User login
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers May Lead to Worse Outcomes in Celiac Disease
PHILADELPHIA — , according to a study presented at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting.
The association may be related to the similar pathophysiology between ARB-associated enteropathy and celiac disease, though additional research is needed.
“Based on our findings, people should take caution when prescribing angiotensin receptor blockers to people with celiac disease,” said lead author Isabel Hujoel, MD, clinical assistant professor of gastroenterology and clinic director of the Celiac Disease Center at the University of Washington, Seattle.
“When we see someone with nonresponsive celiac disease, meaning persistent symptoms despite a gluten-free diet, I do think we should review their medication list, and if they’re on an ARB, we should consider a trial off those medications to see if they respond,” she said. “A primary care provider may choose other hypertensives as well.”
Hujoel and co-author Margaux Hujoel, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston; Broad Institute, Cambridge; and Harvard Medical School, Boston, analyzed data from the National Institutes of Health’s All of Us, a large publicly available US longitudinal dataset.
The researchers conducted a survival analysis of time-to-first event after celiac disease diagnosis, allowing patients to have a time-dependent covariate of ARB use. They looked at outcomes such as iron deficiency, diarrhea, abdominal pain, vitamin deficiency, vitamin D deficiency, malabsorption, low hemoglobin, and weight loss.
The analysis included 1849 patients with celiac disease, including 1460 women and 389 men, with a median age of nearly 50 years at diagnosis. While the vast majority of patients (nearly 1600) didn’t take an ARB, 120 started one before celiac disease diagnosis and 142 started one after diagnosis.
Overall, taking an ARB was associated with increased hazard ratios [HRs] for low hemoglobin, iron deficiency, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. There weren’t increased risks for weight loss, malabsorption, or vitamin deficiencies.
When excluding those who had an ARB prescription before diagnosis, the HRs remained significantly higher for low hemoglobin (HR, 1.98) and iron deficiency (HR, 1.72) for those who started an ARB after diagnosis.
“The use of angiotensin receptor blockers may be associated with worse outcomes in the setting of celiac disease, specifically persistent symptoms and possibly poor small bowel healing as evidenced by malabsorption,” Hujoel said.
Future studies could look specifically at losartan, which was the most common ARB prescribed in this analysis, she said. Other studies could also analyze different patient outcomes, whether patients were on a gluten-free diet, medication adherence, and recurrence or persistence of symptoms rather than initial occurrence. The associations between ARB use and celiac disease could shift among patients who are in remission, for instance.
“ARBs are some of the most widely used medications, so studies like these can help people to understand that they may have symptoms but not know it’s related to their medication. Public awareness of this fact is key,” said Patricia Jones, MD, a hepatologist and associate professor of clinical medicine at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami. Jones co-moderated the plenary session on small intestine, functional, and liver research.
“There are many types of antihypertensives, so while ARBs are used often, other options are available if people have symptoms, especially if they have worsening symptoms with celiac disease,” she said. “It’s important to make changes in your practice.”
The study was named an ACG Newsworthy Abstract. Isabel Hujoel and Patricia Jones reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA — , according to a study presented at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting.
The association may be related to the similar pathophysiology between ARB-associated enteropathy and celiac disease, though additional research is needed.
“Based on our findings, people should take caution when prescribing angiotensin receptor blockers to people with celiac disease,” said lead author Isabel Hujoel, MD, clinical assistant professor of gastroenterology and clinic director of the Celiac Disease Center at the University of Washington, Seattle.
“When we see someone with nonresponsive celiac disease, meaning persistent symptoms despite a gluten-free diet, I do think we should review their medication list, and if they’re on an ARB, we should consider a trial off those medications to see if they respond,” she said. “A primary care provider may choose other hypertensives as well.”
Hujoel and co-author Margaux Hujoel, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston; Broad Institute, Cambridge; and Harvard Medical School, Boston, analyzed data from the National Institutes of Health’s All of Us, a large publicly available US longitudinal dataset.
The researchers conducted a survival analysis of time-to-first event after celiac disease diagnosis, allowing patients to have a time-dependent covariate of ARB use. They looked at outcomes such as iron deficiency, diarrhea, abdominal pain, vitamin deficiency, vitamin D deficiency, malabsorption, low hemoglobin, and weight loss.
The analysis included 1849 patients with celiac disease, including 1460 women and 389 men, with a median age of nearly 50 years at diagnosis. While the vast majority of patients (nearly 1600) didn’t take an ARB, 120 started one before celiac disease diagnosis and 142 started one after diagnosis.
Overall, taking an ARB was associated with increased hazard ratios [HRs] for low hemoglobin, iron deficiency, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. There weren’t increased risks for weight loss, malabsorption, or vitamin deficiencies.
When excluding those who had an ARB prescription before diagnosis, the HRs remained significantly higher for low hemoglobin (HR, 1.98) and iron deficiency (HR, 1.72) for those who started an ARB after diagnosis.
“The use of angiotensin receptor blockers may be associated with worse outcomes in the setting of celiac disease, specifically persistent symptoms and possibly poor small bowel healing as evidenced by malabsorption,” Hujoel said.
Future studies could look specifically at losartan, which was the most common ARB prescribed in this analysis, she said. Other studies could also analyze different patient outcomes, whether patients were on a gluten-free diet, medication adherence, and recurrence or persistence of symptoms rather than initial occurrence. The associations between ARB use and celiac disease could shift among patients who are in remission, for instance.
“ARBs are some of the most widely used medications, so studies like these can help people to understand that they may have symptoms but not know it’s related to their medication. Public awareness of this fact is key,” said Patricia Jones, MD, a hepatologist and associate professor of clinical medicine at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami. Jones co-moderated the plenary session on small intestine, functional, and liver research.
“There are many types of antihypertensives, so while ARBs are used often, other options are available if people have symptoms, especially if they have worsening symptoms with celiac disease,” she said. “It’s important to make changes in your practice.”
The study was named an ACG Newsworthy Abstract. Isabel Hujoel and Patricia Jones reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA — , according to a study presented at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting.
The association may be related to the similar pathophysiology between ARB-associated enteropathy and celiac disease, though additional research is needed.
“Based on our findings, people should take caution when prescribing angiotensin receptor blockers to people with celiac disease,” said lead author Isabel Hujoel, MD, clinical assistant professor of gastroenterology and clinic director of the Celiac Disease Center at the University of Washington, Seattle.
“When we see someone with nonresponsive celiac disease, meaning persistent symptoms despite a gluten-free diet, I do think we should review their medication list, and if they’re on an ARB, we should consider a trial off those medications to see if they respond,” she said. “A primary care provider may choose other hypertensives as well.”
Hujoel and co-author Margaux Hujoel, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston; Broad Institute, Cambridge; and Harvard Medical School, Boston, analyzed data from the National Institutes of Health’s All of Us, a large publicly available US longitudinal dataset.
The researchers conducted a survival analysis of time-to-first event after celiac disease diagnosis, allowing patients to have a time-dependent covariate of ARB use. They looked at outcomes such as iron deficiency, diarrhea, abdominal pain, vitamin deficiency, vitamin D deficiency, malabsorption, low hemoglobin, and weight loss.
The analysis included 1849 patients with celiac disease, including 1460 women and 389 men, with a median age of nearly 50 years at diagnosis. While the vast majority of patients (nearly 1600) didn’t take an ARB, 120 started one before celiac disease diagnosis and 142 started one after diagnosis.
Overall, taking an ARB was associated with increased hazard ratios [HRs] for low hemoglobin, iron deficiency, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. There weren’t increased risks for weight loss, malabsorption, or vitamin deficiencies.
When excluding those who had an ARB prescription before diagnosis, the HRs remained significantly higher for low hemoglobin (HR, 1.98) and iron deficiency (HR, 1.72) for those who started an ARB after diagnosis.
“The use of angiotensin receptor blockers may be associated with worse outcomes in the setting of celiac disease, specifically persistent symptoms and possibly poor small bowel healing as evidenced by malabsorption,” Hujoel said.
Future studies could look specifically at losartan, which was the most common ARB prescribed in this analysis, she said. Other studies could also analyze different patient outcomes, whether patients were on a gluten-free diet, medication adherence, and recurrence or persistence of symptoms rather than initial occurrence. The associations between ARB use and celiac disease could shift among patients who are in remission, for instance.
“ARBs are some of the most widely used medications, so studies like these can help people to understand that they may have symptoms but not know it’s related to their medication. Public awareness of this fact is key,” said Patricia Jones, MD, a hepatologist and associate professor of clinical medicine at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami. Jones co-moderated the plenary session on small intestine, functional, and liver research.
“There are many types of antihypertensives, so while ARBs are used often, other options are available if people have symptoms, especially if they have worsening symptoms with celiac disease,” she said. “It’s important to make changes in your practice.”
The study was named an ACG Newsworthy Abstract. Isabel Hujoel and Patricia Jones reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACG 2024
Liquid Fasting Mitigates Negative Pre-Surgery Impact of Semaglutide
These findings suggest that patients taking GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) may benefit from a 24-hour liquid fast before anesthetic procedures without the need for a medication hold, reported lead author Haarika Korlipara, MD, of NewYork–Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, and colleagues.
“[T]he effects of delayed gastric emptying in patients on long-acting GLP-1RAs are clinically important in the management of anesthetized patients, who may develop periprocedural complications in the setting of retained solid gastric contents,” the investigators wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed clinical data from 1,212 patients undergoing upper endoscopy at a tertiary care center. Among them, 602 were on semaglutide for more than four weeks, while 610 were controls not taking the medication.
The primary outcome was the presence of retained solid gastric contents. Secondary outcomes included the need for intubation, early procedure termination, and recommendations for repeat endoscopy.
Semaglutide use was an independent predictor of retained solid gastric contents (odds ratio [OR], 4.74; 95% CI, 2.40-9.35; P less than .0001). Multivariable propensity-matched analysis showed a 6% absolute increase in retained gastric contents in the semaglutide group compared to controls (P less than .0001).
This increase appeared clinically relevant, as semaglutide use was associated with a higher rate of early procedure termination (OR, 3.09; P = 0.02) and recommendations for repeat endoscopies (OR, 3.61; P = 0.02), “indicating the degree of retained solid gastric contents was enough to limit the intended gastric mucosal examination,” the investigators wrote.
However, patients who underwent same-day colonoscopy, which included a 24-hour clear liquid fast leading up to the procedure, were less likely to have retained gastric contents (OR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.23-0.73; P = 0.003), suggesting that extended fasting protocols may mitigate the risk of procedural complications.
“Patients with a history of gastroparesis are often advised to stop ingesting solid foods and maintain a clear liquid diet for a longer period than standard ASA guidance before anesthetized procedures,” Dr. Korlipara and colleagues wrote. “In our opinion, this recommendation should be considered in patients on long-term GLP-1RA therapy, in response to the findings reported in this study and others about the protective effects of a 24-hour liquid fast.”
Point-of-care gastric ultrasound may also be considered to evaluate patients at higher risk of retained stomach contents, they added, especially in patients with additional risk factors for delayed gastric emptying.
“Previously published data have linked prolonged gastric emptying delays in patients chronically using these medications,” they wrote. “Considering the effect on blood sugar and associated procedural risk, especially in patients taking this medication for diabetes management, more studies are warranted to determine the effect of medication on periprocedural complications and recommend repeat evaluation.”
After this study was released, new clinical guidance on the use of GLP-1RAs before surgery was co-published by AGA and four other societies. The guidance notes that, in most cases, patients can continue to take GLP-1RAs, but individual risk factors for complications should be assessed prior to surgery. The guidance cautions that patients at high risk for significant GI side effects should follow a liquid diet for 24 hours before a procedure and the anesthesia plan be adjusted accordingly. In rare cases, the procedure should be delayed.
Dr. Korlipara disclosed no conflicts of interest.
These findings suggest that patients taking GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) may benefit from a 24-hour liquid fast before anesthetic procedures without the need for a medication hold, reported lead author Haarika Korlipara, MD, of NewYork–Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, and colleagues.
“[T]he effects of delayed gastric emptying in patients on long-acting GLP-1RAs are clinically important in the management of anesthetized patients, who may develop periprocedural complications in the setting of retained solid gastric contents,” the investigators wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed clinical data from 1,212 patients undergoing upper endoscopy at a tertiary care center. Among them, 602 were on semaglutide for more than four weeks, while 610 were controls not taking the medication.
The primary outcome was the presence of retained solid gastric contents. Secondary outcomes included the need for intubation, early procedure termination, and recommendations for repeat endoscopy.
Semaglutide use was an independent predictor of retained solid gastric contents (odds ratio [OR], 4.74; 95% CI, 2.40-9.35; P less than .0001). Multivariable propensity-matched analysis showed a 6% absolute increase in retained gastric contents in the semaglutide group compared to controls (P less than .0001).
This increase appeared clinically relevant, as semaglutide use was associated with a higher rate of early procedure termination (OR, 3.09; P = 0.02) and recommendations for repeat endoscopies (OR, 3.61; P = 0.02), “indicating the degree of retained solid gastric contents was enough to limit the intended gastric mucosal examination,” the investigators wrote.
However, patients who underwent same-day colonoscopy, which included a 24-hour clear liquid fast leading up to the procedure, were less likely to have retained gastric contents (OR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.23-0.73; P = 0.003), suggesting that extended fasting protocols may mitigate the risk of procedural complications.
“Patients with a history of gastroparesis are often advised to stop ingesting solid foods and maintain a clear liquid diet for a longer period than standard ASA guidance before anesthetized procedures,” Dr. Korlipara and colleagues wrote. “In our opinion, this recommendation should be considered in patients on long-term GLP-1RA therapy, in response to the findings reported in this study and others about the protective effects of a 24-hour liquid fast.”
Point-of-care gastric ultrasound may also be considered to evaluate patients at higher risk of retained stomach contents, they added, especially in patients with additional risk factors for delayed gastric emptying.
“Previously published data have linked prolonged gastric emptying delays in patients chronically using these medications,” they wrote. “Considering the effect on blood sugar and associated procedural risk, especially in patients taking this medication for diabetes management, more studies are warranted to determine the effect of medication on periprocedural complications and recommend repeat evaluation.”
After this study was released, new clinical guidance on the use of GLP-1RAs before surgery was co-published by AGA and four other societies. The guidance notes that, in most cases, patients can continue to take GLP-1RAs, but individual risk factors for complications should be assessed prior to surgery. The guidance cautions that patients at high risk for significant GI side effects should follow a liquid diet for 24 hours before a procedure and the anesthesia plan be adjusted accordingly. In rare cases, the procedure should be delayed.
Dr. Korlipara disclosed no conflicts of interest.
These findings suggest that patients taking GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) may benefit from a 24-hour liquid fast before anesthetic procedures without the need for a medication hold, reported lead author Haarika Korlipara, MD, of NewYork–Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, and colleagues.
“[T]he effects of delayed gastric emptying in patients on long-acting GLP-1RAs are clinically important in the management of anesthetized patients, who may develop periprocedural complications in the setting of retained solid gastric contents,” the investigators wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed clinical data from 1,212 patients undergoing upper endoscopy at a tertiary care center. Among them, 602 were on semaglutide for more than four weeks, while 610 were controls not taking the medication.
The primary outcome was the presence of retained solid gastric contents. Secondary outcomes included the need for intubation, early procedure termination, and recommendations for repeat endoscopy.
Semaglutide use was an independent predictor of retained solid gastric contents (odds ratio [OR], 4.74; 95% CI, 2.40-9.35; P less than .0001). Multivariable propensity-matched analysis showed a 6% absolute increase in retained gastric contents in the semaglutide group compared to controls (P less than .0001).
This increase appeared clinically relevant, as semaglutide use was associated with a higher rate of early procedure termination (OR, 3.09; P = 0.02) and recommendations for repeat endoscopies (OR, 3.61; P = 0.02), “indicating the degree of retained solid gastric contents was enough to limit the intended gastric mucosal examination,” the investigators wrote.
However, patients who underwent same-day colonoscopy, which included a 24-hour clear liquid fast leading up to the procedure, were less likely to have retained gastric contents (OR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.23-0.73; P = 0.003), suggesting that extended fasting protocols may mitigate the risk of procedural complications.
“Patients with a history of gastroparesis are often advised to stop ingesting solid foods and maintain a clear liquid diet for a longer period than standard ASA guidance before anesthetized procedures,” Dr. Korlipara and colleagues wrote. “In our opinion, this recommendation should be considered in patients on long-term GLP-1RA therapy, in response to the findings reported in this study and others about the protective effects of a 24-hour liquid fast.”
Point-of-care gastric ultrasound may also be considered to evaluate patients at higher risk of retained stomach contents, they added, especially in patients with additional risk factors for delayed gastric emptying.
“Previously published data have linked prolonged gastric emptying delays in patients chronically using these medications,” they wrote. “Considering the effect on blood sugar and associated procedural risk, especially in patients taking this medication for diabetes management, more studies are warranted to determine the effect of medication on periprocedural complications and recommend repeat evaluation.”
After this study was released, new clinical guidance on the use of GLP-1RAs before surgery was co-published by AGA and four other societies. The guidance notes that, in most cases, patients can continue to take GLP-1RAs, but individual risk factors for complications should be assessed prior to surgery. The guidance cautions that patients at high risk for significant GI side effects should follow a liquid diet for 24 hours before a procedure and the anesthesia plan be adjusted accordingly. In rare cases, the procedure should be delayed.
Dr. Korlipara disclosed no conflicts of interest.
FROM TECHNIQUES AND INNOVATIONS IN GASTROINTESTINAL ENDOSCOPY
GLP-1 RAs Safe in the Perioperative Period: New Guidance
The new guidance, contrasting with earlier recommendations, says these incrementally used agents can be taken up until the day of surgery, but patients are advised to follow a liquid diet for 24 hours before the procedure. The decision to proceed with endoscopy and other procedures should be based on shared decision-making with the patient and interdisciplinary care teams in conjunction with minimization of the aspiration risk from delayed gastric emptying, the guidance stresses.
The five endorsing organizations are the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA), American Gastroenterological Association, International Society of Perioperative Care of Patients with Obesity, and Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons. The societies emphasize that the statement is intended as guidance only and is not an evidence-based formal guideline.
GLP-1 RAs are known to delay gastric emptying, raising concerns about regurgitation, aspiration, and airway compromise during anesthesia. Rare serious adverse events have also been observed, prompting the ASA in 2023 to recommend holding these agents for 1 week for the injectable form and 1 day for the oral form before all procedures requiring anesthesia.
That abundance of caution, however, had negative impacts of its own. “This guidance has led to cancellations and postponements of many endoscopic and surgical procedures or required patients to undergo general anesthesia who may otherwise have had their procedures performed under moderate sedation,” said guidance coauthor Allison R. Schulman, MD, MPH, an associate professor of medicine and surgery and chief of endoscopy at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. “Nearly all institutions have been forced to revise preprocedural protocols, despite a lack of high-level evidence to suggest that these adjustments are necessary.”
“Studies have yielded mixed results as to whether patients on GLP-1s are at increased risk of these events, and the limited data available are inconsistent,” Schulman said. “As a result, there are inconsistencies in the recommendations from various societies leading to growing uncertainty with proceduralists on how to provide safe, effective, and timely procedural care to patients taking GLP-1 RAs.”
The new joint-society guidance may alleviate some of the uncertainty. Among the recommendations:
- Continuing GLP-1 RAs in the perioperative period should be based on shared decision-making with the patient and all care teams balancing the metabolic need for the GLP-1 RA with individual patient risk.
- Certain variables may increase the risk for delayed gastric emptying and aspiration with the periprocedural use of GLP-1 RAs: escalation phase — This phase vs the maintenance phase is associated with a higher risk for delayed gastric emptying; higher dose — the higher the dose, the greater the risk for gastrointestinal (GI) side effects; weekly dosing — GI side effects are more common with weekly vs daily formulations; presence of GI symptoms — nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, and constipation may suggest delayed gastric emptying; and medical problems beyond GLP-1 RA indications with GI effects — assess for such conditions as bowel dysmotility, gastroparesis, and Parkinson’s disease.
- Risk factors should be assessed in advance to allow sufficient time to adjust preoperative care, including diet modification and medication bridging if GLP-1 RA cessation is deemed advisable.
- If retained gastric contents are a concern on the day of a procedure, point-of-care gastric ultrasound could be used to assess aspiration risk, resources permitting.
- The aspiration risk from delayed gastric emptying should be minimized by preoperative diet modification and/or altering the anesthesia plan to consider rapid sequence induction of general anesthesia for tracheal intubation. A 24-hour preoperative liquid diet, as before colonoscopy and bariatric surgery, can be utilized when delayed gastric emptying is a concern.
- When concern about retained gastric contents exists on procedure day, providers should engage patients in a shared decision-making model and consider the benefits and risks of rapid-sequence induction of general anesthesia for tracheal intubation to minimize aspiration risk vs procedure cancellation.
“Safe continuation of surgery and gastrointestinal endoscopy, and prevention of procedure cancellation, for patients on GLP-1 RAs can be prioritized following the recommendations above, as would occur for other patient populations with gastroparesis,” the guidance panel wrote.
Commenting on the statement but not involved in it, David B. Purow, MD, managing director of the Digestive Health Center at Northwell Health/Huntington Hospital in Huntington, New York, said the recommendations will encourage clinicians to be more discerning about actual risk in individual cases rather than follow the previous blanket recommendation to stop these agents before procedures requiring sedation.
While GLP-1 RAs were prescribed for the relatively small number of patients with diabetes, he said, the risk was not apparent but became clearer with the widespread use of these agents for weight loss — often unregulated and undisclosed to care providers.
“The pendulum shifted too far the other way, and now it’s shifted back,” he said in an interview. “The new guidance is great because now we can be more thoughtful about managing individual patients.” He cited, for instance, the recommendations on the greater risk in patients in the dose escalation phase or on higher doses, and the risk-reducing measure of a liquid diet for 24 hours before surgery.
His center is already using point-of-care ultrasound and recently had a case in which a patient who forgot and took his GLP-1 RA before a scheduled procedure was found on ultrasound to have a full stomach. “In some cases, these drugs can cause an almost gastroparesis level of delayed emptying,” Purow said.
Purow thinks this early guidance will probably progress to firm guidelines within a year. Schulman is more cautious. “Our understanding of this complex topic is increasing rapidly, and ongoing clinical research will ultimately lead to evidence-based guidelines in this changing landscape,” she said.
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. Schulman is a consultant for Apollo Endosurgery, Boston Scientific, Olympus, Microtech, and Fractyl. Purow had no competing interests to declare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new guidance, contrasting with earlier recommendations, says these incrementally used agents can be taken up until the day of surgery, but patients are advised to follow a liquid diet for 24 hours before the procedure. The decision to proceed with endoscopy and other procedures should be based on shared decision-making with the patient and interdisciplinary care teams in conjunction with minimization of the aspiration risk from delayed gastric emptying, the guidance stresses.
The five endorsing organizations are the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA), American Gastroenterological Association, International Society of Perioperative Care of Patients with Obesity, and Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons. The societies emphasize that the statement is intended as guidance only and is not an evidence-based formal guideline.
GLP-1 RAs are known to delay gastric emptying, raising concerns about regurgitation, aspiration, and airway compromise during anesthesia. Rare serious adverse events have also been observed, prompting the ASA in 2023 to recommend holding these agents for 1 week for the injectable form and 1 day for the oral form before all procedures requiring anesthesia.
That abundance of caution, however, had negative impacts of its own. “This guidance has led to cancellations and postponements of many endoscopic and surgical procedures or required patients to undergo general anesthesia who may otherwise have had their procedures performed under moderate sedation,” said guidance coauthor Allison R. Schulman, MD, MPH, an associate professor of medicine and surgery and chief of endoscopy at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. “Nearly all institutions have been forced to revise preprocedural protocols, despite a lack of high-level evidence to suggest that these adjustments are necessary.”
“Studies have yielded mixed results as to whether patients on GLP-1s are at increased risk of these events, and the limited data available are inconsistent,” Schulman said. “As a result, there are inconsistencies in the recommendations from various societies leading to growing uncertainty with proceduralists on how to provide safe, effective, and timely procedural care to patients taking GLP-1 RAs.”
The new joint-society guidance may alleviate some of the uncertainty. Among the recommendations:
- Continuing GLP-1 RAs in the perioperative period should be based on shared decision-making with the patient and all care teams balancing the metabolic need for the GLP-1 RA with individual patient risk.
- Certain variables may increase the risk for delayed gastric emptying and aspiration with the periprocedural use of GLP-1 RAs: escalation phase — This phase vs the maintenance phase is associated with a higher risk for delayed gastric emptying; higher dose — the higher the dose, the greater the risk for gastrointestinal (GI) side effects; weekly dosing — GI side effects are more common with weekly vs daily formulations; presence of GI symptoms — nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, and constipation may suggest delayed gastric emptying; and medical problems beyond GLP-1 RA indications with GI effects — assess for such conditions as bowel dysmotility, gastroparesis, and Parkinson’s disease.
- Risk factors should be assessed in advance to allow sufficient time to adjust preoperative care, including diet modification and medication bridging if GLP-1 RA cessation is deemed advisable.
- If retained gastric contents are a concern on the day of a procedure, point-of-care gastric ultrasound could be used to assess aspiration risk, resources permitting.
- The aspiration risk from delayed gastric emptying should be minimized by preoperative diet modification and/or altering the anesthesia plan to consider rapid sequence induction of general anesthesia for tracheal intubation. A 24-hour preoperative liquid diet, as before colonoscopy and bariatric surgery, can be utilized when delayed gastric emptying is a concern.
- When concern about retained gastric contents exists on procedure day, providers should engage patients in a shared decision-making model and consider the benefits and risks of rapid-sequence induction of general anesthesia for tracheal intubation to minimize aspiration risk vs procedure cancellation.
“Safe continuation of surgery and gastrointestinal endoscopy, and prevention of procedure cancellation, for patients on GLP-1 RAs can be prioritized following the recommendations above, as would occur for other patient populations with gastroparesis,” the guidance panel wrote.
Commenting on the statement but not involved in it, David B. Purow, MD, managing director of the Digestive Health Center at Northwell Health/Huntington Hospital in Huntington, New York, said the recommendations will encourage clinicians to be more discerning about actual risk in individual cases rather than follow the previous blanket recommendation to stop these agents before procedures requiring sedation.
While GLP-1 RAs were prescribed for the relatively small number of patients with diabetes, he said, the risk was not apparent but became clearer with the widespread use of these agents for weight loss — often unregulated and undisclosed to care providers.
“The pendulum shifted too far the other way, and now it’s shifted back,” he said in an interview. “The new guidance is great because now we can be more thoughtful about managing individual patients.” He cited, for instance, the recommendations on the greater risk in patients in the dose escalation phase or on higher doses, and the risk-reducing measure of a liquid diet for 24 hours before surgery.
His center is already using point-of-care ultrasound and recently had a case in which a patient who forgot and took his GLP-1 RA before a scheduled procedure was found on ultrasound to have a full stomach. “In some cases, these drugs can cause an almost gastroparesis level of delayed emptying,” Purow said.
Purow thinks this early guidance will probably progress to firm guidelines within a year. Schulman is more cautious. “Our understanding of this complex topic is increasing rapidly, and ongoing clinical research will ultimately lead to evidence-based guidelines in this changing landscape,” she said.
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. Schulman is a consultant for Apollo Endosurgery, Boston Scientific, Olympus, Microtech, and Fractyl. Purow had no competing interests to declare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new guidance, contrasting with earlier recommendations, says these incrementally used agents can be taken up until the day of surgery, but patients are advised to follow a liquid diet for 24 hours before the procedure. The decision to proceed with endoscopy and other procedures should be based on shared decision-making with the patient and interdisciplinary care teams in conjunction with minimization of the aspiration risk from delayed gastric emptying, the guidance stresses.
The five endorsing organizations are the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA), American Gastroenterological Association, International Society of Perioperative Care of Patients with Obesity, and Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons. The societies emphasize that the statement is intended as guidance only and is not an evidence-based formal guideline.
GLP-1 RAs are known to delay gastric emptying, raising concerns about regurgitation, aspiration, and airway compromise during anesthesia. Rare serious adverse events have also been observed, prompting the ASA in 2023 to recommend holding these agents for 1 week for the injectable form and 1 day for the oral form before all procedures requiring anesthesia.
That abundance of caution, however, had negative impacts of its own. “This guidance has led to cancellations and postponements of many endoscopic and surgical procedures or required patients to undergo general anesthesia who may otherwise have had their procedures performed under moderate sedation,” said guidance coauthor Allison R. Schulman, MD, MPH, an associate professor of medicine and surgery and chief of endoscopy at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. “Nearly all institutions have been forced to revise preprocedural protocols, despite a lack of high-level evidence to suggest that these adjustments are necessary.”
“Studies have yielded mixed results as to whether patients on GLP-1s are at increased risk of these events, and the limited data available are inconsistent,” Schulman said. “As a result, there are inconsistencies in the recommendations from various societies leading to growing uncertainty with proceduralists on how to provide safe, effective, and timely procedural care to patients taking GLP-1 RAs.”
The new joint-society guidance may alleviate some of the uncertainty. Among the recommendations:
- Continuing GLP-1 RAs in the perioperative period should be based on shared decision-making with the patient and all care teams balancing the metabolic need for the GLP-1 RA with individual patient risk.
- Certain variables may increase the risk for delayed gastric emptying and aspiration with the periprocedural use of GLP-1 RAs: escalation phase — This phase vs the maintenance phase is associated with a higher risk for delayed gastric emptying; higher dose — the higher the dose, the greater the risk for gastrointestinal (GI) side effects; weekly dosing — GI side effects are more common with weekly vs daily formulations; presence of GI symptoms — nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, and constipation may suggest delayed gastric emptying; and medical problems beyond GLP-1 RA indications with GI effects — assess for such conditions as bowel dysmotility, gastroparesis, and Parkinson’s disease.
- Risk factors should be assessed in advance to allow sufficient time to adjust preoperative care, including diet modification and medication bridging if GLP-1 RA cessation is deemed advisable.
- If retained gastric contents are a concern on the day of a procedure, point-of-care gastric ultrasound could be used to assess aspiration risk, resources permitting.
- The aspiration risk from delayed gastric emptying should be minimized by preoperative diet modification and/or altering the anesthesia plan to consider rapid sequence induction of general anesthesia for tracheal intubation. A 24-hour preoperative liquid diet, as before colonoscopy and bariatric surgery, can be utilized when delayed gastric emptying is a concern.
- When concern about retained gastric contents exists on procedure day, providers should engage patients in a shared decision-making model and consider the benefits and risks of rapid-sequence induction of general anesthesia for tracheal intubation to minimize aspiration risk vs procedure cancellation.
“Safe continuation of surgery and gastrointestinal endoscopy, and prevention of procedure cancellation, for patients on GLP-1 RAs can be prioritized following the recommendations above, as would occur for other patient populations with gastroparesis,” the guidance panel wrote.
Commenting on the statement but not involved in it, David B. Purow, MD, managing director of the Digestive Health Center at Northwell Health/Huntington Hospital in Huntington, New York, said the recommendations will encourage clinicians to be more discerning about actual risk in individual cases rather than follow the previous blanket recommendation to stop these agents before procedures requiring sedation.
While GLP-1 RAs were prescribed for the relatively small number of patients with diabetes, he said, the risk was not apparent but became clearer with the widespread use of these agents for weight loss — often unregulated and undisclosed to care providers.
“The pendulum shifted too far the other way, and now it’s shifted back,” he said in an interview. “The new guidance is great because now we can be more thoughtful about managing individual patients.” He cited, for instance, the recommendations on the greater risk in patients in the dose escalation phase or on higher doses, and the risk-reducing measure of a liquid diet for 24 hours before surgery.
His center is already using point-of-care ultrasound and recently had a case in which a patient who forgot and took his GLP-1 RA before a scheduled procedure was found on ultrasound to have a full stomach. “In some cases, these drugs can cause an almost gastroparesis level of delayed emptying,” Purow said.
Purow thinks this early guidance will probably progress to firm guidelines within a year. Schulman is more cautious. “Our understanding of this complex topic is increasing rapidly, and ongoing clinical research will ultimately lead to evidence-based guidelines in this changing landscape,” she said.
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. Schulman is a consultant for Apollo Endosurgery, Boston Scientific, Olympus, Microtech, and Fractyl. Purow had no competing interests to declare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Shorter H pylori Treatment With Vonoprazan Shows Better Results
PHILADELPHIA — with omeprazole, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin, according to the results of a randomized, multicenter study.
In addition, the triple therapy regimen with vonoprazan was generally better tolerated than the 14-day omeprazole-based regimen.
The new treatment combination was created to tackle the two main reasons that patients with H pylori experience treatment failure: Inadequate acid suppressant activity and antibiotic resistance, said principal investigator Kachonsak Yongwatana, MD, from Phramongkutklao Hospital in Bangkok, Thailand.
“Vonoprazan” is the more potent option for acid suppression, and “levofloxacin” addresses antibiotic resistance, he explained.
Yongwatana presented the findings (Abstract 41) at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting. The ACG recently released a clinical guideline on the treatment of H pylori infection.
Robust Eradication Rates
Yongwatana and colleagues enrolled adult patients with H pylori infections at four hospitals in Thailand between December 2022 and September 2023. The presence of H pylori was confirmed by upper gastrointestinal endoscopy with positive rapid urease test or positive test on tissue biopsy.
Patients were then randomized into two treatment groups: The 10-day VAL group (vonoprazan 20 mg twice daily, amoxicillin 1000 mg twice daily, and levofloxacin 500 mg once daily for 10 days) and the 14-day OAC group (omeprazole 20 mg twice daily, amoxicillin 1000 mg twice daily, and clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily for 14 days). Eradication was assessed by urea breath test 4 weeks after completion of treatment.
There were 280 patients in total, with 140 in each group. There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics between the groups. The most common endoscopic findings among all participants included erosive gastritis (38%), nonerosive gastritis (27%), and gastric ulcer (17%).
In comparing the treatments, the researchers found that 10-day VAL led to significantly greater H pylori eradication rate than the 14-day OAC group in both intention-to-treat analysis (91.4 % vs 80.7%, P = .009) and per-protocol analysis (93.4% vs 83.7%, P = .012).
Vonoprazan-based therapy was also well tolerated by participants. Patients in the 10-day VAL group had significantly lower rates of experiencing a bitter taste (2.1% vs 42.9%, P < .001) and bloating (5% vs 12.1%, P = .033) than those in the 14-day OAC group.
Isolating the BMI Effect
The researchers conducted a subgroup analysis on potential factors influencing response, which revealed that having a body mass index (BMI) < 23.5 was significantly associated with a higher chance at successful H pylori eradication (relative risk [RR], 2.27; P = .049).
They then analyzed whether this BMI threshold was predictive in the separate treatment regimens. Although having a BMI < 23.5 was significantly associated with a higher eradication rate in the 14-day OAC group (RR, 3.34; P = .026), no such effect was noted in the 10-day VAL group (RR, 1.10; P = .888).
The influence of BMI could be caused by the bioavailability of the treatments used in the regimen, Younwatana said in an interview. He and his colleagues recommended against using the 14-day OAC regimen in those with BMI ≥ 23.5.
“In patients with a high BMI, we should be concerned that normal proton pump inhibitors may not work,” he said. “You have to step up to the higher-potency options.”
Seeking Confirmation in Other Populations
Session comoderator Felice Schnoll-Sussman, MD, MSc, professor of clinical medicine and the director of the Jay Monahan Center for Gastrointestinal Health, director of the DIGEST program, and the associate chair of medicine for Outreach and Network at New York–Presbyterian Brooklyn Methodist Hospital in New York City, said in an interview that the promising results merit confirmation in other populations.
“When you see a study that is coming out of one country, when there could be issues related to antibiotic sensitivity in H pylori, it really is important to decide whether or not this is applicable to other patient populations,” said Schnoll-Sussman, who was not involved in the study.
She noted that this is also true of the findings from the subgroup as it is unclear whether average rates of BMI are notably lower in Thailand from other countries.
“As we know, BMI affects so many things with disease states. So, it’s a possibility in a country where the BMI is actually lower, there may be something else about these individuals in terms of their wellness status that could be underlying the effect.”
The study had no specific funding, although Takeda supplied treatments used in the analysis. Yongwatana reported no relevant financial relationships. Schnoll-Sussman reported serving as an advisory committee/board member for Braintree, Ethicon, Implantica, and Phathom.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA — with omeprazole, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin, according to the results of a randomized, multicenter study.
In addition, the triple therapy regimen with vonoprazan was generally better tolerated than the 14-day omeprazole-based regimen.
The new treatment combination was created to tackle the two main reasons that patients with H pylori experience treatment failure: Inadequate acid suppressant activity and antibiotic resistance, said principal investigator Kachonsak Yongwatana, MD, from Phramongkutklao Hospital in Bangkok, Thailand.
“Vonoprazan” is the more potent option for acid suppression, and “levofloxacin” addresses antibiotic resistance, he explained.
Yongwatana presented the findings (Abstract 41) at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting. The ACG recently released a clinical guideline on the treatment of H pylori infection.
Robust Eradication Rates
Yongwatana and colleagues enrolled adult patients with H pylori infections at four hospitals in Thailand between December 2022 and September 2023. The presence of H pylori was confirmed by upper gastrointestinal endoscopy with positive rapid urease test or positive test on tissue biopsy.
Patients were then randomized into two treatment groups: The 10-day VAL group (vonoprazan 20 mg twice daily, amoxicillin 1000 mg twice daily, and levofloxacin 500 mg once daily for 10 days) and the 14-day OAC group (omeprazole 20 mg twice daily, amoxicillin 1000 mg twice daily, and clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily for 14 days). Eradication was assessed by urea breath test 4 weeks after completion of treatment.
There were 280 patients in total, with 140 in each group. There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics between the groups. The most common endoscopic findings among all participants included erosive gastritis (38%), nonerosive gastritis (27%), and gastric ulcer (17%).
In comparing the treatments, the researchers found that 10-day VAL led to significantly greater H pylori eradication rate than the 14-day OAC group in both intention-to-treat analysis (91.4 % vs 80.7%, P = .009) and per-protocol analysis (93.4% vs 83.7%, P = .012).
Vonoprazan-based therapy was also well tolerated by participants. Patients in the 10-day VAL group had significantly lower rates of experiencing a bitter taste (2.1% vs 42.9%, P < .001) and bloating (5% vs 12.1%, P = .033) than those in the 14-day OAC group.
Isolating the BMI Effect
The researchers conducted a subgroup analysis on potential factors influencing response, which revealed that having a body mass index (BMI) < 23.5 was significantly associated with a higher chance at successful H pylori eradication (relative risk [RR], 2.27; P = .049).
They then analyzed whether this BMI threshold was predictive in the separate treatment regimens. Although having a BMI < 23.5 was significantly associated with a higher eradication rate in the 14-day OAC group (RR, 3.34; P = .026), no such effect was noted in the 10-day VAL group (RR, 1.10; P = .888).
The influence of BMI could be caused by the bioavailability of the treatments used in the regimen, Younwatana said in an interview. He and his colleagues recommended against using the 14-day OAC regimen in those with BMI ≥ 23.5.
“In patients with a high BMI, we should be concerned that normal proton pump inhibitors may not work,” he said. “You have to step up to the higher-potency options.”
Seeking Confirmation in Other Populations
Session comoderator Felice Schnoll-Sussman, MD, MSc, professor of clinical medicine and the director of the Jay Monahan Center for Gastrointestinal Health, director of the DIGEST program, and the associate chair of medicine for Outreach and Network at New York–Presbyterian Brooklyn Methodist Hospital in New York City, said in an interview that the promising results merit confirmation in other populations.
“When you see a study that is coming out of one country, when there could be issues related to antibiotic sensitivity in H pylori, it really is important to decide whether or not this is applicable to other patient populations,” said Schnoll-Sussman, who was not involved in the study.
She noted that this is also true of the findings from the subgroup as it is unclear whether average rates of BMI are notably lower in Thailand from other countries.
“As we know, BMI affects so many things with disease states. So, it’s a possibility in a country where the BMI is actually lower, there may be something else about these individuals in terms of their wellness status that could be underlying the effect.”
The study had no specific funding, although Takeda supplied treatments used in the analysis. Yongwatana reported no relevant financial relationships. Schnoll-Sussman reported serving as an advisory committee/board member for Braintree, Ethicon, Implantica, and Phathom.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA — with omeprazole, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin, according to the results of a randomized, multicenter study.
In addition, the triple therapy regimen with vonoprazan was generally better tolerated than the 14-day omeprazole-based regimen.
The new treatment combination was created to tackle the two main reasons that patients with H pylori experience treatment failure: Inadequate acid suppressant activity and antibiotic resistance, said principal investigator Kachonsak Yongwatana, MD, from Phramongkutklao Hospital in Bangkok, Thailand.
“Vonoprazan” is the more potent option for acid suppression, and “levofloxacin” addresses antibiotic resistance, he explained.
Yongwatana presented the findings (Abstract 41) at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting. The ACG recently released a clinical guideline on the treatment of H pylori infection.
Robust Eradication Rates
Yongwatana and colleagues enrolled adult patients with H pylori infections at four hospitals in Thailand between December 2022 and September 2023. The presence of H pylori was confirmed by upper gastrointestinal endoscopy with positive rapid urease test or positive test on tissue biopsy.
Patients were then randomized into two treatment groups: The 10-day VAL group (vonoprazan 20 mg twice daily, amoxicillin 1000 mg twice daily, and levofloxacin 500 mg once daily for 10 days) and the 14-day OAC group (omeprazole 20 mg twice daily, amoxicillin 1000 mg twice daily, and clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily for 14 days). Eradication was assessed by urea breath test 4 weeks after completion of treatment.
There were 280 patients in total, with 140 in each group. There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics between the groups. The most common endoscopic findings among all participants included erosive gastritis (38%), nonerosive gastritis (27%), and gastric ulcer (17%).
In comparing the treatments, the researchers found that 10-day VAL led to significantly greater H pylori eradication rate than the 14-day OAC group in both intention-to-treat analysis (91.4 % vs 80.7%, P = .009) and per-protocol analysis (93.4% vs 83.7%, P = .012).
Vonoprazan-based therapy was also well tolerated by participants. Patients in the 10-day VAL group had significantly lower rates of experiencing a bitter taste (2.1% vs 42.9%, P < .001) and bloating (5% vs 12.1%, P = .033) than those in the 14-day OAC group.
Isolating the BMI Effect
The researchers conducted a subgroup analysis on potential factors influencing response, which revealed that having a body mass index (BMI) < 23.5 was significantly associated with a higher chance at successful H pylori eradication (relative risk [RR], 2.27; P = .049).
They then analyzed whether this BMI threshold was predictive in the separate treatment regimens. Although having a BMI < 23.5 was significantly associated with a higher eradication rate in the 14-day OAC group (RR, 3.34; P = .026), no such effect was noted in the 10-day VAL group (RR, 1.10; P = .888).
The influence of BMI could be caused by the bioavailability of the treatments used in the regimen, Younwatana said in an interview. He and his colleagues recommended against using the 14-day OAC regimen in those with BMI ≥ 23.5.
“In patients with a high BMI, we should be concerned that normal proton pump inhibitors may not work,” he said. “You have to step up to the higher-potency options.”
Seeking Confirmation in Other Populations
Session comoderator Felice Schnoll-Sussman, MD, MSc, professor of clinical medicine and the director of the Jay Monahan Center for Gastrointestinal Health, director of the DIGEST program, and the associate chair of medicine for Outreach and Network at New York–Presbyterian Brooklyn Methodist Hospital in New York City, said in an interview that the promising results merit confirmation in other populations.
“When you see a study that is coming out of one country, when there could be issues related to antibiotic sensitivity in H pylori, it really is important to decide whether or not this is applicable to other patient populations,” said Schnoll-Sussman, who was not involved in the study.
She noted that this is also true of the findings from the subgroup as it is unclear whether average rates of BMI are notably lower in Thailand from other countries.
“As we know, BMI affects so many things with disease states. So, it’s a possibility in a country where the BMI is actually lower, there may be something else about these individuals in terms of their wellness status that could be underlying the effect.”
The study had no specific funding, although Takeda supplied treatments used in the analysis. Yongwatana reported no relevant financial relationships. Schnoll-Sussman reported serving as an advisory committee/board member for Braintree, Ethicon, Implantica, and Phathom.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACG 2024
Weight Loss Surgery, Obesity Drugs Achieve Similar Results but Have Different Safety Profiles
PHILADELPHIA — according to a meta-analysis comparing the efficacy and safety of the different treatment options.
However, tirzepatide, a long-acting glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptor agonist and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA), produces comparable weight loss and has a favorable safety profile, reported principal investigator Jena Velji-Ibrahim, MD, MSc, from Prisma Health–Upstate/University of South Carolina School of Medicine in Greenville.
In addition, there was “no significant difference in percentage total body weight loss between tirzepatide when comparing it to one-anastomosis gastric bypass (OAGB), as well as laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy,” she said.
All 11 interventions studied exerted weight loss effects, and side-effect profiles were also deemed largely favorable, particularly for endoscopic interventions, she added.
“When we compare bariatric surgery to bariatric endoscopy, endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty and transpyloric shuttle offer a minimally invasive alternative with good weight loss outcomes and fewer adverse events,” she said.
Velji-Ibrahim presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG).
Comparing Weight Loss Interventions
Many of the studies comparing weight loss interventions to date have been limited by relatively small sample sizes, observational designs, and inconsistent results. This prompted Velji-Ibrahim and her colleagues to conduct what they believe to be the first-of-its-kind meta-analysis on this topic.
They began by conducting a systematic search of the literature to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared the efficacy of Food and Drug Administration–approved bariatric surgeries, bariatric endoscopies, and medications — against each other or with placebo — in adults with a body mass index of 25-45, with or without concurrent type 2 diabetes.
A network meta-analysis was then performed to assess the various interventions’ impact on percentage total weight loss and side-effect profiles. P-scores were calculated to rank the treatments and identify the preferred interventions. The duration of therapy was 52 weeks.
In total, 34 eligible RCTs with 15,660 patients were included. Overall, the RCTs analyzed 11 weight loss treatments, including bariatric surgeries (four studies), bariatric endoscopies (three studies), and medications (four studies).
Specifically, the bariatric surgeries included RYGB, laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, OAGB, and laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding; bariatric endoscopies included endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty, transpyloric shuttle, and intragastric balloon; and medications included tirzepatide, semaglutide, and liraglutide.
Although all interventions were associated with reductions in percentage total weight loss compared with placebo, RYGB led to the greatest reductions (19.29%) and was ranked as the first preferred treatment (97% probability). It was followed in the rankings by OAGB, tirzepatide 15 mg, laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, and semaglutide 2.4 mg.
Tirzepatide 15 mg had a slightly lower percentage total weight loss (15.18%) but a favorable safety profile. There was no significant difference in percentage total weight loss between tirzepatide 15 mg and OAGB (mean difference, 2.97%) or laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (mean difference, 0.43%).
There was also no significant difference in percentage total weight loss between semaglutide 2.4 mg, compared with endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty and transpyloric shuttle.
Endoscopic sleeve, transpyloric shuttle, and intragastric balloon all resulted in weight loss > 5%.
When compared with bariatric surgery, “endoscopic interventions had a better side-effect profile, with no increased odds of mortality and intensive care needs,” Velji-Ibrahim said.
When it came to the medications, “the most common side effects were gastrointestinal in nature, which included nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation,” she said.
Combining, Rather Than Comparing, Therapies
Following the presentation, session co-moderator Shivangi T. Kothari, MD, assistant professor of medicine and associate director of endoscopy at the University of Rochester Medical Center in New York, shared her thoughts of what the future of obesity management research might look like.
It’s not just going to be about percentage total weight loss, she said, but about how well the effect is sustained following the intervention.
And we might move “away from comparing one modality to another” and instead study combination therapies, “which would be ideal,” said Kothari.
This was the focus of another meta-analysis presented at ACG 2024, in which Nihal Ijaz I. Khan, MD, and colleagues compared the efficacy of endoscopic bariatric treatment alone vs its combined use with GLP-1 RAs.
The researchers identified three retrospective studies with 266 patients, of whom 143 underwent endoscopic bariatric treatment alone (either endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty or intragastric balloon) and 123 had it combined with GLP-1 RAs, specifically liraglutide.
They reported that superior absolute weight loss was achieved in the group of patients receiving GLP-1 RAs in combination with endoscopic bariatric treatment. The standardized mean difference in body weight loss at treatment follow-up was 0.61 (P <.01).
“Further studies are required to evaluate the safety and adverse events comparing these two treatment modalities and to discover differences between comparing the two endoscopic options to various GLP-1 receptor agonists,” Khan noted.
Neither study had specific funding. Velji-Ibrahim and Khan reported no relevant financial relationships. Kothari reported serving as a consultant for Boston Scientific and Olympus, as well as serving as an advisory committee/board member for Castle Biosciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA — according to a meta-analysis comparing the efficacy and safety of the different treatment options.
However, tirzepatide, a long-acting glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptor agonist and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA), produces comparable weight loss and has a favorable safety profile, reported principal investigator Jena Velji-Ibrahim, MD, MSc, from Prisma Health–Upstate/University of South Carolina School of Medicine in Greenville.
In addition, there was “no significant difference in percentage total body weight loss between tirzepatide when comparing it to one-anastomosis gastric bypass (OAGB), as well as laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy,” she said.
All 11 interventions studied exerted weight loss effects, and side-effect profiles were also deemed largely favorable, particularly for endoscopic interventions, she added.
“When we compare bariatric surgery to bariatric endoscopy, endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty and transpyloric shuttle offer a minimally invasive alternative with good weight loss outcomes and fewer adverse events,” she said.
Velji-Ibrahim presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG).
Comparing Weight Loss Interventions
Many of the studies comparing weight loss interventions to date have been limited by relatively small sample sizes, observational designs, and inconsistent results. This prompted Velji-Ibrahim and her colleagues to conduct what they believe to be the first-of-its-kind meta-analysis on this topic.
They began by conducting a systematic search of the literature to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared the efficacy of Food and Drug Administration–approved bariatric surgeries, bariatric endoscopies, and medications — against each other or with placebo — in adults with a body mass index of 25-45, with or without concurrent type 2 diabetes.
A network meta-analysis was then performed to assess the various interventions’ impact on percentage total weight loss and side-effect profiles. P-scores were calculated to rank the treatments and identify the preferred interventions. The duration of therapy was 52 weeks.
In total, 34 eligible RCTs with 15,660 patients were included. Overall, the RCTs analyzed 11 weight loss treatments, including bariatric surgeries (four studies), bariatric endoscopies (three studies), and medications (four studies).
Specifically, the bariatric surgeries included RYGB, laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, OAGB, and laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding; bariatric endoscopies included endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty, transpyloric shuttle, and intragastric balloon; and medications included tirzepatide, semaglutide, and liraglutide.
Although all interventions were associated with reductions in percentage total weight loss compared with placebo, RYGB led to the greatest reductions (19.29%) and was ranked as the first preferred treatment (97% probability). It was followed in the rankings by OAGB, tirzepatide 15 mg, laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, and semaglutide 2.4 mg.
Tirzepatide 15 mg had a slightly lower percentage total weight loss (15.18%) but a favorable safety profile. There was no significant difference in percentage total weight loss between tirzepatide 15 mg and OAGB (mean difference, 2.97%) or laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (mean difference, 0.43%).
There was also no significant difference in percentage total weight loss between semaglutide 2.4 mg, compared with endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty and transpyloric shuttle.
Endoscopic sleeve, transpyloric shuttle, and intragastric balloon all resulted in weight loss > 5%.
When compared with bariatric surgery, “endoscopic interventions had a better side-effect profile, with no increased odds of mortality and intensive care needs,” Velji-Ibrahim said.
When it came to the medications, “the most common side effects were gastrointestinal in nature, which included nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation,” she said.
Combining, Rather Than Comparing, Therapies
Following the presentation, session co-moderator Shivangi T. Kothari, MD, assistant professor of medicine and associate director of endoscopy at the University of Rochester Medical Center in New York, shared her thoughts of what the future of obesity management research might look like.
It’s not just going to be about percentage total weight loss, she said, but about how well the effect is sustained following the intervention.
And we might move “away from comparing one modality to another” and instead study combination therapies, “which would be ideal,” said Kothari.
This was the focus of another meta-analysis presented at ACG 2024, in which Nihal Ijaz I. Khan, MD, and colleagues compared the efficacy of endoscopic bariatric treatment alone vs its combined use with GLP-1 RAs.
The researchers identified three retrospective studies with 266 patients, of whom 143 underwent endoscopic bariatric treatment alone (either endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty or intragastric balloon) and 123 had it combined with GLP-1 RAs, specifically liraglutide.
They reported that superior absolute weight loss was achieved in the group of patients receiving GLP-1 RAs in combination with endoscopic bariatric treatment. The standardized mean difference in body weight loss at treatment follow-up was 0.61 (P <.01).
“Further studies are required to evaluate the safety and adverse events comparing these two treatment modalities and to discover differences between comparing the two endoscopic options to various GLP-1 receptor agonists,” Khan noted.
Neither study had specific funding. Velji-Ibrahim and Khan reported no relevant financial relationships. Kothari reported serving as a consultant for Boston Scientific and Olympus, as well as serving as an advisory committee/board member for Castle Biosciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA — according to a meta-analysis comparing the efficacy and safety of the different treatment options.
However, tirzepatide, a long-acting glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptor agonist and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA), produces comparable weight loss and has a favorable safety profile, reported principal investigator Jena Velji-Ibrahim, MD, MSc, from Prisma Health–Upstate/University of South Carolina School of Medicine in Greenville.
In addition, there was “no significant difference in percentage total body weight loss between tirzepatide when comparing it to one-anastomosis gastric bypass (OAGB), as well as laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy,” she said.
All 11 interventions studied exerted weight loss effects, and side-effect profiles were also deemed largely favorable, particularly for endoscopic interventions, she added.
“When we compare bariatric surgery to bariatric endoscopy, endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty and transpyloric shuttle offer a minimally invasive alternative with good weight loss outcomes and fewer adverse events,” she said.
Velji-Ibrahim presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG).
Comparing Weight Loss Interventions
Many of the studies comparing weight loss interventions to date have been limited by relatively small sample sizes, observational designs, and inconsistent results. This prompted Velji-Ibrahim and her colleagues to conduct what they believe to be the first-of-its-kind meta-analysis on this topic.
They began by conducting a systematic search of the literature to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared the efficacy of Food and Drug Administration–approved bariatric surgeries, bariatric endoscopies, and medications — against each other or with placebo — in adults with a body mass index of 25-45, with or without concurrent type 2 diabetes.
A network meta-analysis was then performed to assess the various interventions’ impact on percentage total weight loss and side-effect profiles. P-scores were calculated to rank the treatments and identify the preferred interventions. The duration of therapy was 52 weeks.
In total, 34 eligible RCTs with 15,660 patients were included. Overall, the RCTs analyzed 11 weight loss treatments, including bariatric surgeries (four studies), bariatric endoscopies (three studies), and medications (four studies).
Specifically, the bariatric surgeries included RYGB, laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, OAGB, and laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding; bariatric endoscopies included endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty, transpyloric shuttle, and intragastric balloon; and medications included tirzepatide, semaglutide, and liraglutide.
Although all interventions were associated with reductions in percentage total weight loss compared with placebo, RYGB led to the greatest reductions (19.29%) and was ranked as the first preferred treatment (97% probability). It was followed in the rankings by OAGB, tirzepatide 15 mg, laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, and semaglutide 2.4 mg.
Tirzepatide 15 mg had a slightly lower percentage total weight loss (15.18%) but a favorable safety profile. There was no significant difference in percentage total weight loss between tirzepatide 15 mg and OAGB (mean difference, 2.97%) or laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (mean difference, 0.43%).
There was also no significant difference in percentage total weight loss between semaglutide 2.4 mg, compared with endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty and transpyloric shuttle.
Endoscopic sleeve, transpyloric shuttle, and intragastric balloon all resulted in weight loss > 5%.
When compared with bariatric surgery, “endoscopic interventions had a better side-effect profile, with no increased odds of mortality and intensive care needs,” Velji-Ibrahim said.
When it came to the medications, “the most common side effects were gastrointestinal in nature, which included nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation,” she said.
Combining, Rather Than Comparing, Therapies
Following the presentation, session co-moderator Shivangi T. Kothari, MD, assistant professor of medicine and associate director of endoscopy at the University of Rochester Medical Center in New York, shared her thoughts of what the future of obesity management research might look like.
It’s not just going to be about percentage total weight loss, she said, but about how well the effect is sustained following the intervention.
And we might move “away from comparing one modality to another” and instead study combination therapies, “which would be ideal,” said Kothari.
This was the focus of another meta-analysis presented at ACG 2024, in which Nihal Ijaz I. Khan, MD, and colleagues compared the efficacy of endoscopic bariatric treatment alone vs its combined use with GLP-1 RAs.
The researchers identified three retrospective studies with 266 patients, of whom 143 underwent endoscopic bariatric treatment alone (either endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty or intragastric balloon) and 123 had it combined with GLP-1 RAs, specifically liraglutide.
They reported that superior absolute weight loss was achieved in the group of patients receiving GLP-1 RAs in combination with endoscopic bariatric treatment. The standardized mean difference in body weight loss at treatment follow-up was 0.61 (P <.01).
“Further studies are required to evaluate the safety and adverse events comparing these two treatment modalities and to discover differences between comparing the two endoscopic options to various GLP-1 receptor agonists,” Khan noted.
Neither study had specific funding. Velji-Ibrahim and Khan reported no relevant financial relationships. Kothari reported serving as a consultant for Boston Scientific and Olympus, as well as serving as an advisory committee/board member for Castle Biosciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACG 2024
Medical, Endoscopic, and Surgical Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Introduction
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a frequently encountered condition, and rising annually.1 A recent meta-analysis suggests nearly 14% (1.03 billion) of the population are affected worldwide. Differences may range by region from 12% in Latin America to 20% in North America, and by country from 4% in China to 23% in Turkey.1 In the United States, 21% of the population are afflicted with weekly GERD symptoms.2 Novel medical therapies and endoscopic options provide clinicians with opportunities to help patients with GERD.3
Diagnosis
Definition
GERD was originally defined by the Montreal consensus as a condition that develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications.4 Heartburn and regurgitation are common symptoms of GERD, with a sensitivity of 30%-76% and specificity of 62%-96% for erosive esophagitis (EE), which occurs when the reflux of stomach content causes esophageal mucosal breaks.5 The presence of characteristic mucosal injury observed during an upper endoscopy or abnormal esophageal acid exposure on ambulatory reflux monitoring are objective evidence of GERD. A trial of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) may function as a diagnostic test for patients exhibiting the typical symptoms of GERD without any alarm symptoms.3,6
Endoscopic Evaluation and Confirmation
The 2022 American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) clinical practice update recommends diagnostic endoscopy, after PPIs are stopped for 2-4 weeks, in patients whose GERD symptoms do not respond adequately to an empiric trial of a PPI.3 Those with GERD and alarm symptoms such as dysphagia, weight loss, bleeding, and vomiting should undergo endoscopy as soon as possible. Endoscopic findings of EE (Los Angeles Grade B or more severe) and long-segment Barrett’s esophagus (> 3-cm segment with intestinal metaplasia on biopsy) are diagnostic of GERD.3
Reflux Monitoring
With ambulatory reflux monitoring (pH or impedance-pH), esophageal acid exposure (or neutral refluxate in impedance testing) can be measured to confirm GERD diagnosis and to correlate symptoms with reflux episodes. Patients with atypical GERD symptoms or patients with a confirmed diagnosis of GERD whose symptoms have not improved sufficiently with twice-daily PPI therapy should have esophageal impedance-pH monitoring while on PPIs.6,7
Esophageal Manometry
High-resolution esophageal manometry can be used to assess motility abnormalities associated with GERD.
Although no manometric abnormality is unique to GERD, weak lower esophageal sphincter (LES) resting pressure and ineffective esophageal motility frequently coexist with severe GERD.6
Manometry is particularly useful in patients considering surgical or endoscopic anti-reflux procedures to evaluate for achalasia,3 an important contraindication to surgery.
Medical Management
Management of GERD requires a multidisciplinary and personalized approach based on symptom presentation, body mass index, endoscopic findings (e.g., presence of EE, Barrett’s esophagus, hiatal hernia), and physiological abnormalities (e.g., gastroparesis or ineffective motility).3
Lifestyle Modifications
Recommended lifestyle modifications include weight loss for patients with obesity, stress reduction, tobacco and alcohol cessation, elevating the head of the bed, staying upright during and after meals, avoidance of food intake < 3 hours before bedtime, and cessation of foods that potentially aggravate reflux symptoms such as coffee, chocolate, carbonated beverages, spicy foods, acidic foods, and foods with high fat content.6,8
Medications
Pharmacologic therapy for GERD includes medications that primarily aim to neutralize or reduce gastric acid -- we summarize options in Table 1.3,8
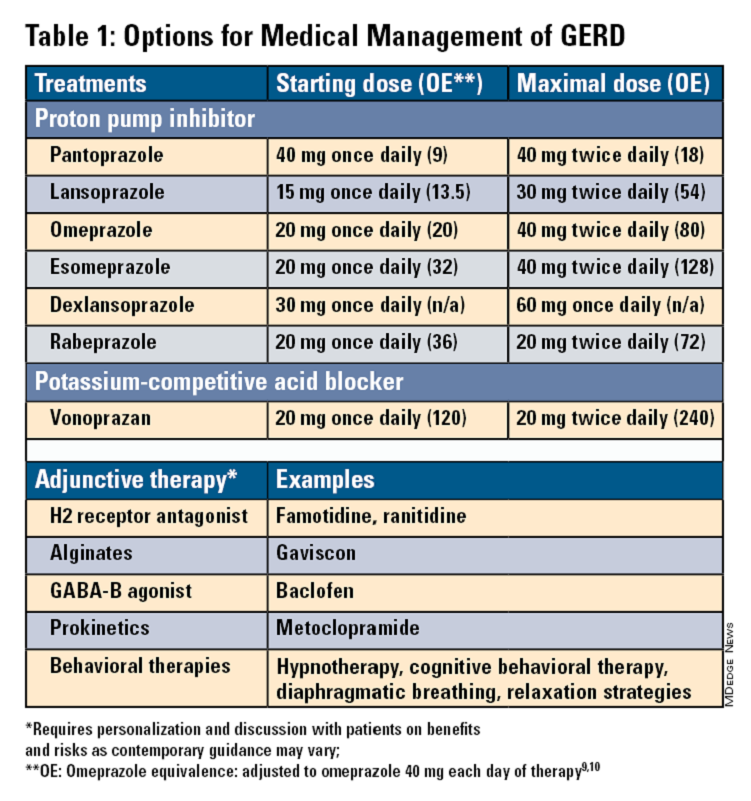
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Most guidelines suggest a trial of 4-8 weeks of once-daily enteric-coated PPI before meals in patients with typical GERD symptoms and no alarm symptoms. Escalation to double-dose PPI may be considered in the case of persistent symptoms. The relative potencies of standard-dose pantoprazole, lansoprazole, esomeprazole, and rabeprazole are presented in Table 1.9 When a PPI switch is needed, rabeprazole may be considered as it is a PPI that does not rely on CYP2C19 for primary metabolism.9
Acid suppression should be weaned down to the lowest effective dose or converted to H2RAs or other antacids once symptoms are sufficiently controlled unless patients have EE, Barrett’s esophagus, or peptic stricture.3 Patients with severe GERD may require long-term PPI therapy or an invasive anti-reflux procedure.
Recent studies have shown that potassium-competitive acid blockers (PCAB) like vonoprazan may offer more effective gastric acid inhibition. While not included in the latest clinical practice update, vonoprazan is thought to be superior to lansoprazole for those with LA Grade C/D esophagitis for both symptom relief and healing at 2 weeks.10
Adjunctive Therapies
Alginates can function as a physical barrier to even neutral reflux and may be helpful for patients with postprandial or nighttime symptoms as well as those with hiatal hernia.3 H2RAs can also help mitigate nighttime symptoms.3 Baclofen is a gamma-aminobutyric acid–B agonist which inhibits transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation (TLESR) and may be effective for patients with belching.3 Prokinetics may be helpful for GERD with concomitant gastroparesis.3 Sucralfate is a mucosal protective agent, but there is a lack of data supporting its efficacy in GERD treatment. Consider referral to a behavioral therapist for supplemental therapies, hypnotherapy, cognitive-behavior therapy, diaphragmatic breathing, and relaxation strategies for functional heartburn or reflux-associated esophageal hypervigilance or reflux hypersensitivity.3
When to Refer to Higher Level of Care
For patients who do not wish to remain on longer-term pharmacologic therapy or would benefit from anatomic repair, clinicians should have a discussion of risks and benefits prior to consideration of referral for anti-reflux procedures.3,6,8 We advise this conversation should include review of patient health status, postsurgical side effects such as increased flatus, bloating and dysphagia as well as the potential need to still resume PPI post operation.8
Endoscopic Management
Patient Selection And Evaluation
For the groups indicated for a higher level of care, we agree with AGA recommendations, multi-society guidelines, and expert review,3,7,11,12 and highlight potential options in Table 2. Step-up options should be based on patient characteristics and reviewed carefully with patients. Endoscopic therapies are less invasive than surgery and may be considered for those who do not require anatomic repair of hiatal hernia, do not want surgery, or are not suitable for surgery.
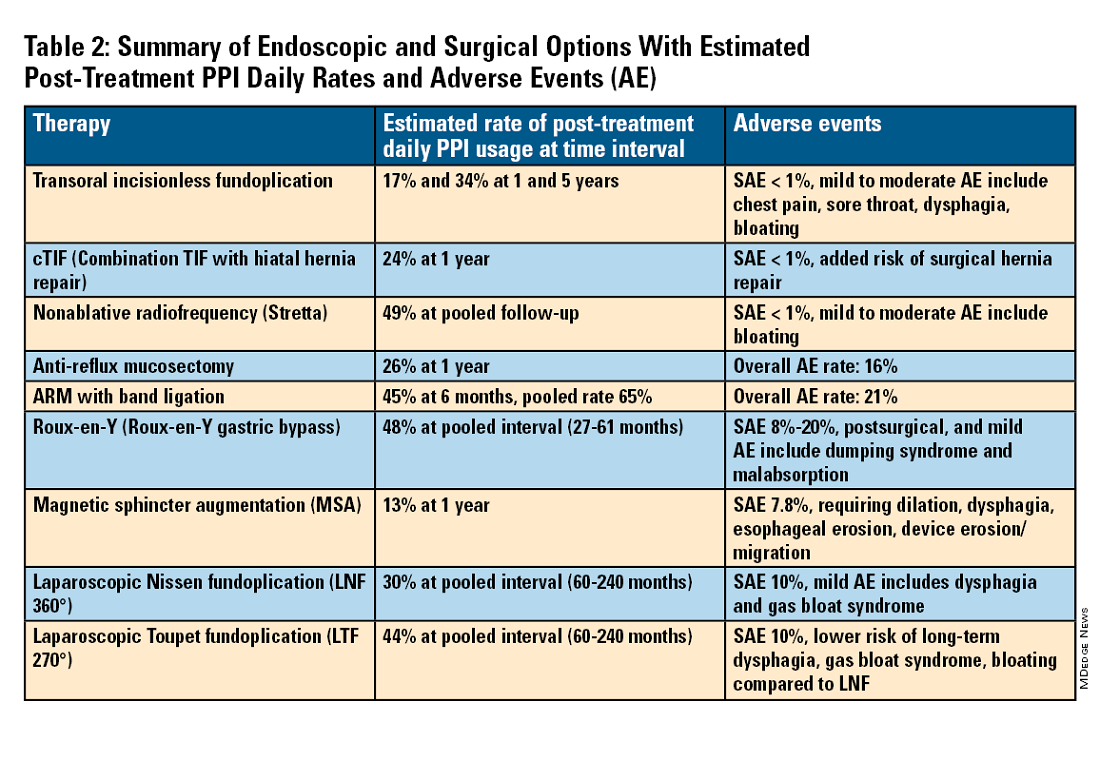
The pathophysiology of GERD is from a loss of the anti-reflux barrier of the esophageal gastric junction (EGJ) at the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) leading to unintended retrograde movement of gastric contents.6 Anatomically, the LES is composed of muscles of the distal esophagus and sling fibers of the proximal stomach, the “external valve” from the diaphragmatic crura, and the “internal valve” from the gastroesophageal flap valve (GEFV). GERD occurs from mechanical failure of the LES. First, there may be disproportional dilation of the diaphragmatic crura as categorized by Hill Grade of the GEFV as seen by a retroflexed view of EGJ after 30-45 seconds of insufflation.13 Second, there may be a migration of the LES away from the diaphragmatic crura as in the case of a hiatal hernia. Provocative maneuvers may reveal a sliding hernia by gentle retraction of the endoscope while under retroflexed view.13 Third, there may be more frequent TLESR associated with GERD.12
The aim of most interventions is to restore competency of the LES by reconstruction of the GEFV via suture or staple-based approximation of tissue.11,12 Intraluminal therapy may only target the GEFV at the internal valve. Therefore, most endoscopic interventions are limited to patients with intact diaphragmatic crura (ie, small to no hiatal hernia and GEFV Hill Grade 1 to 2). Contraindications for endoscopic therapy are moderate to severe reflux (ie, LA Grade C/ D), hiatus hernia 2 cm or larger, strictures, or long-segment Barrett’s esophagus.
Utility, Safety, and Outcomes of TIF
Historically, endoscopic therapy targeting endoscopic fundoplication started with EndoLuminal gastro-gastric fundoplication (ELF, 2005) which was a proof of concept of safe manipulation and suture for gastro-gastric plication to below the Z-line. Transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) 1.0 was suggested in 2007 for clinical application by proposing a longitudinal oriented esophago-gastric plication 1 cm above the Z-line.
In 2009, TIF2.0 was proposed as a rotational 270° wrap of the cardia and fundus to a full-thickness esophago-gastric fundoplication around 2-4 cm of the distal esophagus. Like a surgical fundoplication, this reinforces sling fibers, increases the Angle of His and improves the cardiac notch. TIF 2.0 is indicated for those with small (< 2 cm) or no hiatal hernia and a GEFV Hill Grade 1 or 2. The present iteration of TIF2.0 uses EsophyX-Z (EndoGastric Solutions; Redmond, Washington) which features dual fastener deployment and a simplified firing mechanism. Plication is secured via nonresorbable polypropylene T-fasteners with strength equivalence of 3-0 sutures.
Compared with the original, TIF2.0 represents a decrease of severe adverse events from 2%-2.5% to 0.4%-1%.11,14 Based on longitudinal TEMPO data, patient satisfaction ranges between 70% and 90% and rates of patients reverting to daily PPI use are 17% and 34% at 1 and 5 years. A 5% reintervention rate was noted to be comparable with surgical reoperation for fundoplication.15 One retrospective evaluation of patients with failed TIF followed by successful cTIF noted that in all failures there was a documented underestimation of a much larger crura defect at time of index procedure.16 Chest pain is common post procedure and patients and collaborating providers should be counseled on the expected course. In our practice, we admit patients for at least 1 postprocedure day and consider scheduling symptom control medications for those with significant pain.
TIF2.0 for Special Populations
Indications for TIF2.0 continue to evolve. In 2017, concomitant TIF2.0 with hiatal hernia repair (cTIF or HH-TIF) for hernia > 2 cm was accepted for expanded use. In one study, cTIF has been shown to have similar outcomes for postprocedural PPI use, dysphagia, wrap disruption, and hiatal hernia recurrence, compared with hiatal hernia repair paired with laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication with possibly shorter postadmission stay, serious adverse events, and bloating.17 A cTIF may be performed in a single general anesthetic session typically with a surgical hiatal hernia repair followed by TIF2.0.
Other Endoscopic Procedures
Several other endoscopic interventions have been proposed for GERD management. The following procedures are under continuous study and should be considered only by those with expertise.
Stretta
The Stretta device (Restech; Houston, Texas) was approved in 2000 for use of a radiofrequency (RF) generator and catheter applied to the squamocolumnar junction under irrigation. Ideal candidates for this nonablative procedure may include patients with confirmed GERD, low-grade EE, without Barrett’s esophagus, small hiatal hernia, and a competent LES with pressure > 5 mmHg. Meta-analysis has yielded conflicting results in terms of its efficacy, compared with TIF2.0, and recent multi-society guidance suggests fundoplication over Stretta.7
ARM, MASE, and RAP
Anti-reflux mucosectomy (ARM) has been proposed based on the observation that patients undergoing mucosectomy for neoplasms in the cardia had improvement of reflux symptoms.11,12 Systematic review has suggested a clinical response of 80% of either PPI discontinuation or reduction, but 17% of adverse events include development of strictures. Iterations of ARM continue to be studied including ARM with band ligation (L-ARM) and endoscopic submucosal dissection for GERD (ESD-G).12
Experts have proposed incorporating endoscopic suturing of the EGJ to modulate the LES. Mucosal ablation and suturing of the EG junction (MASE) has been proposed by first priming tissue via argon plasma coagulation (APC) prior to endoscopic overstitch of two to three interrupted sutures below the EGJ to narrow and elongate the EGJ. The resection and plication (RAP) procedure performs a mucosal resection prior to full-thickness plication of the LES and cardia.11,12 Expert opinion has suggested that RAP may be used in patients with altered anatomy whereas MASE may be used when resection is not possible (eg, prior scarring, resection or ablation).12
Surgical Management
We agree with a recent multi-society guideline recommending that an interdisciplinary consultation with surgery for indicated patients with refractory GERD and underlying hiatal hernia, or who do not want lifelong medical therapy.
Fundoplication creates a surgical wrap to reinforce the LES and may be performed laparoscopically. Contraindications include body mass index (BMI) >35 kg/m2 and significantly impaired dysmotility. Fundoplication of 180°, 270°, and 360° may achieve comparable outcomes, but a laparoscopic toupet fundoplication (LTF 270°) may have fewer postsurgical issues of dysphagia and bloating. Advantages for both anterior and posterior partial fundoplications have been demonstrated by network meta-analysis. Therefore, a multi-society guideline for GERD suggests partial over complete fundoplication.7 Compared with posterior techniques, anterior fundoplication (Watson fundoplication) led to more recurrent reflux symptoms but less dysphagia and other side effects.19
Magnetic sphincter augmentation (MSA) is a surgical option that strengthens the LES with magnets to improve sphincter competence. In addition to listed contraindications of fundoplication, patients with an allergy to nickel and/or titanium are also contraindicated to receive MSA.7 MSA has been suggested to be equivalent to LNF although there may be less gas bloat and greater ability to belch on follow up.20
Surgical Options for Special Populations
Patients with medically refractory GERD and a BMI ≥ 35 kg/m2 may benefit from either Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) or fundoplication, however sleeve gastrectomy is not advised.7 In patients with BMI > 50 kg/m2, RYGB may provide an optimal choice. We agree with consultation with a bariatric surgeon when reviewing these situations.
Conclusion
Patients with GERD are commonly encountered worldwide. Empiric PPI are effective mainstays for medical treatment of GERD. Novel PCABs (e.g., vonoprazan) may present new options for GERD with LA Grade C/D esophagitis EE and merit more study. In refractory cases or for patients who do not want long term medical therapy, step-up therapy may be considered via endoscopic or surgical interventions. Patient anatomy and comorbidities should be considered by the clinician to inform treatment options. Surgery may have the most durable outcomes for those requiring step-up therapy. Improvements in technique, devices and patient selection have allowed TIF2.0 to grow as a viable offering with excellent 5-year outcomes for indicated patients.
Dr. Chang, Dr. Tintara, and Dr. Phan are based in the Division of Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease at the University of Southern California in Los Angeles. They have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Richter JE andRubenstein JH. Gastroenterology. 2018 Jan. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.07.045.
2. El-Serag HB et al. Gut. 2014 Jun. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-304269.
3. Yadlapati R et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 May. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.01.025.
4. Vakil N et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006 Aug. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00630.x.
5. Numans ME et al. Ann Intern Med. 2004 Apr. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-140-7-200404060-00011.
6. Kahrilas PJ et al. Gastroenterology. 2008 Oct. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.08.045.
7. Slater BJ et al. Surg Endosc. 2023 Feb. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09817-3.
8. Gyawali CP et al. Gut. 2018 Jul. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314722.
9. Graham DY and Tansel A. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.09.033.
10. Graham DY and Dore MP. Gastroenterology. 2018 Feb. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.018.
11. Haseeb M and Thompson CC. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2023 Sep. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000968.
12. Kolb JM and Chang KJ. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2023 Jul. doi:10.1097/MOG.0000000000000944.
13. Nguyen NT et al. Foregut. 2022 Sep. doi: 10.1177/26345161221126961.
14. Mazzoleni G et al. Endosc Int Open. 2021 Feb. doi: 10.1055/a-1322-2209.
15. Trad KS et al. Surg Innov. 2018 Apr. doi: 10.1177/1553350618755214.
16. Kolb JM et al. Gastroenterology. 2021 May. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(21)02953-X.
17. Jaruvongvanich VK et al. Endosc Int Open. 2023 Jan. doi: 10.1055/a-1972-9190.
18. Lee Y et al. Surg Endosc. 2023 Jul. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-10151-5.
19. Andreou A et al. Surg Endosc. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1007/s00464-019-07208-9.
20. Guidozzi N et al. Dis Esophagus. 2019 Nov. doi: 10.1093/dote/doz031.
Introduction
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a frequently encountered condition, and rising annually.1 A recent meta-analysis suggests nearly 14% (1.03 billion) of the population are affected worldwide. Differences may range by region from 12% in Latin America to 20% in North America, and by country from 4% in China to 23% in Turkey.1 In the United States, 21% of the population are afflicted with weekly GERD symptoms.2 Novel medical therapies and endoscopic options provide clinicians with opportunities to help patients with GERD.3
Diagnosis
Definition
GERD was originally defined by the Montreal consensus as a condition that develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications.4 Heartburn and regurgitation are common symptoms of GERD, with a sensitivity of 30%-76% and specificity of 62%-96% for erosive esophagitis (EE), which occurs when the reflux of stomach content causes esophageal mucosal breaks.5 The presence of characteristic mucosal injury observed during an upper endoscopy or abnormal esophageal acid exposure on ambulatory reflux monitoring are objective evidence of GERD. A trial of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) may function as a diagnostic test for patients exhibiting the typical symptoms of GERD without any alarm symptoms.3,6
Endoscopic Evaluation and Confirmation
The 2022 American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) clinical practice update recommends diagnostic endoscopy, after PPIs are stopped for 2-4 weeks, in patients whose GERD symptoms do not respond adequately to an empiric trial of a PPI.3 Those with GERD and alarm symptoms such as dysphagia, weight loss, bleeding, and vomiting should undergo endoscopy as soon as possible. Endoscopic findings of EE (Los Angeles Grade B or more severe) and long-segment Barrett’s esophagus (> 3-cm segment with intestinal metaplasia on biopsy) are diagnostic of GERD.3
Reflux Monitoring
With ambulatory reflux monitoring (pH or impedance-pH), esophageal acid exposure (or neutral refluxate in impedance testing) can be measured to confirm GERD diagnosis and to correlate symptoms with reflux episodes. Patients with atypical GERD symptoms or patients with a confirmed diagnosis of GERD whose symptoms have not improved sufficiently with twice-daily PPI therapy should have esophageal impedance-pH monitoring while on PPIs.6,7
Esophageal Manometry
High-resolution esophageal manometry can be used to assess motility abnormalities associated with GERD.
Although no manometric abnormality is unique to GERD, weak lower esophageal sphincter (LES) resting pressure and ineffective esophageal motility frequently coexist with severe GERD.6
Manometry is particularly useful in patients considering surgical or endoscopic anti-reflux procedures to evaluate for achalasia,3 an important contraindication to surgery.
Medical Management
Management of GERD requires a multidisciplinary and personalized approach based on symptom presentation, body mass index, endoscopic findings (e.g., presence of EE, Barrett’s esophagus, hiatal hernia), and physiological abnormalities (e.g., gastroparesis or ineffective motility).3
Lifestyle Modifications
Recommended lifestyle modifications include weight loss for patients with obesity, stress reduction, tobacco and alcohol cessation, elevating the head of the bed, staying upright during and after meals, avoidance of food intake < 3 hours before bedtime, and cessation of foods that potentially aggravate reflux symptoms such as coffee, chocolate, carbonated beverages, spicy foods, acidic foods, and foods with high fat content.6,8
Medications
Pharmacologic therapy for GERD includes medications that primarily aim to neutralize or reduce gastric acid -- we summarize options in Table 1.3,8

Proton Pump Inhibitors
Most guidelines suggest a trial of 4-8 weeks of once-daily enteric-coated PPI before meals in patients with typical GERD symptoms and no alarm symptoms. Escalation to double-dose PPI may be considered in the case of persistent symptoms. The relative potencies of standard-dose pantoprazole, lansoprazole, esomeprazole, and rabeprazole are presented in Table 1.9 When a PPI switch is needed, rabeprazole may be considered as it is a PPI that does not rely on CYP2C19 for primary metabolism.9
Acid suppression should be weaned down to the lowest effective dose or converted to H2RAs or other antacids once symptoms are sufficiently controlled unless patients have EE, Barrett’s esophagus, or peptic stricture.3 Patients with severe GERD may require long-term PPI therapy or an invasive anti-reflux procedure.
Recent studies have shown that potassium-competitive acid blockers (PCAB) like vonoprazan may offer more effective gastric acid inhibition. While not included in the latest clinical practice update, vonoprazan is thought to be superior to lansoprazole for those with LA Grade C/D esophagitis for both symptom relief and healing at 2 weeks.10
Adjunctive Therapies
Alginates can function as a physical barrier to even neutral reflux and may be helpful for patients with postprandial or nighttime symptoms as well as those with hiatal hernia.3 H2RAs can also help mitigate nighttime symptoms.3 Baclofen is a gamma-aminobutyric acid–B agonist which inhibits transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation (TLESR) and may be effective for patients with belching.3 Prokinetics may be helpful for GERD with concomitant gastroparesis.3 Sucralfate is a mucosal protective agent, but there is a lack of data supporting its efficacy in GERD treatment. Consider referral to a behavioral therapist for supplemental therapies, hypnotherapy, cognitive-behavior therapy, diaphragmatic breathing, and relaxation strategies for functional heartburn or reflux-associated esophageal hypervigilance or reflux hypersensitivity.3
When to Refer to Higher Level of Care
For patients who do not wish to remain on longer-term pharmacologic therapy or would benefit from anatomic repair, clinicians should have a discussion of risks and benefits prior to consideration of referral for anti-reflux procedures.3,6,8 We advise this conversation should include review of patient health status, postsurgical side effects such as increased flatus, bloating and dysphagia as well as the potential need to still resume PPI post operation.8
Endoscopic Management
Patient Selection And Evaluation
For the groups indicated for a higher level of care, we agree with AGA recommendations, multi-society guidelines, and expert review,3,7,11,12 and highlight potential options in Table 2. Step-up options should be based on patient characteristics and reviewed carefully with patients. Endoscopic therapies are less invasive than surgery and may be considered for those who do not require anatomic repair of hiatal hernia, do not want surgery, or are not suitable for surgery.

The pathophysiology of GERD is from a loss of the anti-reflux barrier of the esophageal gastric junction (EGJ) at the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) leading to unintended retrograde movement of gastric contents.6 Anatomically, the LES is composed of muscles of the distal esophagus and sling fibers of the proximal stomach, the “external valve” from the diaphragmatic crura, and the “internal valve” from the gastroesophageal flap valve (GEFV). GERD occurs from mechanical failure of the LES. First, there may be disproportional dilation of the diaphragmatic crura as categorized by Hill Grade of the GEFV as seen by a retroflexed view of EGJ after 30-45 seconds of insufflation.13 Second, there may be a migration of the LES away from the diaphragmatic crura as in the case of a hiatal hernia. Provocative maneuvers may reveal a sliding hernia by gentle retraction of the endoscope while under retroflexed view.13 Third, there may be more frequent TLESR associated with GERD.12
The aim of most interventions is to restore competency of the LES by reconstruction of the GEFV via suture or staple-based approximation of tissue.11,12 Intraluminal therapy may only target the GEFV at the internal valve. Therefore, most endoscopic interventions are limited to patients with intact diaphragmatic crura (ie, small to no hiatal hernia and GEFV Hill Grade 1 to 2). Contraindications for endoscopic therapy are moderate to severe reflux (ie, LA Grade C/ D), hiatus hernia 2 cm or larger, strictures, or long-segment Barrett’s esophagus.
Utility, Safety, and Outcomes of TIF
Historically, endoscopic therapy targeting endoscopic fundoplication started with EndoLuminal gastro-gastric fundoplication (ELF, 2005) which was a proof of concept of safe manipulation and suture for gastro-gastric plication to below the Z-line. Transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) 1.0 was suggested in 2007 for clinical application by proposing a longitudinal oriented esophago-gastric plication 1 cm above the Z-line.
In 2009, TIF2.0 was proposed as a rotational 270° wrap of the cardia and fundus to a full-thickness esophago-gastric fundoplication around 2-4 cm of the distal esophagus. Like a surgical fundoplication, this reinforces sling fibers, increases the Angle of His and improves the cardiac notch. TIF 2.0 is indicated for those with small (< 2 cm) or no hiatal hernia and a GEFV Hill Grade 1 or 2. The present iteration of TIF2.0 uses EsophyX-Z (EndoGastric Solutions; Redmond, Washington) which features dual fastener deployment and a simplified firing mechanism. Plication is secured via nonresorbable polypropylene T-fasteners with strength equivalence of 3-0 sutures.
Compared with the original, TIF2.0 represents a decrease of severe adverse events from 2%-2.5% to 0.4%-1%.11,14 Based on longitudinal TEMPO data, patient satisfaction ranges between 70% and 90% and rates of patients reverting to daily PPI use are 17% and 34% at 1 and 5 years. A 5% reintervention rate was noted to be comparable with surgical reoperation for fundoplication.15 One retrospective evaluation of patients with failed TIF followed by successful cTIF noted that in all failures there was a documented underestimation of a much larger crura defect at time of index procedure.16 Chest pain is common post procedure and patients and collaborating providers should be counseled on the expected course. In our practice, we admit patients for at least 1 postprocedure day and consider scheduling symptom control medications for those with significant pain.
TIF2.0 for Special Populations
Indications for TIF2.0 continue to evolve. In 2017, concomitant TIF2.0 with hiatal hernia repair (cTIF or HH-TIF) for hernia > 2 cm was accepted for expanded use. In one study, cTIF has been shown to have similar outcomes for postprocedural PPI use, dysphagia, wrap disruption, and hiatal hernia recurrence, compared with hiatal hernia repair paired with laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication with possibly shorter postadmission stay, serious adverse events, and bloating.17 A cTIF may be performed in a single general anesthetic session typically with a surgical hiatal hernia repair followed by TIF2.0.
Other Endoscopic Procedures
Several other endoscopic interventions have been proposed for GERD management. The following procedures are under continuous study and should be considered only by those with expertise.
Stretta
The Stretta device (Restech; Houston, Texas) was approved in 2000 for use of a radiofrequency (RF) generator and catheter applied to the squamocolumnar junction under irrigation. Ideal candidates for this nonablative procedure may include patients with confirmed GERD, low-grade EE, without Barrett’s esophagus, small hiatal hernia, and a competent LES with pressure > 5 mmHg. Meta-analysis has yielded conflicting results in terms of its efficacy, compared with TIF2.0, and recent multi-society guidance suggests fundoplication over Stretta.7
ARM, MASE, and RAP
Anti-reflux mucosectomy (ARM) has been proposed based on the observation that patients undergoing mucosectomy for neoplasms in the cardia had improvement of reflux symptoms.11,12 Systematic review has suggested a clinical response of 80% of either PPI discontinuation or reduction, but 17% of adverse events include development of strictures. Iterations of ARM continue to be studied including ARM with band ligation (L-ARM) and endoscopic submucosal dissection for GERD (ESD-G).12
Experts have proposed incorporating endoscopic suturing of the EGJ to modulate the LES. Mucosal ablation and suturing of the EG junction (MASE) has been proposed by first priming tissue via argon plasma coagulation (APC) prior to endoscopic overstitch of two to three interrupted sutures below the EGJ to narrow and elongate the EGJ. The resection and plication (RAP) procedure performs a mucosal resection prior to full-thickness plication of the LES and cardia.11,12 Expert opinion has suggested that RAP may be used in patients with altered anatomy whereas MASE may be used when resection is not possible (eg, prior scarring, resection or ablation).12
Surgical Management
We agree with a recent multi-society guideline recommending that an interdisciplinary consultation with surgery for indicated patients with refractory GERD and underlying hiatal hernia, or who do not want lifelong medical therapy.
Fundoplication creates a surgical wrap to reinforce the LES and may be performed laparoscopically. Contraindications include body mass index (BMI) >35 kg/m2 and significantly impaired dysmotility. Fundoplication of 180°, 270°, and 360° may achieve comparable outcomes, but a laparoscopic toupet fundoplication (LTF 270°) may have fewer postsurgical issues of dysphagia and bloating. Advantages for both anterior and posterior partial fundoplications have been demonstrated by network meta-analysis. Therefore, a multi-society guideline for GERD suggests partial over complete fundoplication.7 Compared with posterior techniques, anterior fundoplication (Watson fundoplication) led to more recurrent reflux symptoms but less dysphagia and other side effects.19
Magnetic sphincter augmentation (MSA) is a surgical option that strengthens the LES with magnets to improve sphincter competence. In addition to listed contraindications of fundoplication, patients with an allergy to nickel and/or titanium are also contraindicated to receive MSA.7 MSA has been suggested to be equivalent to LNF although there may be less gas bloat and greater ability to belch on follow up.20
Surgical Options for Special Populations
Patients with medically refractory GERD and a BMI ≥ 35 kg/m2 may benefit from either Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) or fundoplication, however sleeve gastrectomy is not advised.7 In patients with BMI > 50 kg/m2, RYGB may provide an optimal choice. We agree with consultation with a bariatric surgeon when reviewing these situations.
Conclusion
Patients with GERD are commonly encountered worldwide. Empiric PPI are effective mainstays for medical treatment of GERD. Novel PCABs (e.g., vonoprazan) may present new options for GERD with LA Grade C/D esophagitis EE and merit more study. In refractory cases or for patients who do not want long term medical therapy, step-up therapy may be considered via endoscopic or surgical interventions. Patient anatomy and comorbidities should be considered by the clinician to inform treatment options. Surgery may have the most durable outcomes for those requiring step-up therapy. Improvements in technique, devices and patient selection have allowed TIF2.0 to grow as a viable offering with excellent 5-year outcomes for indicated patients.
Dr. Chang, Dr. Tintara, and Dr. Phan are based in the Division of Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease at the University of Southern California in Los Angeles. They have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Richter JE andRubenstein JH. Gastroenterology. 2018 Jan. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.07.045.
2. El-Serag HB et al. Gut. 2014 Jun. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-304269.
3. Yadlapati R et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 May. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.01.025.
4. Vakil N et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006 Aug. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00630.x.
5. Numans ME et al. Ann Intern Med. 2004 Apr. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-140-7-200404060-00011.
6. Kahrilas PJ et al. Gastroenterology. 2008 Oct. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.08.045.
7. Slater BJ et al. Surg Endosc. 2023 Feb. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09817-3.
8. Gyawali CP et al. Gut. 2018 Jul. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314722.
9. Graham DY and Tansel A. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.09.033.
10. Graham DY and Dore MP. Gastroenterology. 2018 Feb. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.018.
11. Haseeb M and Thompson CC. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2023 Sep. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000968.
12. Kolb JM and Chang KJ. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2023 Jul. doi:10.1097/MOG.0000000000000944.
13. Nguyen NT et al. Foregut. 2022 Sep. doi: 10.1177/26345161221126961.
14. Mazzoleni G et al. Endosc Int Open. 2021 Feb. doi: 10.1055/a-1322-2209.
15. Trad KS et al. Surg Innov. 2018 Apr. doi: 10.1177/1553350618755214.
16. Kolb JM et al. Gastroenterology. 2021 May. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(21)02953-X.
17. Jaruvongvanich VK et al. Endosc Int Open. 2023 Jan. doi: 10.1055/a-1972-9190.
18. Lee Y et al. Surg Endosc. 2023 Jul. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-10151-5.
19. Andreou A et al. Surg Endosc. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1007/s00464-019-07208-9.
20. Guidozzi N et al. Dis Esophagus. 2019 Nov. doi: 10.1093/dote/doz031.
Introduction
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a frequently encountered condition, and rising annually.1 A recent meta-analysis suggests nearly 14% (1.03 billion) of the population are affected worldwide. Differences may range by region from 12% in Latin America to 20% in North America, and by country from 4% in China to 23% in Turkey.1 In the United States, 21% of the population are afflicted with weekly GERD symptoms.2 Novel medical therapies and endoscopic options provide clinicians with opportunities to help patients with GERD.3
Diagnosis
Definition
GERD was originally defined by the Montreal consensus as a condition that develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications.4 Heartburn and regurgitation are common symptoms of GERD, with a sensitivity of 30%-76% and specificity of 62%-96% for erosive esophagitis (EE), which occurs when the reflux of stomach content causes esophageal mucosal breaks.5 The presence of characteristic mucosal injury observed during an upper endoscopy or abnormal esophageal acid exposure on ambulatory reflux monitoring are objective evidence of GERD. A trial of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) may function as a diagnostic test for patients exhibiting the typical symptoms of GERD without any alarm symptoms.3,6
Endoscopic Evaluation and Confirmation
The 2022 American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) clinical practice update recommends diagnostic endoscopy, after PPIs are stopped for 2-4 weeks, in patients whose GERD symptoms do not respond adequately to an empiric trial of a PPI.3 Those with GERD and alarm symptoms such as dysphagia, weight loss, bleeding, and vomiting should undergo endoscopy as soon as possible. Endoscopic findings of EE (Los Angeles Grade B or more severe) and long-segment Barrett’s esophagus (> 3-cm segment with intestinal metaplasia on biopsy) are diagnostic of GERD.3
Reflux Monitoring
With ambulatory reflux monitoring (pH or impedance-pH), esophageal acid exposure (or neutral refluxate in impedance testing) can be measured to confirm GERD diagnosis and to correlate symptoms with reflux episodes. Patients with atypical GERD symptoms or patients with a confirmed diagnosis of GERD whose symptoms have not improved sufficiently with twice-daily PPI therapy should have esophageal impedance-pH monitoring while on PPIs.6,7
Esophageal Manometry
High-resolution esophageal manometry can be used to assess motility abnormalities associated with GERD.
Although no manometric abnormality is unique to GERD, weak lower esophageal sphincter (LES) resting pressure and ineffective esophageal motility frequently coexist with severe GERD.6
Manometry is particularly useful in patients considering surgical or endoscopic anti-reflux procedures to evaluate for achalasia,3 an important contraindication to surgery.
Medical Management
Management of GERD requires a multidisciplinary and personalized approach based on symptom presentation, body mass index, endoscopic findings (e.g., presence of EE, Barrett’s esophagus, hiatal hernia), and physiological abnormalities (e.g., gastroparesis or ineffective motility).3
Lifestyle Modifications
Recommended lifestyle modifications include weight loss for patients with obesity, stress reduction, tobacco and alcohol cessation, elevating the head of the bed, staying upright during and after meals, avoidance of food intake < 3 hours before bedtime, and cessation of foods that potentially aggravate reflux symptoms such as coffee, chocolate, carbonated beverages, spicy foods, acidic foods, and foods with high fat content.6,8
Medications
Pharmacologic therapy for GERD includes medications that primarily aim to neutralize or reduce gastric acid -- we summarize options in Table 1.3,8

Proton Pump Inhibitors
Most guidelines suggest a trial of 4-8 weeks of once-daily enteric-coated PPI before meals in patients with typical GERD symptoms and no alarm symptoms. Escalation to double-dose PPI may be considered in the case of persistent symptoms. The relative potencies of standard-dose pantoprazole, lansoprazole, esomeprazole, and rabeprazole are presented in Table 1.9 When a PPI switch is needed, rabeprazole may be considered as it is a PPI that does not rely on CYP2C19 for primary metabolism.9
Acid suppression should be weaned down to the lowest effective dose or converted to H2RAs or other antacids once symptoms are sufficiently controlled unless patients have EE, Barrett’s esophagus, or peptic stricture.3 Patients with severe GERD may require long-term PPI therapy or an invasive anti-reflux procedure.
Recent studies have shown that potassium-competitive acid blockers (PCAB) like vonoprazan may offer more effective gastric acid inhibition. While not included in the latest clinical practice update, vonoprazan is thought to be superior to lansoprazole for those with LA Grade C/D esophagitis for both symptom relief and healing at 2 weeks.10
Adjunctive Therapies
Alginates can function as a physical barrier to even neutral reflux and may be helpful for patients with postprandial or nighttime symptoms as well as those with hiatal hernia.3 H2RAs can also help mitigate nighttime symptoms.3 Baclofen is a gamma-aminobutyric acid–B agonist which inhibits transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation (TLESR) and may be effective for patients with belching.3 Prokinetics may be helpful for GERD with concomitant gastroparesis.3 Sucralfate is a mucosal protective agent, but there is a lack of data supporting its efficacy in GERD treatment. Consider referral to a behavioral therapist for supplemental therapies, hypnotherapy, cognitive-behavior therapy, diaphragmatic breathing, and relaxation strategies for functional heartburn or reflux-associated esophageal hypervigilance or reflux hypersensitivity.3
When to Refer to Higher Level of Care
For patients who do not wish to remain on longer-term pharmacologic therapy or would benefit from anatomic repair, clinicians should have a discussion of risks and benefits prior to consideration of referral for anti-reflux procedures.3,6,8 We advise this conversation should include review of patient health status, postsurgical side effects such as increased flatus, bloating and dysphagia as well as the potential need to still resume PPI post operation.8
Endoscopic Management
Patient Selection And Evaluation
For the groups indicated for a higher level of care, we agree with AGA recommendations, multi-society guidelines, and expert review,3,7,11,12 and highlight potential options in Table 2. Step-up options should be based on patient characteristics and reviewed carefully with patients. Endoscopic therapies are less invasive than surgery and may be considered for those who do not require anatomic repair of hiatal hernia, do not want surgery, or are not suitable for surgery.

The pathophysiology of GERD is from a loss of the anti-reflux barrier of the esophageal gastric junction (EGJ) at the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) leading to unintended retrograde movement of gastric contents.6 Anatomically, the LES is composed of muscles of the distal esophagus and sling fibers of the proximal stomach, the “external valve” from the diaphragmatic crura, and the “internal valve” from the gastroesophageal flap valve (GEFV). GERD occurs from mechanical failure of the LES. First, there may be disproportional dilation of the diaphragmatic crura as categorized by Hill Grade of the GEFV as seen by a retroflexed view of EGJ after 30-45 seconds of insufflation.13 Second, there may be a migration of the LES away from the diaphragmatic crura as in the case of a hiatal hernia. Provocative maneuvers may reveal a sliding hernia by gentle retraction of the endoscope while under retroflexed view.13 Third, there may be more frequent TLESR associated with GERD.12
The aim of most interventions is to restore competency of the LES by reconstruction of the GEFV via suture or staple-based approximation of tissue.11,12 Intraluminal therapy may only target the GEFV at the internal valve. Therefore, most endoscopic interventions are limited to patients with intact diaphragmatic crura (ie, small to no hiatal hernia and GEFV Hill Grade 1 to 2). Contraindications for endoscopic therapy are moderate to severe reflux (ie, LA Grade C/ D), hiatus hernia 2 cm or larger, strictures, or long-segment Barrett’s esophagus.
Utility, Safety, and Outcomes of TIF
Historically, endoscopic therapy targeting endoscopic fundoplication started with EndoLuminal gastro-gastric fundoplication (ELF, 2005) which was a proof of concept of safe manipulation and suture for gastro-gastric plication to below the Z-line. Transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) 1.0 was suggested in 2007 for clinical application by proposing a longitudinal oriented esophago-gastric plication 1 cm above the Z-line.
In 2009, TIF2.0 was proposed as a rotational 270° wrap of the cardia and fundus to a full-thickness esophago-gastric fundoplication around 2-4 cm of the distal esophagus. Like a surgical fundoplication, this reinforces sling fibers, increases the Angle of His and improves the cardiac notch. TIF 2.0 is indicated for those with small (< 2 cm) or no hiatal hernia and a GEFV Hill Grade 1 or 2. The present iteration of TIF2.0 uses EsophyX-Z (EndoGastric Solutions; Redmond, Washington) which features dual fastener deployment and a simplified firing mechanism. Plication is secured via nonresorbable polypropylene T-fasteners with strength equivalence of 3-0 sutures.
Compared with the original, TIF2.0 represents a decrease of severe adverse events from 2%-2.5% to 0.4%-1%.11,14 Based on longitudinal TEMPO data, patient satisfaction ranges between 70% and 90% and rates of patients reverting to daily PPI use are 17% and 34% at 1 and 5 years. A 5% reintervention rate was noted to be comparable with surgical reoperation for fundoplication.15 One retrospective evaluation of patients with failed TIF followed by successful cTIF noted that in all failures there was a documented underestimation of a much larger crura defect at time of index procedure.16 Chest pain is common post procedure and patients and collaborating providers should be counseled on the expected course. In our practice, we admit patients for at least 1 postprocedure day and consider scheduling symptom control medications for those with significant pain.
TIF2.0 for Special Populations
Indications for TIF2.0 continue to evolve. In 2017, concomitant TIF2.0 with hiatal hernia repair (cTIF or HH-TIF) for hernia > 2 cm was accepted for expanded use. In one study, cTIF has been shown to have similar outcomes for postprocedural PPI use, dysphagia, wrap disruption, and hiatal hernia recurrence, compared with hiatal hernia repair paired with laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication with possibly shorter postadmission stay, serious adverse events, and bloating.17 A cTIF may be performed in a single general anesthetic session typically with a surgical hiatal hernia repair followed by TIF2.0.
Other Endoscopic Procedures
Several other endoscopic interventions have been proposed for GERD management. The following procedures are under continuous study and should be considered only by those with expertise.
Stretta
The Stretta device (Restech; Houston, Texas) was approved in 2000 for use of a radiofrequency (RF) generator and catheter applied to the squamocolumnar junction under irrigation. Ideal candidates for this nonablative procedure may include patients with confirmed GERD, low-grade EE, without Barrett’s esophagus, small hiatal hernia, and a competent LES with pressure > 5 mmHg. Meta-analysis has yielded conflicting results in terms of its efficacy, compared with TIF2.0, and recent multi-society guidance suggests fundoplication over Stretta.7
ARM, MASE, and RAP
Anti-reflux mucosectomy (ARM) has been proposed based on the observation that patients undergoing mucosectomy for neoplasms in the cardia had improvement of reflux symptoms.11,12 Systematic review has suggested a clinical response of 80% of either PPI discontinuation or reduction, but 17% of adverse events include development of strictures. Iterations of ARM continue to be studied including ARM with band ligation (L-ARM) and endoscopic submucosal dissection for GERD (ESD-G).12
Experts have proposed incorporating endoscopic suturing of the EGJ to modulate the LES. Mucosal ablation and suturing of the EG junction (MASE) has been proposed by first priming tissue via argon plasma coagulation (APC) prior to endoscopic overstitch of two to three interrupted sutures below the EGJ to narrow and elongate the EGJ. The resection and plication (RAP) procedure performs a mucosal resection prior to full-thickness plication of the LES and cardia.11,12 Expert opinion has suggested that RAP may be used in patients with altered anatomy whereas MASE may be used when resection is not possible (eg, prior scarring, resection or ablation).12
Surgical Management
We agree with a recent multi-society guideline recommending that an interdisciplinary consultation with surgery for indicated patients with refractory GERD and underlying hiatal hernia, or who do not want lifelong medical therapy.
Fundoplication creates a surgical wrap to reinforce the LES and may be performed laparoscopically. Contraindications include body mass index (BMI) >35 kg/m2 and significantly impaired dysmotility. Fundoplication of 180°, 270°, and 360° may achieve comparable outcomes, but a laparoscopic toupet fundoplication (LTF 270°) may have fewer postsurgical issues of dysphagia and bloating. Advantages for both anterior and posterior partial fundoplications have been demonstrated by network meta-analysis. Therefore, a multi-society guideline for GERD suggests partial over complete fundoplication.7 Compared with posterior techniques, anterior fundoplication (Watson fundoplication) led to more recurrent reflux symptoms but less dysphagia and other side effects.19
Magnetic sphincter augmentation (MSA) is a surgical option that strengthens the LES with magnets to improve sphincter competence. In addition to listed contraindications of fundoplication, patients with an allergy to nickel and/or titanium are also contraindicated to receive MSA.7 MSA has been suggested to be equivalent to LNF although there may be less gas bloat and greater ability to belch on follow up.20
Surgical Options for Special Populations
Patients with medically refractory GERD and a BMI ≥ 35 kg/m2 may benefit from either Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) or fundoplication, however sleeve gastrectomy is not advised.7 In patients with BMI > 50 kg/m2, RYGB may provide an optimal choice. We agree with consultation with a bariatric surgeon when reviewing these situations.
Conclusion
Patients with GERD are commonly encountered worldwide. Empiric PPI are effective mainstays for medical treatment of GERD. Novel PCABs (e.g., vonoprazan) may present new options for GERD with LA Grade C/D esophagitis EE and merit more study. In refractory cases or for patients who do not want long term medical therapy, step-up therapy may be considered via endoscopic or surgical interventions. Patient anatomy and comorbidities should be considered by the clinician to inform treatment options. Surgery may have the most durable outcomes for those requiring step-up therapy. Improvements in technique, devices and patient selection have allowed TIF2.0 to grow as a viable offering with excellent 5-year outcomes for indicated patients.
Dr. Chang, Dr. Tintara, and Dr. Phan are based in the Division of Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease at the University of Southern California in Los Angeles. They have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Richter JE andRubenstein JH. Gastroenterology. 2018 Jan. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.07.045.
2. El-Serag HB et al. Gut. 2014 Jun. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-304269.
3. Yadlapati R et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 May. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.01.025.
4. Vakil N et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006 Aug. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00630.x.
5. Numans ME et al. Ann Intern Med. 2004 Apr. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-140-7-200404060-00011.
6. Kahrilas PJ et al. Gastroenterology. 2008 Oct. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.08.045.
7. Slater BJ et al. Surg Endosc. 2023 Feb. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09817-3.
8. Gyawali CP et al. Gut. 2018 Jul. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314722.
9. Graham DY and Tansel A. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.09.033.
10. Graham DY and Dore MP. Gastroenterology. 2018 Feb. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.018.
11. Haseeb M and Thompson CC. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2023 Sep. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000968.
12. Kolb JM and Chang KJ. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2023 Jul. doi:10.1097/MOG.0000000000000944.
13. Nguyen NT et al. Foregut. 2022 Sep. doi: 10.1177/26345161221126961.
14. Mazzoleni G et al. Endosc Int Open. 2021 Feb. doi: 10.1055/a-1322-2209.
15. Trad KS et al. Surg Innov. 2018 Apr. doi: 10.1177/1553350618755214.
16. Kolb JM et al. Gastroenterology. 2021 May. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(21)02953-X.
17. Jaruvongvanich VK et al. Endosc Int Open. 2023 Jan. doi: 10.1055/a-1972-9190.
18. Lee Y et al. Surg Endosc. 2023 Jul. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-10151-5.
19. Andreou A et al. Surg Endosc. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1007/s00464-019-07208-9.
20. Guidozzi N et al. Dis Esophagus. 2019 Nov. doi: 10.1093/dote/doz031.
Cendakimab That Targets IL-13 Shows Promise in Eosinophilic Esophagitis
VIENNA — , according to interim results of a pivotal phase 3 trial.
Treatment with cendakimab also improved key endoscopic and histologic features, even in patients who had an inadequate response or intolerance to steroids, reported Alain Schoepfer, MD, gastroenterologist from Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois and University of Lausanne, in Switzerland.
The drug was generally safe and well tolerated up to 24 weeks of treatment, added Schoepfer, who presented the results during a presentation at the United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024.
Targeting IL-13 Shows ‘Surprisingly Good Results’
EoE is a chronic, progressive, immune-mediated, inflammatory disease that is mainly driven by the cytokine, IL-13.
In a prior phase 2 study, cendakimab, which selectively binds to IL-13 and blocks its interaction with both the IL-13Ra1 and the IL-13Ra2 receptors, was shown to improve symptoms and endoscopic features of EoE.
For the current phase 3 trial, participants were required to have a peak eosinophil count (PEC) of ≥ 15 eosinophils (eos)/high power field (hpf) and 4 or more days of dysphagia over the 2 weeks prior to the start of the study. In addition, they had to have shown a complete lack of response to proton pump inhibitor (PPI) treatment for 8 weeks or more.
A total of 430 patients were randomized 1:1:1 to subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 48 weeks; subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 24 weeks, then once every 2 weeks for a further 24 weeks; or subcutaneous placebo once weekly for 48 weeks.
Patient characteristics were similar across randomization groups. The majority of participants were men, with a mean age of 35 years (range, 12-75 years); adolescents comprised 6%-11% of the total. The disease duration was around 5-6 years for all participants, of which 45% were on a stable PPI dosage and around 65% had steroid intolerance or an inadequate response. The endoscopic reference score was around 10 across all groups. The mean PEC was around 160 eos/hpf in the cendakimab arms vs 200 eos/hpf in the placebo arm.
Schoepfer reported results for the coprimary endpoints — the mean change from baseline in dysphagia days and the proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response (PEC ≤ 6 eos/hpf) — at week 24. At this point, a total of 286 patients had received treatment with 360 mg of cendakimab once weekly, and 143 had received placebo.
The change in dysphagia days was −6.1 in patients on cendakimab once weekly vs −4.2 in patients on placebo (P = .0005). The proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response was 28.6% in the treatment arm vs 2.2% in the placebo arm.
The results were similar for patients who were classified as having had a steroid inadequate response. The change in dysphagia days was −6.3 in the cendakimab group vs −4.7 in the placebo group (P = .0156). The eosinophil histologic response was 29.5% in the treatment group vs 2.1% in the placebo group (P < .0001).
Endoscopic response, a key secondary endpoint, showed a change from baseline to week 24 in the endoscopic features of EoE. The total endoscopic reference scores were −5.2 for patients on cendakimab once weekly and −1.2 for patients on placebo (P < .0001).
The safety profile of cendakimab was “unspectacular,” Schoepfer said, with adverse events related to the study drug occurring in 30% of patients in the treatment arm vs 18.9% of those in the placebo arm. He noted that as the trial was conducted during the COVID pandemic, there were some infections.
Serious adverse events, which were assessed by investigators to not be related to the study drug, occurred in 1.8% and 2.8% of patients on cendakimab and placebo, respectively. Drug discontinuation occurred in 1.4% in the cendakimab group and 0.7% in the placebo group. There were no deaths.
“We really need drugs for this disease, given that there are very few alternatives to steroids and PPIs,” Co-moderator Ram Dickman, MD, Division of Gastroenterology, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, said in an interview.
Right now, we have dupilumab, which targets two receptors: IL-4 and IL-13. But targeting IL-13 by itself “is showing surprisingly good results,” so cendakimab is a good candidate to be in “the first line of biologic treatments,” Dickman said.
“It’s safe and works rapidly,” he added. “Given this is a phase 3 study, I believe we’ll see it on the market.”
Schoepfer has served as a consultant for Regeneron/Sanofi, Adare/Ellodi, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, Dr. Falk Pharma, Gossamer Bio, GSK, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, Regeneron/Sanofi, Takeda, and Vifor; received grant/research support from Adare/Ellodi, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, and Regeneron/Sanofi. Dickman has declared no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — , according to interim results of a pivotal phase 3 trial.
Treatment with cendakimab also improved key endoscopic and histologic features, even in patients who had an inadequate response or intolerance to steroids, reported Alain Schoepfer, MD, gastroenterologist from Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois and University of Lausanne, in Switzerland.
The drug was generally safe and well tolerated up to 24 weeks of treatment, added Schoepfer, who presented the results during a presentation at the United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024.
Targeting IL-13 Shows ‘Surprisingly Good Results’
EoE is a chronic, progressive, immune-mediated, inflammatory disease that is mainly driven by the cytokine, IL-13.
In a prior phase 2 study, cendakimab, which selectively binds to IL-13 and blocks its interaction with both the IL-13Ra1 and the IL-13Ra2 receptors, was shown to improve symptoms and endoscopic features of EoE.
For the current phase 3 trial, participants were required to have a peak eosinophil count (PEC) of ≥ 15 eosinophils (eos)/high power field (hpf) and 4 or more days of dysphagia over the 2 weeks prior to the start of the study. In addition, they had to have shown a complete lack of response to proton pump inhibitor (PPI) treatment for 8 weeks or more.
A total of 430 patients were randomized 1:1:1 to subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 48 weeks; subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 24 weeks, then once every 2 weeks for a further 24 weeks; or subcutaneous placebo once weekly for 48 weeks.
Patient characteristics were similar across randomization groups. The majority of participants were men, with a mean age of 35 years (range, 12-75 years); adolescents comprised 6%-11% of the total. The disease duration was around 5-6 years for all participants, of which 45% were on a stable PPI dosage and around 65% had steroid intolerance or an inadequate response. The endoscopic reference score was around 10 across all groups. The mean PEC was around 160 eos/hpf in the cendakimab arms vs 200 eos/hpf in the placebo arm.
Schoepfer reported results for the coprimary endpoints — the mean change from baseline in dysphagia days and the proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response (PEC ≤ 6 eos/hpf) — at week 24. At this point, a total of 286 patients had received treatment with 360 mg of cendakimab once weekly, and 143 had received placebo.
The change in dysphagia days was −6.1 in patients on cendakimab once weekly vs −4.2 in patients on placebo (P = .0005). The proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response was 28.6% in the treatment arm vs 2.2% in the placebo arm.
The results were similar for patients who were classified as having had a steroid inadequate response. The change in dysphagia days was −6.3 in the cendakimab group vs −4.7 in the placebo group (P = .0156). The eosinophil histologic response was 29.5% in the treatment group vs 2.1% in the placebo group (P < .0001).
Endoscopic response, a key secondary endpoint, showed a change from baseline to week 24 in the endoscopic features of EoE. The total endoscopic reference scores were −5.2 for patients on cendakimab once weekly and −1.2 for patients on placebo (P < .0001).
The safety profile of cendakimab was “unspectacular,” Schoepfer said, with adverse events related to the study drug occurring in 30% of patients in the treatment arm vs 18.9% of those in the placebo arm. He noted that as the trial was conducted during the COVID pandemic, there were some infections.
Serious adverse events, which were assessed by investigators to not be related to the study drug, occurred in 1.8% and 2.8% of patients on cendakimab and placebo, respectively. Drug discontinuation occurred in 1.4% in the cendakimab group and 0.7% in the placebo group. There were no deaths.
“We really need drugs for this disease, given that there are very few alternatives to steroids and PPIs,” Co-moderator Ram Dickman, MD, Division of Gastroenterology, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, said in an interview.
Right now, we have dupilumab, which targets two receptors: IL-4 and IL-13. But targeting IL-13 by itself “is showing surprisingly good results,” so cendakimab is a good candidate to be in “the first line of biologic treatments,” Dickman said.
“It’s safe and works rapidly,” he added. “Given this is a phase 3 study, I believe we’ll see it on the market.”
Schoepfer has served as a consultant for Regeneron/Sanofi, Adare/Ellodi, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, Dr. Falk Pharma, Gossamer Bio, GSK, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, Regeneron/Sanofi, Takeda, and Vifor; received grant/research support from Adare/Ellodi, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, and Regeneron/Sanofi. Dickman has declared no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — , according to interim results of a pivotal phase 3 trial.
Treatment with cendakimab also improved key endoscopic and histologic features, even in patients who had an inadequate response or intolerance to steroids, reported Alain Schoepfer, MD, gastroenterologist from Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois and University of Lausanne, in Switzerland.
The drug was generally safe and well tolerated up to 24 weeks of treatment, added Schoepfer, who presented the results during a presentation at the United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024.
Targeting IL-13 Shows ‘Surprisingly Good Results’
EoE is a chronic, progressive, immune-mediated, inflammatory disease that is mainly driven by the cytokine, IL-13.
In a prior phase 2 study, cendakimab, which selectively binds to IL-13 and blocks its interaction with both the IL-13Ra1 and the IL-13Ra2 receptors, was shown to improve symptoms and endoscopic features of EoE.
For the current phase 3 trial, participants were required to have a peak eosinophil count (PEC) of ≥ 15 eosinophils (eos)/high power field (hpf) and 4 or more days of dysphagia over the 2 weeks prior to the start of the study. In addition, they had to have shown a complete lack of response to proton pump inhibitor (PPI) treatment for 8 weeks or more.
A total of 430 patients were randomized 1:1:1 to subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 48 weeks; subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 24 weeks, then once every 2 weeks for a further 24 weeks; or subcutaneous placebo once weekly for 48 weeks.
Patient characteristics were similar across randomization groups. The majority of participants were men, with a mean age of 35 years (range, 12-75 years); adolescents comprised 6%-11% of the total. The disease duration was around 5-6 years for all participants, of which 45% were on a stable PPI dosage and around 65% had steroid intolerance or an inadequate response. The endoscopic reference score was around 10 across all groups. The mean PEC was around 160 eos/hpf in the cendakimab arms vs 200 eos/hpf in the placebo arm.
Schoepfer reported results for the coprimary endpoints — the mean change from baseline in dysphagia days and the proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response (PEC ≤ 6 eos/hpf) — at week 24. At this point, a total of 286 patients had received treatment with 360 mg of cendakimab once weekly, and 143 had received placebo.
The change in dysphagia days was −6.1 in patients on cendakimab once weekly vs −4.2 in patients on placebo (P = .0005). The proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response was 28.6% in the treatment arm vs 2.2% in the placebo arm.
The results were similar for patients who were classified as having had a steroid inadequate response. The change in dysphagia days was −6.3 in the cendakimab group vs −4.7 in the placebo group (P = .0156). The eosinophil histologic response was 29.5% in the treatment group vs 2.1% in the placebo group (P < .0001).
Endoscopic response, a key secondary endpoint, showed a change from baseline to week 24 in the endoscopic features of EoE. The total endoscopic reference scores were −5.2 for patients on cendakimab once weekly and −1.2 for patients on placebo (P < .0001).
The safety profile of cendakimab was “unspectacular,” Schoepfer said, with adverse events related to the study drug occurring in 30% of patients in the treatment arm vs 18.9% of those in the placebo arm. He noted that as the trial was conducted during the COVID pandemic, there were some infections.
Serious adverse events, which were assessed by investigators to not be related to the study drug, occurred in 1.8% and 2.8% of patients on cendakimab and placebo, respectively. Drug discontinuation occurred in 1.4% in the cendakimab group and 0.7% in the placebo group. There were no deaths.
“We really need drugs for this disease, given that there are very few alternatives to steroids and PPIs,” Co-moderator Ram Dickman, MD, Division of Gastroenterology, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, said in an interview.
Right now, we have dupilumab, which targets two receptors: IL-4 and IL-13. But targeting IL-13 by itself “is showing surprisingly good results,” so cendakimab is a good candidate to be in “the first line of biologic treatments,” Dickman said.
“It’s safe and works rapidly,” he added. “Given this is a phase 3 study, I believe we’ll see it on the market.”
Schoepfer has served as a consultant for Regeneron/Sanofi, Adare/Ellodi, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, Dr. Falk Pharma, Gossamer Bio, GSK, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, Regeneron/Sanofi, Takeda, and Vifor; received grant/research support from Adare/Ellodi, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, and Regeneron/Sanofi. Dickman has declared no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM UEG 2024
Vonoprazan Offers PPI Alternative for Heartburn with Non-Erosive Reflux
according to investigators.
Benefits of vonoprazan were seen as soon as the first day of treatment and persisted through the 20-week extension period, lead author Loren Laine, MD, AGAF, of Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, and colleagues reported.
“A potential alternative to PPI therapy is a potassium-competitive acid blocker, a new class of antisecretory agents that provide more potent inhibition of gastric acid secretion than PPIs,” the investigators wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
While a small observational study found that 18 out of 26 patients (69%) with PPI-resistant NERD had improved symptoms with vonoprazan, subsequent randomized trials in Japan failed to meet their primary endpoints, Laine and colleagues noted. The present randomized trial was therefore conducted to determine how vonoprazan might help a US patient population.
The study involved 772 patients who reported heartburn at least 4 days per week during screening, but without erosive esophagitis on endoscopy. Participants were randomized into three groups: placebo, vonoprazan 10 mg, or vonoprazan 20 mg. These protocols were administered for 4 weeks, followed by a 20-week extension, in which placebo patients were rerandomized to receive one of the two vonoprazan dose levels.
The primary endpoint was the percentage of days without daytime or nighttime heartburn (24-hour heartburn-free days) during the initial 4-week treatment period. The secondary endpoint, assessed during the same timeframe, was percentage of days without need for a rescue antacid.
In the 4-week placebo-controlled period, patients treated with vonoprazan 10 mg and 20 mg showed a significant improvement in heartburn-free days, compared with placebo. The percentage of 24-hour heartburn-free days was 27.7% in the placebo group vs 44.8% in the 10-mg vonoprazan group (least squares mean difference 17.1%; P < .0001) and 44.4% in the 20 mg vonoprazan group (least squares mean difference 16.7%; P < .0001).
Benefits of vonoprazan were seen as early as the first day of treatment, with 8.3% and 11.6% more patients in the 10-mg and 20-mg groups, respectively, experiencing a heartburn-free day, compared with placebo. By day 2, these differences increased to 18.1% and 23.2%, respectively.
The percentage of days without rescue antacid use was also significantly higher in both vonoprazan groups. Patients in the 10 mg and 20 mg groups had 63.3% and 61.2% of days without antacid use, respectively, compared with 47.6% in the placebo group (P < .0001 for both comparisons).
These benefits persisted throughout the 20-week extension period, with similar percentages of heartburn-free days across all groups. Mean percentages of 24-hour heartburn-free days ranged from 61% to 63% in the extension phase, while median percentages spanned 76%-79%.
Adverse events were infrequent and comparable across all groups. The most common adverse event was nausea, occurring slightly more frequently in the vonoprazan groups (2.3% in the 10-mg group and 3.1% in the 20-mg group) vs placebo (0.4%). Serious adverse events were rare and were deemed unrelated to treatment. No new safety signals were identified during the 20-week extension period. Increases in serum gastrin levels, a marker of acid suppression, returned to near baseline after discontinuation of vonoprazan.
“In conclusion, the potassium-competitive acid blocker vonoprazan was efficacious in reducing heartburn symptoms in patients with NERD, with the benefit appearing to begin as early as the first day of therapy,” Laine and colleagues wrote.
In July 2024, the Food and Drug Administration approved vonoprazan for treating heartburn in patients with nonerosive gastroesophageal reflux disease.This study was funded by Phathom Pharmaceuticals. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Takeda, Medtronic, Carnot, and others.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) have revolutionized the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). One might ask what the reason would be to challenge this giant of the pharmacopeia with another medication for GERD.
In this important study by Laine et al, vonoprazan is expectedly efficacious in treating nonerosive GERD (NERD) but notably less so when compared with the authors’ trial for erosive GERD. This is not surprising owing to the multiple and common acid independent etiologies of NERD, such as esophageal hypersensitivity. The high placebo response supports this. Two notable results, however, merit emphasis in potential advantages over PPIs.
First, vonoprazan is effective at day 1 of therapy by eliminating the need for loading. Second, nocturnal reflux, a purer form of GERD, is better controlled with a morning dose of vonopazan mitigating against nocturnal acid breakthrough and the need for twice-daily dosing with PPIs and/or addition of an H2 antagonist. These results by no means advocate for replacement of PPIs with PCABs, but at least suggest specific populations of GERD patients who may specifically benefit from PCAB use. The study also indirectly emphasizes that careful selection of NERD patients whose GERD symptoms are predominantly caused by increased esophageal acid exposure are the most appropriate candidates. The ultimate answer as to where vonoprazan will be used in our practice is evolving.
David Katzka, MD, is based in the Division of Digestive and Liver Diseases, Columbia University Medical Center, New York City. He has received research support from Takeda, Sanofi, and Regeneron. He is also an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) have revolutionized the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). One might ask what the reason would be to challenge this giant of the pharmacopeia with another medication for GERD.
In this important study by Laine et al, vonoprazan is expectedly efficacious in treating nonerosive GERD (NERD) but notably less so when compared with the authors’ trial for erosive GERD. This is not surprising owing to the multiple and common acid independent etiologies of NERD, such as esophageal hypersensitivity. The high placebo response supports this. Two notable results, however, merit emphasis in potential advantages over PPIs.
First, vonoprazan is effective at day 1 of therapy by eliminating the need for loading. Second, nocturnal reflux, a purer form of GERD, is better controlled with a morning dose of vonopazan mitigating against nocturnal acid breakthrough and the need for twice-daily dosing with PPIs and/or addition of an H2 antagonist. These results by no means advocate for replacement of PPIs with PCABs, but at least suggest specific populations of GERD patients who may specifically benefit from PCAB use. The study also indirectly emphasizes that careful selection of NERD patients whose GERD symptoms are predominantly caused by increased esophageal acid exposure are the most appropriate candidates. The ultimate answer as to where vonoprazan will be used in our practice is evolving.
David Katzka, MD, is based in the Division of Digestive and Liver Diseases, Columbia University Medical Center, New York City. He has received research support from Takeda, Sanofi, and Regeneron. He is also an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) have revolutionized the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). One might ask what the reason would be to challenge this giant of the pharmacopeia with another medication for GERD.
In this important study by Laine et al, vonoprazan is expectedly efficacious in treating nonerosive GERD (NERD) but notably less so when compared with the authors’ trial for erosive GERD. This is not surprising owing to the multiple and common acid independent etiologies of NERD, such as esophageal hypersensitivity. The high placebo response supports this. Two notable results, however, merit emphasis in potential advantages over PPIs.
First, vonoprazan is effective at day 1 of therapy by eliminating the need for loading. Second, nocturnal reflux, a purer form of GERD, is better controlled with a morning dose of vonopazan mitigating against nocturnal acid breakthrough and the need for twice-daily dosing with PPIs and/or addition of an H2 antagonist. These results by no means advocate for replacement of PPIs with PCABs, but at least suggest specific populations of GERD patients who may specifically benefit from PCAB use. The study also indirectly emphasizes that careful selection of NERD patients whose GERD symptoms are predominantly caused by increased esophageal acid exposure are the most appropriate candidates. The ultimate answer as to where vonoprazan will be used in our practice is evolving.
David Katzka, MD, is based in the Division of Digestive and Liver Diseases, Columbia University Medical Center, New York City. He has received research support from Takeda, Sanofi, and Regeneron. He is also an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
according to investigators.
Benefits of vonoprazan were seen as soon as the first day of treatment and persisted through the 20-week extension period, lead author Loren Laine, MD, AGAF, of Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, and colleagues reported.
“A potential alternative to PPI therapy is a potassium-competitive acid blocker, a new class of antisecretory agents that provide more potent inhibition of gastric acid secretion than PPIs,” the investigators wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
While a small observational study found that 18 out of 26 patients (69%) with PPI-resistant NERD had improved symptoms with vonoprazan, subsequent randomized trials in Japan failed to meet their primary endpoints, Laine and colleagues noted. The present randomized trial was therefore conducted to determine how vonoprazan might help a US patient population.
The study involved 772 patients who reported heartburn at least 4 days per week during screening, but without erosive esophagitis on endoscopy. Participants were randomized into three groups: placebo, vonoprazan 10 mg, or vonoprazan 20 mg. These protocols were administered for 4 weeks, followed by a 20-week extension, in which placebo patients were rerandomized to receive one of the two vonoprazan dose levels.
The primary endpoint was the percentage of days without daytime or nighttime heartburn (24-hour heartburn-free days) during the initial 4-week treatment period. The secondary endpoint, assessed during the same timeframe, was percentage of days without need for a rescue antacid.
In the 4-week placebo-controlled period, patients treated with vonoprazan 10 mg and 20 mg showed a significant improvement in heartburn-free days, compared with placebo. The percentage of 24-hour heartburn-free days was 27.7% in the placebo group vs 44.8% in the 10-mg vonoprazan group (least squares mean difference 17.1%; P < .0001) and 44.4% in the 20 mg vonoprazan group (least squares mean difference 16.7%; P < .0001).
Benefits of vonoprazan were seen as early as the first day of treatment, with 8.3% and 11.6% more patients in the 10-mg and 20-mg groups, respectively, experiencing a heartburn-free day, compared with placebo. By day 2, these differences increased to 18.1% and 23.2%, respectively.
The percentage of days without rescue antacid use was also significantly higher in both vonoprazan groups. Patients in the 10 mg and 20 mg groups had 63.3% and 61.2% of days without antacid use, respectively, compared with 47.6% in the placebo group (P < .0001 for both comparisons).
These benefits persisted throughout the 20-week extension period, with similar percentages of heartburn-free days across all groups. Mean percentages of 24-hour heartburn-free days ranged from 61% to 63% in the extension phase, while median percentages spanned 76%-79%.
Adverse events were infrequent and comparable across all groups. The most common adverse event was nausea, occurring slightly more frequently in the vonoprazan groups (2.3% in the 10-mg group and 3.1% in the 20-mg group) vs placebo (0.4%). Serious adverse events were rare and were deemed unrelated to treatment. No new safety signals were identified during the 20-week extension period. Increases in serum gastrin levels, a marker of acid suppression, returned to near baseline after discontinuation of vonoprazan.
“In conclusion, the potassium-competitive acid blocker vonoprazan was efficacious in reducing heartburn symptoms in patients with NERD, with the benefit appearing to begin as early as the first day of therapy,” Laine and colleagues wrote.
In July 2024, the Food and Drug Administration approved vonoprazan for treating heartburn in patients with nonerosive gastroesophageal reflux disease.This study was funded by Phathom Pharmaceuticals. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Takeda, Medtronic, Carnot, and others.
according to investigators.
Benefits of vonoprazan were seen as soon as the first day of treatment and persisted through the 20-week extension period, lead author Loren Laine, MD, AGAF, of Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, and colleagues reported.
“A potential alternative to PPI therapy is a potassium-competitive acid blocker, a new class of antisecretory agents that provide more potent inhibition of gastric acid secretion than PPIs,” the investigators wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
While a small observational study found that 18 out of 26 patients (69%) with PPI-resistant NERD had improved symptoms with vonoprazan, subsequent randomized trials in Japan failed to meet their primary endpoints, Laine and colleagues noted. The present randomized trial was therefore conducted to determine how vonoprazan might help a US patient population.
The study involved 772 patients who reported heartburn at least 4 days per week during screening, but without erosive esophagitis on endoscopy. Participants were randomized into three groups: placebo, vonoprazan 10 mg, or vonoprazan 20 mg. These protocols were administered for 4 weeks, followed by a 20-week extension, in which placebo patients were rerandomized to receive one of the two vonoprazan dose levels.
The primary endpoint was the percentage of days without daytime or nighttime heartburn (24-hour heartburn-free days) during the initial 4-week treatment period. The secondary endpoint, assessed during the same timeframe, was percentage of days without need for a rescue antacid.
In the 4-week placebo-controlled period, patients treated with vonoprazan 10 mg and 20 mg showed a significant improvement in heartburn-free days, compared with placebo. The percentage of 24-hour heartburn-free days was 27.7% in the placebo group vs 44.8% in the 10-mg vonoprazan group (least squares mean difference 17.1%; P < .0001) and 44.4% in the 20 mg vonoprazan group (least squares mean difference 16.7%; P < .0001).
Benefits of vonoprazan were seen as early as the first day of treatment, with 8.3% and 11.6% more patients in the 10-mg and 20-mg groups, respectively, experiencing a heartburn-free day, compared with placebo. By day 2, these differences increased to 18.1% and 23.2%, respectively.
The percentage of days without rescue antacid use was also significantly higher in both vonoprazan groups. Patients in the 10 mg and 20 mg groups had 63.3% and 61.2% of days without antacid use, respectively, compared with 47.6% in the placebo group (P < .0001 for both comparisons).
These benefits persisted throughout the 20-week extension period, with similar percentages of heartburn-free days across all groups. Mean percentages of 24-hour heartburn-free days ranged from 61% to 63% in the extension phase, while median percentages spanned 76%-79%.
Adverse events were infrequent and comparable across all groups. The most common adverse event was nausea, occurring slightly more frequently in the vonoprazan groups (2.3% in the 10-mg group and 3.1% in the 20-mg group) vs placebo (0.4%). Serious adverse events were rare and were deemed unrelated to treatment. No new safety signals were identified during the 20-week extension period. Increases in serum gastrin levels, a marker of acid suppression, returned to near baseline after discontinuation of vonoprazan.
“In conclusion, the potassium-competitive acid blocker vonoprazan was efficacious in reducing heartburn symptoms in patients with NERD, with the benefit appearing to begin as early as the first day of therapy,” Laine and colleagues wrote.
In July 2024, the Food and Drug Administration approved vonoprazan for treating heartburn in patients with nonerosive gastroesophageal reflux disease.This study was funded by Phathom Pharmaceuticals. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Takeda, Medtronic, Carnot, and others.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Celiac Screening in Kids Appears Cost-Effective
If these screening strategies are deemed feasible by clinicians and patients, then implementation in routine care is needed, lead author Jan Heijdra Suasnabar, MSc, of Leiden University Medical Centre in the Netherlands, and colleagues reported.
“Cohort studies have shown that CD likely develops early in life and can be easily diagnosed by detection of CD-specific antibodies against the enzyme tissue transglutaminase type 2 (IgA-TG2),” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology.
Despite the ease of diagnosis, as few as one in five cases of CD are detected using current clinical strategies, meaning many cases are diagnosed years after symptom onset.
“Such high rates of missed/delayed diagnoses have been attributed to CD’s varied and nonspecific symptoms, lack of awareness, and the resource-intensive process necessary to establish the diagnosis,” Heijdra Suasnabar and colleagues wrote. “From an economic perspective, the burden of CD translates into substantial excess healthcare and societal costs.”
These practice gaps prompted the present study, which explored the long-term cost effectiveness of mass CD screening and active case finding among pediatric patients.
The investigators employed a model-based cost-effectiveness analysis with a hypothetical cohort representing all children with CD in the Netherlands. Iterations of this model evaluated long-term costs as these children moved through the healthcare system along various CD detection strategies.
The first strategy was based on the current Dutch approach, which is the same as that in the United States: Patients are only evaluated for CD if they present with symptoms that prompt suspicion of disease. Based on data from population-based studies, the model assumed that approximately one in three cases would be detected using this strategy.
The second strategy involved mass screening using IgA-TG2 point-of-care testing (sensitivity, 0.94; specificity, 0.944) via youth health care clinics, regardless of symptoms.
The third strategy, called “active case finding,” represented something of an intermediate approach, in which children with at least 1 CD-related symptom underwent point-of-care antibody testing.
For both mass screening and active case finding strategies, a positive antibody test was followed with confirmatory diagnostic testing.
Compared with current clinical approach, mass screening added 7.46 more quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) per CD patient with an increased cost of €28,635 per CD patient. Active case finding gained 4.33 QALYs per CD patient while incurring an additional cost of €15,585 per CD patient.
Based on a willingness-to-pay threshold of €20,000 per QALY, the investigators deemed both strategies “highly cost effective,” compared with current standard of care. Some of these costs were offset by “substantial” reductions in productivity losses, they noted, including CD-related absences from work and school.
“Our results illustrate how an earlier detection of CD through screening or case finding, although more costly, leads to improved health outcomes and a reduction in disease burden, compared with current care,” Heijdra Suasnabar and colleagues wrote.
Their concluding remarks highlighted the conservative scenarios built into their model, and suggested that their findings offer solid evidence for implementing new CD-testing strategies.
“If found to be feasible and acceptable by clinicians and patients, these strategies should be implemented in the Netherlands,” they wrote.This study was supported by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Celiac disease (CD) is common, affecting about 1% of the population, but it remains underdiagnosed because of its heterogeneous presentation and limited provider awareness. Most cases are detected only after patients develop gastrointestinal symptoms or laboratory abnormalities.
In this cost-effectiveness analysis, Suasnabar and colleagues demonstrate that screening children for celiac disease would be highly cost-effective relative to the current practice of clinical detection. They modeled point-of-care-testing using tissue transglutaminase IgA in all 3-year-old children in the Netherlands. While both mass screening and case-finding (via a standardized questionnaire) would increase healthcare costs relative to current care, both strategies would improve quality of life (QoL), reduce long-term complications (such as osteoporosis and non-Hodgkin lymphoma), and minimize productivity losses in individuals with CD. In sensitivity analyses accounting for uncertainty in QoL inputs and in the utility of diagnosing and treating asymptomatic CD, each screening strategy remained well below accepted willingness-to-pay thresholds.
John B. Doyle, MD, is a gastroenterology fellow in the Division of Digestive and Liver Diseases at Columbia University Medical Center, New York City. Benjamin Lebwohl, MD, MS, AGAF, is professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University Medical Center and director of clinical research at The Celiac Disease Center at Columbia. They have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Celiac disease (CD) is common, affecting about 1% of the population, but it remains underdiagnosed because of its heterogeneous presentation and limited provider awareness. Most cases are detected only after patients develop gastrointestinal symptoms or laboratory abnormalities.
In this cost-effectiveness analysis, Suasnabar and colleagues demonstrate that screening children for celiac disease would be highly cost-effective relative to the current practice of clinical detection. They modeled point-of-care-testing using tissue transglutaminase IgA in all 3-year-old children in the Netherlands. While both mass screening and case-finding (via a standardized questionnaire) would increase healthcare costs relative to current care, both strategies would improve quality of life (QoL), reduce long-term complications (such as osteoporosis and non-Hodgkin lymphoma), and minimize productivity losses in individuals with CD. In sensitivity analyses accounting for uncertainty in QoL inputs and in the utility of diagnosing and treating asymptomatic CD, each screening strategy remained well below accepted willingness-to-pay thresholds.
John B. Doyle, MD, is a gastroenterology fellow in the Division of Digestive and Liver Diseases at Columbia University Medical Center, New York City. Benjamin Lebwohl, MD, MS, AGAF, is professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University Medical Center and director of clinical research at The Celiac Disease Center at Columbia. They have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Celiac disease (CD) is common, affecting about 1% of the population, but it remains underdiagnosed because of its heterogeneous presentation and limited provider awareness. Most cases are detected only after patients develop gastrointestinal symptoms or laboratory abnormalities.
In this cost-effectiveness analysis, Suasnabar and colleagues demonstrate that screening children for celiac disease would be highly cost-effective relative to the current practice of clinical detection. They modeled point-of-care-testing using tissue transglutaminase IgA in all 3-year-old children in the Netherlands. While both mass screening and case-finding (via a standardized questionnaire) would increase healthcare costs relative to current care, both strategies would improve quality of life (QoL), reduce long-term complications (such as osteoporosis and non-Hodgkin lymphoma), and minimize productivity losses in individuals with CD. In sensitivity analyses accounting for uncertainty in QoL inputs and in the utility of diagnosing and treating asymptomatic CD, each screening strategy remained well below accepted willingness-to-pay thresholds.
John B. Doyle, MD, is a gastroenterology fellow in the Division of Digestive and Liver Diseases at Columbia University Medical Center, New York City. Benjamin Lebwohl, MD, MS, AGAF, is professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University Medical Center and director of clinical research at The Celiac Disease Center at Columbia. They have no conflicts of interest to declare.
If these screening strategies are deemed feasible by clinicians and patients, then implementation in routine care is needed, lead author Jan Heijdra Suasnabar, MSc, of Leiden University Medical Centre in the Netherlands, and colleagues reported.
“Cohort studies have shown that CD likely develops early in life and can be easily diagnosed by detection of CD-specific antibodies against the enzyme tissue transglutaminase type 2 (IgA-TG2),” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology.
Despite the ease of diagnosis, as few as one in five cases of CD are detected using current clinical strategies, meaning many cases are diagnosed years after symptom onset.
“Such high rates of missed/delayed diagnoses have been attributed to CD’s varied and nonspecific symptoms, lack of awareness, and the resource-intensive process necessary to establish the diagnosis,” Heijdra Suasnabar and colleagues wrote. “From an economic perspective, the burden of CD translates into substantial excess healthcare and societal costs.”
These practice gaps prompted the present study, which explored the long-term cost effectiveness of mass CD screening and active case finding among pediatric patients.
The investigators employed a model-based cost-effectiveness analysis with a hypothetical cohort representing all children with CD in the Netherlands. Iterations of this model evaluated long-term costs as these children moved through the healthcare system along various CD detection strategies.
The first strategy was based on the current Dutch approach, which is the same as that in the United States: Patients are only evaluated for CD if they present with symptoms that prompt suspicion of disease. Based on data from population-based studies, the model assumed that approximately one in three cases would be detected using this strategy.
The second strategy involved mass screening using IgA-TG2 point-of-care testing (sensitivity, 0.94; specificity, 0.944) via youth health care clinics, regardless of symptoms.
The third strategy, called “active case finding,” represented something of an intermediate approach, in which children with at least 1 CD-related symptom underwent point-of-care antibody testing.
For both mass screening and active case finding strategies, a positive antibody test was followed with confirmatory diagnostic testing.
Compared with current clinical approach, mass screening added 7.46 more quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) per CD patient with an increased cost of €28,635 per CD patient. Active case finding gained 4.33 QALYs per CD patient while incurring an additional cost of €15,585 per CD patient.
Based on a willingness-to-pay threshold of €20,000 per QALY, the investigators deemed both strategies “highly cost effective,” compared with current standard of care. Some of these costs were offset by “substantial” reductions in productivity losses, they noted, including CD-related absences from work and school.
“Our results illustrate how an earlier detection of CD through screening or case finding, although more costly, leads to improved health outcomes and a reduction in disease burden, compared with current care,” Heijdra Suasnabar and colleagues wrote.
Their concluding remarks highlighted the conservative scenarios built into their model, and suggested that their findings offer solid evidence for implementing new CD-testing strategies.
“If found to be feasible and acceptable by clinicians and patients, these strategies should be implemented in the Netherlands,” they wrote.This study was supported by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
If these screening strategies are deemed feasible by clinicians and patients, then implementation in routine care is needed, lead author Jan Heijdra Suasnabar, MSc, of Leiden University Medical Centre in the Netherlands, and colleagues reported.
“Cohort studies have shown that CD likely develops early in life and can be easily diagnosed by detection of CD-specific antibodies against the enzyme tissue transglutaminase type 2 (IgA-TG2),” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology.
Despite the ease of diagnosis, as few as one in five cases of CD are detected using current clinical strategies, meaning many cases are diagnosed years after symptom onset.
“Such high rates of missed/delayed diagnoses have been attributed to CD’s varied and nonspecific symptoms, lack of awareness, and the resource-intensive process necessary to establish the diagnosis,” Heijdra Suasnabar and colleagues wrote. “From an economic perspective, the burden of CD translates into substantial excess healthcare and societal costs.”
These practice gaps prompted the present study, which explored the long-term cost effectiveness of mass CD screening and active case finding among pediatric patients.
The investigators employed a model-based cost-effectiveness analysis with a hypothetical cohort representing all children with CD in the Netherlands. Iterations of this model evaluated long-term costs as these children moved through the healthcare system along various CD detection strategies.
The first strategy was based on the current Dutch approach, which is the same as that in the United States: Patients are only evaluated for CD if they present with symptoms that prompt suspicion of disease. Based on data from population-based studies, the model assumed that approximately one in three cases would be detected using this strategy.
The second strategy involved mass screening using IgA-TG2 point-of-care testing (sensitivity, 0.94; specificity, 0.944) via youth health care clinics, regardless of symptoms.
The third strategy, called “active case finding,” represented something of an intermediate approach, in which children with at least 1 CD-related symptom underwent point-of-care antibody testing.
For both mass screening and active case finding strategies, a positive antibody test was followed with confirmatory diagnostic testing.
Compared with current clinical approach, mass screening added 7.46 more quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) per CD patient with an increased cost of €28,635 per CD patient. Active case finding gained 4.33 QALYs per CD patient while incurring an additional cost of €15,585 per CD patient.
Based on a willingness-to-pay threshold of €20,000 per QALY, the investigators deemed both strategies “highly cost effective,” compared with current standard of care. Some of these costs were offset by “substantial” reductions in productivity losses, they noted, including CD-related absences from work and school.
“Our results illustrate how an earlier detection of CD through screening or case finding, although more costly, leads to improved health outcomes and a reduction in disease burden, compared with current care,” Heijdra Suasnabar and colleagues wrote.
Their concluding remarks highlighted the conservative scenarios built into their model, and suggested that their findings offer solid evidence for implementing new CD-testing strategies.
“If found to be feasible and acceptable by clinicians and patients, these strategies should be implemented in the Netherlands,” they wrote.This study was supported by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Navigating Ethical and Clinical Considerations Relating to Percutaneous Gastrostomy (PEG) Tubes
Cases
Consults for percutaneous gastrostomy (PEG) tube placement for a patient ...
- With dysphagia after stroke: A 70-year-old female with a history of hypertension presented to the hospital with altered mental status and left-sided weakness. She was previously active and independently living. MRI of the brain revealed a right basal ganglia infarct. As a result, she developed dysphagia. She was evaluated by speech and language pathology and underwent a modified barium swallow. Given concerns for aspiration, the recommendation was made for gastroenterology (GI) consultation to place PEG tube for nutrition and medication administration.
- With advanced dementia: An 85-year-old male with an extensive medical history including advanced dementia was admitted from his nursing home for decreased oral intake. His baseline mental status is awake and alert, but he is nonverbal and does not follow commands. Upon 72-hour calorie count, the nutrition consultants determined that he cannot independently meet his nutrition goals. His family wants “everything done” and are asking about a “feeding tube.” The primary team has now consulted GI for PEG tube placement.
- Who is being discharged to a long-term care facility: A 45-year-old male was admitted to the ICU after a heroin overdose. CPR was initiated in the field and return of spontaneous circulation was obtained after 25 minutes. The patient has minimal brainstem reflexes. He is ventilator dependent. He has no family, and now is status-post tracheostomy placement by two-physician consent. The patient is ready for discharge to a long-term care facility that will not accept patients with nasogastric tubes. GI is consulted for PEG tube placement.
Discussion
Gastroenterologists are often consulted for PEG tube placement. However, This is rooted in the fact that, as one expert wrote, “feeding, unlike any other medical treatment, has a moral and emotional significance derived from culture.”1 Understanding the evidence, ethical considerations, and team dynamic behind PEG tube placement is critical for every gastroenterologist. Herein we review these topics and offer guidelines for having patient-centered conversations involving these fundamental concepts.
First, the gastroenterologist should understand the evidence to debunk myths and clarify truths surrounding PEG tube placement. While PEG tubes may help patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis stabilize their weight and can even be prophylactically placed in select patients with head and neck cancer,2,3 they are not always appropriate in patients in early recovery from stroke and have not been shown to improve outcomes in patients with advanced dementia. At least 50% of stroke-related dysphagia resolves within 1-2 weeks, and so the American Heart Association Stroke Council recommends continuing nasogastric tube feeding for 2-3 weeks in patients such as the one presented in case 1 before considering PEG tube placement.4
In situations of advanced dementia such as in case,2 several studies demonstrate that PEG tubes do not reduce or prevent aspiration pneumonia, prevent consequences of malnutrition, prolong life, reduce pressure ulcers, reduce urinary of gastrointestinal tract infections, lead to functional improvement, mitigate decline, or even improve comfort or quality of life for patients or their caregivers.5-7 Despite this evidence, as demonstrated in case,3 it is true that many American skilled nursing facilities will not accept a patient without a PEG if enteral feeding is needed. This restriction may vary by state: One study found that skilled nursing facilities in New York City are much less likely to accept patients with nasogastric feeding tubes than randomly selected skilled nursing facilities throughout the country.6 Nonetheless, gastroenterologists should look to the literature to understand the outcomes of populations of patients after PEG tube placement and use that data to guide decision-making.
Secondly, the five ethical principles that inform all medical decision making – autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, and futility – should also inform the gastroenterologist’s rationale in offering PEG placement.8
Autonomy implies that the medical team has determined who is able to make the decision regarding PEG tube placement for the patient. Beneficence connects the patient’s medical diagnosis and technical parameters of PEG tube placement with his or her goals of care. Nonmaleficence ensures the decision-making party understands the benefits and risks of the procedure, including anticipatory guidance on possible PEG tube management, complications, risks, and need for replacement. Justice incorporates the context of the patient’s life, including family dynamics, religious, cultural, and financial factors. Futility connects the patient’s prognosis with practical aspects of having a PEG tube.
The complexity of PEG placement lies in the fact that these ethical principles are often at odds with each other. For example, case 2 highlights the conflicting principles of autonomy and futility for elderly dementia patients: While PEG tube placements do not improve comfort or quality of life in advanced dementia (futility), the family representing the patient has stated they want everything done for his care, including PEG tube placement (autonomy). Navigating these ethical principles can be difficult, but having a framework to organize the different factors offers sound guidance for the gastroenterologist.
Finally, the gastroenterologist should recognize the roles of the multidisciplinary team members, including the patient and their representatives, regarding PEG tube placement consults. While gastroenterologists can be viewed as the technicians consulted to simply “place the tube,” they must seek to understand the members of the team representing the patient to be stewards of their skill set. Consulting team physicians carry great responsibility in organizing the medical and psychosocial aspects of each patient’s care, and their proper goals to relieve suffering and prevent death may color their judgment regarding who they believe is a candidate for a PEG tube. Nutritionists, speech therapists, and case managers can help provide objective data on the practicality and feasibility of a PEG tube in their patients. The healthcare system may influence the decision to consult heavily, as seen in the rules of the long-term care facility in case.3 While it is the job of the multidisciplinary medical team to explain the evidence and ethical considerations of PEG tube placement in a patient-centered manner, ultimately the decision belongs to the patient and their family or representatives.
The moral burden of not pursuing PEG placement may supersede the medical advice in many situations. There is an emotionally taxing perception that withholding nutrition via PEG is “starving the patient,” despite literature showing many terminally ill patients do not experience thirst or hunger, and those who do have alleviation of these symptoms with small amounts of food or liquid, not with PEG placement.5 As every patient is unique, PEG tube consultation guidelines created with input from all stakeholders have been utilized to ensure that patients are medically optimized for PEG tube placement and that evidence and ethics-based considerations are evaluated by the multidisciplinary team. An example of such a guideline is shown in Figure 1.
If the gastroenterologist encounters more contentious consultations, there are ways to build consensus to both alleviate patient and family suffering as well as elevate the discussions between teams.
First, identify the type of consult that is repeatedly bringing differing viewpoints and differing ethical principles into play. Second, get representatives from teams together in a neutral environment to understand stakeholders needs. New data suggest, in stroke cases like case 1, there may be dramatic benefit in long-term ability to recover if patients can get early intensive rehabilitation.9 This intense daily rehabilitation is not available within the hospital setting at many locations, and facilitation of discharge may be requested earlier than usually advised tube placement. Third, build a common language for requests and responses between teams. For instance, neurologists can identify and document which patients have less likelihood of early spontaneous recovery, and this can allow gastroenterologists to understand that those patients with little potential for early swallowing recovery can safely be targeted for PEG earlier during the hospital course. Other patients described as having a potential for spontaneous improvement should be given time to recover before an intervention is considered.10 Having a common understanding of goals and a better-informed decision pathway helps each team member feel fulfilled and rewarded, which will ultimately help reduce compassion fatigue and moral burden on providers.
In conclusion, PEG tube placement can be a challenging consultation for gastroenterologists because of the clinical, social, and ethical ramifications at stake for the patient. Even when PEG tube placement is technically feasible, the gastroenterologist should feel empowered to address the evidence-based outcomes of PEG tube placement, discuss the ethical principles of the decision-making process, and communicate with a multidisciplinary team using guidelines as set forth by this paper to best serve the patient.
Dr. Seltzer is based in the Department of Internal Medicine, Mount Sinai Morningside-West, New York City. Dr. Pusateri is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus. Dr. Nguyen is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Center for Esophageal Diseases, Baylor Scott & White Health, Dallas, Texas. Dr. Stein is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, New Jersey. All authors contributed equally to this manuscript, and have no disclosures related to this article.
References
1. Mackie S. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2001 May-Jun;24(3):138-42.
2. Miller RG et al. Neurology. 2009 Oct. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181bc0141.
3. Colevas AD et al. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018 May. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2018.0026.
4. Holloway RG et al. Stroke. 2014 Jun. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000015.
5. Finucane TE et al. JAMA. 1999 Oct. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.14.1365.
6. Burgermaster M et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2016 Jun. doi: 10.1177/0884533616629636.
7. American Geriatrics Society Ethics C, Clinical P, Models of Care C. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014 Aug. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12924.
8. Beauchamp TL. Principlism in Bioethics. In: Serna P, eds. Bioethical Decision Making and Argumentation. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 70. Springer; Cham. 2016 Sept:1-16. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-43419-3_1.
9. Powers WJ et al. Stroke. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211.
10. Galovic M et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 May. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.4858.
Cases
Consults for percutaneous gastrostomy (PEG) tube placement for a patient ...
- With dysphagia after stroke: A 70-year-old female with a history of hypertension presented to the hospital with altered mental status and left-sided weakness. She was previously active and independently living. MRI of the brain revealed a right basal ganglia infarct. As a result, she developed dysphagia. She was evaluated by speech and language pathology and underwent a modified barium swallow. Given concerns for aspiration, the recommendation was made for gastroenterology (GI) consultation to place PEG tube for nutrition and medication administration.
- With advanced dementia: An 85-year-old male with an extensive medical history including advanced dementia was admitted from his nursing home for decreased oral intake. His baseline mental status is awake and alert, but he is nonverbal and does not follow commands. Upon 72-hour calorie count, the nutrition consultants determined that he cannot independently meet his nutrition goals. His family wants “everything done” and are asking about a “feeding tube.” The primary team has now consulted GI for PEG tube placement.
- Who is being discharged to a long-term care facility: A 45-year-old male was admitted to the ICU after a heroin overdose. CPR was initiated in the field and return of spontaneous circulation was obtained after 25 minutes. The patient has minimal brainstem reflexes. He is ventilator dependent. He has no family, and now is status-post tracheostomy placement by two-physician consent. The patient is ready for discharge to a long-term care facility that will not accept patients with nasogastric tubes. GI is consulted for PEG tube placement.
Discussion
Gastroenterologists are often consulted for PEG tube placement. However, This is rooted in the fact that, as one expert wrote, “feeding, unlike any other medical treatment, has a moral and emotional significance derived from culture.”1 Understanding the evidence, ethical considerations, and team dynamic behind PEG tube placement is critical for every gastroenterologist. Herein we review these topics and offer guidelines for having patient-centered conversations involving these fundamental concepts.
First, the gastroenterologist should understand the evidence to debunk myths and clarify truths surrounding PEG tube placement. While PEG tubes may help patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis stabilize their weight and can even be prophylactically placed in select patients with head and neck cancer,2,3 they are not always appropriate in patients in early recovery from stroke and have not been shown to improve outcomes in patients with advanced dementia. At least 50% of stroke-related dysphagia resolves within 1-2 weeks, and so the American Heart Association Stroke Council recommends continuing nasogastric tube feeding for 2-3 weeks in patients such as the one presented in case 1 before considering PEG tube placement.4
In situations of advanced dementia such as in case,2 several studies demonstrate that PEG tubes do not reduce or prevent aspiration pneumonia, prevent consequences of malnutrition, prolong life, reduce pressure ulcers, reduce urinary of gastrointestinal tract infections, lead to functional improvement, mitigate decline, or even improve comfort or quality of life for patients or their caregivers.5-7 Despite this evidence, as demonstrated in case,3 it is true that many American skilled nursing facilities will not accept a patient without a PEG if enteral feeding is needed. This restriction may vary by state: One study found that skilled nursing facilities in New York City are much less likely to accept patients with nasogastric feeding tubes than randomly selected skilled nursing facilities throughout the country.6 Nonetheless, gastroenterologists should look to the literature to understand the outcomes of populations of patients after PEG tube placement and use that data to guide decision-making.
Secondly, the five ethical principles that inform all medical decision making – autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, and futility – should also inform the gastroenterologist’s rationale in offering PEG placement.8
Autonomy implies that the medical team has determined who is able to make the decision regarding PEG tube placement for the patient. Beneficence connects the patient’s medical diagnosis and technical parameters of PEG tube placement with his or her goals of care. Nonmaleficence ensures the decision-making party understands the benefits and risks of the procedure, including anticipatory guidance on possible PEG tube management, complications, risks, and need for replacement. Justice incorporates the context of the patient’s life, including family dynamics, religious, cultural, and financial factors. Futility connects the patient’s prognosis with practical aspects of having a PEG tube.
The complexity of PEG placement lies in the fact that these ethical principles are often at odds with each other. For example, case 2 highlights the conflicting principles of autonomy and futility for elderly dementia patients: While PEG tube placements do not improve comfort or quality of life in advanced dementia (futility), the family representing the patient has stated they want everything done for his care, including PEG tube placement (autonomy). Navigating these ethical principles can be difficult, but having a framework to organize the different factors offers sound guidance for the gastroenterologist.
Finally, the gastroenterologist should recognize the roles of the multidisciplinary team members, including the patient and their representatives, regarding PEG tube placement consults. While gastroenterologists can be viewed as the technicians consulted to simply “place the tube,” they must seek to understand the members of the team representing the patient to be stewards of their skill set. Consulting team physicians carry great responsibility in organizing the medical and psychosocial aspects of each patient’s care, and their proper goals to relieve suffering and prevent death may color their judgment regarding who they believe is a candidate for a PEG tube. Nutritionists, speech therapists, and case managers can help provide objective data on the practicality and feasibility of a PEG tube in their patients. The healthcare system may influence the decision to consult heavily, as seen in the rules of the long-term care facility in case.3 While it is the job of the multidisciplinary medical team to explain the evidence and ethical considerations of PEG tube placement in a patient-centered manner, ultimately the decision belongs to the patient and their family or representatives.
The moral burden of not pursuing PEG placement may supersede the medical advice in many situations. There is an emotionally taxing perception that withholding nutrition via PEG is “starving the patient,” despite literature showing many terminally ill patients do not experience thirst or hunger, and those who do have alleviation of these symptoms with small amounts of food or liquid, not with PEG placement.5 As every patient is unique, PEG tube consultation guidelines created with input from all stakeholders have been utilized to ensure that patients are medically optimized for PEG tube placement and that evidence and ethics-based considerations are evaluated by the multidisciplinary team. An example of such a guideline is shown in Figure 1.
If the gastroenterologist encounters more contentious consultations, there are ways to build consensus to both alleviate patient and family suffering as well as elevate the discussions between teams.
First, identify the type of consult that is repeatedly bringing differing viewpoints and differing ethical principles into play. Second, get representatives from teams together in a neutral environment to understand stakeholders needs. New data suggest, in stroke cases like case 1, there may be dramatic benefit in long-term ability to recover if patients can get early intensive rehabilitation.9 This intense daily rehabilitation is not available within the hospital setting at many locations, and facilitation of discharge may be requested earlier than usually advised tube placement. Third, build a common language for requests and responses between teams. For instance, neurologists can identify and document which patients have less likelihood of early spontaneous recovery, and this can allow gastroenterologists to understand that those patients with little potential for early swallowing recovery can safely be targeted for PEG earlier during the hospital course. Other patients described as having a potential for spontaneous improvement should be given time to recover before an intervention is considered.10 Having a common understanding of goals and a better-informed decision pathway helps each team member feel fulfilled and rewarded, which will ultimately help reduce compassion fatigue and moral burden on providers.
In conclusion, PEG tube placement can be a challenging consultation for gastroenterologists because of the clinical, social, and ethical ramifications at stake for the patient. Even when PEG tube placement is technically feasible, the gastroenterologist should feel empowered to address the evidence-based outcomes of PEG tube placement, discuss the ethical principles of the decision-making process, and communicate with a multidisciplinary team using guidelines as set forth by this paper to best serve the patient.
Dr. Seltzer is based in the Department of Internal Medicine, Mount Sinai Morningside-West, New York City. Dr. Pusateri is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus. Dr. Nguyen is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Center for Esophageal Diseases, Baylor Scott & White Health, Dallas, Texas. Dr. Stein is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, New Jersey. All authors contributed equally to this manuscript, and have no disclosures related to this article.
References
1. Mackie S. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2001 May-Jun;24(3):138-42.
2. Miller RG et al. Neurology. 2009 Oct. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181bc0141.
3. Colevas AD et al. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018 May. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2018.0026.
4. Holloway RG et al. Stroke. 2014 Jun. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000015.
5. Finucane TE et al. JAMA. 1999 Oct. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.14.1365.
6. Burgermaster M et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2016 Jun. doi: 10.1177/0884533616629636.
7. American Geriatrics Society Ethics C, Clinical P, Models of Care C. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014 Aug. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12924.
8. Beauchamp TL. Principlism in Bioethics. In: Serna P, eds. Bioethical Decision Making and Argumentation. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 70. Springer; Cham. 2016 Sept:1-16. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-43419-3_1.
9. Powers WJ et al. Stroke. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211.
10. Galovic M et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 May. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.4858.
Cases
Consults for percutaneous gastrostomy (PEG) tube placement for a patient ...
- With dysphagia after stroke: A 70-year-old female with a history of hypertension presented to the hospital with altered mental status and left-sided weakness. She was previously active and independently living. MRI of the brain revealed a right basal ganglia infarct. As a result, she developed dysphagia. She was evaluated by speech and language pathology and underwent a modified barium swallow. Given concerns for aspiration, the recommendation was made for gastroenterology (GI) consultation to place PEG tube for nutrition and medication administration.
- With advanced dementia: An 85-year-old male with an extensive medical history including advanced dementia was admitted from his nursing home for decreased oral intake. His baseline mental status is awake and alert, but he is nonverbal and does not follow commands. Upon 72-hour calorie count, the nutrition consultants determined that he cannot independently meet his nutrition goals. His family wants “everything done” and are asking about a “feeding tube.” The primary team has now consulted GI for PEG tube placement.
- Who is being discharged to a long-term care facility: A 45-year-old male was admitted to the ICU after a heroin overdose. CPR was initiated in the field and return of spontaneous circulation was obtained after 25 minutes. The patient has minimal brainstem reflexes. He is ventilator dependent. He has no family, and now is status-post tracheostomy placement by two-physician consent. The patient is ready for discharge to a long-term care facility that will not accept patients with nasogastric tubes. GI is consulted for PEG tube placement.
Discussion
Gastroenterologists are often consulted for PEG tube placement. However, This is rooted in the fact that, as one expert wrote, “feeding, unlike any other medical treatment, has a moral and emotional significance derived from culture.”1 Understanding the evidence, ethical considerations, and team dynamic behind PEG tube placement is critical for every gastroenterologist. Herein we review these topics and offer guidelines for having patient-centered conversations involving these fundamental concepts.
First, the gastroenterologist should understand the evidence to debunk myths and clarify truths surrounding PEG tube placement. While PEG tubes may help patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis stabilize their weight and can even be prophylactically placed in select patients with head and neck cancer,2,3 they are not always appropriate in patients in early recovery from stroke and have not been shown to improve outcomes in patients with advanced dementia. At least 50% of stroke-related dysphagia resolves within 1-2 weeks, and so the American Heart Association Stroke Council recommends continuing nasogastric tube feeding for 2-3 weeks in patients such as the one presented in case 1 before considering PEG tube placement.4
In situations of advanced dementia such as in case,2 several studies demonstrate that PEG tubes do not reduce or prevent aspiration pneumonia, prevent consequences of malnutrition, prolong life, reduce pressure ulcers, reduce urinary of gastrointestinal tract infections, lead to functional improvement, mitigate decline, or even improve comfort or quality of life for patients or their caregivers.5-7 Despite this evidence, as demonstrated in case,3 it is true that many American skilled nursing facilities will not accept a patient without a PEG if enteral feeding is needed. This restriction may vary by state: One study found that skilled nursing facilities in New York City are much less likely to accept patients with nasogastric feeding tubes than randomly selected skilled nursing facilities throughout the country.6 Nonetheless, gastroenterologists should look to the literature to understand the outcomes of populations of patients after PEG tube placement and use that data to guide decision-making.
Secondly, the five ethical principles that inform all medical decision making – autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, and futility – should also inform the gastroenterologist’s rationale in offering PEG placement.8
Autonomy implies that the medical team has determined who is able to make the decision regarding PEG tube placement for the patient. Beneficence connects the patient’s medical diagnosis and technical parameters of PEG tube placement with his or her goals of care. Nonmaleficence ensures the decision-making party understands the benefits and risks of the procedure, including anticipatory guidance on possible PEG tube management, complications, risks, and need for replacement. Justice incorporates the context of the patient’s life, including family dynamics, religious, cultural, and financial factors. Futility connects the patient’s prognosis with practical aspects of having a PEG tube.
The complexity of PEG placement lies in the fact that these ethical principles are often at odds with each other. For example, case 2 highlights the conflicting principles of autonomy and futility for elderly dementia patients: While PEG tube placements do not improve comfort or quality of life in advanced dementia (futility), the family representing the patient has stated they want everything done for his care, including PEG tube placement (autonomy). Navigating these ethical principles can be difficult, but having a framework to organize the different factors offers sound guidance for the gastroenterologist.
Finally, the gastroenterologist should recognize the roles of the multidisciplinary team members, including the patient and their representatives, regarding PEG tube placement consults. While gastroenterologists can be viewed as the technicians consulted to simply “place the tube,” they must seek to understand the members of the team representing the patient to be stewards of their skill set. Consulting team physicians carry great responsibility in organizing the medical and psychosocial aspects of each patient’s care, and their proper goals to relieve suffering and prevent death may color their judgment regarding who they believe is a candidate for a PEG tube. Nutritionists, speech therapists, and case managers can help provide objective data on the practicality and feasibility of a PEG tube in their patients. The healthcare system may influence the decision to consult heavily, as seen in the rules of the long-term care facility in case.3 While it is the job of the multidisciplinary medical team to explain the evidence and ethical considerations of PEG tube placement in a patient-centered manner, ultimately the decision belongs to the patient and their family or representatives.
The moral burden of not pursuing PEG placement may supersede the medical advice in many situations. There is an emotionally taxing perception that withholding nutrition via PEG is “starving the patient,” despite literature showing many terminally ill patients do not experience thirst or hunger, and those who do have alleviation of these symptoms with small amounts of food or liquid, not with PEG placement.5 As every patient is unique, PEG tube consultation guidelines created with input from all stakeholders have been utilized to ensure that patients are medically optimized for PEG tube placement and that evidence and ethics-based considerations are evaluated by the multidisciplinary team. An example of such a guideline is shown in Figure 1.
If the gastroenterologist encounters more contentious consultations, there are ways to build consensus to both alleviate patient and family suffering as well as elevate the discussions between teams.
First, identify the type of consult that is repeatedly bringing differing viewpoints and differing ethical principles into play. Second, get representatives from teams together in a neutral environment to understand stakeholders needs. New data suggest, in stroke cases like case 1, there may be dramatic benefit in long-term ability to recover if patients can get early intensive rehabilitation.9 This intense daily rehabilitation is not available within the hospital setting at many locations, and facilitation of discharge may be requested earlier than usually advised tube placement. Third, build a common language for requests and responses between teams. For instance, neurologists can identify and document which patients have less likelihood of early spontaneous recovery, and this can allow gastroenterologists to understand that those patients with little potential for early swallowing recovery can safely be targeted for PEG earlier during the hospital course. Other patients described as having a potential for spontaneous improvement should be given time to recover before an intervention is considered.10 Having a common understanding of goals and a better-informed decision pathway helps each team member feel fulfilled and rewarded, which will ultimately help reduce compassion fatigue and moral burden on providers.
In conclusion, PEG tube placement can be a challenging consultation for gastroenterologists because of the clinical, social, and ethical ramifications at stake for the patient. Even when PEG tube placement is technically feasible, the gastroenterologist should feel empowered to address the evidence-based outcomes of PEG tube placement, discuss the ethical principles of the decision-making process, and communicate with a multidisciplinary team using guidelines as set forth by this paper to best serve the patient.
Dr. Seltzer is based in the Department of Internal Medicine, Mount Sinai Morningside-West, New York City. Dr. Pusateri is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus. Dr. Nguyen is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Center for Esophageal Diseases, Baylor Scott & White Health, Dallas, Texas. Dr. Stein is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, New Jersey. All authors contributed equally to this manuscript, and have no disclosures related to this article.
References
1. Mackie S. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2001 May-Jun;24(3):138-42.
2. Miller RG et al. Neurology. 2009 Oct. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181bc0141.
3. Colevas AD et al. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018 May. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2018.0026.
4. Holloway RG et al. Stroke. 2014 Jun. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000015.
5. Finucane TE et al. JAMA. 1999 Oct. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.14.1365.
6. Burgermaster M et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2016 Jun. doi: 10.1177/0884533616629636.
7. American Geriatrics Society Ethics C, Clinical P, Models of Care C. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014 Aug. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12924.
8. Beauchamp TL. Principlism in Bioethics. In: Serna P, eds. Bioethical Decision Making and Argumentation. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 70. Springer; Cham. 2016 Sept:1-16. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-43419-3_1.
9. Powers WJ et al. Stroke. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211.
10. Galovic M et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 May. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.4858.