolemia occurring during a low-carb, high-fat diet should not be assumed to be benign,” she concluded.
Dr. Iatan presented the study March 5 at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
The presentation received much media attention, with headlines implying a causal relationship with cardiac events based on these observational results. But lipid expert Steven Nissen, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic, warned against paying much attention to the headlines or to the study’s conclusions.
In an interview, Dr. Nissen pointed out that the LDL increase in the “keto-like” diet group was relatively small and “certainly not enough to produce a doubling in cardiovascular risk.
“The people who were on the ‘keto-like’ diet in this study were different than those who were on the standard diet,” he said. “Those on the ‘keto-like’ diet were on it for a reason – they were more overweight, they had a higher incidence of diabetes, so their risk profile was completely different. Even though the researchers tried to adjust for other cardiovascular risk factors, there will be unmeasured confounding in a study like this.”
He said he doesn’t think this study “answers any significant questions in a way that we want to have them answered. I’m not a big fan of this type of diet, but I don’t think it doubles the risk of adverse cardiovascular events, and I don’t think this study tells us one way or another.”
For the study, Dr. Iatan and colleagues defined a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet as consisting of no more than 25% of total daily energy from carbohydrates and more than 45% of total daily calories from fat. This is somewhat higher in carbohydrates and lower in fat than a strict ketogenic diet but could be thought of as a ‘keto-like’ diet.
They analyzed data from the UK Biobank, a large-scale prospective database with health information from over half a million people living in the United Kingdom who were followed for at least 10 years.
On enrollment in the Biobank, participants completed a one-time, self-reported 24-hour diet questionnaire and, at the same time, had blood drawn to check their levels of cholesterol. The researchers identified 305 participants whose questionnaire responses indicated that they followed a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet. These participants were matched by age and sex with 1,220 individuals who reported being on a standard diet.
Of the study population, 73% were women and the average age was 54 years. Those on a low carbohydrate/high fat diet had a higher average body mass index (27.7 vs. 26.7) and a higher incidence of diabetes (4.9% vs. 1.7%).
Results showed that compared with participants on a standard diet, those on the “keto-like” diet had significantly higher levels of both LDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein B (ApoB).
Levels of LDL were 3.80 mmol/L (147 mg/dL) in the keto-like group vs. 3.64 mmol/L (141 mg/dL) in the standard group (P = .004). Levels of ApoB were 1.09 g/L (109 mg/dL) in the keto-like group and 1.04 g/L (104 mg/dL) in the standard group (P < .001).
After an average of 11.8 years of follow-up, 9.8% of participants on the low-carbohydrate/high-fat diet vs. 4.3% in the standard diet group experienced one of the events included in the composite event endpoint: Angina, myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, ischemic stroke, peripheral arterial disease, or coronary/carotid revascularization.
After adjustment for other risk factors for heart disease – diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and smoking – individuals on a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet were found to have a twofold risk of having a cardiovascular event (HR, 2.18; P < .001).
‘Closer monitoring needed’
“Our results have shown, I think for the first time, that there is an association between this increasingly popular dietary pattern and high LDL cholesterol and an increased future risk of cardiovascular events,” senior author Liam Brunham, MD, of the University of British Columbia, said in an interview. “This is concerning as there are many people out there following this type of diet, and I think it suggests there is a need for closer monitoring of these people.”
He explained that while it would be expected for cholesterol levels to rise on a high-fat diet, “there has been a perception by some that this is not worrisome as it is reflecting certain metabolic changes. What we’ve shown in this study is that if your cholesterol does increase significantly on this diet then you should not assume that this is not a problem.
“For some people with diabetes this diet can help lower blood sugar and some people can lose weight on it,” he noted, “but what our data show is that there is a subgroup of people who experience high levels of LDL and ApoB and that seems to be driving the risk.”
He pointed out that overall the mean level of LDL was only slightly increased in the individuals on the low-carb/high-fat diet but severe high cholesterol (more than 5 mmol/L or 190 mg/dL) was about doubled in that group (10% vs. 5%). And these patients had a sixfold increase in risk of cardiovascular disease (P < .001).
“This suggests that there is a subgroup of people who are susceptible to this exacerbation of hypercholesterolemia in response to a low-carb/high-fat diet.”
Dr. Brunham said his advice would be that if people choose to follow this diet, they should have their cholesterol monitored, and manage their cardiovascular risk factors.
“I wouldn’t say it is not appropriate to follow this diet based on this study,” he added. “This is just an observational study. It is not definitive. But if people do want to follow this dietary pattern because they feel there would be some benefits, then they should be aware of the potential risks and take steps to mitigate those risks.”
Jury still out
Dr. Nissen said in his view “the jury was still out” on this type of diet. “I’m open to the possibility that, particularly in the short run, a ‘keto-like’ diet may help some people lose weight and that’s a good thing. But I do not generally recommend this type of diet.”
Rather, he advises patients to follow a Mediterranean diet, which has been proven to reduce cardiovascular events in a randomized study, the PREDIMED trial.
“We can’t make decisions on what type of diet to recommend to patients based on observational studies like this where there is a lot of subtlety missing. But when studies like this are reported, the mass media seize on it. That’s not the way the public needs to be educated,” Dr. Nissen said.
“We refer to this type of study as hypothesis-generating. It raises a hypothesis. It doesn’t answer the question. It is worth looking at the question of whether a ketogenic-like diet is harmful. We don’t know at present, and I don’t think we know any more after this study,” he added.
The authors of the study reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACC 2023
In early days, bioabsorbable stent rivals nonabsorbable devices
At 6 months follow-up, a new-generation resorbable stent with a magnesium scaffold appears to perform at a level comparable to nonabsorbable drug-eluting stents (DES), according to first-in-man results presented as a late-breaker at the Cardiovascular Research Technologies conference, sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
“IVUS [intravascular ultrasound] assessment demonstrated preservation of the scaffold area from post procedure up to 6 months with a low mean neointimal area,” reported Michael Haude, MD, PhD, director of the Heart & Vascular Center, Neuss, Germany.
Neointimal formation and late lumen loss (LLL) have been the Achilles’ heel of previous efforts to develop a viable fully absorbable stent, making these 6-month data highly encouraging.
The tested device is the most recent iteration of the DREAMS (drug-eluting resorbable magnesium scaffold) technology. Relative to DREAMS 2G, the DREAMS 3G device has several design changes, including a higher radial force and reduced strut thickness.
The goal was to build on the promise of DREAMS 2G while avoiding its limitations.
“The problem with DREAMS 2G was that it showed low–target lesion failure and scaffold thrombosis rates in multiple trials, but in-scaffold LLL was not comparable to LLL values observed with historical PLLA [poly-L-lactic acid]–based scaffolds or contemporary DES,” Dr. Haude said.
The 6-month data with DREAMS 3G were drawn from the BIOMAG-I study. Patients with stable or unstable angina were enrolled if they had no angiographic evidence of thrombus at the target lesion. Patients were also required to have no more than two single de novo lesions requiring revascularization.
Of 116 patients enrolled, 115 were available for evaluation at 6 months. The study was not controlled, but outcomes were compared at 6 months to those observed with the DREAMS 2G device in the BIOSOLVE-II trial, published several years ago in the Lancet.
For the primary outcome of in-scaffold LLL at 6 months, the mean LLL from baseline at 6 months was more than 50% lower with the DREAMS 3G device in BIOMAG-I than DREAMS 2G in BIOSOLVE-II (0.21 vs. 0.44 mm). In a post hoc superiority analysis employing a weighted mean, a superiority analysis supported a highly significant difference in favor of the newer device (P < .0001).
More importantly, the low LLL in BIOMAG-I was not just favorable relative to previously evaluated bioabsorbable stents, but it appears to compete with nonabsorbable options at least after this length of follow-up.
In terms of LLL at 6 months, “these data suggested that DREAMS 3G “is now on the level of contemporary DES,” Dr. Haude said.
The relative difference in favor of DREAMS 3G was even greater at 6 months for the secondary endpoint of in-segment LLL (0.05 vs. 0.27 mm) with similar significance for the superiority margin in a post hoc analysis (P < .0001).
Serial optical coherence tomography (OCT) was conducted post procedure, and indicated that the struts “were well embedded in the vessel wall,” according to Dr. Haude. Only 4.4% of struts on average were malapposed. The total incomplete strut apposition area was on average 0.08 mm. At 6 months, most struts were no long discernible on OCT, documenting device resorption.
Clinical results at 6 months were supportive. There were no cases of definite or probable scaffold thrombosis, and there were no target vessel myocardial infarctions or cardiac deaths. There was one clinically driven target lesion revascularization.
DREAMS 3G has other features designed to make it easier to deploy, Dr. Haude said. For example, radiopaque markers are now situated on both ends of the stent, making it easier to see on imaging. There are also plans to make these stents available in 15 sizes to accommodate a broad range of anatomy.
The data were impressive for many of the panelists invited to discuss the results.
“For the first time, we are seeing a bioabsorbable device showing excellent healing and very little late lumen loss,” said Michael H. Joner, MD, professor of early clinical trials at the German Center for Cardiovascular Research, Munich. “The next step is some sort of direct comparison with a drug-eluting stent.”
Describing himself as “a little more skeptical,” Aoke V Finn, MD, medical director and chief scientific officer, CVPath Institute, University of Maryland, Baltimore, said he wants to know more about the speed of device degradation and to see more long-term results in terms of clinical events. Although he considers the data promising so far, he considers it too early to embark on a randomized trial.
Longer-term data are coming, according to Dr. Haude. In addition to the 12-month follow-up that will include OCT and IVUS evaluations, there are annual clinical follow-up analyses planned to 5 years.
Dr. Haude reports financial relationships with Biotronik, Cardiac Dimensions, OrbusNeich, and Philips. Dr. Joner reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Finn reports financial relationships with 19 pharmaceutical companies including those that manufacture cardiovascular stents.
At 6 months follow-up, a new-generation resorbable stent with a magnesium scaffold appears to perform at a level comparable to nonabsorbable drug-eluting stents (DES), according to first-in-man results presented as a late-breaker at the Cardiovascular Research Technologies conference, sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
“IVUS [intravascular ultrasound] assessment demonstrated preservation of the scaffold area from post procedure up to 6 months with a low mean neointimal area,” reported Michael Haude, MD, PhD, director of the Heart & Vascular Center, Neuss, Germany.
Neointimal formation and late lumen loss (LLL) have been the Achilles’ heel of previous efforts to develop a viable fully absorbable stent, making these 6-month data highly encouraging.
The tested device is the most recent iteration of the DREAMS (drug-eluting resorbable magnesium scaffold) technology. Relative to DREAMS 2G, the DREAMS 3G device has several design changes, including a higher radial force and reduced strut thickness.
The goal was to build on the promise of DREAMS 2G while avoiding its limitations.
“The problem with DREAMS 2G was that it showed low–target lesion failure and scaffold thrombosis rates in multiple trials, but in-scaffold LLL was not comparable to LLL values observed with historical PLLA [poly-L-lactic acid]–based scaffolds or contemporary DES,” Dr. Haude said.
The 6-month data with DREAMS 3G were drawn from the BIOMAG-I study. Patients with stable or unstable angina were enrolled if they had no angiographic evidence of thrombus at the target lesion. Patients were also required to have no more than two single de novo lesions requiring revascularization.
Of 116 patients enrolled, 115 were available for evaluation at 6 months. The study was not controlled, but outcomes were compared at 6 months to those observed with the DREAMS 2G device in the BIOSOLVE-II trial, published several years ago in the Lancet.
For the primary outcome of in-scaffold LLL at 6 months, the mean LLL from baseline at 6 months was more than 50% lower with the DREAMS 3G device in BIOMAG-I than DREAMS 2G in BIOSOLVE-II (0.21 vs. 0.44 mm). In a post hoc superiority analysis employing a weighted mean, a superiority analysis supported a highly significant difference in favor of the newer device (P < .0001).
More importantly, the low LLL in BIOMAG-I was not just favorable relative to previously evaluated bioabsorbable stents, but it appears to compete with nonabsorbable options at least after this length of follow-up.
In terms of LLL at 6 months, “these data suggested that DREAMS 3G “is now on the level of contemporary DES,” Dr. Haude said.
The relative difference in favor of DREAMS 3G was even greater at 6 months for the secondary endpoint of in-segment LLL (0.05 vs. 0.27 mm) with similar significance for the superiority margin in a post hoc analysis (P < .0001).
Serial optical coherence tomography (OCT) was conducted post procedure, and indicated that the struts “were well embedded in the vessel wall,” according to Dr. Haude. Only 4.4% of struts on average were malapposed. The total incomplete strut apposition area was on average 0.08 mm. At 6 months, most struts were no long discernible on OCT, documenting device resorption.
Clinical results at 6 months were supportive. There were no cases of definite or probable scaffold thrombosis, and there were no target vessel myocardial infarctions or cardiac deaths. There was one clinically driven target lesion revascularization.
DREAMS 3G has other features designed to make it easier to deploy, Dr. Haude said. For example, radiopaque markers are now situated on both ends of the stent, making it easier to see on imaging. There are also plans to make these stents available in 15 sizes to accommodate a broad range of anatomy.
The data were impressive for many of the panelists invited to discuss the results.
“For the first time, we are seeing a bioabsorbable device showing excellent healing and very little late lumen loss,” said Michael H. Joner, MD, professor of early clinical trials at the German Center for Cardiovascular Research, Munich. “The next step is some sort of direct comparison with a drug-eluting stent.”
Describing himself as “a little more skeptical,” Aoke V Finn, MD, medical director and chief scientific officer, CVPath Institute, University of Maryland, Baltimore, said he wants to know more about the speed of device degradation and to see more long-term results in terms of clinical events. Although he considers the data promising so far, he considers it too early to embark on a randomized trial.
Longer-term data are coming, according to Dr. Haude. In addition to the 12-month follow-up that will include OCT and IVUS evaluations, there are annual clinical follow-up analyses planned to 5 years.
Dr. Haude reports financial relationships with Biotronik, Cardiac Dimensions, OrbusNeich, and Philips. Dr. Joner reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Finn reports financial relationships with 19 pharmaceutical companies including those that manufacture cardiovascular stents.
At 6 months follow-up, a new-generation resorbable stent with a magnesium scaffold appears to perform at a level comparable to nonabsorbable drug-eluting stents (DES), according to first-in-man results presented as a late-breaker at the Cardiovascular Research Technologies conference, sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
“IVUS [intravascular ultrasound] assessment demonstrated preservation of the scaffold area from post procedure up to 6 months with a low mean neointimal area,” reported Michael Haude, MD, PhD, director of the Heart & Vascular Center, Neuss, Germany.
Neointimal formation and late lumen loss (LLL) have been the Achilles’ heel of previous efforts to develop a viable fully absorbable stent, making these 6-month data highly encouraging.
The tested device is the most recent iteration of the DREAMS (drug-eluting resorbable magnesium scaffold) technology. Relative to DREAMS 2G, the DREAMS 3G device has several design changes, including a higher radial force and reduced strut thickness.
The goal was to build on the promise of DREAMS 2G while avoiding its limitations.
“The problem with DREAMS 2G was that it showed low–target lesion failure and scaffold thrombosis rates in multiple trials, but in-scaffold LLL was not comparable to LLL values observed with historical PLLA [poly-L-lactic acid]–based scaffolds or contemporary DES,” Dr. Haude said.
The 6-month data with DREAMS 3G were drawn from the BIOMAG-I study. Patients with stable or unstable angina were enrolled if they had no angiographic evidence of thrombus at the target lesion. Patients were also required to have no more than two single de novo lesions requiring revascularization.
Of 116 patients enrolled, 115 were available for evaluation at 6 months. The study was not controlled, but outcomes were compared at 6 months to those observed with the DREAMS 2G device in the BIOSOLVE-II trial, published several years ago in the Lancet.
For the primary outcome of in-scaffold LLL at 6 months, the mean LLL from baseline at 6 months was more than 50% lower with the DREAMS 3G device in BIOMAG-I than DREAMS 2G in BIOSOLVE-II (0.21 vs. 0.44 mm). In a post hoc superiority analysis employing a weighted mean, a superiority analysis supported a highly significant difference in favor of the newer device (P < .0001).
More importantly, the low LLL in BIOMAG-I was not just favorable relative to previously evaluated bioabsorbable stents, but it appears to compete with nonabsorbable options at least after this length of follow-up.
In terms of LLL at 6 months, “these data suggested that DREAMS 3G “is now on the level of contemporary DES,” Dr. Haude said.
The relative difference in favor of DREAMS 3G was even greater at 6 months for the secondary endpoint of in-segment LLL (0.05 vs. 0.27 mm) with similar significance for the superiority margin in a post hoc analysis (P < .0001).
Serial optical coherence tomography (OCT) was conducted post procedure, and indicated that the struts “were well embedded in the vessel wall,” according to Dr. Haude. Only 4.4% of struts on average were malapposed. The total incomplete strut apposition area was on average 0.08 mm. At 6 months, most struts were no long discernible on OCT, documenting device resorption.
Clinical results at 6 months were supportive. There were no cases of definite or probable scaffold thrombosis, and there were no target vessel myocardial infarctions or cardiac deaths. There was one clinically driven target lesion revascularization.
DREAMS 3G has other features designed to make it easier to deploy, Dr. Haude said. For example, radiopaque markers are now situated on both ends of the stent, making it easier to see on imaging. There are also plans to make these stents available in 15 sizes to accommodate a broad range of anatomy.
The data were impressive for many of the panelists invited to discuss the results.
“For the first time, we are seeing a bioabsorbable device showing excellent healing and very little late lumen loss,” said Michael H. Joner, MD, professor of early clinical trials at the German Center for Cardiovascular Research, Munich. “The next step is some sort of direct comparison with a drug-eluting stent.”
Describing himself as “a little more skeptical,” Aoke V Finn, MD, medical director and chief scientific officer, CVPath Institute, University of Maryland, Baltimore, said he wants to know more about the speed of device degradation and to see more long-term results in terms of clinical events. Although he considers the data promising so far, he considers it too early to embark on a randomized trial.
Longer-term data are coming, according to Dr. Haude. In addition to the 12-month follow-up that will include OCT and IVUS evaluations, there are annual clinical follow-up analyses planned to 5 years.
Dr. Haude reports financial relationships with Biotronik, Cardiac Dimensions, OrbusNeich, and Philips. Dr. Joner reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Finn reports financial relationships with 19 pharmaceutical companies including those that manufacture cardiovascular stents.
FROM CRT 2023
20 years of clinical research in cardiology
In February 2003, when Cardiology News published its first edition, there were a handful of articles reporting results from randomized clinical trials. These included a trial of bivalirudin for percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) anticoagulation (REPLACE-2) and a small controlled pilot study of soy nuts for blood pressure reduction in postmenopausal women. Also included was a considered discussion of the ALLHAT findings.
These trials and the incremental gain they offered belie the enormous global impact the cardiology community has had in clinical research over the last several decades. In fact, more than any other medical specialty, cardiology has led the way in evidence-based practice.
“When you step back and take a look at the compendium of cardiology advances, it’s unbelievable how much we’ve accomplished in the last 20 years,” said Steven E. Nissen, MD.
Dr. Nissen, a prodigious researcher, is the chief academic officer at the Sydell and Arnold Miller Family Heart, Vascular and Thoracic Institute, and holds the Lewis and Patricia Dickey Chair in Cardiovascular Medicine at the Cleveland Clinic.
The needle mover: LDL lowering
“From a population health perspective, LDL cholesterol lowering is clearly the big winner,” said Christopher Cannon, MD, from Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview.
“We’ve been at it with LDL cholesterol for about 50 years now, but I think things really accelerated over the last 20 years when the conversation shifted from just lowering LDL-C to recognizing that lower is better. This pushed us toward high-intensity statin treatment and add-on drugs to push LDL down further,” he said.
“Concurrent with this increase in the use of statins and other LDL-lowering drugs, cardiovascular death has fallen significantly, which in my mind is likely a result of better LDL lowering and getting people to stop smoking, which we’ve also done a better job of in the last 20 years,” said Dr. Cannon.
Indeed, until cardiovascular mortality started rising in 2020, the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, mortality rates had been dropping steadily for several decades. The progress in the past 2 decades has been so fast, noted Dr. Cannon, that the American Heart Association’s stated goal in 1998 of reducing coronary heart disease, stroke, and risk by 25% by the year 2008 was accomplished about 4 years ahead of schedule.
Coincidentally, Dr. Cannon and Dr. Nissen were both important players in this advance. Dr. Cannon led the PROVE-IT trial, which showed in 2004 that an intensive lipid-lowering statin regimen offers greater protection against death or major cardiovascular events than does a standard regimen in patients with recent acute coronary syndrome.
That trial was published just months after REVERSAL, Dr. Nissen’s trial that showed for the first time that intensive lipid-lowering treatment reduced progression of coronary atherosclerosis, compared with a moderate lipid-lowering approach.
“Added to this, we have drugs like ezetimibe and the PCSK9 [proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9] inhibitor, and now they’re even using CRISPR gene editing to permanently switch off the gene that codes for PCSK9, testing this in people with familial hypercholesterolemia,” said Dr. Cannon. “In the preclinical study, they showed that with one treatment they lowered blood PCSK9 protein levels by 83% and LDL-C by 69%..”
At the same time as we’ve seen what works, we’ve also seen what doesn’t work, added Dr. Nissen. “Shortly after we saw the power of LDL lowering, everyone wanted to target HDL and we had epidemiological evidence suggesting this was a good idea, but several landmark trials testing the HDL hypothesis were complete failures.” Debate continues as to whether HDL cholesterol is a suitable target for prevention.
Not only has the recent past in lipidology been needle-moving, but the hits keep coming. Inclisiran, a first-in-class LDL cholesterol–lowering drug that shows potent lipid-lowering efficacy and excellent safety and tolerability in phase 3 study, received Food and Drug Administration approval in December 2021. The drugs twice-a-year dosing has been called a game changer for adherence.
And at the 2023 annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology in March, Dr. Nissen presented results of the CLEAR Outcomes trial on bempedoic acid (Nexletol), a 14,000-patient, placebo-controlled trial of bempedoic acid in statin intolerant patients at high cardiovascular risk. Bempedoic acid is a novel compound that inhibits ATP citrate lyase, which catalyzes a step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol upstream of HMG-CoA reductase, the target of statins.
Findings revealed a significant reduction in risk for a composite 4-point major adverse cardiovascular events endpoint of time to first cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or coronary revascularization. The trial marks the first time an oral nonstatin drug has met the MACE-4 primary endpoint, Dr. Nissen reported.
“We also have new therapies for lowering lipoprotein(a) and outcome trials underway for antisense and short interfering RNA targeting of Lp(a), which I frankly think herald a new era in which we can have these longer-acting directly targeted drugs that work at the translation level to prevent a protein that is not desirable,” added Dr. Nissen. “These drugs will undoubtedly change the face of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in the next 2 decades.”
Other important successes and equally important failures
Perhaps consideration of some of the treatments we didn’t have 20 years ago is more revealing than a list of advances. Two decades ago, there were no direct direct-acting anticoagulants on the market, “so no alternative to warfarin, which is difficult to use and associated with excess bleeding,” said Dr. Cannon. These days, warfarin is little used, mostly after valve replacement, Dr. Nissen added.
There were also no percutaneous options for the treatment of valvular heart disease and no catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation, “huge developments that are now being done everywhere,” Dr. Nissen said.
Also in the catheterization laboratory, there was also a far less sophisticated understanding of the optimal role of PCI in treating coronary artery disease.
“We’ve moved from what we called the ‘oculostenotic reflex’– if you see an obstruction, you treat it – to a far more nuanced understanding of who should and shouldn’t have PCI, such that now PCI has contracted to the point where most of the time it’s being done for urgent indications like ST-segment elevation MI or an unstable non-STEMI. And this is based on a solid evidence base, which is terribly important,” said Dr. Nissen.
The rise and fall of CVOTs
Certainly, the heart failure world has seen important advances in recent years, including the first mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, spironolactone, shown in the 1999 RALES trial to be life prolonging in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and a first in class angiotensin neprilysin inhibitor, sacubitril/valsartan. But it’s a fair guess that heart failure has never seen anything like the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors.
Likely very few in the cardiology world had ever heard of SGLT2 inhibition 20 years ago, even though the idea of SGLT2 inhibition dates back more than 150 years, to when a French chemist isolated a substance known as phlorizin from the bark of the apple tree and subsequent investigations found that ingestion of it caused glucosuria. The SGLT2 story is one of great serendipity and one in which Dr. Nissen played a prominent role. It also hints to something that has both come and gone in the last 20 years: the FDA-mandated cardiovascular outcome trial (CVOT).
It was Dr. Nissen’s meta-analysis published in 2007 that started the ball rolling for what has been dubbed the CVOT or cardiovascular outcomes trials.
His analysis suggested increased cardiovascular risk associated with the thiazolidinedione rosiglitazone (Avandia), then a best-selling diabetes drug.
“At the time, Avandia was the top selling diabetes drug in the world, and our meta-analysis was terribly controversial,” said Dr. Nissen. In 2008, he gave a presentation to the FDA where he suggested they should require properly powered trials to rule out excess cardiovascular risk for any new diabetes drugs.
Others also recognized that the findings of his meta-analysis hinted to a failure of the approval process and the postapproval monitoring process, something which had been seen previously, with cardiac safety concerns emerging over other antihyperglycemic medications. The FDA was also responding to concerns that, given the high prevalence of cardiovascular disease in diabetes, approving a drug with cardiovascular risk could be disastrous.
In 2008 they mandated the CVOT, one of which, the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial, showed that the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin significantly reduced the risk of a composite of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke by 14% (P = .04), driven by a 38% relative risk reduction in cardiovascular death (P < .001).Treatment with empagliflozin was also associated with a 35% reduction in heart failure hospitalization and a 32% reduction in all-cause death in that trial.
Additional groundbreaking CVOTs of empagliflozin and other SGLT2 inhibitors went on to show significant cardiorenal benefits and risk reduction in patients across the spectrum of heart failure, including those with preserved ejection fraction and in those with kidney disease.
“I think it’s fair to say that, had the FDA not mandated CVOTs for all new diabetes drugs, then the SGLT2 inhibitors and the GLP-1 [glucagonlike peptide–1] receptor agonists would have been approved on the basis of trials involving a few thousand patients showing that they lowered blood sugar, and we might never have found out what we know now about their benefits in individuals with established cardiovascular disease, in heart failure, and their ability to help people lose weight,” said Dr. Nissen. “And, of course, Avandia is long gone, which is a good thing.”
Interestingly, the FDA no longer requires extensive cardiovascular testing for new glucose-lowering agents in the absence of specific safety signals, replacing the CVOT mandate with one requiring broader inclusion of patients with underlying CV disease, chronic kidney disease, and older patients in stage 3 clinical trials of new agents.
“The SGLT2 inhibitors are already hugely important and with the growing prevalence of diabetes, their role is just going to get bigger. And it looks like the same thing will happen with the GLP-1 receptor agonists and obesity. We don’t have the outcomes trials for semaglutide and tirzepatide yet in patients with obesity, but given every other trial of this class in patients with diabetes has shown cardiovascular benefit, assuming those trials do too, those drugs are going to be very important,” added Dr. Cannon.
“The truth is, everywhere you look in cardiology, there have been major advances,” Dr. Cannon said. “It’s a wonderful time to work in this field because we’re making important progress across the board and it doesn’t appear to be slowing down at all.”
Clinical research for the next 20 years
Twenty years ago, clinical research was relatively simple, or at least it seemed so. All that was needed was a basic understanding of the scientific method and randomized controlled trials (RCTs), a solid research question, a target sample of sufficient size to ensure statistical power, and some basic statistical analysis, et violà, evidence generation.
Turns out, that might have been in large part true because medicine was in a more simplistic age. While RCTs remain the cornerstone of determining the safety and efficacy of new therapeutic strategies, they traditionally have severely lacked in age, gender, ethnic, and racial diversity. These issues limit their clinical relevance, to the chagrin of the large proportion of the population (women, minorities, children, and anyone with comorbidities) not included in most studies.
RCTs have also grown exceedingly time consuming and expensive. “We really saw the limitations of our clinical trial system during the pandemic when so many of the randomized COVID-19 trials done in the United States had complex protocols with a focus on surrogate outcomes such that, with only the 500 patients they enrolled, they ended up showing nothing,” Dr. Cannon said in an interview.
“And then we looked at the RECOVERY trial program that Martin Landray, MBChB, PhD, and the folks at Oxford [England] University pioneered. They ran multiple trials for relatively little costs, used a pragmatic design, and asked simple straightforward questions, and included 10,000-15,000 patients in each trial and gave us answers quickly,” he said.
RECOVERY is an ongoing adaptive multicenter randomized controlled trial evaluating several potential treatments for COVID-19. The RECOVERY Collaborative are credited with running multiple streamlined and easy to administer trials that included more than 47,000 participants spread across almost 200 hospital sites in six countries. The trials resulted in finding four effective COVID-19 treatments and proving that five others clearly were not effective.
Importantly, only essential data were collected and, wherever possible, much of the follow-up information was derived from national electronic health records.
“Now the question is, Can the U.S. move to doing more of these pragmatic trials?” asked Dr. Cannon.
Time to be inclusive
Where the rules of generating evidence have changed and will continue to change over the next many years is inclusivity. Gone are the days when researchers can get away with running a randomized trial with, say, few minority patients, 20% representation of women, and no elderly patients with comorbidities.
“I’m proud of the fact that 48% of more than 14,000 participants in the CLEAR outcomes trial that I presented at the ACC meeting are women,” Dr. Nissen said in an interview.
“Should it have been like that 20 years ago? Yes, probably. But we weren’t as conscious of these things. Now we’re working very hard to enroll more women and more underrepresented groups into trials, and this is a good thing.”
In a joint statement entitled “Randomized trials fit for the 21st century,” the leadership of the European Society of Cardiology, American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology, and the World Heart Federation urge investigators and professional societies to “promote trials that are relevant to a broad and varied population; assuring diversity of participants and funded researchers (e.g., with appropriate sex, age, racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic diversity).”
The statement also recognizes that the present clinical research model is “unsustainable” and encourages wider adoption of “highly streamlined” conduct like that taken by the RECOVERY investigators during the pandemic.
Stick with randomization
Some have suggested that loosening the standards for evidence generation in medicine to include observational data, big data, artificial intelligence, and alternative trial strategies, such as Mendelian randomization and causal inference of nonrandomized data, might help drive new treatments to the clinic faster. To this, Dr. Nissen and Dr. Cannon offer an emphatic no.
“The idea that you can use big data or any kind of nonrandomized data to replace randomized control trials is a bad idea, and the reason is that nonrandomized data is often bad data,” Dr. Nissen said in an interview.
“I can’t count how many bad studies we’ve seen that were enormous in size, and where they tried to control the variables to balance it out, and they still get the wrong answer,” he added. “The bottom line is that observational data has failed us over and over again.”
Not to say that observational studies have no value, it’s just not for determining which treatments are most efficacious or safe, said Dr. Cannon. “If you want to identify markers of disease or risk factors, you can use observational data like data collected from wearables and screen for patients who, say, might be at high risk of dying of COVID-19. Or even more directly, you can use a heart rate and temperature monitor to identify people who are about to test positive for COVID-19.
“But the findings of observational analyses, no matter how much you try to control for confounding, are only ever going to be hypothesis generating. They can’t be used to say this biomarker causes death from COVID or this blood thinner is better than that blood thinner.”
Concurring with this, the ESC, AHA, ACC, and WHF statement authors acknowledged the value of nonrandomized evidence in today’s big data, electronic world, but advocated for the “appropriate use of routine EHRs (i.e. ‘real-world’ data) within randomized trials, recognizing the huge potential of centrally or regionally held electronic health data for trial recruitment and follow-up, as well as to highlight the severe limitations of using observational analyses when the purpose is to draw causal inference about the risks and benefits of an intervention.”
In February 2003, when Cardiology News published its first edition, there were a handful of articles reporting results from randomized clinical trials. These included a trial of bivalirudin for percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) anticoagulation (REPLACE-2) and a small controlled pilot study of soy nuts for blood pressure reduction in postmenopausal women. Also included was a considered discussion of the ALLHAT findings.
These trials and the incremental gain they offered belie the enormous global impact the cardiology community has had in clinical research over the last several decades. In fact, more than any other medical specialty, cardiology has led the way in evidence-based practice.
“When you step back and take a look at the compendium of cardiology advances, it’s unbelievable how much we’ve accomplished in the last 20 years,” said Steven E. Nissen, MD.
Dr. Nissen, a prodigious researcher, is the chief academic officer at the Sydell and Arnold Miller Family Heart, Vascular and Thoracic Institute, and holds the Lewis and Patricia Dickey Chair in Cardiovascular Medicine at the Cleveland Clinic.
The needle mover: LDL lowering
“From a population health perspective, LDL cholesterol lowering is clearly the big winner,” said Christopher Cannon, MD, from Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview.
“We’ve been at it with LDL cholesterol for about 50 years now, but I think things really accelerated over the last 20 years when the conversation shifted from just lowering LDL-C to recognizing that lower is better. This pushed us toward high-intensity statin treatment and add-on drugs to push LDL down further,” he said.
“Concurrent with this increase in the use of statins and other LDL-lowering drugs, cardiovascular death has fallen significantly, which in my mind is likely a result of better LDL lowering and getting people to stop smoking, which we’ve also done a better job of in the last 20 years,” said Dr. Cannon.
Indeed, until cardiovascular mortality started rising in 2020, the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, mortality rates had been dropping steadily for several decades. The progress in the past 2 decades has been so fast, noted Dr. Cannon, that the American Heart Association’s stated goal in 1998 of reducing coronary heart disease, stroke, and risk by 25% by the year 2008 was accomplished about 4 years ahead of schedule.
Coincidentally, Dr. Cannon and Dr. Nissen were both important players in this advance. Dr. Cannon led the PROVE-IT trial, which showed in 2004 that an intensive lipid-lowering statin regimen offers greater protection against death or major cardiovascular events than does a standard regimen in patients with recent acute coronary syndrome.
That trial was published just months after REVERSAL, Dr. Nissen’s trial that showed for the first time that intensive lipid-lowering treatment reduced progression of coronary atherosclerosis, compared with a moderate lipid-lowering approach.
“Added to this, we have drugs like ezetimibe and the PCSK9 [proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9] inhibitor, and now they’re even using CRISPR gene editing to permanently switch off the gene that codes for PCSK9, testing this in people with familial hypercholesterolemia,” said Dr. Cannon. “In the preclinical study, they showed that with one treatment they lowered blood PCSK9 protein levels by 83% and LDL-C by 69%..”
At the same time as we’ve seen what works, we’ve also seen what doesn’t work, added Dr. Nissen. “Shortly after we saw the power of LDL lowering, everyone wanted to target HDL and we had epidemiological evidence suggesting this was a good idea, but several landmark trials testing the HDL hypothesis were complete failures.” Debate continues as to whether HDL cholesterol is a suitable target for prevention.
Not only has the recent past in lipidology been needle-moving, but the hits keep coming. Inclisiran, a first-in-class LDL cholesterol–lowering drug that shows potent lipid-lowering efficacy and excellent safety and tolerability in phase 3 study, received Food and Drug Administration approval in December 2021. The drugs twice-a-year dosing has been called a game changer for adherence.
And at the 2023 annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology in March, Dr. Nissen presented results of the CLEAR Outcomes trial on bempedoic acid (Nexletol), a 14,000-patient, placebo-controlled trial of bempedoic acid in statin intolerant patients at high cardiovascular risk. Bempedoic acid is a novel compound that inhibits ATP citrate lyase, which catalyzes a step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol upstream of HMG-CoA reductase, the target of statins.
Findings revealed a significant reduction in risk for a composite 4-point major adverse cardiovascular events endpoint of time to first cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or coronary revascularization. The trial marks the first time an oral nonstatin drug has met the MACE-4 primary endpoint, Dr. Nissen reported.
“We also have new therapies for lowering lipoprotein(a) and outcome trials underway for antisense and short interfering RNA targeting of Lp(a), which I frankly think herald a new era in which we can have these longer-acting directly targeted drugs that work at the translation level to prevent a protein that is not desirable,” added Dr. Nissen. “These drugs will undoubtedly change the face of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in the next 2 decades.”
Other important successes and equally important failures
Perhaps consideration of some of the treatments we didn’t have 20 years ago is more revealing than a list of advances. Two decades ago, there were no direct direct-acting anticoagulants on the market, “so no alternative to warfarin, which is difficult to use and associated with excess bleeding,” said Dr. Cannon. These days, warfarin is little used, mostly after valve replacement, Dr. Nissen added.
There were also no percutaneous options for the treatment of valvular heart disease and no catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation, “huge developments that are now being done everywhere,” Dr. Nissen said.
Also in the catheterization laboratory, there was also a far less sophisticated understanding of the optimal role of PCI in treating coronary artery disease.
“We’ve moved from what we called the ‘oculostenotic reflex’– if you see an obstruction, you treat it – to a far more nuanced understanding of who should and shouldn’t have PCI, such that now PCI has contracted to the point where most of the time it’s being done for urgent indications like ST-segment elevation MI or an unstable non-STEMI. And this is based on a solid evidence base, which is terribly important,” said Dr. Nissen.
The rise and fall of CVOTs
Certainly, the heart failure world has seen important advances in recent years, including the first mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, spironolactone, shown in the 1999 RALES trial to be life prolonging in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and a first in class angiotensin neprilysin inhibitor, sacubitril/valsartan. But it’s a fair guess that heart failure has never seen anything like the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors.
Likely very few in the cardiology world had ever heard of SGLT2 inhibition 20 years ago, even though the idea of SGLT2 inhibition dates back more than 150 years, to when a French chemist isolated a substance known as phlorizin from the bark of the apple tree and subsequent investigations found that ingestion of it caused glucosuria. The SGLT2 story is one of great serendipity and one in which Dr. Nissen played a prominent role. It also hints to something that has both come and gone in the last 20 years: the FDA-mandated cardiovascular outcome trial (CVOT).
It was Dr. Nissen’s meta-analysis published in 2007 that started the ball rolling for what has been dubbed the CVOT or cardiovascular outcomes trials.
His analysis suggested increased cardiovascular risk associated with the thiazolidinedione rosiglitazone (Avandia), then a best-selling diabetes drug.
“At the time, Avandia was the top selling diabetes drug in the world, and our meta-analysis was terribly controversial,” said Dr. Nissen. In 2008, he gave a presentation to the FDA where he suggested they should require properly powered trials to rule out excess cardiovascular risk for any new diabetes drugs.
Others also recognized that the findings of his meta-analysis hinted to a failure of the approval process and the postapproval monitoring process, something which had been seen previously, with cardiac safety concerns emerging over other antihyperglycemic medications. The FDA was also responding to concerns that, given the high prevalence of cardiovascular disease in diabetes, approving a drug with cardiovascular risk could be disastrous.
In 2008 they mandated the CVOT, one of which, the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial, showed that the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin significantly reduced the risk of a composite of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke by 14% (P = .04), driven by a 38% relative risk reduction in cardiovascular death (P < .001).Treatment with empagliflozin was also associated with a 35% reduction in heart failure hospitalization and a 32% reduction in all-cause death in that trial.
Additional groundbreaking CVOTs of empagliflozin and other SGLT2 inhibitors went on to show significant cardiorenal benefits and risk reduction in patients across the spectrum of heart failure, including those with preserved ejection fraction and in those with kidney disease.
“I think it’s fair to say that, had the FDA not mandated CVOTs for all new diabetes drugs, then the SGLT2 inhibitors and the GLP-1 [glucagonlike peptide–1] receptor agonists would have been approved on the basis of trials involving a few thousand patients showing that they lowered blood sugar, and we might never have found out what we know now about their benefits in individuals with established cardiovascular disease, in heart failure, and their ability to help people lose weight,” said Dr. Nissen. “And, of course, Avandia is long gone, which is a good thing.”
Interestingly, the FDA no longer requires extensive cardiovascular testing for new glucose-lowering agents in the absence of specific safety signals, replacing the CVOT mandate with one requiring broader inclusion of patients with underlying CV disease, chronic kidney disease, and older patients in stage 3 clinical trials of new agents.
“The SGLT2 inhibitors are already hugely important and with the growing prevalence of diabetes, their role is just going to get bigger. And it looks like the same thing will happen with the GLP-1 receptor agonists and obesity. We don’t have the outcomes trials for semaglutide and tirzepatide yet in patients with obesity, but given every other trial of this class in patients with diabetes has shown cardiovascular benefit, assuming those trials do too, those drugs are going to be very important,” added Dr. Cannon.
“The truth is, everywhere you look in cardiology, there have been major advances,” Dr. Cannon said. “It’s a wonderful time to work in this field because we’re making important progress across the board and it doesn’t appear to be slowing down at all.”
Clinical research for the next 20 years
Twenty years ago, clinical research was relatively simple, or at least it seemed so. All that was needed was a basic understanding of the scientific method and randomized controlled trials (RCTs), a solid research question, a target sample of sufficient size to ensure statistical power, and some basic statistical analysis, et violà, evidence generation.
Turns out, that might have been in large part true because medicine was in a more simplistic age. While RCTs remain the cornerstone of determining the safety and efficacy of new therapeutic strategies, they traditionally have severely lacked in age, gender, ethnic, and racial diversity. These issues limit their clinical relevance, to the chagrin of the large proportion of the population (women, minorities, children, and anyone with comorbidities) not included in most studies.
RCTs have also grown exceedingly time consuming and expensive. “We really saw the limitations of our clinical trial system during the pandemic when so many of the randomized COVID-19 trials done in the United States had complex protocols with a focus on surrogate outcomes such that, with only the 500 patients they enrolled, they ended up showing nothing,” Dr. Cannon said in an interview.
“And then we looked at the RECOVERY trial program that Martin Landray, MBChB, PhD, and the folks at Oxford [England] University pioneered. They ran multiple trials for relatively little costs, used a pragmatic design, and asked simple straightforward questions, and included 10,000-15,000 patients in each trial and gave us answers quickly,” he said.
RECOVERY is an ongoing adaptive multicenter randomized controlled trial evaluating several potential treatments for COVID-19. The RECOVERY Collaborative are credited with running multiple streamlined and easy to administer trials that included more than 47,000 participants spread across almost 200 hospital sites in six countries. The trials resulted in finding four effective COVID-19 treatments and proving that five others clearly were not effective.
Importantly, only essential data were collected and, wherever possible, much of the follow-up information was derived from national electronic health records.
“Now the question is, Can the U.S. move to doing more of these pragmatic trials?” asked Dr. Cannon.
Time to be inclusive
Where the rules of generating evidence have changed and will continue to change over the next many years is inclusivity. Gone are the days when researchers can get away with running a randomized trial with, say, few minority patients, 20% representation of women, and no elderly patients with comorbidities.
“I’m proud of the fact that 48% of more than 14,000 participants in the CLEAR outcomes trial that I presented at the ACC meeting are women,” Dr. Nissen said in an interview.
“Should it have been like that 20 years ago? Yes, probably. But we weren’t as conscious of these things. Now we’re working very hard to enroll more women and more underrepresented groups into trials, and this is a good thing.”
In a joint statement entitled “Randomized trials fit for the 21st century,” the leadership of the European Society of Cardiology, American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology, and the World Heart Federation urge investigators and professional societies to “promote trials that are relevant to a broad and varied population; assuring diversity of participants and funded researchers (e.g., with appropriate sex, age, racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic diversity).”
The statement also recognizes that the present clinical research model is “unsustainable” and encourages wider adoption of “highly streamlined” conduct like that taken by the RECOVERY investigators during the pandemic.
Stick with randomization
Some have suggested that loosening the standards for evidence generation in medicine to include observational data, big data, artificial intelligence, and alternative trial strategies, such as Mendelian randomization and causal inference of nonrandomized data, might help drive new treatments to the clinic faster. To this, Dr. Nissen and Dr. Cannon offer an emphatic no.
“The idea that you can use big data or any kind of nonrandomized data to replace randomized control trials is a bad idea, and the reason is that nonrandomized data is often bad data,” Dr. Nissen said in an interview.
“I can’t count how many bad studies we’ve seen that were enormous in size, and where they tried to control the variables to balance it out, and they still get the wrong answer,” he added. “The bottom line is that observational data has failed us over and over again.”
Not to say that observational studies have no value, it’s just not for determining which treatments are most efficacious or safe, said Dr. Cannon. “If you want to identify markers of disease or risk factors, you can use observational data like data collected from wearables and screen for patients who, say, might be at high risk of dying of COVID-19. Or even more directly, you can use a heart rate and temperature monitor to identify people who are about to test positive for COVID-19.
“But the findings of observational analyses, no matter how much you try to control for confounding, are only ever going to be hypothesis generating. They can’t be used to say this biomarker causes death from COVID or this blood thinner is better than that blood thinner.”
Concurring with this, the ESC, AHA, ACC, and WHF statement authors acknowledged the value of nonrandomized evidence in today’s big data, electronic world, but advocated for the “appropriate use of routine EHRs (i.e. ‘real-world’ data) within randomized trials, recognizing the huge potential of centrally or regionally held electronic health data for trial recruitment and follow-up, as well as to highlight the severe limitations of using observational analyses when the purpose is to draw causal inference about the risks and benefits of an intervention.”
In February 2003, when Cardiology News published its first edition, there were a handful of articles reporting results from randomized clinical trials. These included a trial of bivalirudin for percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) anticoagulation (REPLACE-2) and a small controlled pilot study of soy nuts for blood pressure reduction in postmenopausal women. Also included was a considered discussion of the ALLHAT findings.
These trials and the incremental gain they offered belie the enormous global impact the cardiology community has had in clinical research over the last several decades. In fact, more than any other medical specialty, cardiology has led the way in evidence-based practice.
“When you step back and take a look at the compendium of cardiology advances, it’s unbelievable how much we’ve accomplished in the last 20 years,” said Steven E. Nissen, MD.
Dr. Nissen, a prodigious researcher, is the chief academic officer at the Sydell and Arnold Miller Family Heart, Vascular and Thoracic Institute, and holds the Lewis and Patricia Dickey Chair in Cardiovascular Medicine at the Cleveland Clinic.
The needle mover: LDL lowering
“From a population health perspective, LDL cholesterol lowering is clearly the big winner,” said Christopher Cannon, MD, from Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview.
“We’ve been at it with LDL cholesterol for about 50 years now, but I think things really accelerated over the last 20 years when the conversation shifted from just lowering LDL-C to recognizing that lower is better. This pushed us toward high-intensity statin treatment and add-on drugs to push LDL down further,” he said.
“Concurrent with this increase in the use of statins and other LDL-lowering drugs, cardiovascular death has fallen significantly, which in my mind is likely a result of better LDL lowering and getting people to stop smoking, which we’ve also done a better job of in the last 20 years,” said Dr. Cannon.
Indeed, until cardiovascular mortality started rising in 2020, the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, mortality rates had been dropping steadily for several decades. The progress in the past 2 decades has been so fast, noted Dr. Cannon, that the American Heart Association’s stated goal in 1998 of reducing coronary heart disease, stroke, and risk by 25% by the year 2008 was accomplished about 4 years ahead of schedule.
Coincidentally, Dr. Cannon and Dr. Nissen were both important players in this advance. Dr. Cannon led the PROVE-IT trial, which showed in 2004 that an intensive lipid-lowering statin regimen offers greater protection against death or major cardiovascular events than does a standard regimen in patients with recent acute coronary syndrome.
That trial was published just months after REVERSAL, Dr. Nissen’s trial that showed for the first time that intensive lipid-lowering treatment reduced progression of coronary atherosclerosis, compared with a moderate lipid-lowering approach.
“Added to this, we have drugs like ezetimibe and the PCSK9 [proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9] inhibitor, and now they’re even using CRISPR gene editing to permanently switch off the gene that codes for PCSK9, testing this in people with familial hypercholesterolemia,” said Dr. Cannon. “In the preclinical study, they showed that with one treatment they lowered blood PCSK9 protein levels by 83% and LDL-C by 69%..”
At the same time as we’ve seen what works, we’ve also seen what doesn’t work, added Dr. Nissen. “Shortly after we saw the power of LDL lowering, everyone wanted to target HDL and we had epidemiological evidence suggesting this was a good idea, but several landmark trials testing the HDL hypothesis were complete failures.” Debate continues as to whether HDL cholesterol is a suitable target for prevention.
Not only has the recent past in lipidology been needle-moving, but the hits keep coming. Inclisiran, a first-in-class LDL cholesterol–lowering drug that shows potent lipid-lowering efficacy and excellent safety and tolerability in phase 3 study, received Food and Drug Administration approval in December 2021. The drugs twice-a-year dosing has been called a game changer for adherence.
And at the 2023 annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology in March, Dr. Nissen presented results of the CLEAR Outcomes trial on bempedoic acid (Nexletol), a 14,000-patient, placebo-controlled trial of bempedoic acid in statin intolerant patients at high cardiovascular risk. Bempedoic acid is a novel compound that inhibits ATP citrate lyase, which catalyzes a step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol upstream of HMG-CoA reductase, the target of statins.
Findings revealed a significant reduction in risk for a composite 4-point major adverse cardiovascular events endpoint of time to first cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or coronary revascularization. The trial marks the first time an oral nonstatin drug has met the MACE-4 primary endpoint, Dr. Nissen reported.
“We also have new therapies for lowering lipoprotein(a) and outcome trials underway for antisense and short interfering RNA targeting of Lp(a), which I frankly think herald a new era in which we can have these longer-acting directly targeted drugs that work at the translation level to prevent a protein that is not desirable,” added Dr. Nissen. “These drugs will undoubtedly change the face of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in the next 2 decades.”
Other important successes and equally important failures
Perhaps consideration of some of the treatments we didn’t have 20 years ago is more revealing than a list of advances. Two decades ago, there were no direct direct-acting anticoagulants on the market, “so no alternative to warfarin, which is difficult to use and associated with excess bleeding,” said Dr. Cannon. These days, warfarin is little used, mostly after valve replacement, Dr. Nissen added.
There were also no percutaneous options for the treatment of valvular heart disease and no catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation, “huge developments that are now being done everywhere,” Dr. Nissen said.
Also in the catheterization laboratory, there was also a far less sophisticated understanding of the optimal role of PCI in treating coronary artery disease.
“We’ve moved from what we called the ‘oculostenotic reflex’– if you see an obstruction, you treat it – to a far more nuanced understanding of who should and shouldn’t have PCI, such that now PCI has contracted to the point where most of the time it’s being done for urgent indications like ST-segment elevation MI or an unstable non-STEMI. And this is based on a solid evidence base, which is terribly important,” said Dr. Nissen.
The rise and fall of CVOTs
Certainly, the heart failure world has seen important advances in recent years, including the first mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, spironolactone, shown in the 1999 RALES trial to be life prolonging in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and a first in class angiotensin neprilysin inhibitor, sacubitril/valsartan. But it’s a fair guess that heart failure has never seen anything like the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors.
Likely very few in the cardiology world had ever heard of SGLT2 inhibition 20 years ago, even though the idea of SGLT2 inhibition dates back more than 150 years, to when a French chemist isolated a substance known as phlorizin from the bark of the apple tree and subsequent investigations found that ingestion of it caused glucosuria. The SGLT2 story is one of great serendipity and one in which Dr. Nissen played a prominent role. It also hints to something that has both come and gone in the last 20 years: the FDA-mandated cardiovascular outcome trial (CVOT).
It was Dr. Nissen’s meta-analysis published in 2007 that started the ball rolling for what has been dubbed the CVOT or cardiovascular outcomes trials.
His analysis suggested increased cardiovascular risk associated with the thiazolidinedione rosiglitazone (Avandia), then a best-selling diabetes drug.
“At the time, Avandia was the top selling diabetes drug in the world, and our meta-analysis was terribly controversial,” said Dr. Nissen. In 2008, he gave a presentation to the FDA where he suggested they should require properly powered trials to rule out excess cardiovascular risk for any new diabetes drugs.
Others also recognized that the findings of his meta-analysis hinted to a failure of the approval process and the postapproval monitoring process, something which had been seen previously, with cardiac safety concerns emerging over other antihyperglycemic medications. The FDA was also responding to concerns that, given the high prevalence of cardiovascular disease in diabetes, approving a drug with cardiovascular risk could be disastrous.
In 2008 they mandated the CVOT, one of which, the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial, showed that the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin significantly reduced the risk of a composite of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke by 14% (P = .04), driven by a 38% relative risk reduction in cardiovascular death (P < .001).Treatment with empagliflozin was also associated with a 35% reduction in heart failure hospitalization and a 32% reduction in all-cause death in that trial.
Additional groundbreaking CVOTs of empagliflozin and other SGLT2 inhibitors went on to show significant cardiorenal benefits and risk reduction in patients across the spectrum of heart failure, including those with preserved ejection fraction and in those with kidney disease.
“I think it’s fair to say that, had the FDA not mandated CVOTs for all new diabetes drugs, then the SGLT2 inhibitors and the GLP-1 [glucagonlike peptide–1] receptor agonists would have been approved on the basis of trials involving a few thousand patients showing that they lowered blood sugar, and we might never have found out what we know now about their benefits in individuals with established cardiovascular disease, in heart failure, and their ability to help people lose weight,” said Dr. Nissen. “And, of course, Avandia is long gone, which is a good thing.”
Interestingly, the FDA no longer requires extensive cardiovascular testing for new glucose-lowering agents in the absence of specific safety signals, replacing the CVOT mandate with one requiring broader inclusion of patients with underlying CV disease, chronic kidney disease, and older patients in stage 3 clinical trials of new agents.
“The SGLT2 inhibitors are already hugely important and with the growing prevalence of diabetes, their role is just going to get bigger. And it looks like the same thing will happen with the GLP-1 receptor agonists and obesity. We don’t have the outcomes trials for semaglutide and tirzepatide yet in patients with obesity, but given every other trial of this class in patients with diabetes has shown cardiovascular benefit, assuming those trials do too, those drugs are going to be very important,” added Dr. Cannon.
“The truth is, everywhere you look in cardiology, there have been major advances,” Dr. Cannon said. “It’s a wonderful time to work in this field because we’re making important progress across the board and it doesn’t appear to be slowing down at all.”
Clinical research for the next 20 years
Twenty years ago, clinical research was relatively simple, or at least it seemed so. All that was needed was a basic understanding of the scientific method and randomized controlled trials (RCTs), a solid research question, a target sample of sufficient size to ensure statistical power, and some basic statistical analysis, et violà, evidence generation.
Turns out, that might have been in large part true because medicine was in a more simplistic age. While RCTs remain the cornerstone of determining the safety and efficacy of new therapeutic strategies, they traditionally have severely lacked in age, gender, ethnic, and racial diversity. These issues limit their clinical relevance, to the chagrin of the large proportion of the population (women, minorities, children, and anyone with comorbidities) not included in most studies.
RCTs have also grown exceedingly time consuming and expensive. “We really saw the limitations of our clinical trial system during the pandemic when so many of the randomized COVID-19 trials done in the United States had complex protocols with a focus on surrogate outcomes such that, with only the 500 patients they enrolled, they ended up showing nothing,” Dr. Cannon said in an interview.
“And then we looked at the RECOVERY trial program that Martin Landray, MBChB, PhD, and the folks at Oxford [England] University pioneered. They ran multiple trials for relatively little costs, used a pragmatic design, and asked simple straightforward questions, and included 10,000-15,000 patients in each trial and gave us answers quickly,” he said.
RECOVERY is an ongoing adaptive multicenter randomized controlled trial evaluating several potential treatments for COVID-19. The RECOVERY Collaborative are credited with running multiple streamlined and easy to administer trials that included more than 47,000 participants spread across almost 200 hospital sites in six countries. The trials resulted in finding four effective COVID-19 treatments and proving that five others clearly were not effective.
Importantly, only essential data were collected and, wherever possible, much of the follow-up information was derived from national electronic health records.
“Now the question is, Can the U.S. move to doing more of these pragmatic trials?” asked Dr. Cannon.
Time to be inclusive
Where the rules of generating evidence have changed and will continue to change over the next many years is inclusivity. Gone are the days when researchers can get away with running a randomized trial with, say, few minority patients, 20% representation of women, and no elderly patients with comorbidities.
“I’m proud of the fact that 48% of more than 14,000 participants in the CLEAR outcomes trial that I presented at the ACC meeting are women,” Dr. Nissen said in an interview.
“Should it have been like that 20 years ago? Yes, probably. But we weren’t as conscious of these things. Now we’re working very hard to enroll more women and more underrepresented groups into trials, and this is a good thing.”
In a joint statement entitled “Randomized trials fit for the 21st century,” the leadership of the European Society of Cardiology, American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology, and the World Heart Federation urge investigators and professional societies to “promote trials that are relevant to a broad and varied population; assuring diversity of participants and funded researchers (e.g., with appropriate sex, age, racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic diversity).”
The statement also recognizes that the present clinical research model is “unsustainable” and encourages wider adoption of “highly streamlined” conduct like that taken by the RECOVERY investigators during the pandemic.
Stick with randomization
Some have suggested that loosening the standards for evidence generation in medicine to include observational data, big data, artificial intelligence, and alternative trial strategies, such as Mendelian randomization and causal inference of nonrandomized data, might help drive new treatments to the clinic faster. To this, Dr. Nissen and Dr. Cannon offer an emphatic no.
“The idea that you can use big data or any kind of nonrandomized data to replace randomized control trials is a bad idea, and the reason is that nonrandomized data is often bad data,” Dr. Nissen said in an interview.
“I can’t count how many bad studies we’ve seen that were enormous in size, and where they tried to control the variables to balance it out, and they still get the wrong answer,” he added. “The bottom line is that observational data has failed us over and over again.”
Not to say that observational studies have no value, it’s just not for determining which treatments are most efficacious or safe, said Dr. Cannon. “If you want to identify markers of disease or risk factors, you can use observational data like data collected from wearables and screen for patients who, say, might be at high risk of dying of COVID-19. Or even more directly, you can use a heart rate and temperature monitor to identify people who are about to test positive for COVID-19.
“But the findings of observational analyses, no matter how much you try to control for confounding, are only ever going to be hypothesis generating. They can’t be used to say this biomarker causes death from COVID or this blood thinner is better than that blood thinner.”
Concurring with this, the ESC, AHA, ACC, and WHF statement authors acknowledged the value of nonrandomized evidence in today’s big data, electronic world, but advocated for the “appropriate use of routine EHRs (i.e. ‘real-world’ data) within randomized trials, recognizing the huge potential of centrally or regionally held electronic health data for trial recruitment and follow-up, as well as to highlight the severe limitations of using observational analyses when the purpose is to draw causal inference about the risks and benefits of an intervention.”